Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 673-681.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2440
Previous Articles Next Articles
Lovastatin combined with insulin effects on fracture healing in rat models of bilateral ovariectomized type 2 diabetic mellitus
Cao Guolong1, Tian Faming2, Liu Jiayin3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Worker’s Hospital of Tangshan, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; 2Medical Experimental Research Center of North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Tangshan, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2019-06-26Revised:2019-06-29Accepted:2019-08-07Online:2020-02-18Published:2020-01-08 -
Contact:Cao Guolong, Department of Orthopedics, Worker’s Hospital of Tangshan, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Cao Guolong, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Worker’s Hospital of Tangshan, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81874029; the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, No. H2013209255; the Science and Technology Program of Tangshan City, No. 12130236b
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Guolong, Tian Faming, Liu Jiayin. Lovastatin combined with insulin effects on fracture healing in rat models of bilateral ovariectomized type 2 diabetic mellitus[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 673-681.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
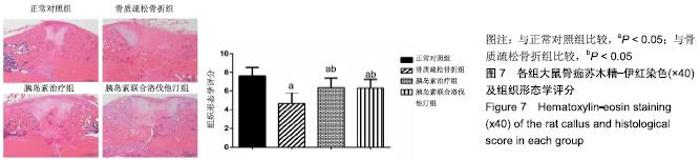
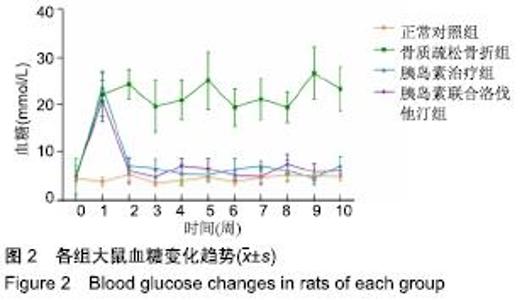
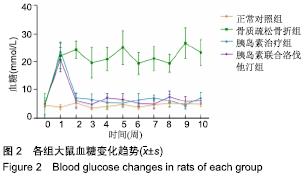
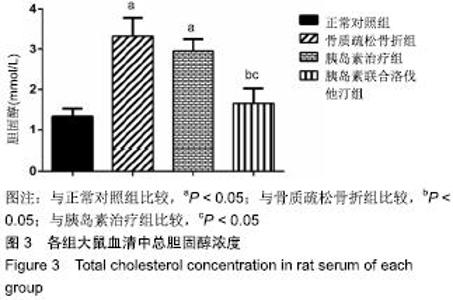
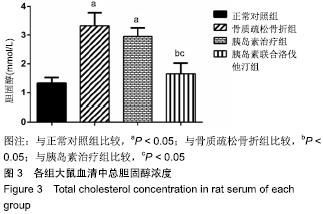
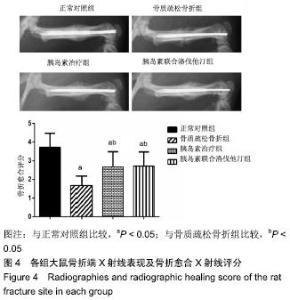
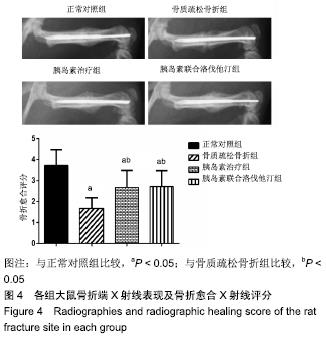
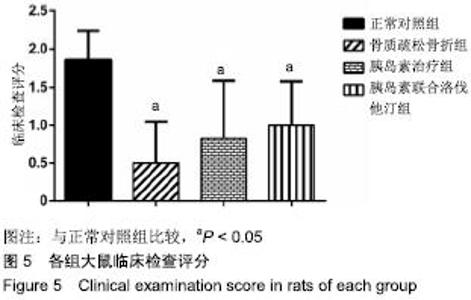
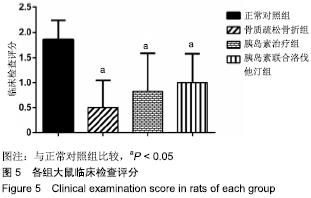
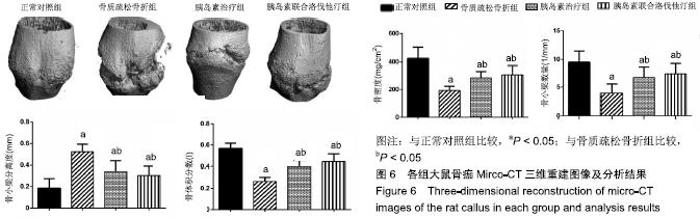
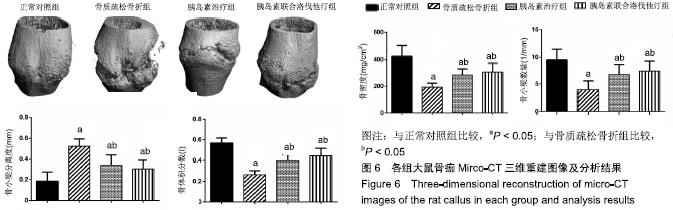
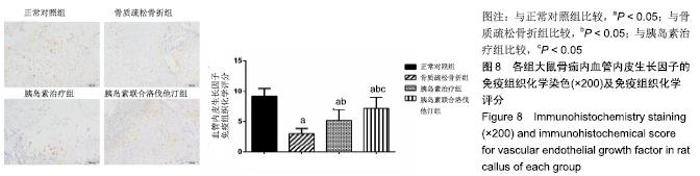
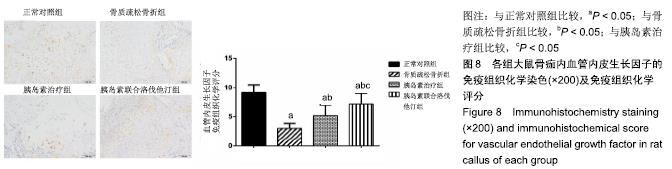
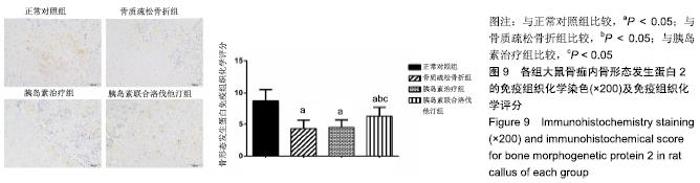
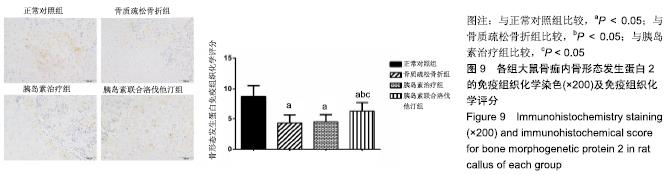
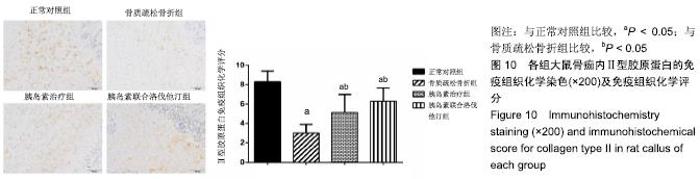
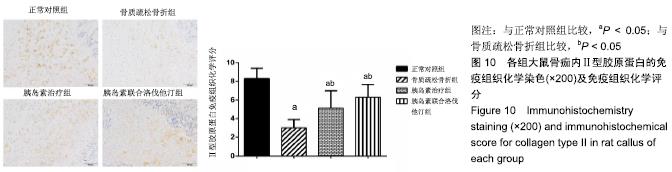
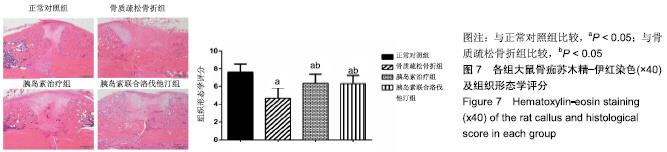
2.7 各组大鼠组织形态学评分 苏木精-伊红染色切片观察可见,正常对照组骨折端已出现较多的骨性骨痂,而软骨组织相对较少,局部可见骨性骨痂连接骨折端;骨质疏松骨折组骨折端仍可见较多软骨组织及纤维组织,而骨性骨痂相对较少,未见骨性骨痂连接骨折端;胰岛素治疗组和胰岛素联合洛伐他汀组虽然未见明显骨性骨痂连接骨折端,但与骨质疏松骨折组相比,其内骨性骨痂相对较多,而只有少量纤维组织存在,余下部分被软骨组织所填充。组织形态学评分结果分析显示,骨质疏松骨折组、胰岛素治疗组和胰岛素联合洛伐他汀组显著低于正常对照组(P < 0.05),胰岛素治疗组和胰岛素联合洛伐他汀组显著高于骨质疏松骨折组(P < 0.05),胰岛素治疗组和胰岛素联合洛伐他汀组间无显著差异(图7)。"
| [1] ENSRUD KE, KATS AM, BOYD CM, et al.Association of Disease Definition, Comorbidity Burden, and Prognosis With Hip Fracture Probability Among Late-Life Women.JAMA Intern Med.2019;17:E1-E9. [2] DYTFELD J, MICHALAK M.Type 2 diabetes and risk of low-energy fractures in postmenopausal women: meta-analysis of observational studies.Aging Clin Exp Res.2017;29(2):301-309. [3] MARIN C, LUYTEN FP, VAN DER SCHUEREN B, et al. The Impact of Type 2 Diabetes on Bone Fracture Healing. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).2018;9(6):1-15. [4] LA FONTAINE J, CHEN C, HUNT N, et al.Type 2 Diabetes and Metformin Influence on Fracture Healing in an Experimental Rat Model.J Foot Ankle Surg.2016;55(5):955-960. [5] NAMKUNG-MATTHAI H, APPLEYARD R, JANSEN J, et al. Osteoporosis influences the early period of fracture healing in a rat osteoporotic model.Bone.2001;28(1):80-86. [6] WANG JW, LI W, XU SW, et al. Osteoporosis influences the middle and late periods of fracture healing in a rat osteoporotic model.Chin J Traumatol.2005;8(2):111-116. [7] HAK DJ.The biology of fracture healing in osteoporosis and in the presence of anti-osteoporotic drugs.Injury. 2018;49(8):1461-1465. [8] KLEIN GL.Insulin and bone: Recent developments.World J Diabetes. 2014;5(1):14-16. [9] KENDRICK J, SHLIPAK MG, TARGHER G, et al.Effect of lovastatin on primary prevention of cardiovascular events in mild CKD and kidney function loss: A post hoc analysis of the Air Force/Texas Coronary Atherosclerosis Prevention Study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;55(1):42-49. [10] GIANNOTTI S, BOTTAI V, DELL’OSSO G, et al.Current medical strategies concerning fracture healing. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab.2013;10(2):116-120. [11] IBRAHIM N', KHAMIS MF, MOD YUNOH MF, et al.Targeted delivery of lovastatin and tocotrienol to fracture site promotes fracture healing in osteoporosis model: micro-computed tomography and biomechanical evaluation.PLoS One.2014;9(12):1-18. [12] SRINIVASAN K, VISWANAD B, ASRAT L, et al.Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening.Pharmacol Res.2005;52(4):313–320. [13] ACAR B, KÖSE Ö, AYTAÇ G, et al.Diabetes mellitus accelerates fatty degeneration of the supraspinatus muscle after tendon tear: An experimental study in rats.Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2018; 29(3):176-183. [14] HOLSTEIN JH, MENGER MD, CULEMANN U, et al.Development of a locking femur nail for mice. J Biomech. 2007;40(1):215-219. [15] WONG E, SANGADALA S, BODEN SD, et al.A novel low-molecular- weight compound enhances ectopic bone formation and fracture repair.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2013;95(5):454-461. [16] SUZUKI K, MIYAKOSHI N, TSUCHIDA T, et al. Effects of combined treatment of insulin and human parathyroid hormone (1-34) on cancellousbone mass and structure in streptozotocin- induced diabetic rats.Bone.2003;33(1):108-114. [17] SHAHREZAEE M, ORYAN A, BASTAMI F, et al.Comparative impact of systemic delivery of atorvastatin, simvastatin, and lovastatin on bone mineral density of the ovariectomized rats. Endocrine.2018;60(1):138-150. [18] CHUENG KM, KALUARACHI K, ANDREW G, et al. An externally fixed femoral fracture model for mice. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(4):685-690. [19] AKMAN S, GÖGÜS A, SENER N, et al.Effect of diclofenac sodium on union of tibial fractures in rats. Adv Ther.2002;19(3):119-125. [20] WANG L, HSIAO EC, LIEU S, et al. Loss of Gi G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling in Osteoblasts Accelerates Bone Fracture Healing.J Bone Miner Res.2015;30(10):1896-1904. [21] NYMAN JS, MUNOZ S, JADHAV S, et al.Quantitative measures of femoral fracture repair in rats derived by micro-computed tomography.J Biomech.2009;42(7):891-897. [22] HUO MH, TROIANO NW, PELKER RR, et al.The influence of ibuprofen on fracture repair: Biomechanical, biochemical, histologic, and histomorphometric parameters in rats. J Orthop Res. 1991;9(3): 383-390. [23] LI B, WANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Altered gene expression involved in insulin signaling pathway in type II diabetic osteoporosis rats model. Endocrine.2013;43(1):136-146. [24] JIAO H, XIAO E, GRAVES DT. Diabetes and Its Effect on Bone and Fracture Healing. Curr Osteoporos Rep.2015;13(5):327-335. [25] HERNANDEZ RK, DO TP, CRITCHLOW CW, et al. Patient‐related risk factors for fracture‐healing complications in the United Kingdom General Practice Research Database.Acta Orthop. 2012;83(6):653-660. [26] CUNHA JS, FERREIRA VM, MAQUIGUSSA E, et al.Effects of high glucose and high insulin concentrations on osteoblast function in vitro.Cell Tissue Res.2014;358(1):249-256. [27] BOTOLIN S, MCCABE LR.Chronic hyperglycemia modulates osteoblast gene expression through osmotic and non-osmotic pathways.J Cell Biochem.2006;99(2):411-424. [28] SUN M, YANG J, WANG J, et al. TNF-α is upregulated in T2DM patients with fracture and promotes the apoptosis of osteoblast cells in vitro in the presence of high glucose.Cytokine. 2016;80: 35-42. [29] KO KI, COIMBRA LS, TIAN C, et al.Diabetes reduces mesenchymal stem cells in fracture healing through a TNFalpha-mediated mechanism. Diabetologia.2015;58(3):633-642. [30] KAYAL RA, TSATSAS D, BAUER MA, et al. Diminished bone formation during diabetic fracture healing is related to the premature resorption of cartilage associated with increased osteoclast activity. JBoneMiner Res.2007;22(4):560-568. [31] HAN D, ZHANG P, JIANG B.Local administration of IKK small molecule inhibitor may enhance fracture healing in osteoporosis patient.Int J Clin Exp Med.2015;8(1):1411-1415. [32] JAHNG JS, KIM HW.Effect of intermittent administration of parathyroid hormone on fracture healing in ovariectomized rats. Orthopedics.2000;23(10):1089-1094. [33] BEIL FT, BARVENCIK F, GEBAUER M, et al.Effects of estrogen on fracture healing in mice.J Trauma.2010;69(5):1259-1265. [34] ISLAM AA, RASUBALA L, YOSHIKAWA H, et al. Healing of fractures in osteoporotic rat mandible shown by the expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and tumour necrosis factor-α.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2005;43(5):383-391. [35] SAITO M, MARUMO K.Collagen cross-links as a determinant of bone quality:A possible explanation for bone fragility in aging, osteoporosis,and diabetes mellitus.Osteoporos Int.2010;21(2): 195-214. [36] WEINBERG E, MAYMON T, WEINREB M. Ages induce caspase- mediated apoptosis of rat bmscs via tnfalpha production and oxidative stress.J Mol Endocrinol.2014;52(1):67-76. [37] PENTTI K, TUPPURAINEN MT, HONKANEN R, et al. Hormone therapy protects from diabetes: the Kuopio osteoporosis risk factor and prevention study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009;160(6):979-983. [38] BRYZGALOVA G, GAO H, AHREN B, et al. Evidence that oestrogen receptor-α plays an important role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis in mice:insulin sensitivity in the liver. Diabetologia.2006;49(3):588-597. [39] LUNDHOLM L, BRYZGALOVA G, GAO H, et al.The estrogen receptor alpha-selective agonist propyl pyrazole triol improves glucose tolerance in ob/ob mice; potential molecular mechanisms.J Endocrinol.2008;199(2):275-286. [40] BRAGDON B, LYBRAND K, GERSTENFELD L.Overview of Biological Mechanisms and Applications of Three Murine Models of Bone Repair:Closed Fracture with Intramedullary Fixation, Distraction Osteogenesis, and Marrow Ablation by Reaming.Curr Protoc Mouse Biol.2015;5(1):21-34. [41] PICKE AK, GORDALIZA ALAGUERO I, CAMPBELL GM. Campbell. Bone defect regeneration and cortical bone parameters of type 2 diabetic rats are improved by insulin therapy.Bone. 2016; 82:108-115. [42] PARK AG, PAGLIA DN, AL-ZUBE L, et al.Local Insulin Therapy Affects Fracture Healing in a Rat Model.J Orthop Res.2013; 31(5):776-782. [43] WANG DW, DU SL, XU MT, et al.Effects of insulin therapy on fracture healing and expression of VEGF in diabetic rats.J Appl Biomed.2013; 11:33-40. [44] HU KAI, OLSEN BR.Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Control Mechanisms in Skeletal Growth and Repair.Dev Dyn.2017;246(4): 227-234. [45] ZHANG R, LIANG Y, WEI S.The expressions of NGF and VEGF in the fracture tissues are closely associated with accelerated clavicle fracture healing in patients with traumatic brain injury. Ther Clin Risk Manag.2018;14:2315-2322. [46] DING Q, SUN P, ZHOU H, et al.Lack of endogenous parathyroid hormone delays fracture healing by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis.Int J Mol Med.2018;42(1): 171-181. [47] MAYR-WOHLFART U, WALTENBERGER J, HAUSSER H, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates chemotactic migration of primary human osteoblasts.Bone.2002;30(3):472-477. [48] HU K, OLSEN BR.Osteoblast-derived VEGF regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone repair.J Clin Invest. 2016;126(2):509-526. [49] LIAN C, WANG X, QIU X, et al. Collagen type II suppresses articular chondrocyte hypertrophy and osteoarthritis progression by promoting integrin β1−SMAD1 interaction.Bone Res.2019; 7(8):1-15. [50] TIRUVANNAMALAI ANNAMALAI R, MERTZ DR, DALEY EL. Collagen Type II enhances chondrogenic differentiation in agarose-based modular microtissues.Cytotherapy. 2016;18(2): 263-277. [51] BIBBINS-DOMINGO K, GROSSMAN DC, CURRY SJ, et al.Statin use for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: US preventive services task force recommendation statement. JAMA.2016;316(19):1997-2007. [52] CHIN KY, ABDUL-MAJEED S, MOHAMED N, et al.The Effects of Tocotrienol and Lovastatin Co-Supplementation on Bone Dynamic Histomorphometry and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Expression in Rats with Estrogen Deficiency. Nutrients.2017;9(2): 1-12. [53] JADHAV SB, NARAYANA MURTHY PS, SINGH MM, et al. Distribution of lovastatin to bone and its effect on bone turnover in rats.J Pharm Pharmacol.2006;58(11):1451-1458. [54] MOSHIRI A, SHARIFI AM, ORYAN A.Role of Simvastatin on fracture healing and osteoporosis: a systematic review on in vivo investigations. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016;43(7):659-684. [55] MAEDA T, KAWANE T, HORIUCHI N. Statins augment vascular endothelial growth factor expression in osteoblastic cells via inhibition of protein prenylation.Endocrinology.2003;144(2): 681-692. [56] BRAMONO DS, MURALI S, RAI B, et al.Bone marrow-derived heparan sulfate potentiates the osteogenic activity of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2).Bone.2012;50(4):954-964. [57] LI J, WANG JJ, CHEN D, et al. Systemic administration of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor protects the blood-retinal barrier and ameliorates retinal inflammation in type 2 diabetes.Exp Eye Res. 2009; 89(1): 71-78. [58] AWAD E, OTHMAN EM, STOPPER H.Effects of Resveratrol, Lovastatin and the mTOR-Inhibitor RAD-001 on Insulin-Induced Genomic Damage In Vitro.Molecules.2017;22(12):1-12. [59] TANG QO, TRAN GT, GAMIE Z, et al.Statins: under investigation for increasing bone mineral density and augmenting fracture healing. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.2008;17(10):1435-1463. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [3] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [4] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [5] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [6] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [7] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [8] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [9] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [10] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [11] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [12] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [13] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [14] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [15] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||