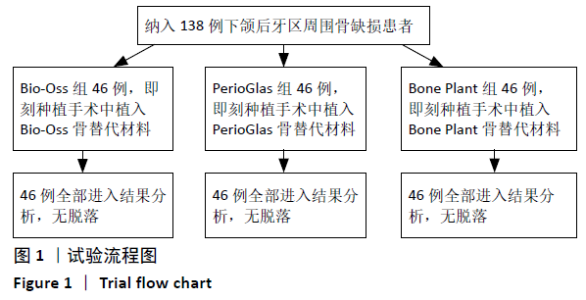
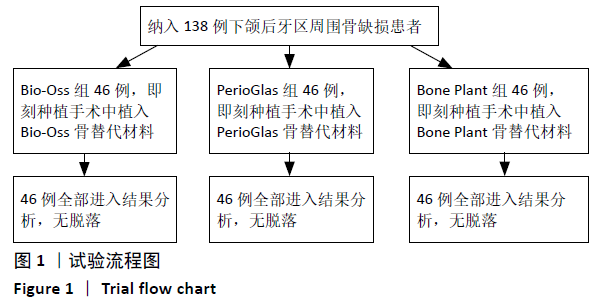
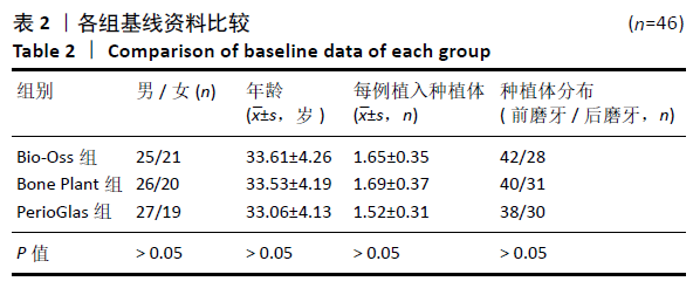
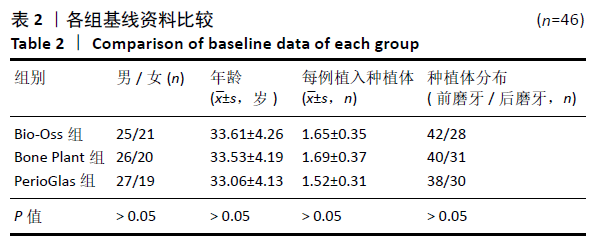
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (34): 5495-5500.doi: 10.12307/2021.245
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of three kinds of bone replacement materials in the treatment of bone defects around the mandibular posterior teeth with immediate implantation
Xiao Sha, Gao Chengzhi, Zhou Dongping
- Department of Stomatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
-
Received:2020-06-17Revised:2020-06-24Accepted:2020-08-25Online:2021-12-08Published:2021-07-27 -
About author:Xiao Sha, Master, Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, Peking University People’s Hospital, Beijing 100044, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiao Sha, Gao Chengzhi, Zhou Dongping. Comparison of three kinds of bone replacement materials in the treatment of bone defects around the mandibular posterior teeth with immediate implantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5495-5500.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
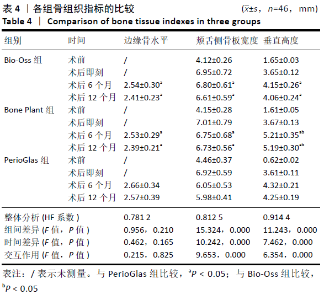
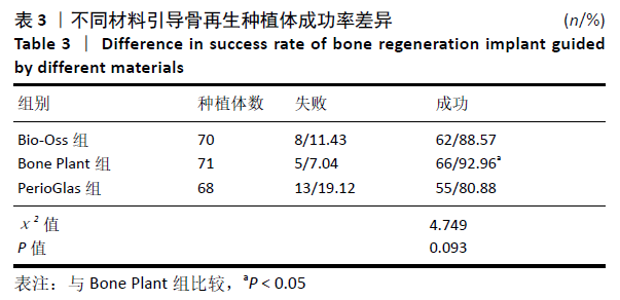
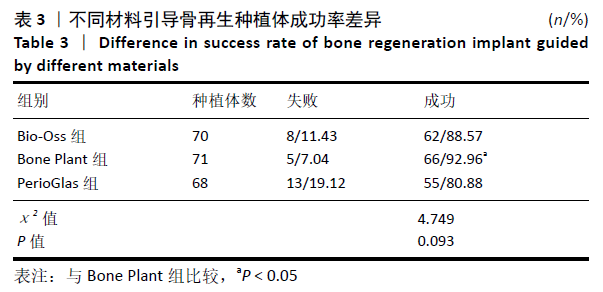
2.5 各组骨组织指标比较 3组术前颊舌侧骨板宽度、垂直高度比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),术后6,12个月的边缘骨水平与术前相比无明显变化(P > 0.05),颊舌侧骨板宽度、垂直高度呈先增加后稍降低趋势(P < 0.05)。Bio-Oss组、Bone Plant组术后6,12个月的边缘骨水平低于PerioGlas组(P < 0.05),Bio-Oss组、Bone Plant组之间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。Bio-Oss组、Bone Plant组术后6,12个月的颊舌侧骨板宽度、垂直高度高于PerioGlas组(P < 0.05);Bone Plant组术后6,12个月的垂直高度高于Bio-Oss组(P < 0.05),颊舌侧骨板宽度与Bio-Oss组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表4。"
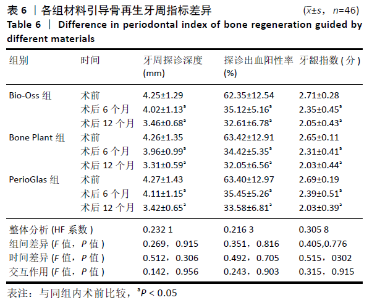
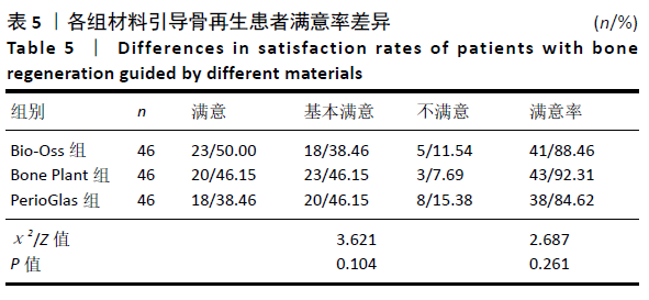
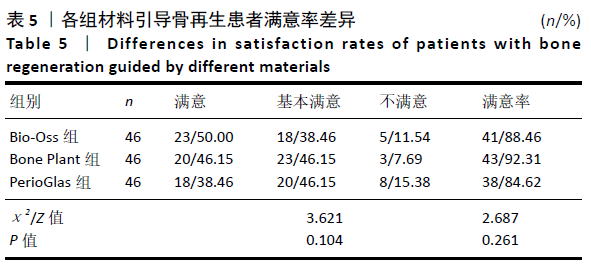
2.7 牙周指标比较 3组患者术前牙周探诊深度、探诊出血阳性率、牙龈指数比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),术后6,12个月牙周探诊深度、探诊出血阳性率、牙龈指数均出现不同程度下降(P < 0.05),3组间术后牙周探诊深度、探诊出血阳性率、牙龈指数比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表6。 2.8 不良反应 3组均未出现牙髓神经损伤、急慢性牙周炎、种植体周围炎、种植体脱落等严重并发症,亦未出现与骨替代材料相关的不良反应。Bio-Oss组术后1例牙龈红肿、疼痛伴出血,给予消炎、止血药物应用后改善;PerioGlas组1例术后10个月时出现种植体松动明显,后取出种植体,待植入窝愈合后行二次种植手术;Bone Plant组1例术后种植体区牙龈红肿,未特殊处理后好转。 "
| [1] BUSENLECHNER D, MAILATH-POKORNY G, HAAS R, et al. Graftless full-arch implant rehabilitation with interantral implants and immediate or delayed loading-part Ⅱ: transition from the failing maxillary dentition. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(5):1150-1155. [2] FÜRHAUSER R, MAILATH-POKORNY G, HAAS R, et al. Patient-perceived morbidity and subjective functional impairment following immediate transition from a failing dentition to fixed implant rehabilitation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(3):651-656. [3] ELGALI I, OMAR O, DAHLIN C, et al. Guided bone regeneration: materials and biological mechanisms revisited. Eur J Oral Sci. 2017;125(5):315-337. [4] WESSING B, LETTNER S, ZECHNER W. Guided Bone Regeneration with Collagen Membranes and Particulate Graft Materials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(1): 87-100. [5] TETTAMANTI L, ANDRISANI C, BASSI MA, et al. Immediate loading implants: review of the critical aspects. Oral Implantol (Rome). 2017; 10(2):129-139. [6] FILLINGHAM Y, JACOBS J. Bone grafts and their substitutes. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(1 Suppl A):6-9. [7] ALUDDEN HC, MORDENFELD A, HALLMAN M, et al. Lateral ridge augmentation with Bio-Oss alone or Bio-Oss mixed with particulate autogenous bone graft: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;46(8):1030-1038. [8] ASMITA, GUPTA V, BAINS VK, et al. Clinical and cone beam computed tomography comparison of NovaBone Dental Putty and PerioGlas in the treatment of mandibular Class II furcations. Indian J Dent Res. 2014; 25(2):166-173. [9] 王鸣照,何家才.两种不同骨替代材料在上颌前牙区种植体周围骨缺损中的应用效果评价[J].安徽医药,2018,22(3):440-444. [10] 刘晓庆.两种不同骨替代材料在即刻种植下颌后牙区周围骨缺损中的临床效果对比[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2019,27(S1):17-19. [11] ALBREKTSSON T, ZARB G, WORTHINGTON P, et al. The longterm efficacy of currently used dental implants: a review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1986;1(1):11-25. [12] 胡兴周.丁硼乳膏在牙齿正畸固定矫正中对牙龈炎患者牙龈指数、菌斑指数与龈沟出血指数的影响[J].中国美容医学,2019,28(11): 111-114. [13] MUÑOZ V, DUQUE A, GIRALDO A, et al. Prevalence of Peri-implant Disease According to Periodontal Probing Depth and Bleeding on Probing: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(4):e89-e105. [14] 李林峰,李月,李瑞玉,等.骨移植和组织工程支架材料在上颌窦提升口腔种植修复中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(34): 5558-5564. [15] RODRIGUEZ AE, MONZAVI M, YOKOYAMA CL, et al. Zirconia dental implants: A clinical and radiographic evaluation. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2018;30(6):538-544. [16] 康博,潘颖菁,温玉洁,等.钛网结合无机牛骨在磨牙区种植同期垂直骨增量的应用[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2019,24(3):106-109. [17] 李林芝,陈丹,黄元丁,等.三维打印个性化钛网联合引导骨再生术修复牙槽骨缺损的临床初探[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2019,54(9): 623-627. [18] LIU HY, ZHENG H, HOU XP, et al. Bio-Oss(®) for delayed osseointegration of implants in dogs: a histological study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 52(8):729-734. [19] DE MELO PEREIRA D, HABIBOVIC P. Biomineralization-Inspired Material Design for Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(22): e1800700. [20] KLUGE A, NEUDERT M, KUNERT-KEIL C, et al. The Obliteration of Noncritical Size Bone Defects With Bone Dust or Bone Replacement Material (Bioactive Glass S53P4). Otol Neurotol. 2019;40(4):e415-e423. [21] 吕娟,高子龙,朱友家,等.梯度脱矿自体牙配合Bio-Oss骨粉用于牙槽骨缺损修复的研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2018,34(4):205-208. [22] VIVAN RR, MECCA CE, BIGUETTI CC, et al. Experimental maxillary sinus augmentation using a highly bioactive glass ceramic. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(2):41. [23] VAN HOUDT CIA, ULRICH DJO, JANSEN JA, et al. The performance of CPC/PLGA and Bio-Oss ® for bone regeneration in healthy and osteoporotic rats. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(1): 131-142. [24] 赖思煜,习利军,倪俊鑫.两种材料在拔牙后引导骨组织再生位点保存术中的应用效果[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版),2019, 13(5):284-290. [25] 马晓杰,卞一峰,吴大明,等.两种人工骨粉进行拔牙位点保存的临床对比研究[J].口腔生物医学,2019,10(3):139-142. [26] 何浩,徐梦婷,肖强,等.富血小板纤维蛋白联合人工骨粉在口腔种植引导性骨再生中的临床应用价值[J].现代生物医学进展,2019, 19(10):1920-1923. [27] 黄海霞,兰玉燕,付小明,等.浓缩生长因子对慢性牙周炎患者即刻种植修复的影响[J].中国临床研究,2018,31(6):741-743,748. [28] 董瑶,董飞君,潘凌峰,等. Bio-Oss骨粉联合富血小板纤维蛋白对口腔种植引导性骨再生术后黏膜愈合和骨缺损再生的影响研究[J].中国全科医学,2017,20(B12):152-154. [29] 许明悠,刘永恒,汪鹏生,等.生物活性玻璃基骨修复材料的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(7):440-448. [30] DA FONSECA GF, AVELINO SOM, MELLO DCR, et al. Scaffolds of PCL combined to bioglass: synthesis, characterization and biological performance. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(5):41. [31] SIDDESHAPPA ST, BHATNAGAR S, DIWAN V, et al. Regenerative potential of subepithelial connective tissue graft in the treatment of periodontal infrabony defects. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018;22(6):492-497. [32] SAURO S, BABBAR A, GHARIBI B, et al. Cellular differentiation, bioactive and mechanical properties of experimental light-curing pulp protection materials. Dent Mater. 2018;34(6):868-878. [33] SLEIBI A, TAPPUNI A, MILLS D, et al. Comparison of the Efficacy of Different Fluoride Varnishes on Dentin Remineralization During a Critical pH Exposure Using Quantitative X-Ray Microtomography. Oper Dent. 2018;43(6):E308-E316. [34] ZENG Q, DESAI MS, JIN HE, et al. Self-Healing Elastin-Bioglass Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2016;17(8):2619-2625. [35] PINTADO-PALOMINO K, PEITL FILHO O, ZANOTTO ED, et al. A clinical, randomized, controlled study on the use of desensitizing agents during tooth bleaching. J Dent. 2015;43(9):1099-1105. [36] 王晓娜,赵静辉,储顺礼,等.骨替代材料在口种植领域中的成骨效果[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2016,43(1):113-117. [37] D’ALESSANDRO D, PERALE G, MILAZZO M, et al. Bovine bone matrix/poly(l-lactic-co-ε-caprolactone)/gelatin hybrid scaffold (SmartBone®) for maxillary sinus augmentation: A histologic study on bone regeneration. Int J Pharm. 2017;523(2):534-544. [38] SCAGLIONE S, LAZZARINI E, ILENGO C, et al. A composite material model for improved bone formation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2010; 4(7):505-513. [39] 马杰.两种不同口腔修复膜材料对牙种植引导骨再生的作用及效果分析[J].中南医学科学杂志,2016,44(1):87-90. [40] PACHIMALLA PR, MISHRA SK, CHOWDHARY R. Evaluation of hydrophilic gel made from Acemannan and Moringa oleifera in enhancing osseointegration of dental implants. A preliminary study in rabbits. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2020;10(2):13-19. |
| [1] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [2] | Kong Lingbao, Lü Xin. Effect of implant selection and approach on support in the operation of posterolateral tibial plateau fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 942-947. |
| [3] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [4] | Zheng Xiaolong, He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Pang Fengxiang, Yang Fan, He Wei, Liu Shaojun, Wei Qiushi. Bone turnover characteristics in patients with alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 657-661. |
| [5] | Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Expression of interleukin-24 in a mouse model of periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 679-684. |
| [6] | Jing Huimin, Yu Wenjuan, Wang Sijia, Chen Cong, Li Yifan, Wang Yonglan, Li Xin, Zhang Juan, Liang Meng. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of the brain’s default mode network in patients with sleep bruxism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 685-689. |
| [7] | Li Wenjing, Li Haobo, Liu Congna, Cheng Dongmei, Chen Huizhen, Zhang Zhiyong. Comparison of different bioactive scaffolds in the treatment of regenerative pulp of young permanent teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 499-503. |
| [8] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [9] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [10] | Sun Qi, Zhou Yanan, Dong Xin, Li Ning, Yan Jiazhen, Shi Haojiang, Xu Sheng, Zhang Biao. Metal-ceramic interface characteristics of Co-Cr alloy fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 521-525. |
| [11] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [12] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [13] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [14] | Li Quanxi, Shen Yu, Wan Wei, Sun Shanzhi. Changes of abdominal wall mechanics and pain after tension-free inguinal hernia repair with polypropylene mesh [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 548-552. |
| [15] | Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Zhao Qiao, Chen Shuo, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and properties of copper-loaded antibacterial functional film on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||