Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (24): 3928-3936.doi: 10.12307/2022.578
Role and clinical application prospects of exosomal non-coding RNAs in the occurrence and development of glioma
Liu Chao, Zeng Zhaomu, Wen Xichao, Wu Wensong, Sun Chengyuan, Zheng Kebin
- Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2021-05-21Revised:2021-05-24Accepted:2021-06-21Online:2022-08-28Published:2022-01-24 -
Contact:Zheng Kebin, MD, Chief physician, Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Liu Chao, Master candidate, Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation Project of Hebei Province, No. H2016201238 (to ZKB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Chao, Zeng Zhaomu, Wen Xichao, Wu Wensong, Sun Chengyuan, Zheng Kebin. Role and clinical application prospects of exosomal non-coding RNAs in the occurrence and development of glioma[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3928-3936.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
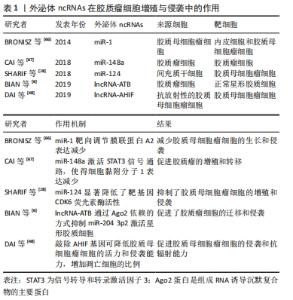
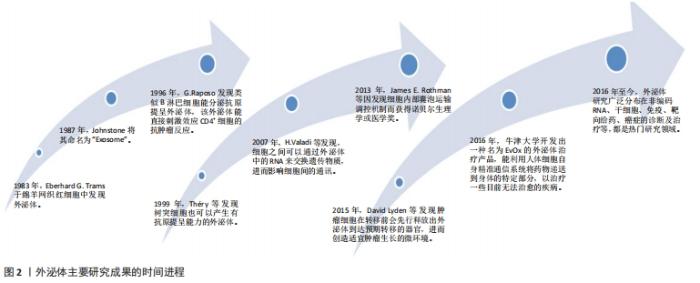
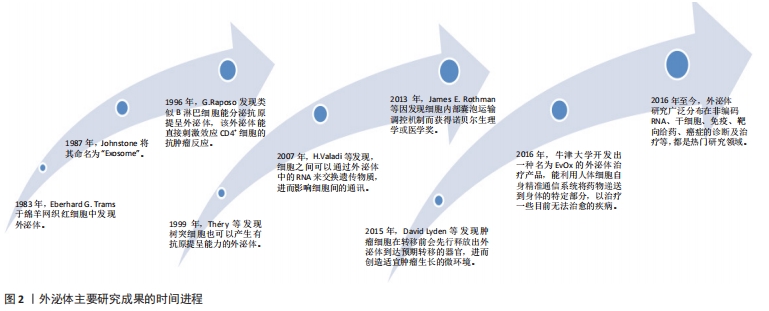
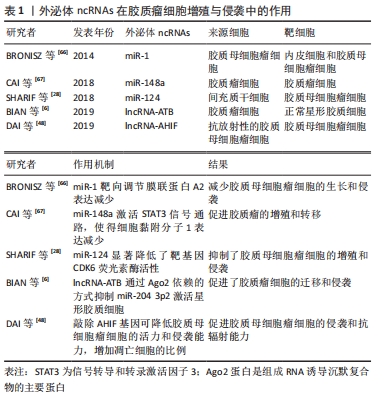
外泌体是由核内体衍生的小细胞外囊泡,直径40-150 nm,由多种细胞分泌,存在于几乎所有体液中,包括血液、脑脊液、尿液、唾液和母乳[13]。外泌体的分泌量和内容物可根据其生物发生、细胞来源和细胞状态的不同而有所不同。有研究表明,一些分子在外泌体中富集,而其他分子几乎不存在,这表明了外泌体具有选择性分类的特征[14]。外泌体的生物发生始于质膜内吞形成核内体,早期核内体成熟为多泡核内体。外泌体在内体系统中以腔内小泡的形式产生,它是由血管内皮细胞的限制膜向内萌发而形成的[13]。外泌体的生物发生涉及一系列连续的分子机制,其中最重要的是转运所需的内泌体分选复合体机制,它作为膜形成和断裂的驱动力,在腔内小泡和多泡核内体的形成中起着重要作用[13,15]。内泌体分选复合体系统由内泌体分选复合体-0、-Ⅰ、-Ⅱ和-Ⅲ组成,它们以循序渐进的方式发挥作用,其中内泌体分选复合体-0和内泌体分选复合体-Ⅰ参与货物聚类和泛素化跨膜货物的招募,内泌体分选复合体-Ⅱ负责启动向内出芽过程,内泌体分选复合体-Ⅲ负责出芽和囊泡裂变。经典的内泌体分选复合体通路可以与syntenin和内泌体分选复合体辅助蛋白ALG2相互作用蛋白X(ALIX,也称为程序性细胞死亡6β相互作用蛋白)相互作用,调控外泌体的生物发生过程[16] 。 此外,一些研究表明,尽管内泌体分选复合体复合物耗尽,外泌体仍然可以形成,这表明还存在独立于内泌体分选复合体的通路[17]。据报道,四跨膜蛋白超家族特别是CD9,CD63和CD81在内泌体分选复合体非依赖性内泌体的分选中起重要作用[18]。因此,依赖和非依赖内泌体分选复合体的途径都涉及外泌体的生物发生,它们的作用可能取决于特定的物质和细胞类型。一般来说,多泡核内体要么与溶酶体融合进行降解,要么与质膜融合,由质膜分泌外泌体到细胞外空间。外泌体的释放涉及到几个关键因素,Rab GTPase家族,如Rab27a和Rab27b,参与了多泡体到特定细胞膜区域的运输[19]。外泌体分泌后,通过配体/受体相互作用、直接膜融合和内吞作用等多种方式与相邻或远处的受体细胞相互作用,调节受体细胞的活性[20]。 外泌体释放到细胞外环境最初被认为是消除细胞内废物的一种手段,其生物学意义长期被忽视[21]。然而,目前广泛的研究表明,外泌体是细胞间通信的关键介质,并参与包括癌症在内的许多疾病的发病机制[22-23]。肿瘤来源的外泌体可以改变周围基质细胞的行为,最终为肿瘤生长创造一个合适的微环境[24]。同时,肿瘤微环境中的基质细胞可以通过释放外泌体进而影响肿瘤进展[25-30]。因此,肿瘤和基质细胞之间通过外泌体在局部或远处的微环境中进行复杂的相互作用,促进肿瘤的增殖、侵袭、血管生成、免疫逃逸、转移和治疗耐药性[31]。此外,外泌体能作为疾病的生物标记物和治疗性运载工具[12],有重要的潜在临床应用。 2.2 外泌体中的ncRNA 外泌体中已经发现了多种分子,包括蛋白质、脂质和核酸[32]。外泌体的双层膜保护这些分子免受蛋白酶、核酸酶和其他环境的影响[33]。此外,外泌体中的这些分子被选择性地包装、分泌和在细胞间转移,并且随亲本细胞和病理生理条件的不同而变化很大[34]。越来越多的证据表明,外泌体富含ncRNAs,包括microRNA (miRNAs)、长链非编码RNA(Long-noncoding RNA,lncRNAs)、环状RNA (circRNA)、Piwi相互作用RNA (piRNAs)和tRNA衍生的小非编码RNA(TsRNA),它们在各种病理生理过程特别是在癌症中发挥重要作用[35-38]。 随着外泌体中ncRNAs的发现和进一步的研究,从细胞间通信到潜在的疾病生物标记物,出现了许多新的功能和应用,鉴于外泌体的生物相容性,可能有新的治疗应用。该综述主要关注胶质瘤中的外泌体miRNAs、lncRNAs和circRNAs的研究进展。 2.2.1 microRNA (miRNA) MiRNAs是由21-25个核苷酸组成的小ncRNAs,它通过与靶mRNA的3'非翻译区(UTR)互补结合来调节基因表达,从而降低或抑制靶基因的稳定性或翻译[39]。每个miRNA可能有多个靶向mRNA,一个mRNA可能被多个miRNA靶向,从而形成一个复杂的调控网络。miRNA的生物发生始于将miRNA基因转录为大型初级转录本(pri-miRNA),然后通过微处理器复合体(包括Ⅲ型RNase Drosha和RNA结合蛋白DGCR8)将其切割成一个85个核苷酸的茎环结构,称为前miRNA (pre-miRNA)。pre-miRNA然后被RNase Ⅲ酶Dicer加工成20-22个核苷酸的miRNA/miRNA双链。这些miRNA双链是不稳定的,很快被分裂成单链成熟的miRNA。成熟的miRNA被装载到Argonaute蛋白上,形成RNA诱导沉默复合体,然后与靶mRNA结合,进行转录后基因沉默[39]。目前,最新版本的miRBase数据库(V22)包含了1 917个带注释的发夹前体,以及人类基因组中2 654个成熟的miRNA[40]。大量研究表明,miRNA表达失调与包括癌症在内的许多人类疾病密切相关。在一定条件下,miRNAs可能发挥致癌作用或作为肿瘤抑制因子的作用[41]。 近年来,外泌体中miRNAs的发现引起了越来越多的关注。大量研究表明,miRNAs被选择性地分类为外泌体,参与肿瘤微环境中的细胞间通信,并在肿瘤生物学中发挥重要作用[5]。此外,外体miRNAs在生物体液中的易得性、丰富性和稳定性,使其可能成为包括胶质瘤在内的各种癌症的理想生物标记物[42]。 2.2.2 lncRNAs lncRNAs被定义为长度超过200个核苷酸的转录本,不具有或具有有限的蛋白质编码能力[43]。lncRNAs既存在于细胞核中,也存在于细胞质中,并根据其亚细胞定位发挥不同的功能。在细胞核中,lncRNAs可能参与基因表达和mRNA剪接的转录调控,而在细胞质中,它们可以影响mRNA的稳定性,调节蛋白的功能[44]。此外,lncRNA通过多种分子机制发挥功能,如与DNA结合调节基因转录,作为竞争性内源性RNA (ceRNA)或miRNA海绵在转录后水平调控基因表达,与蛋白质结合,编码功能性小肽[45]。近10年来,越来越多的研究表明,lncRNA参与了许多病理生理过程,如细胞周期调控、细胞分化和先天免疫应 答[45-46]。此外,lncRNAs的表达失调已经在包括胶质瘤在内的许多人类癌症中被观察到,并通过其作为肿瘤抑制因子或致癌基因的作用与癌症的分期和分级密切相关[43]。有趣的是,lncRNAs也可以选择性地分类到外泌体中,并在肿瘤微环境中参与细胞间通信[47]。外泌体lncRNAs可参与胶质瘤的发生发展,如增殖、侵袭、血管生成及耐药等,可能成为潜在的治疗靶点[48-49]。此外,外泌体lncRNAs有可能成为诊断和预后的生物标志物[47]。 2.2.3 circRNA circRNAs是一类新的具有闭环结构的内源性ncRNAs,主要是由pre-mRNAs通过反向剪接产生的[50]。circRNAs最初被认为是RNA拼接的副产品。近年来,随着更多具有重要功能的circRNAs的发现,人们对circRNAs的性质和功能产生了极大的兴趣[51]。此外,circRNA表现出组织和发育阶段特异性的表达,并且它们的表达通常不依赖于相关的线性异构体[52]。目前已有多项研究表明,circRNA在大脑中的表达最丰富,在脑功能和脑疾病中发挥重要作用[53]。虽然大多数circRNAs的确切功能尚不清楚,但越来越多的证据表明,circRNAs可能在多个水平上调节基因的表达,如调节其亲代基因的转录,影响其线性同源基因的剪接,作为miRNA海绵,调节RNA结合蛋白的功能,以及编码肽[52,54]。 据报道,circRNAs参与各种生理和病理过程,特别是在癌症中[55]。许多研究表明,circRNAs在包括胶质瘤在内的肿瘤中异常表达,在肿瘤的发生和发展中起着至关重要的作用[56-57]。 除了miRNAs和lncRNAs,有研究在2015年也在外泌体中检测到了circRNAs的存在[58]。对外泌体circRNAs的研究还处于初级阶段,但少数研究表明,circRNAs富含在外泌体中,通过外泌体开始循环并到达受体细胞,从而实现其各种生物学功能[59]。 与线性RNA不同,具有环状结构的circRNA更稳定,半衰期更长,因此比线性RNA转录本更适合开发生物标志物[60]。 2.3 外泌体ncRNAs在胶质瘤中的功能和作用 胶质瘤是最常见和最致命的原发性脑肿瘤,具有增殖快、侵袭性广、免疫监视逃避、血管生成诱导和耐药等特点,然而其潜在的分子机制仍不清楚。新的证据表明,外泌体通过在不同细胞群之间转移生物活性分子来介导胶质瘤的发生和发展[61]。 2.3.1 外泌体ncRNAs与胶质瘤细胞增殖/侵袭 恶性胶质瘤最重要的特征是增殖快、侵袭性广,涉及复杂的分子通路和肿瘤细胞与微环境之间的相互作用,这些生长特征可能最终导致手术切除不全和不可避免的肿瘤复发[62]。因此,确定与肿瘤增殖和侵袭相关的关键分子机制对于设计新的治疗策略至关重要。许多的证据表明,ncRNAs在胶质瘤的发展过程中起着重要作 用[35]。胶质瘤来源的外泌体携带广泛的ncRNAs,通过调节局部和远处微环境中的细胞间通讯,在胶质瘤增殖和侵袭中发挥重要作用[63]。 在胶质瘤中,某些miRNAs被选择性地包装成外泌体并调节细胞增殖和侵袭[64]。miR-1被认为是几种癌症的肿瘤抑制因子[65]。BRONISZ等[66]发现miR-1可以通过胶质母细胞瘤衍生的细胞外囊泡转移到周围的胶质母细胞瘤细胞中,并通过直接靶向胶质母细胞瘤中重要的促癌因子膜联蛋白A2的表达来减少胶质母细胞瘤的生长和侵袭。CAI等[67]的另一项研究发现,与健康志愿者相比,胶质母细胞瘤患者血清中外泌体miR-148a水平升高。此外,外泌体传递的miR-148a通过靶向细胞黏附分子1增强信号转导和转录激活因子3(STAT3)信号活性,促进胶质母细胞瘤细胞增殖和转移。细胞黏附分子1是一种抑制肿瘤的基因,在胶质瘤组织和大多数胶质瘤细胞系中表达下调。 除了miRNAs,一些外泌体lncRNAs,比如lncRNA-ATB和lncRNA-AHIF[6,48],也被报道在胶质瘤中调节细胞增殖和侵袭。有研究发现,胶质瘤细胞来源的外泌体能够将lncRNA-ATB转运到星形胶质细胞,促进星形胶质细胞的激活,进而促进胶质瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移。更重要的是,lncRNA-ATB以Argonaute 2 (Ago2)依赖的方式通过抑制miR-204-3p激活星形胶质细胞[6]。综上所述,外泌体细胞间选择性分泌和转移ncRNAs在调节胶质瘤的增殖和侵袭中发挥重要作用,见表1。"
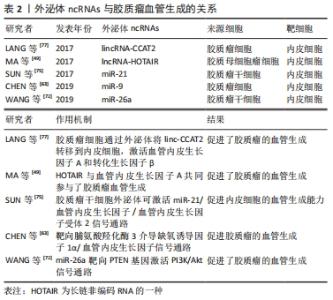
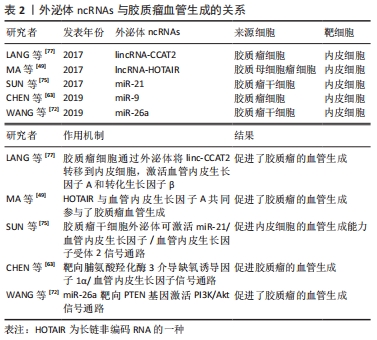
2.3.2 外泌体ncRNAs与胶质瘤血管生成 血管生成是富含血管的肿瘤的一个重要标志,在胶质瘤的发生发展中起着重要的作用,尤其是恶性胶质瘤[68]。肿瘤血管生成是一个复杂的过程,包括基底膜的降解、内皮细胞的增殖、迁移、萌发、分支和管状形成等多个步骤,并依赖于多种调节因子的协同作用[69]。血管供应是胶质瘤增殖和侵袭的基本要求,因为肿瘤的快速生长需要更多的营养物质和氧气供应。相关研究表明,实体瘤在不诱导自身血液供应的情况下,其直径不可能超过2.0-3.0 mm[70]。血管生成的机制尚不完全清楚。缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子通路的异常激活可诱导内皮细胞增殖和迁移,这被认为是血管生成的潜在原因之一[71]。因此,深入了解肿瘤血管生成的分子机制,有助于开发新的抗血管生成疗法。 大量研究表明,ncRNAs在肿瘤血管生成中发挥着重要的调控作用[69]。在肿瘤微环境中,不同类型的细胞(如肿瘤细胞、间充质干细胞和基质细胞)释放的外泌体可以被内皮细胞捕获,从而促进新血管的生长[72]。越来越多的证据表明外泌体部分通过在胶质瘤微环境中传递ncRNAs来发挥血管生成调控的功能[63,73]。作为肿瘤基因,miR-21在多种肿瘤中都有表达,并调控着多种生物学过程[74]。SUN等[75]研究发现,携带miR-21的胶质瘤干细胞来源的外泌体可以通过上调血管内皮生长因子的表达,与血管内皮生长因子受体2相互作用,来促进内皮细胞的血管生成能力。此外,有研究发现miR-9可以通过外泌体从胶质瘤细胞中分泌出来,然后被血管内皮细胞吸收。MIR-9可靶向脯氨酸羟化酶3,激活缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子信号通路促进胶质瘤血管生成,该研究表明miR-9可作为治疗胶质瘤的潜在靶点[63]。许多外泌体lncRNAs,如lncRNA-HOTAIR、lncRNA-CCAT2和lncRNA-po3F3已被证实在胶质瘤血管生成的调控中起重要作用[73]。例如,lncRNA-HOTAIR是一种在包括胶质瘤在内的多种癌症中都有明确特征的癌基因,它与肿瘤的增殖、迁移和侵袭有关,其表达与胶质瘤的分级也密切相关[76]。MA等[49]研究发现,HOTAIR基因可由胶质瘤细胞通过外泌体分泌并传递给内皮细胞,从而通过上调血管内皮生长因子的表达促进胶质瘤血管生成。LANG等[77]的另一项研究表明,胶质瘤细胞可以通过外泌体将linc-CCAT2转移到内皮细胞,激活血管内皮生长因子A和转化生长因子β,从而促进血管生成。 胶质瘤干细胞是一小部分具有多潜能胶质增殖化能力的癌细胞[78]。越来越多的证据表明胶质瘤干细胞与血管龛密切相关[79],而血管支持胶质瘤干细胞,这些干细胞反过来可通过外泌体的分泌来促进胶质瘤的血管生成。WANG等[72]还发现胶质瘤干细胞可以释放外泌体,通过传递miRNAs介导细胞通信,其结果显示,过表达miR-26a的胶质瘤干细胞衍生外泌体通过与PTEN特异性结合,进一步调控胶质瘤中PI3K/Akt信号通路,促进人脑微血管内皮细胞体外增殖和血管生成。这些研究表。胶质瘤干细胞可以通过外泌体ncRNAs促进内皮细胞的血管生成能力,见表2。"
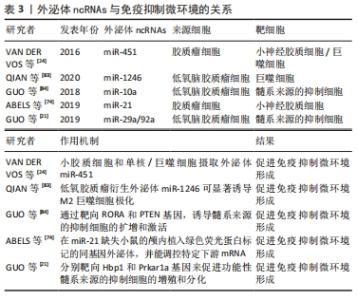
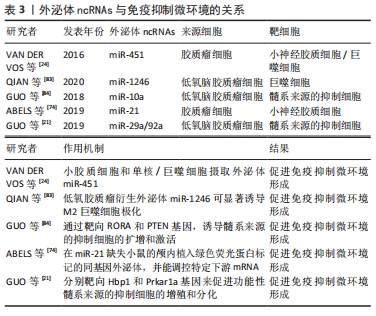
2.3.3 外泌体ncRNAs与免疫抑制微环境 胶质瘤相关免疫细胞作为胶质瘤微环境的重要组成部分,在肿瘤进展和控制抗肿瘤免疫反应中发挥着重要作用[80]。骨髓源性巨噬细胞和中枢神经系统小胶质细胞可构成多种肿瘤,它们发挥促肿瘤功能并创造免疫抑制的微环境[81]。胶质瘤细胞可以通过外泌体塑造免疫细胞,从而为肿瘤的生存和生长创造最佳的微环境[61]。胶质瘤相关的小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞是局部免疫抑制促进肿瘤进展及其对免疫调节治疗策略抵抗的关键驱动细胞[82]。因此,靶向这些免疫细胞和相关分子为胶质瘤患者提供了一种新的治疗策略。 研究表明胶质瘤细胞衍生的外泌体ncRNAs,如miR-451,miR-21和miR-1246 [24,74,83],可以改变小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞的表型,促进胶质瘤的生长和生存。有学者研究了胶质瘤细胞释放的外泌体miRNA,并被小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞吸收,作为肿瘤细胞操纵胶质瘤微环境中正常细胞的一种手段[24],他们进一步监测了在培养中暴露于分离的胶质母细胞瘤衍生细胞外囊泡的小胶质细胞的表型变化对颅内小鼠胶质瘤模型中靶mRNA的影响,结果显示,高水平的miR-451/miR-21通过细胞外囊泡从胶质瘤细胞转移到小胶质细胞,编码c-Myc的共同mRNA靶标降低,导致小胶质细胞增殖增加,细胞因子表型向免疫抑制方向转移[24]。髓系来源的抑制细胞在介导免疫抑制环境的形成和协助胶质瘤逃避宿主免疫应答方面发挥着重要作用,但其具体机制尚未明确。GUO等[84]分离了常氧刺激和缺氧刺激胶质瘤来源的外泌体,这些外泌体可以被髓系来源的抑制细胞吸收,并研究了它们在体内和体外的髓系来源的抑制细胞诱导能力,研究发现,缺氧刺激的胶质瘤来源的外泌体具有更强的诱导髓系来源的抑制细胞的能力,而低氧诱导的外泌体miR-10a和miR-21通过靶向调控RORA基因和PTEN基因,介导了髓系来源的抑制细胞的分化和激活。另一项研究中发现,胶质瘤外泌体miR-29a/miR-92a分别靶向Hbp1和Prkar1a基因来促进功能性髓系来源的抑制细胞的增殖和分化,从而介导免疫抑制微环境的形成[21]。上述研究表明,胶质瘤可通过外泌体miRNAs影响髓系来源的抑制细胞的分化和激活,从而影响整个肿瘤免疫环境,见表3。"
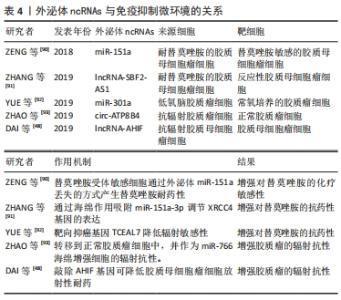
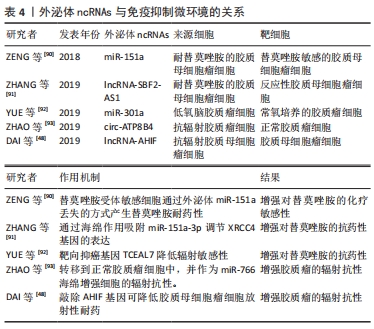
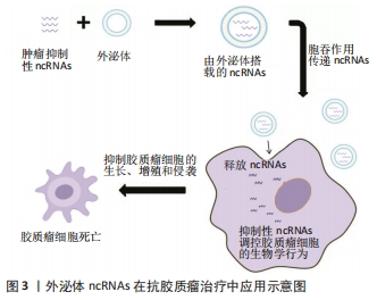
2.3.4 外泌体ncRNAs与治疗耐药性 对于高级别胶质瘤,主要采用的治疗方法是最大安全的手术切除后联合放化疗[2]。然而,高级别胶质瘤,特别是胶质母细胞瘤,常表现出对多种抗肿瘤治疗方法的晚期耐药性[85]。胶质瘤对于放射和化疗产生耐药性是影响治疗效果和导致预后不良的主要因素。有证据表明,胶质瘤的复发主要是由于胶质瘤干细胞对放疗和化疗产生了耐药性[86]。近年来,许多的证据表明,外泌体作为细胞间通信的重要媒介,能导致癌细胞异质群体间耐药性的水平传播,最终阻碍许多癌症的成功治疗[11,14]。最近的研究表明,外泌体传递的ncRNA在促进肿瘤细胞对肿瘤微环境的适应和治疗耐药性方面发挥了重要作用[87-88]。因此,为了根除这些无法治愈的肿瘤,探索治疗耐药性的机制是极为重要的。 替莫唑胺是一种单功能的DNA烷基化剂,通过诱导胶质瘤细胞DNA损伤,作为胶质瘤的一线化疗药物[89],替莫唑胺的耐药性限制了治疗反应的持久性,并影响患者的预后。相关研究表明,替莫唑胺耐药胶质瘤细胞来源的外泌体可以将替莫唑胺耐药性转移给替莫唑胺受体敏感细胞[90]。有研究发现lncRNA SBF2-AS1在替莫唑胺耐药的胶质母细胞瘤细胞和胶质瘤组织中表达上调,并与替莫唑胺耐药相关。同时,外泌体可以将lncRNA SBF2-AS1从化疗耐药的胶质母细胞瘤细胞转移到化疗反应性胶质母细胞瘤细胞,传播替莫唑胺耐药。进一步研究发现lncRNA SBF2AS1具有ceRNA的功能,可以通过海绵作用吸附miR-151a-3p调节XRCC4的表达,从而促进替莫唑胺诱导的DNA损伤的修复过程[91]。 胶质瘤细胞释放的外泌体ncRNAs也会干扰放射治疗的敏感性,从而影响治疗效率。有研究报道,缺氧胶质母细胞瘤细胞特异性分泌的外泌体miR-301a可以转移到相应的常氧培养细胞中,通过靶向TCEAL7基因促进辐射抗性[92]。另一项研究表明,抗辐射胶质母细胞瘤衍生细胞外囊泡中的circRNA-ATP8B4也可以通过海绵化miR-766来促进胶质瘤的辐射耐药[93]。因此,这些外泌体ncRNAs作为一种有前途的药物,在未来的临床应用中调节胶质瘤治疗中的放疗和化疗耐药,具有重要的治疗意义,见表4。"
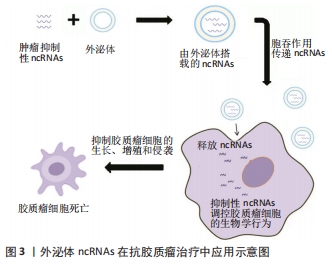
2.4 外泌体ncRNAs在胶质瘤治疗中的潜在临床应用 2.4.1 外泌体ncRNAs是很有潜力的生物标志物 目前,最新的神经成像技术如MRI,是诊断疑似颅内病变的主要方法,虽然神经影像学可能提示胶质瘤的诊断,但其他颅内病变可能具有非常相似的放射学特征,这使其难以鉴别诊断[94]。此外,在术后随访中,也很难区分真正的胶质瘤影像学病情进展[95]。与组织学检查相比,最低的MRI分辨率范围在毫米量级,而肿瘤细胞的尺寸是微米量级[96],这种度量上的差异可能导致疾病的延误诊断和治疗。通过活检或手术获得的肿瘤组织的组织学检查是目前确诊的金标准。然而,活检或手术与显著的发病率相关,并且肿瘤组织的重复取样并不总是合适的。此外,由于组织样本较少,活检可能无法反映胶质瘤的异质性。而替莫唑胺被视为高级别胶质瘤术后的一线化疗药物[89],替莫唑胺耐药性限制了治疗反应的持久性。因此,监测生物体液中的替莫唑胺耐药性对于调整治疗非常重要。 虽然传统的组织活检是诊断胶质瘤的金标准,但开发临床有效的肿瘤生物标记物对于胶质瘤的监测仍有重大意义。目前已被广泛研究的生物标志物包括循环肿瘤细胞、循环肿瘤DNA、循环蛋白和肠病毒[97]。对于各种类型的循环生物标志物,最主要的问题是它们对整个肿瘤的代表性如何,能否反映肿瘤的主要生物学特征。在理想情况下,循环肿瘤细胞可以对所有肿瘤基因组进行分析,但循环肿瘤细胞数量太少,很难检测,只能反映异质性肿瘤的单一细胞类型。循环肿瘤DNA含有肿瘤中存在的突变,似乎比循环肿瘤细胞丰富得多,但却不能反映肿瘤的异质性。然而,外泌体包含多种功能分子,可以反映整个肿瘤复杂的异质性,最重要的是,它们非常稳定,并且在几乎所有类型的体液中都很容易获得[98]。这些因素使外泌体成为最有潜力的生物标记物。 大量的研究证明,ncRNAs在包括神经胶质瘤在内的各种癌症的发生和发展中起着关键作用[99]。肿瘤细胞能分泌ncRNAs到循环系统中,这些ncRNAs既可以自由循环,也可以选择性包装到外泌体中,这些分子有望作为新的生物标志物。外泌体的双层脂质膜可以保护ncRNAs免受核糖核酸酶介导的降解,还有研究表明外泌体可以穿过血脑屏障 [100]。因此,外泌体ncRNAs在胶质瘤的诊断中具有广阔的临床应用前景,受到越来越多的关注[101-105]。 脑脊液检查在临床上已广泛用于中枢神经系统疾病的监测,但在胶质瘤中的应用较少。以往的研究表明miR-21在胶质瘤中的表达上调,并且miR-21的表达水平也与胶质瘤的组织学分级有关[106-107]。因此,miR-21因其作为诊断和预后标志物的潜力而受到广泛关注。AKERS等[108]发现胶质母细胞瘤患者脑脊液细胞外囊泡miR-21水平平均比对照组高10倍,这表明脑脊液细胞外囊泡中 miR-21可能作为胶质母细胞瘤患者的诊断生物标志物。SHI等[106]的一项类似研究也发现,胶质瘤患者脑脊液中的外泌体miR-21水平明显高于对照组,而血清来源的外泌体miR-21表达却没有差异。此外,脑脊液中外泌体miR-21水平与肿瘤复发和脊髓/脑室转移相关。这些研究表明,脑脊液来源的外泌体ncRNAs可作为胶质瘤诊断和预后具有潜力的生物标志物。 在血液中,发现了另一个神经胶质瘤生物标志物。YANG等[87]发现高级别胶质瘤组织中miR-221表达水平升高,进一步分析发现胶质瘤患者的血清外泌体miR-221水平显著高于对照组,更重要的是,血清外泌体miR-221水平随着胶质瘤的分级而升高,这项研究表明,外泌体miR-221有潜力作为胶质瘤患者的一种新的诊断生物标志物,这能为特别需要关注的胶质瘤患者提供长期预后的信息。寻找一种非侵入性、快速、高灵敏度的生物标记物来评估患者的预后具有重要的临床意义。有研究表明外泌体ncRNAs可以作为胶质瘤的独立预后参数[102]。还有研究发现,血清外泌体miR-301a水平的增加与更长的总生存期相关,进一步的Cox回归分析结果证实血清外泌体miR-301a水平与患者的总生存期独立相关[102]。获得性耐药是制约胶质瘤临床治疗的主要因素,因此及时发现潜在的耐药患者并寻找替代的治疗方法对胶质瘤患者改善预后极为重要。ZHANG等[91]发现复发性胶质母细胞瘤患者的血清外泌体lncRNA SBF2-AS1水平升高与患者预后差成正相关。综上所述,体液中的外泌体ncRNAs在生物标志物研究方面具有巨大潜力,其临床应用值得进一步研究。 2.4.2 外泌体ncRNAs在抗胶质瘤治疗中的潜在应用 考虑到外泌体ncRNAs在胶质瘤中的重要生物学功能,靶向阻止外泌体或其载物(如ncRNAs)可能是治疗胶质瘤很有潜力的选择。因此,许多研究如何调节外泌体的产生或者阻断肿瘤摄取外泌体的途径,从而达到治疗癌症的目的[109]。有研究提出了一种新的治疗方法,通过采用血液过滤系统(如Aethlon ADAPT TM system),能够快速体外捕获和选择性保留整个循环系统中< 200 nm的目标粒子,进而去除或减少外周循坏中外泌体含量,可为胶质瘤的治疗提供新方法[110]。在丙型肝炎病毒感染患者中,使用ADAPT TM的治疗方法来降低病毒粒子的含量,这些病毒粒子的大小与癌症来源的外泌体大小相似,该治疗方法的安全性和有效性得到了临床经验的支持[111]。因此,去除或减少外周循坏中外泌体含量可为肿瘤的治疗提供新方法。ncRNAs(如miRNAs、lncRNAs和circRNAs等)是胶质瘤发生和发展的重要调控分子,在肿瘤增殖、侵袭、血管生成和治疗耐药性等生物学过程中发挥着重要作用[35]。随着对ncRNAs研究的深入,外泌体ncRNAs将成为治疗胶质瘤的重要靶点。 血脑屏障虽然有助于保护大脑,但它也给治疗神经胶质瘤带来了困难[112]。外泌体作为磷脂双层膜囊泡,内含丰富的生物活性分子,其作为基因治疗的载体有着明显的优势;此外,外泌体还具有体积小、灵活性强及组织相容性良好等自身特点,使它们能够跨越体内主要的生物屏障,如血脑屏障 [100]。LAI等[113]设计了一种高灵敏度的外泌体成像系统,这个系统能够随着时间推移在活体组织中密切追踪外泌体的体内分布并将其成像。通过这个系统,他们发现被注射的外泌体能够在1 h内运送到肿瘤部位。因此,外泌体将有潜力作为治疗的传递媒介,通过外泌体携带药物,运送到胶质瘤中,达到治疗胶质瘤的目的。 外泌体是天然的ncRNAs载体,它们可递送肿瘤抑制性ncRNAs。一般来说,肿瘤抑制性ncRNAs在癌症中被下调,而通过外泌体在肿瘤细胞中过表达这些ncRNAs可抑制肿瘤的进展。有研究发现,在大鼠原发性脑瘤模型中,在肿瘤内注射外泌体可以显著减少胶质瘤异种移植瘤的生长,该外泌体是由过表达miR-146b的骨髓间充质干细胞释放的,miR-146b是一种抗胶质瘤的miRNA,可以减少胶质瘤细胞的侵袭、迁移和活力[25]。FAREH等[64]进行了一项类似的研究,通过基因工程使原代胶质瘤细胞稳定表达miR-302-367,这种抑制肿瘤的miRNA主要被包裹于外泌体中,并被相邻的基底膜细胞摄取,从而在体内和体外诱导抗肿瘤细胞效应。此外,MUNOZ等[114]发现,通过间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体将功能性的抗-miR-9传递到胶质母细胞瘤细胞,可以使胶质母细胞瘤对替莫唑胺的反应更加敏感。这些研究表明,外泌体可以作为传递抗肿瘤ncRNAs的载体,发挥治疗方面的潜在应用。除了传递各种ncRNAs外,其他类型的内源性和外源性治疗载体,如蛋白质和亲脂性小分子,也可以装载到这些颗粒中用于癌症治疗[109]。然而,在这些治疗方法还未运用到临床,需要进一步的研究,见图3。"
| [1] MOLINARO AM, TAYLOR JW, WIENCKE JK, et al. Genetic and molecular epidemiology of adult diffuse glioma. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(7):405-417. [2] STUPP R, MASON WP, VAN DEN BENT MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987-996. [3] ALIFIERIS C, TRAFALIS DT. Glioblastoma multiforme: pathogenesis and treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;152:63-82. [4] QUAIL DF, JOYCE JA. The microenvironmental landscape of brain tumors. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(3):326-341. [5] GODLEWSKI J, KRICHEVSKY AM, JOHNSON MD, et al. Belonging to a network--microRNAs, extracellular vesicles, and the glioblastoma microenvironment. Neuro Oncol. 2015;17(5):652-662. [6] BIAN EB, CHEN EF, XU YD, et al. Exosomal lncRNA‑ATB activates astrocytes that promote glioma cell invasion. Int J Oncol. 2019;54(2):713-721. [7] ELLERT-MIKLASZEWSKA A, PASIERBINSKA M, POLESZAK K, et al. Molecular interactions between tumor and its microenvironment in malignant gliomas. Postepy Biochem. 2018;64(2):129-140. [8] CHIODONI C, DI MARTINO MT, ZAZZERONI F, et al. Cell communication and signaling: how to turn bad language into positive one. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):128. [9] RAPOSO G, STAHL PD. Extracellular vesicles: a new communication paradigm? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(9):509-510. [10] TKACH M, THÉRY C. Communication by extracellular vesicles: where we are and where we need to go. Cell. 2016;164(6):1226-1232. [11] XIE Y, DANG W, ZHANG S, et al. The role of exosomal noncoding RNAs in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):37. [12] JIANG L, GU Y, DU Y, et al. Exosomes: diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic delivery vehicles for cancer. Mol Pharm. 2019;16(8):3333-3349. [13] VAN NIEL G, D’ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213-228. [14] SUN Z, YANG S, ZHOU Q, et al. Emerging role of exosome-derived long non-coding RNAs in tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):82. [15] HURLEY JH. ESCRT complexes and the biogenesis of multivesicular bodies. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20(1):4-11. [16] BAIETTI MF, ZHANG Z, MORTIER E, et al. yndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(7):677-685. [17] STUFFERS S, SEM WEGNER C, STENMARK H, et al. Multivesicular endosome biogenesis in the absence of ESCRTs. Traffic. 2009;10(7):925-937. [18] CHAIROUNGDUA A, SMITH DL, POCHARD P, et al. Exosome release of β-catenin: a novel mechanism that antagonizes Wnt signaling. J Cell Biol. 2010;190(6): 1079-1091. [19] OSTROWSKI M, CARMO NB, KRUMEICH S, et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(1): 19-30. [20] MULCAHY LA, PINK RC, CARTER DR. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014. doi: 10.3402/jev.v3.24641. [21] GUO X, QIU W, WANG J, et al. Glioma exosomes mediate the expansion and function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells through microRNA-29a/Hbp1 and microRNA-92a/Prkar1a pathways. Int J Cancer. 2019;144(12):3111-3126. [22] COLOMBO M, RAPOSO G, THÉRY C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:255-289. [23] CHISTIAKOV DA, CHEKHONIN VP. Extracellular vesicles shed by glioma cells: pathogenic role and clinical value. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(9):8425-8438. [24] VAN DER VOS KE, ABELS ER, ZHANG X, et al. Directly visualized glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles transfer RNA to microglia/macrophages in the brain. Neuro Oncol. 2016;18(1):58-69. [25] KATAKOWSKI M, BULLER B, ZHENG X, et al. Exosomes from marrow stromal cells expressing miR-146b inhibit glioma growth. Cancer Lett. 2013;335(1): 201-204. [26] DENG SZ, LAI MF, LI YP, et al. Human marrow stromal cells secrete microRNA-375-containing exosomes to regulate glioma progression. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020;27(3-4):203-215. [27] YU L, GUI S, LIU Y, et al. Exosomes derived from microRNA-199a-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells inhibit glioma progression by down-regulating AGAP2. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(15):5300-5318. [28] SHARIF S, GHAHREMANI MH, SOLEIMANI M. Delivery of exogenous mir-124 to glioblastoma multiform cells by wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells decreases cell proliferation and migration, and confers chemosensitivity. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018;14(2):236-246. [29] ZHAO M, XU J, ZHONG S, et al. Expression profiles and potential functions of circular RNAs in extracellular vesicles isolated from radioresistant glioma cells. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(3):1893-1900. [30] ZHANG X, ZHANG X, HU S, et al. Identification of miRNA-7 by genome-wide analysis as a critical sensitizer for TRAIL-induced apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(10):5930-5944. [31] LANG FM, HOSSAIN A, GUMIN J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as natural biofactories for exosomes carrying miR-124a in the treatment of gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(3):380-390. [32] JEPPESEN DK, FENIX AM, FRANKLIN JL, et al. Reassessment of exosome composition. Cell. 2019;177(2):428-445. [33] KIM KM, ABDELMOHSEN K, MUSTAPIC M, et al. RNA in extracellular vesicles. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017;8(4):10. [34] Pegtel DM, Gould SJ. Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:487-514. [35] NIE JH, LI TX, ZHANG XQ, et al. Roles of non-coding rnas in normal human brain development, brain tumor, and neuropsychiatric disorders. Noncoding RNA. 2019;5(2):36. [36] ZHU L, LIU X, PU W, et al. tRNA-derived small non-coding RNAs in human disease. Cancer Lett. 2018;419:1-7. [37] ZHU L, LI J, GONG Y, et al. Exosomal tRNA-derived small RNA as a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):74. [38] LI B, HONG J, HONG M, et al. piRNA-823 delivered by multiple myeloma-derived extracellular vesicles promoted tumorigenesis through re-educating endothelial cells in the tumor environment. Oncogene. 2019;38(26): 5227-5238. [39] PENG Y, CROCE CM. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016;1:15004. [40] MACFARLANE LA, MURPHY PR. MicroRNA: biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr Genomics. 2010;11(7):537-561. [41] KOZOMARA A, BIRGAOANU M, GRIFFITHS-JONES S. miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(1):155-162. [42] SAADATPOUR L, FADAEE E, FADAEI S, et al. Glioblastoma:exosome and microRNA as novel diagnosis biomarkers. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016;23(12):415-418. [43] PENG Z, LIU C, WU M. New insights into long noncoding RNAs and their roles in glioma. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):61. [44] QUINN JJ, CHANG HY. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17(1):47-62. [45] KOPP F, MENDELL JT. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018;172(3):393-407. [46] GOU Q, GAO L, NIE X, et al. Long Noncoding RNA AB074169 Inhibits Cell Proliferation via Modulation of KHSRP-Mediated CDKN1a Expression in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018;78(15):4163-4174. [47] WANG M, ZHOU L, YU F, et al. The functional roles of exosomal long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(11):2059-2076. [48] DAI X, LIAO K, ZHUANG Z, et al. AHIF promotes glioblastoma progression and radioresistance via exosomes. Int J Oncol. 2019;54(1):261-270. [49] MA X, LI Z, LI T, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR enhances angiogenesis by induction of VEGFA expression in glioma cells and transmission to endothelial cells via glioma cell derived-extracellular vesicles. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(11):5012-5021. [50] CHEN LL. The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17(4):205-211. [51] SHANG Q, YANG Z, JIA R, et al. The novel roles of circRNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):6. [52] LI X, YANG L, CHEN LL. The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 2018;71(3):428-442. [53] RYBAK-WOLF A, STOTTMEISTER C, GLAŽAR P, et al. Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell. 2015;58(5):870-885. [54] ZHANG M, ZHAO K, XU X, et al. A peptide encoded by circular form of LINC-PINT suppresses oncogenic transcriptional elongation in glioblastoma. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4475. [55] LIU J, ZHAO K, HUANG N, et al. Circular RNAs and human glioma. Cancer Biol Med. 2019;16(1):11-23. [56] HAO Z, HU S, LIU Z, et al. Circular RNAs: functions and prospects in glioma. J Mol Neurosci. 2019;67(1):72-81. [57] LI Y, ZHENG Q, BAO C, et al. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015;25(8):981-984. [58] WANG Y, LIU J, MA J, et al. Exosomal circRNAs: biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):116. [59] LASDA E, PARKER R. Circular RNAs co-precipitate with extracellular vesicles: a possible mechanism for circRNA clearance. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0148407. [60] TAN S, GOU Q, PU W, et al. Circular RNA F-circEA produced from EML4-ALK fusion gene as a novel liquid biopsy biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Res. 2018;28(6):693-695. [61] ROOJ AK, MINEO M, GODLEWSKI J. MicroRNA and extracellular vesicles in glioblastoma:small but powerful. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2016;33(2):77-88. [62] XIE Q, MITTAL S, BERENS ME. Targeting adaptive glioblastoma:an overview of proliferation and invasion. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16(12):1575-1584. [63] CHEN X, YANG F, ZHANG T, et al. MiR-9 promotes tumorigenesis and angiogenesis and is activated by MYC and OCT4 in human glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):99. [64] FAREH M, ALMAIRAC F, TURCHI L, et al. Cell-based therapy using miR-302-367 expressing cells represses glioblastoma growth. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(3): e2713. [65] NOHATA N, HANAZAWA T, ENOKIDA H, et al. microRNA-1/133a and microRNA-206/133b clusters: dysregulation and functional roles in human cancers. Oncotarget. 2012;3(1):9-21. [66] BRONISZ A, WANG Y, NOWICKI MO, et al. Extracellular vesicles modulate the glioblastoma microenvironment via a tumor suppression signaling network directed by miR-1. Cancer Res. 2014;74(3):738-750. [67] CAI Q, ZHU A, GONG L. Exosomes of glioma cells deliver miR-148a to promote proliferation and metastasis of glioblastoma via targeting CADM1. Bull Cancer. 2018;105(7-8):643-651. [68] ONISHI M, ICHIKAWA T, KUROZUMI K, et al. Angiogenesis and invasion in glioma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2011;28(1):13-24. [69] WANG Y, WANG L, CHEN C, et al. New insights into the regulatory role of microRNA in tumor angiogenesis and clinical implications. Mol Cancer. 2018; 17(1):22. [70] YADAV L, PURI N, RASTOGI V, et al. Tumour Angiogenesis and Angiogenic Inhibitors: a Review. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(6):Xe01-Xe05. [71] VALLÉE A, GUILLEVIN R, VALLÉE JN. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis initiation under normoxic conditions through Wnt/β-catenin pathway in gliomas. Rev Neurosci. 2018;29(1):71-91. [72] WANG ZF, LIAO F, WU H, et al. Glioma stem cells-derived exosomal miR-26a promotes angiogenesis of microvessel endothelial cells in glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):201. [73] LANG HL, HU GW, CHEN Y, et al. Glioma cells promote angiogenesis through the release of exosomes containing long non-coding RNA POU3F3. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(5):959-972. [74] ABELS ER, MAAS SLN, NIELAND L, et al. Glioblastoma-associated microglia reprogramming is mediated by functional transfer of extracellular miR-21. Cell Rep. 2019;28(12):3105-3119. [75] SUN X, MA X, WANG J, et al. Glioma stem cells-derived exosomes promote the angiogenic ability of endothelial cells through miR-21/VEGF signal. Oncotarget. 2017;8(22):36137-36148. [76] PASTORI C, KAPRANOV P, PENAS C, et al. The Bromodomain protein BRD4 controls HOTAIR, a long noncoding RNA essential for glioblastoma proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(27):8326-8331. [77] LANG HL, HU GW, ZHANG B, et al. Glioma cells enhance angiogenesis and inhibit endothelial cell apoptosis through the release of exosomes that contain long non-coding RNA CCAT2. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(2):785-798. [78] LATHIA JD, GALLAGHER J, MYERS JT, et al. Direct in vivo evidence for tumor propagation by glioblastoma cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24807. [79] JHAVERI N, CHEN TC, HOFMAN FM. Tumor vasculature and glioma stem cells: contributions to glioma progression. Cancer Lett. 2016;380(2):545-551. [80] GIERYNG A, PSZCZOLKOWSKA D, WALENTYNOWICZ KA, et al. Immune microenvironment of gliomas. Lab Invest. 2017;97(5):498-518. [81] CHEN Z, HAMBARDZUMYAN D. Immune microenvironment in glioblastoma subtypes. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1004. [82] LOCARNO CV, SIMONELLI M, CARENZA C, et al. Role of myeloid cells in the immunosuppressive microenvironment in gliomas. Immunobiology. 2020; 225(1):151853. [83] QIAN M, WANG S, GUO X, et al. Hypoxic glioma-derived exosomes deliver microRNA-1246 to induce M2 macrophage polarization by targeting TERF2IP via the STAT3 and NF-κB pathways. Oncogene. 2020;39(2):428-442. [84] GUO X, QIU W, LIU Q, et al. Immunosuppressive effects of hypoxia-induced glioma exosomes through myeloid-derived suppressor cells via the miR-10a/Rora and miR-21/Pten Pathways. Oncogene. 2018;37(31):4239-4259. [85] QAZI MA, VORA P, VENUGOPAL C, et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity:pathways to treatment resistance and relapse in human glioblastoma. Ann Oncol. 2017; 28(7):1448-1456. [86] BAO S, WU Q, MCLENDON RE, et al. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature. 2006;444 (7120):756-760. [87] YANG JK, YANG JP, TONG J, et al. Exosomal miR-221 targets DNM3 to induce tumor progression and temozolomide resistance in glioma. J Neurooncol. 2017;131(2):255-265. [88] FAN Q, YANG L, ZHANG X, et al. The emerging role of exosome-derived non-coding RNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Lett. 2018;414:107-115. [89] YOSHIMOTO K, MIZOGUCHI M, HATA N, et al. Complex DNA repair pathways as possible therapeutic targets to overcome temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Front Oncol. 2012;2:186. [90] ZENG A, WEI Z, YAN W, et al. Exosomal transfer of miR-151a enhances chemosensitivity to temozolomide in drug-resistant glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2018;436:10-21. [91] ZHANG Z, YIN J, LU C, et al. Exosomal transfer of long non-coding RNA SBF2-AS1 enhances chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):166. [92] YUE X, LAN F, XIA T. Hypoxic glioma cell-secreted exosomal miR-301a activates wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes radiation resistance by targeting TCEAL7. Mol Ther. 2019;27(11):1939-1949. [93] ZHAO M, XU J, ZHONG S, et al. Expression profiles and potential functions of circular RNAs in extracellular vesicles isolated from radioresistant glioma cells. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(3):1893-1900. [94] SMIRNIOTOPOULOS JG, MURPHY FM, RUSHING EJ, et al. Patterns of contrast enhancement in the brain and meninges. Radiographics. 2007;27(2):525-551. [95] RADBRUCH A, FLADT J, KICKINGEREDER P, et al. Pseudoprogression in patients with glioblastoma: clinical relevance despite low incidence. Neuro Oncol. 2015;17(1):151-159. [96] SORENSEN AG, BATCHELOR TT, WEN PY, et al. Response criteria for glioma, Nature clinical practice. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2008;5(11):634-644. [97] WESTPHAL M, LAMSZUS K. Circulating biomarkers for gliomas. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11(10):556-566. [98] BULLOCK MD, SILVA AM, KANLIKILICER-UNALDI P, et al. Exosomal non-coding rnas: diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic applications in cancer. Noncoding RNA. 2015;1(1):53-68. [99] CECH TR, STEITZ JA. The noncoding RNA revolution-trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell. 2014;157(1):77-94. [100] MATSUMOTO J, STEWART T, BANKS WA, et al. The transport mechanism of extracellular vesicles at the blood-brain barrier. Curr Pharm Des. 2017; 23(40):6206-6214. [101] SANTANGELO A, IMBRUCÈ P, GARDENGHI B, et al. A microRNA signature from serum exosomes of patients with glioma as complementary diagnostic biomarker. J Neurooncol. 2018;136(1):51-62. [102] LAN F, QING Q, PAN Q, et al. Serum exosomal miR-301a as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018;41(1):25-33. [103] SHAO N, XUE L, WANG R, et al. miR-454-3p is an exosomal biomarker and functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019;18(2):459-469. [104] TAN SK, PASTORI C, PENAS C, et al. Serum long noncoding RNA HOTAIR as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):74. [105] MANTEROLA L, GURUCEAGA E, GÁLLEGO PÉREZ-LARRAYA J, et al. A small noncoding RNA signature found in exosomes of GBM patient serum as a diagnostic tool. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16(4) 520-527. [106] SHI R, WANG PY, LI XY, et al. Exosomal levels of miRNA-21 from cerebrospinal fluids associated with poor prognosis and tumor recurrence of glioma patients. Oncotarget. 2015;6(29):26971-2681. [107] CHAN JA, KRICHEVSKY AM, KOSIK KS. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65(14):6029-6033. [108] AKERS JC, RAMAKRISHNAN V, KIM R, et al. MiR-21 in the extracellular vesicles (EVs) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): a platform for glioblastoma biomarker development. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e78115. [109] H Rashed M, Bayraktar E, K Helal G, et al. Exosomes: from garbage bins to promising therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):538. [110] MARLEAU AM, CHEN CS, JOYCE JA, et al. Exosome removal as a therapeutic adjuvant in cancer. J Transl Med. 2012;10:134. [111] TULLIS RH, DUFFIN RP, HANDLEY HH, et al. Reduction of hepatitis C virus using lectin affinity plasmapheresis in dialysis patients. Blood Purif. 2009;27(1):64-69. [112] NAIR KGS, RAMAIYAN V, SUKUMARAN SK. Enhancement of drug permeability across blood brain barrier using nanoparticles in meningitis. Inflammopharmacology. 2018;26(3):675-684. [113] LAI CP, MARDINI O, ERICSSON M, et al. Dynamic biodistribution of extracellular vesicles in vivo using a multimodal imaging reporter. ACS Nano. 2014;8(1):483-494. [114] MUNOZ JL, BLISS SA, GRECO SJ, et al. Delivery of functional anti-mir-9 by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes to glioblastoma multiforme cells conferred chemosensitivity. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013;2(10) e126. |
| [1] | Tang Wenjing, Wu Siyuan, Yang Chen, Tao Xi. Inflammatory responses in post-stroke depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1278-1285. |
| [2] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [3] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [4] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [5] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [6] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [7] | Chen Na, Wang Xiaohan, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells on aging-related ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3914-3920. |
| [8] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Huanan, Chen Feng, Chai Yuan, Gan Bin, Li Song, Chen Dingpeng. Potential molecular mechanism of Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction in the treatment of gouty arthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 245-252. |
| [9] | Shan Zhengming, Tao Shuchun, Hu Chunmei, Zhang Zhiyuan, Ding Yinan, He Mengcheng, Tang Qiusha. Extraction, identification and proteomic analysis of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3036-3042. |
| [10] | Wang Weiwei, Ou Zhixue, Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Shibin, Zhou Yi, Li Tong. Regulatory mechanism of exosomes in signal communication network of steroid induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3056-3064. |
| [11] | Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Zhao Wanhua, Lin Yushi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Important role of exosomes-mediated hypoxia-related signaling pathways in the occurrence and progression of diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3065-3070. |
| [12] | Bai Jiameng, Liu Guangwei, Xie Lu, Mao Yaoyao, He Huichang, Wang Chunjing. Application of mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes in liver regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3071-3077. |
| [13] | Tang Zhihong, Duan Hao, Zhong Zongyu, Wang Weizhou, Chen Yongcheng, Li Xiaozhuang, Wang Yanghao, Liu Zhui, He Fei. Mechanism of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3090-3094. |
| [14] | Wei Jingjing, Li Chenyang, Wang Ping, Li Yaxuan, Ding Xiaofang, Yang Lin. Application and existing problems of polyethylene glycol in the field of neurological reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2618-2624. |
| [15] | Peng Huizhen, Cai Mingxiang, Liu Xiangning. Angiogenesis regulation in bone repair: new ideas and new methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2400-2405. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||