Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (23): 4313-4319.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.23.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of dental and non-dental stem cells in the study of tissue-engineered regenerated teeth
Xu Hang, Nong Xiao-lin
- Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Stomatology, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2013-06-04Published:2013-06-04 -
Contact:Nong Xiao-lin, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Stomatology, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China lab.nong@gmail.com -
About author:Xu Hang★, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Stomatology, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China xhang1105@yahoo.com.cn -
Supported by:the Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. Guikehui 0836013*; the Postgraduate Education Innovation Project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2007 Zhong 16*, 201010598RY10*, 2011105981003M184*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Hang, Nong Xiao-lin. Effects of dental and non-dental stem cells in the study of tissue-engineered regenerated teeth[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(23): 4313-4319.
share this article
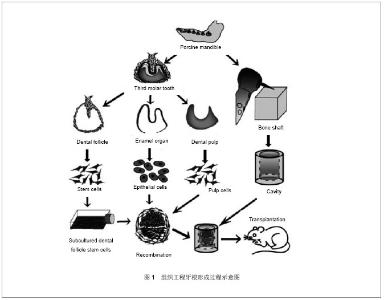
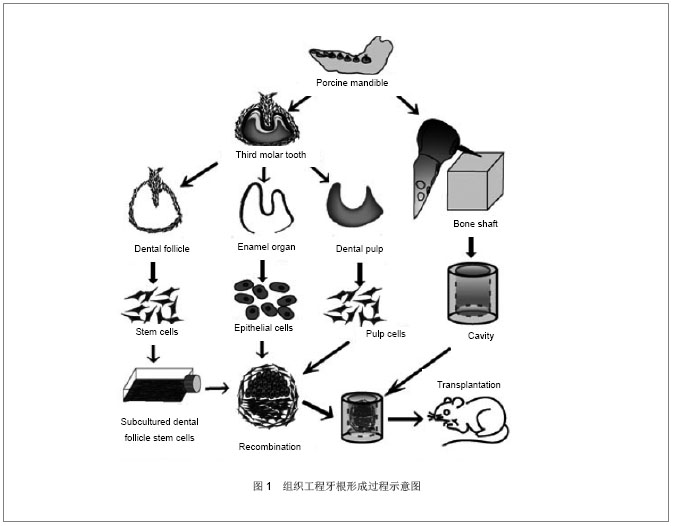
2.1 牙源性干细胞 随着牙组织工程学的发展,多种具有干细胞生物学特性的细胞被成功的从牙颌系统的不同部位分离出,作为再生牙研究中的种子细胞,例如恒牙及乳牙牙髓、牙周韧带、发育过程中的牙根尖以及牙囊组织。所有这些细胞都来源于神经嵴细胞,并且都具有间充质干细胞样特性,即可以分化成间充质细胞系。在体内特殊条件下以及体外诱导下,这些细胞都可以参与牙体硬组织的形成过程,是再生牙研究中的重要种子细胞。 2.1.1 根尖乳头干细胞 在近年的研究中,研究人员从未发育完全的牙根尖部发现了牙根尖乳头干细胞这一间质干细胞。研究者在临床病例中发现在没有牙髓的情况下,根尖仍然可以继续形成,从而推测是牙根尖乳头干细胞分化成为成牙本质细胞进而生成牙本质[7] 。经体外培养诱导,牙根尖乳头干细胞可以向牙本质细胞分化,诱导4周的牙乳头细胞可以表达成牙本质细胞表面标志物——牙本质涎蛋白。将牙根尖乳头干细胞与牙周韧带干细胞共同植入小型猪的牙槽可发现牙本质与牙周韧带形成[8] 。研究人员以羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙和明胶海绵支架作为载体,使用牙根尖乳头干细胞制造生物牙根,植入猪下颌骨3个月后获得了周围有牙周膜包绕的生物牙根[8] 。但是根尖乳头干细胞最大的局限在于此种细胞只能在牙根未完成发育且牙齿未萌出时的根尖获得[9] 。种种证据显示,牙根尖乳头干细胞对于牙根形成、牙根再造有很重要的作用,对其研究有助于从细胞水平上了解牙的发育和组织再生的修复机制。目前,牙根尖乳头干细胞的研究尚处在起步阶段,牙根尖乳头干细胞的分化潜能、表面标志物和组织工程化牙的应用等问题尚未解决,还有待于学者们的深入研究[10] 。 2.1.2 牙髓干细胞 当牙齿受到损伤时,牙髓细胞可以被激活生成修复性牙本质,这一修复过程提示成人牙髓中存在间充质干细胞,2000年Gronthos等[11] 首次提出了牙髓干细胞这一新概念,并说明了其具有自我更新和多向分化的潜能,从第三恒磨牙中分离出的这些牙髓干细胞可零星的产生很强的克隆形成能力,但几乎不见钙化结节形成。另外有研究发现,牙髓干细胞在免疫缺陷小鼠体内可以形成牙髓-牙本质复合体类似物[12] 。也有研究者将牙髓干细胞分化成功能活跃的神经元,并发现其具有治疗神经元紊乱的潜能[13-15] 。体外实验中,在矿化诱导液的作用下,牙髓干细胞可以表达牙本质特异性蛋白,说明其具有向成牙本质细胞分化的能力[16] 。Mohamadreza等[17]将狗的牙髓干细胞回植到自体牙周炎模型,且已行牙周手术的下前牙后,有新生的牙周组织形成。这一实验初步展示了牙髓干细胞在自体分化成牙周细胞的能力。 2.1.3 牙周膜干细胞 试管培养中,发现牙周韧带包含STRO-1抗原阳性细胞,该细胞在其转化为成脂肪、成骨及成软骨表型之前,可保持一定的可塑性[18] 。这就说明牙周韧带中包含着祖细胞,可以被激活而进行自我更新,并且重建其他组织,如牙骨质和软骨[19] 。2004年Seo等采用酶消化法将健康成年人牙周膜组织制成单细胞悬液进行体外培养,首次分离出牙周膜干细胞并证实其是一类具有很强的克隆能力和多向分化潜能的细胞。在牙周组织工程中已将自体牙周膜细胞作为种子细胞[20-21] ,体内外都可诱导分化形成成牙骨质细胞样细胞、脂肪细胞以及富含Ⅰ型胶原的结缔组织[8,22-23] 。研究发现,因为牙周膜干细胞的存在,使得在咀嚼力作用下的牙周韧带数量保持恒定,这一特性也就使得牙周韧带干细胞成为首选的牙周韧带再生种子细胞[24] 。体外实验中,牙周膜干细胞经诱导可形成矿化结节,表达碱性磷酸酶或骨唾液蛋白。将其移植至免疫缺陷的小鼠中,牙周膜干细胞能沿牙周膜结缔组织方向走行产生牙骨质样结构[19]。牙周膜干细胞这一特性的发现,使得再生牙固位问题的解决成为可能。 2.1.4 牙囊干细胞 牙囊是来源于外胚间充质的一种疏松结缔组织,在牙齿发育阶段包绕着成釉器和牙乳头。在牙根发育的过程中,上皮根鞘裂解成碎片使间充质细胞可以接触到牙囊中的牙本质表面,并分化形成成熟的牙周膜。因此认为人牙囊中也含有干细胞,能够分化出牙槽骨中的成骨细胞、牙周韧带中的成纤维细胞和成牙骨质细胞。牙囊干细胞可以转化成为成熟牙周膜中的牙槽骨、牙周韧带以及牙骨质[25] 。在以往的一项关于牙囊干细胞的研究中,研究人员从人类第三磨牙牙囊中分离出的细胞表达了干细胞标志物Notch1、STRO-1和巢蛋白,且具有形成结构致密的钙化结节的能力。已证实人牙囊干细胞具有多向间叶祖细胞的功能[26-27] 。研究发现牙囊细胞可分化成为牙周韧带纤维母细胞,并向周围分泌胶原影响周围牙槽骨及牙骨质表面的纤维,从而控制牙周韧带的形成。将牙囊细胞移植入SCID小鼠体内发现,牙囊细胞可形成成牙骨质样细胞[28-29] 。将牙囊细胞与牙根尖乳头干细胞共培养,结果发现其展现出了比其他牙源性干细胞更强的可塑性[30] 。体外建立牙囊干细胞与牙髓细胞、牙源性上皮细胞共培养系统,模拟牙根形成过程,并将该系统与骨支架一同植入裸鼠网膜内,成功获得了再生牙根,但遗憾的是没有完整的牙周韧带形成,见图1,2[31] 。关于这类细胞潜能的更进一步研究尚还欠缺。"
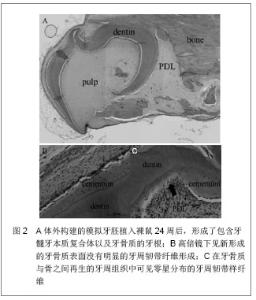
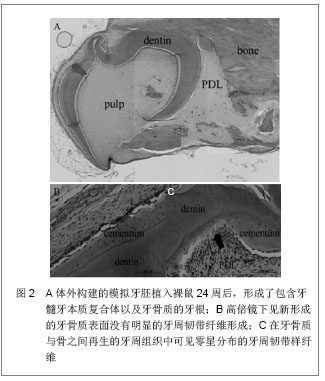
2.1.5 脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞 2003年Miura等[32]首次从人类可自然替换器官乳牙中获取干细胞,即人脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞,该细胞是具有高分化潜能的单克隆干细胞,其可分化出神经元细胞、脂肪细胞、成骨细胞和成牙本质细胞。体外培养脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞显示出了成牙本质细胞特性,经矿化诱导可形成钙化结节,成牙本质相关蛋白表达增加。体内试验将体外扩增的乳牙牙髓干细胞与羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙支架材料一同植入裸鼠皮下,可得到牙本质样结构,且牙本质特异性蛋白表达呈阳性,证实了乳牙牙髓干细胞可在体内、外分化成牙本质细胞。体内试验,人脱落乳牙中的干细胞可以诱导骨和牙齿的形成[33] 。脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞也可在免疫缺陷小鼠皮下产生具有牙本质性能的管状牙本质样物质。有研究者将脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞移植入体内因感染摘除牙髓的牙齿中,结果发现有类似牙髓的组织形成[34] 。Casagrande等[35]发现牙本质来源的骨形成蛋白2能诱导乳牙牙髓干细胞分化为成牙本质细胞,表达成牙本质细胞的表面标志。Cordeiro等[33]将乳牙牙髓干细胞和皮肤血管内皮细胞接种在可降解生物支架的牙切片上并将牙切片植入裸鼠皮下观察,发现乳牙牙髓干细胞可分化成为类成牙本质细胞和类血管内皮细胞,最终可形成牙髓样组织。 2.2 非牙源性干细胞 牙源性干细胞在再生牙研究中展现了诸多优点,但在实际应用牙源性干细胞的过程中还是存在着问题,因其只有在智齿萌出阶段从牙乳头顶部分离的牙囊祖细胞或者干细胞获得的才有活性(通常是15-28岁)。于是研究人员开始在非牙源性干细胞中寻找适合再生牙的种子细胞,在此当中骨髓间充质干细胞和脐血干细胞展现了向成牙细胞分化的能力。 2.2.1 骨髓间充质干细胞 骨髓间充质干细胞在特定条件下可以形成多种间充质细胞,而且具有体外培养增殖稳定、植入体内快速进行成骨活动的特点。近年来,骨髓间充质干细胞也被应用在了再生牙的研究中,并被证实具有向成牙细胞分化并形成牙齿样组织的能力[36-37] 。Hu等[36]的研究发现,牙源性胚胎上皮与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养可获得分泌型成釉细胞样细胞。Modino等[37]发现骨髓间充质干细胞可替代牙间充质,与胚胎上皮细胞共同作用形成牙胚,在此过程中骨髓间充质干细胞分化成为成牙本质细胞,形成牙本质。在试管中将骨髓间充质干细胞植入被损伤的牙周组织中,这些细胞就可以形成牙骨质、牙周韧带和牙槽骨。Song等[38]发现在釉基质蛋白的促进作用下,从猪体内提取的骨髓间充质干细胞可分化为成牙骨质细胞。 但是,骨髓间充质干细胞的成牙能力较牙髓干细胞低[39] 。另外,获取骨髓的过程是一个有巨大创伤的过程,且骨髓间充质干细胞的数量、分化能力以及最大生存跨度都随着增殖代数的增加而降低[40-41] 。 2.2.2 脐血干细胞 由脐血中分离出的多能干细胞具有多向分化潜能,且脐血可以通过对母婴都无创的方式获得[42-44] 。Kem等[45]以及Baksh等[46]比较了脐血中和骨髓中获得的多能干细胞,对其形态、成功分离出多能干细胞的比例、扩增能力、多向分化的能力以及免疫表型进行研究,认为二者在形态和免疫表型方面并没有明显的差异,但是从脐血中获得的干细胞可以长期培养且有较高的扩增能力。脐血干细胞作为成人干细胞的一个来源,不仅可以分化成中胚层发育来的组织,同时也可分化为其他组织。因此,只要在合适的培养条件下,脐血中分离的干细胞与上述多种干细胞一样可能分化为牙源性细胞,进行成牙性诱导[47] 。 2.2.3 第一鳃弓外胚间充质干细胞 近些年来,对于与牙齿发生、发育相关的颅神经嵴细胞、牙乳头细胞、恒牙髓和乳牙髓等细胞的生物学特性方面都有了较多的研究成果[48-52] ,而对于第一鳃弓外胚间充质细胞的细胞生物学研究还未见报道。虽然第一鳃弓只是牙颌面发育过程中的一个过渡性结构,而且,其主体由颅神经嵴细胞迁移衍化形成,但是不能忽视颅神经嵴细胞迁移至此以后,其生物学性状必将发生一定程度的变化,并非所有的第一鳃弓外胚间充质细胞都有成牙的特性,有学者曾经利用第一鳃弓器官异位移植和体外培养的方式进行了成牙潜能和成骨特性的研究[53] ,结果发现,10体节以前的第一鳃弓只能发育成下颌骨并有一部分形成颌骨囊肿,不能形成牙齿,12体节以后,第一鳃弓移植块体内、体外器官培养均可见牙齿形成。因此,建立第一鳃弓外胚间充质细胞的体外培养模型,研究其细胞生物学特性,将对深入研究牙颌面的发育机制具有推动作用。"
| [1]Yildirim S, Fu SY, Kim K, et al. Tooth regeneration: a revolution in stomatology and evolution in regenerative medicine. Int J Oral Sci. 2011;3(3):107-116.[2]Sharpe PT, Young CS.Test-tube teeth. Sci Am. 2005;293(2): 34-41.[3]Modino SA, Sharpe PT. Tissue engineering of teeth using adult stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2005;50(2):255-258.[4]Young CS, Abukawa H, Asrican R, et al. Tissue-engineered hybrid tooth and bone. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(9-10):1599-1610.[5]Mao JJ, Giannobile WV, Helms JA, et al. Craniofacial tissue engineering by stem cells. J Dent Res. 2006;85(11):966-979.[6]Langer R, Vacanti JP.Tissue engineering. Science. 1993; 260(5110):920-926. [7]Wang J, Liu B, Gu S, et al. Effects of Wnt/β-catenin signalling on proliferation and differentiation of apical papilla stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2012;45(2):121-131.[8]Sonoyama W, Liu Y, Fang D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated functional tooth regeneration in swine. PLoS One. 2006;1:e79.[9]Huang GT, Sonoyama W, Liu Y,et al. The hidden treasure in apical papilla: the potential role in pulp/dentin regeneration and bioroot engineering. J Endod. 2008;34(6):645-651.[10]郭俊,杨健.人牙根尖乳头干细胞及其在组织工程中的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2010, 37(4):464-466.[11]Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.[12]Gronthos S, Brahim J, Li W,et al. Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2002;81(8): 531-535.[13]Arthur A, Rychkov G, Shi S, et al. Adult human dental pulp stem cells differentiate toward functionally active neurons under appropriate environmental cues. Stem Cells. 2008; 26(7):1787-1795.[14]Arthur A, Shi S, Zannettino AC, et al. Implanted adult human dental pulp stem cells induce endogenous axon guidance. Stem Cells. 2009;27(9):2229-2237.[15]Yalvac ME, Rizvanov AA, Kilic E, et al. Potential role of dental stem cells in the cellular therapy of cerebral ischemia. Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(33):3908-3916.[16]Zhang J, Jiang D, Zhang J, et al. Synthesis of dental enamel-like hydroxyapatite through solution mediated solid-state conversion. Langmuir. 2010;26(5):2989-2994.[17]Mohamadreza BE, Khorsand A, Arabsolghar M,et al. Autologous Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Regeneration of Defect Created in Canine Periodontal Tissue. J Oral Implantol. 2012. [Epub ahead of print][18]Gay IC, Chen S, MacDougall M. Isolation and characterization of multipotent human periodontal ligament stem cells. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2007;10(3):149-160.[19]Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004;364(9429):149-155.[20]Kitamura M, Akamatsu M, Machigashira M,et al. FGF-2 stimulates periodontal regeneration: results of a multi-center randomized clinical trial. J Dent Res. 2011;90(1):35-40. [21]Somerman M. Growth factors and periodontal engineering: where next. J Dent Res. 2011;90(1):7-8.[22]Gronthos S, Mrozik K, Shi S, et al. Ovine periodontal ligament stem cells: isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006;79(5):310-317.[23]Gault P, Black A, Romette JL,et al. Tissue-engineered ligament: implant constructs for tooth replacement. J Clin Periodontol. 2010;37(8):750-758. [24]Shi S, Bartold PM, Miura M, et al. The efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells to regenerate and repair dental structures. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2005;8(3):191-199.[25]Morsczeck C, Moehl C, Götz W, et al. In vitro differentiation of human dental follicle cells with dexamethasone and insulin. Cell Biol Int. 2005;29(7):567-575.[26]Morsczeck C, Götz W, Schierholz J, et al. Isolation of precursor cells (PCs) from human dental follicle of wisdom teeth. Matrix Biol. 2005;24(2):155-165.[27]Kémoun P, Laurencin-Dalicieux S, Rue J, et al. Human dental follicle cells acquire cementoblast features under stimulation by BMP-2/-7 and enamel matrix derivatives (EMD) in vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 2007;329(2):283-294. [28]Handa K, Saito M, Tsunoda A,et al. Progenitor cells from dental follicle are able to form cementum matrix in vivo. Connect Tissue Res. 2002;43(2-3):406-408.[29]Handa K, Saito M, Yamauchi M,et al. Cementum matrix formation in vivo by cultured dental follicle cells. Bone. 2002; 31(5):606-611.[30]Lin NH, Gronthos S, Bartold PM. Stem cells and periodontal regeneration. Aust Dent J. 2008;53(2):108-121.[31]Honda MJ, Tsuchiya S, Shinohara Y, et al. Recent advance in engineering of tooth and tooth structures using postnatal dental cells. Japanese Dental Science Review. 2010;46(1): 54-66.[32]Miura M, Gronthos S, Zhao M, et al. SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(10):5807-5812. [33]Cordeiro MM, Dong Z, Kaneko T, et al. Dental pulp tissue engineering with stem cells from exfoliated deciduous teeth. J Endod. 2008;34(8):962-969.[34]Li ZY, Chen L, Liu L,et al. Odontogenic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65(3):494-500.[35]Casagrande L, Demarco FF, Zhang Z,et al. Dentin-derived BMP-2 and odontoblast differentiation.J Dent Res. 2010; 89(6):603-608.[36]Hu B, Unda F, Bopp-Kuchler S, et al. Bone marrow cells can give rise to ameloblast-like cells. J Dent Res. 2006;85(5): 416-421.[37]Modino SA, Sharpe PT. Tissue engineering of teeth using adult stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2005;50(2):255-258.[38]Song AM, Shu R, Xie YF, et al. A study of enamel matrix proteins on differentiation of porcine bone marrow stromal cells into cementoblasts. Cell Prolif. 2007;40(3):381-396.[39]Yu J, Wang Y, Deng Z, et al. Odontogenic capability: bone marrow stromal stem cells versus dental pulp stem cells. Biol Cell. 2007;99(8):465-474.[40]Valarmathi MT, Yost MJ, Goodwin RL,et al. The influence of proepicardial cells on the osteogenic potential of marrow stromal cells in a three-dimensional tubular scaffold. Biomaterials. 2008;29(14):2203-2216.[41]Stenderup K, Justesen J, Clausen C, et al. Aging is associated with decreased maximal life span and accelerated senescence of bone marrow stromal cells. Bone. 2003;33(6): 919-926.[42]Bieback K, Kern S, Klüter H,et al. Critical parameters for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells. 2004;22(4):625-634.[43]Lee OK, Kuo TK, Chen WM,et al. Isolation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Blood. 2004;103(5):1669-1675.[44]Kögler G, Sensken S, Airey JA,et al. A new human somatic stem cell from placental cord blood with intrinsic pluripotent differentiation potential. J Exp Med. 2004;200(2):123-135.[45]Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, et al. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue.Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1294-1301.[46]Baksh D, Yao R, Tuan RS. Comparison of proliferative and multilineage differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2007;25(6):1384-1392.[47]Kestendjieva S, Kyurkchiev D, Tsvetkova G,et al. Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the human umbilical cord.Cell Biol Int. 2008;32(7):724-732.[48]Morito A, Kida Y, Suzuki K,et al. Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor on the development of the stem cell properties of human dental pulp cells. Arch Histol Cytol. 2009;72(1): 51-64.[49]Sloan AJ, Waddington RJ. Dental pulp stem cells: what, where, how. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2009;19(1):61-70.[50]Seo BM, Sonoyama W, Yamaza T, et al. SHED repair critical-size calvarial defects in mice. Oral Dis. 2008;14(5): 428-434.[51]Nam H, Lee G. Identification of novel epithelial stem cell-like cells in human deciduous dental pulp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;386(1):135-139.[52]Siqueira da Fonseca SA, Abdelmassih S, de Mello Cintra Lavagnolli T, et al. Human immature dental pulp stem cells' contribution to developing mouse embryos: production of human/mouse preterm chimaeras. Cell Prolif. 2009;42(2): 132-140.[53]Zhang Y, Wang S, Song Y,et al. Timing of odontogenic neural crest cell migration and tooth-forming capability in mice. Dev Dyn. 2003;226(4):713-718. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [5] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [6] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [7] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [8] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [9] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [10] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [11] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [12] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [13] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [14] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [15] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||