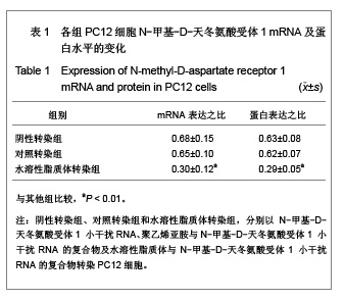
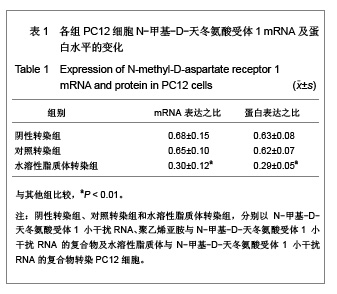
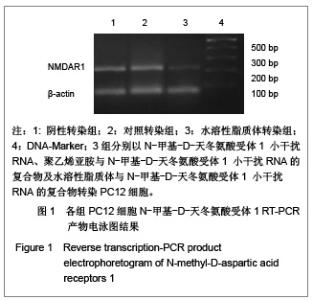
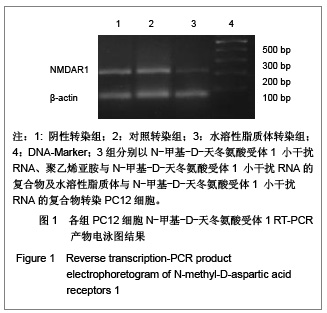
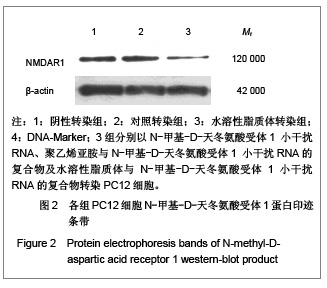
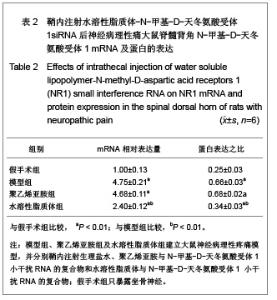
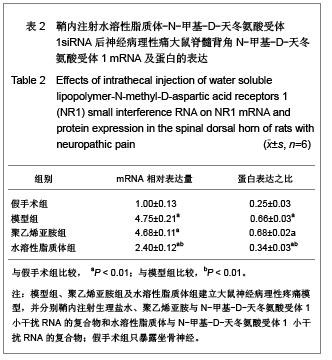
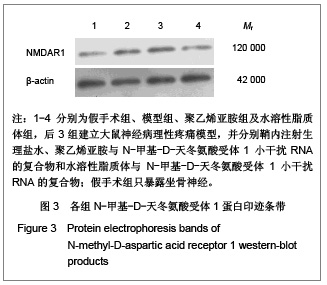
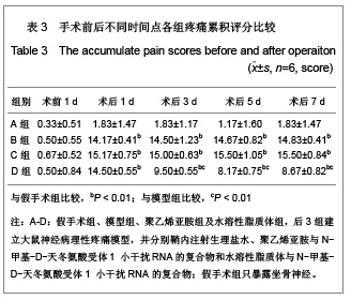
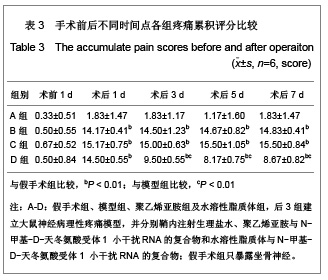
| [1] Cope DK,Lariviere WR. Gene therapy and chronic pain. Scientific World Journal.2006;6:1066-1074.[2] Zhuo M. Plasticity of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit in memory and chronic pain. Mol Brain.2009;2:4.[3] Kim WJ,Chang CW,Lee M,et al.Efficient siRNA delivery using water soluble lipopolymer for anti-angiogenic gene therapy. J Control Release.2007;118(3):357-363.[4] Kim JM,Lee M,Kim KH,et al.Gene therapy of neural cell injuries in vitro using the hypoxia-inducible GM-CSF expression plasmids and water-soluble lipopolymer (WSLP). J Control Release.2009;133(1):60-67.[5] Lee M,Rentz J,Han SO,et al.Water-soluble lipopolymer as an efficient carrier for gene delivery to myocardium.Gene Ther. 2003;10(7):585-593.[6] Tan PH,Chia YY,Chow LH,et al. Gene knockdown of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit with subcutaneous small interfering RNA reduces inflammation-induced nociception in rats. Anesthesiology. 2010;112(6):1482-1493.[7] Garraway SM,Xu Q,Inturrisi CE. siRNA-mediated knockdown of the NR1 subunit gene of the NMDA receptor attenuates formalin-induced pain behaviors in adult rat. J Pain.2009; 10(4): 380-390.[8] Liu GK,Huang YG,Luo AL.Zhongguo Linchuang Yaolixue yu Zhiliaoxue. 2005;10(6):601-603. 刘国凯,黄宇光,罗爱伦. 神经病理性疼痛动物模型及其评价[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2005,10(6):601-603.[9] Jin XG,Luo AL,Zhang GX.linchuang mazuixue zazhi. 2005; 21(5):338-340. 金小高,罗爱林,张广雄.三种大鼠神经病理性疼痛模型的制备和效果比较[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2005,21(5):338-340.[10] Yang JP,Jiang H.Zhonghua Mazuixue Zazhi. 1993;13(2): 110-112. 杨建平,蒋豪.大鼠蛛网膜下腔埋管并长期留置操作的改进[J].中华麻醉学杂志,1993,13(2):110-112.[11] Fan L,Wang GL.Tianjin Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2005;11(2): 165-167. 范隆,王国林.大鼠蛛网膜下腔微创置管方法[J].天津医科大学学报,2005,11(2):165-167.[12] Brennan TJ,Vandermeulen EP,Gebhart GF. Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain.1996;64(3):493-501. |