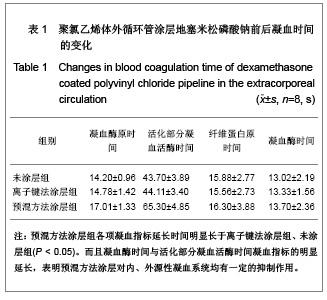
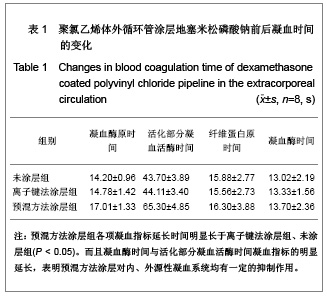
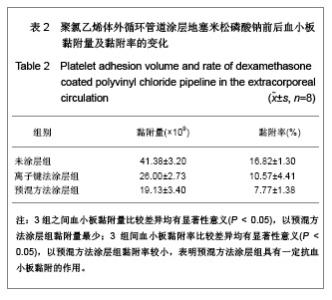
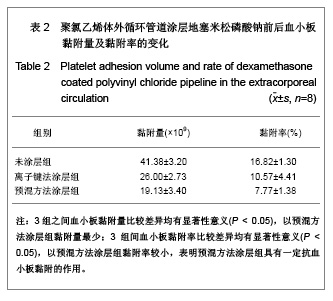
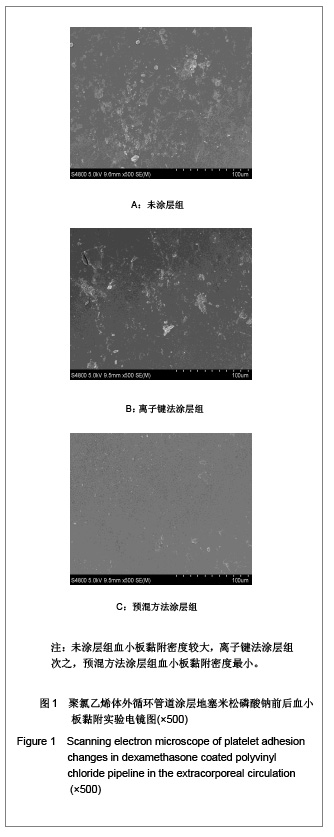
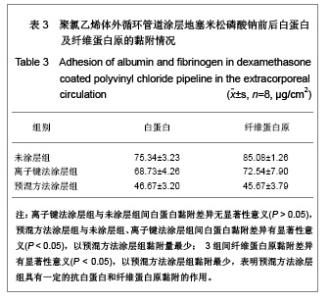
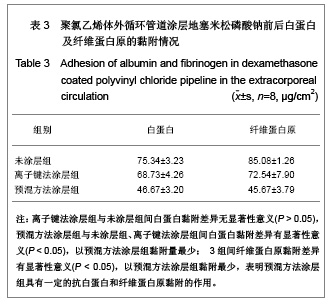
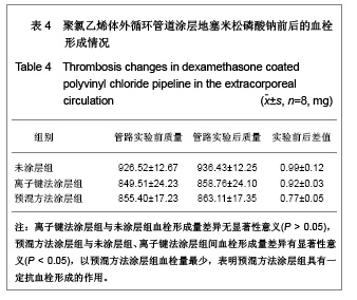
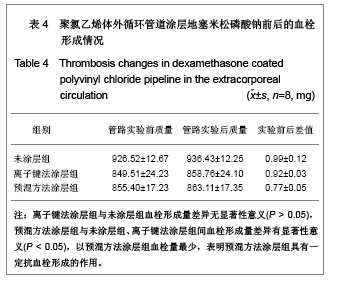
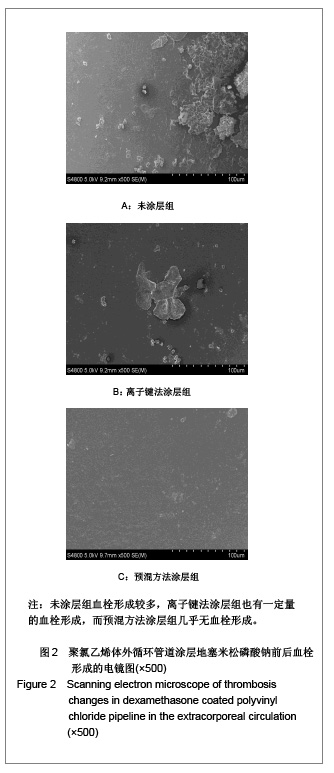
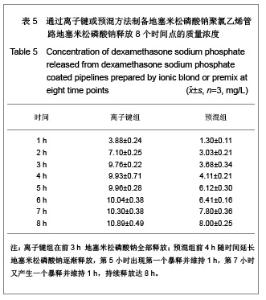
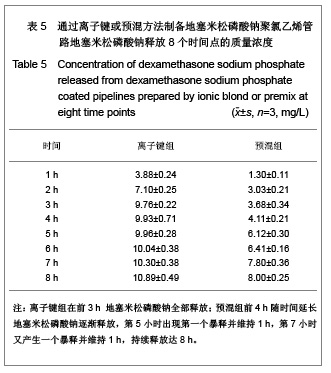
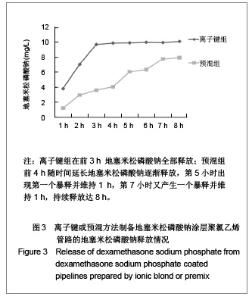
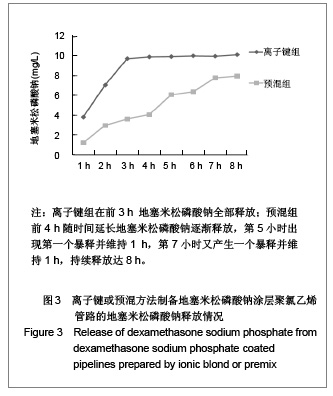
| [1] Goulding NJ.The molecular complexity of glucocorticoid actions in inflammation - a four-ring circus.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004;4(6):629-636.[2] Beato M,Herrlich P,Schutz G.Steroid hormone receptors: many actors in search of a plot.Cell.1995;83(6):851-857.[3] Kirklin JK.The postperfusion syndrome: inflammation and the damaging effects of cardiopulmonary bypass[A].In: Tinker JH(ed):cardiopulmonary bypass: current concept and controversies.Philadelphia:W.B.Saunders,1989:131-146.[4] Replogle RL,Gazzaniga AB,Gross RE.Use of corticosteroid during cardiopulmonary bypass: possible lysosome stabilization.Circulation.1996;33(4 suppl I):86-92.[5] Wu C,Zhu Y,Chang J,et al. Bioactive inorganic-materials/ alginate composite microspheres with controllable drug-delivery ability. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;94(1):32-43.[6] Luo X,Matranga C,Tan S,et al.Carbon nanotube nanoreservior for controlled release of anti-inflammatory dexamethasone.Biomaterials.2011;32(26):6316-6323.[7] Fratoddi I,Venditti I,Cametti C, et al.Functioonal polymeric nanoparticles for dexamethsone loading and release. Colloid Surf B Biointerfaces.2012;5(93):59-66.[8] Chen YP,Wang GX,Chen Y,et al.Disan Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2008;30(10):935-937. 陈勇鹏,王贵学,陈琰,等.地塞米松血管内支架的涂层制备及体外缓释实验研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2008,30(10):935-937.[9] Fan Y,Yao J,Zhou JP.Gaodeng Xuexiao Huaxue Xuebao. 2011;32(12):2916-2922. 范颖,姚静,周建平.细胞核靶向聚乙烯亚胺-地塞米松偶联物的制备及作为基因载体的应用[J].高等学校化学学报,2011,32(12):2916-2922.[10] Yii M,Gourlay T,Fleming J,et al. Evaluation of Carmeda bioactive surface (CBAS), Duraflo II and a novel nonspecific protease-modified surface using a new in vitro model simulating cardiopulmonary bypass.Perfusion.1996;11(3): 229-240.[11] Le-Tien C,Millette M,Lacroix M,et al.Modified alginate matrices for the immobilization of bioactive agents.Biotech Appl Biochem.2004;39(Pt2):189-198.[12] Lee JH,Ju YM,Kim DM.Platelet adhesion onto segmented polyurethane film surfaces modified by addition and crosslinking of PEO-containing block copolymers. Biomaterials. 2000;21(7):683-691.[13] Smith PK,Krohn RI,Hermanson GT,et al.Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid.Anal Biochem.1985;150(1): 76-85.[14] Chandler AB.An examination of the fluid mechanics and thrombus formation time parameters in a Chandler rotating loop system.J Lab Clin Med.1974;84(4):494-507.[15] Guo QK,Lu ZQ,Wang JY,et al.In vivo evaluation of a novel dexamethsaone-heparin-double-coated stent for inhibition of artery restenosis and thrombosis. J Mater SCI Mater Med. 2011;22(6):1615-1623.[16] Ribichini F,Tomai F,Paloscia L,et al. Steroid-eluting stents in patients with acute coronary syndrome: the dexamethasone eluting stent Italian registry. Heart.2007;93(5):598-600.[17] Soares LC,Ribas D,Spring R,et al.Clinical profile of systemic inflammatory response after pediatric cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Arq Bras Cardiol.2010;94(1): 127-133.[18] Liou HL,Shih CC,Chao YF,et al.Inflammatory respose to colloids compared to crystalloid priming in Cardiac surgery patients with cardiopulmonary bypass. Chin J Physio.2012; 55(3):210-218.[19] Heying R,Wehage E,Schumacher K,et al.Dexamethasone pretreatment provides antiinflammatoty and myocardial protection in neonatal arterial switch operation. Ann Thorac Surg.2012;93(3):869-876.[20] Cappabianca G,Rotunno C,De Luca Tuppti Schinosa L,et al.Protetective effects of steroids in cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized double-blind trials.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth.2011;25(1):156-165. |