Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (34): 5508-5515.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1956
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress of smart responsive hydrogel as a drug delivery system
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2019-06-21Online:2019-12-08Published:2019-12-08 -
Contact:Wu Dankai, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Cui Yutao, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81671804, 81772456 (to LH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cui Yutao, Liu He, Ji Xuan, Leng Yi, Ren Zhenxiao, Li Zuhao, Wu Dankai. Research progress of smart responsive hydrogel as a drug delivery system[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5508-5515.
share this article
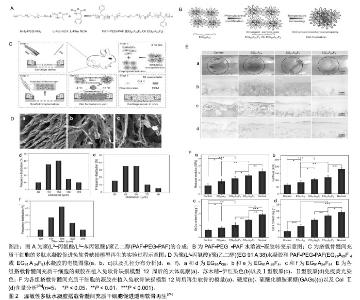
2.2 单一智能响应性水凝胶 刺激响应性水凝胶已被广泛报道用于调节所搭载药物的释放速率[16]。刺激响应性水凝胶暴露于物理、化学和生物刺激时能够通过改变其分子结构内的氢键结合、所带电荷和化学键等从而使其发生构象的变化,它们已成为局部药物递送和组织工程的有力工具。根据所用材料的特性,通过多种方法如自由基的交联,回流沉淀聚合,自由基接枝共聚,蒸馏-沉淀聚合等方法对材料的功能组进行整合,可将这些材料设计为能够“感知”周围的生理环境的响应性药物载体,能够按需将封装在其中的的治疗性药物释放到高度特定的目标中[17]。这里文章介绍常用于局部药物递送的不同单一响应性水凝胶。 2.2.1 温敏性水凝胶 当水凝胶的大分子链上同时具有疏水性和亲水性的两类基团时,线性高分子在溶液中可随着溶液温度的变化而发生分子链构象的变化[18]。其亲水性基团在低温时通过氢键与环境中的水结合,从而水凝胶膨胀呈现溶液状态,而在温度升高至接近人体温度时,氢键减少,水凝胶收缩表现为凝胶化[19]。当温敏性聚合物溶液低温处于溶液状态时,多肽、基因、蛋白、细胞及小分子药物等都可以均匀混入凝胶溶液中,在接近人体温时由 液态转变为凝胶,具有很强的操作性,且温度敏感性水凝胶在转变过程中不涉及到任何有机化学溶剂等有毒物质,具有很好的安全性,因此它们被广泛应用于药物缓释和组织工程等领域[20-21]。Kim等[22]利用F-127和透明质酸制备了一种生物相容性和可注射的温敏水凝胶药物载体,搭载布比卡因后注射入慢性骨性关节炎疼痛模型中,具有持久的镇痛作用。泊洛沙姆407是一种常用的温敏性水凝胶,其搭载辛伐他汀填充于多孔钛支架内部可在骨缺损局部发挥良好的药物缓释并促进成骨的作用[23]。基于氨基酸合成的温敏性水凝胶,其优点在于聚合物在降解过程中没有酸性产物的积累。Liu等[24]将一种疏水性氨基酸(苯丙氨酸)引入基于聚丙氨酸的温敏性水凝胶中,作为一个载细胞支架,可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖,还能诱导透明软骨产生,见图2。"

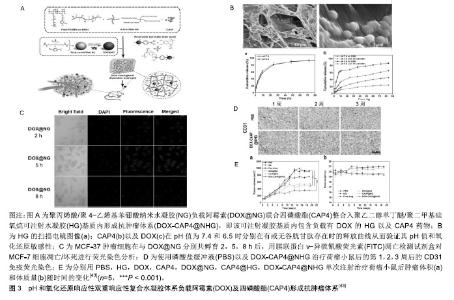
2.2.2 pH响应性水凝胶 由于正常生理环境和患病部位之间pH值有着较大的变化,迄今为止报道的大多数刺激响应性水凝胶都是基于pH响应性。水凝胶被设计成具有可以响应周围环境pH值变化而膨胀,收缩或解离,并且封装其内的药物通过生物材料的扩散或降解而局部递送。pH响应性水凝胶常通过材料在不同pH值环境中内部所带电荷变化,电荷间的相互作用而发生理化性质的改变。这些材料中大多在其侧链中含有羧基,可以在酸性环境中接受质子,在碱性环境中释放质子。在碱性条件下,质子转移到溶液中,这导致羧基带负电荷并形成阴离子链,链的排斥作用导致水凝胶结构链延长,随后从水凝胶网络中释放截留的药物[25-26]。聚丙烯酸是一种弱酸性聚电解质,是合成pH响应性水凝胶的常用材料。以过氧化苯甲酰为催化剂,采用自由基聚合技术可制备由羧甲基壳聚糖、聚丙烯酸、乙二醇二甲基丙烯酸酯组成的pH响应性水凝胶。这种水凝胶搭载5-氟尿嘧啶后能稳定控制性释放药物,并具有结肠靶向作用,是结肠癌的有潜力的治疗方案[27]。Cevik等[28]以聚甲基丙烯酸-乙二醇作为基础材料制备水凝胶聚合物网络,并在其中加入通过可视光照交联的苯乙烯-丁二烯-苯乙烯为水凝胶提供了疏水结构域,使水凝胶的溶胀率显著下降,提高了交联密度,该组合物具有良好的生物相容性,可在中性pH值条件下控制释放抗惊厥模型药物普瑞巴林。羧甲基纤维素也是常用的pH响应性水凝胶的常用材料,其含有羧基和羟基作为官能团,并具有生物降解性强、无毒及生物相容性好等优点。丙烯酸2-羟乙酯可以接枝到羧甲基纤维素上,并与聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯交联,组合成pH响应性水凝胶。正常皮肤角质层呈现微酸性的环境,当皮肤pH值异常升高时,皮肤则会出现干燥,感染等疾病。该水凝胶在pH值为7.5及8.5时溶胀率升高,释放柚皮素,并且其可将皮肤表面水化,暂时屏蔽皮肤的屏障功能,可达到良好的药物透皮效率,具有较好的治疗pH值失调性皮肤疾病的潜能[29]。此外一些无机材料如α-磷酸锆也可用作pH响应性的水凝胶材料,其作为载体搭载药物也可获得良好的释放的效应[30]。 由于葡萄糖在经葡萄糖氧化酶作用转化为葡萄糖酸的过程中会产生局部酸性的微环境,所以pH响应性水凝胶还常和葡萄糖响应系统相结合,用于糖尿病治疗的研究[31]。葡萄糖响应系统通常包括葡萄糖氧化酶,过氧化氢酶,葡萄糖结合蛋白以及胰岛素[32]。将这一系统整合入pH响应性水凝胶基质中,在血糖升高时,葡萄糖可进入水凝胶基质中,经过酶的氧化作用产生的酸性环境使水凝胶构象改变,释放胰岛素用于降低血糖,并且过氧化氢酶可以降解反应过程中所产生的过氧化氢[33-34]。Li等[35]制作了一种pH响应性的自组装肽水凝胶,将其和葡萄糖氧化酶,胰岛素,过氧化氢酶结合应用于血糖的控制。当葡萄糖浓度升高时,经氧化酶的作用可使水凝胶周围的pH值下降,当pH值低于多肽链中赖氨酸/鸟氨酸侧链的pKa时,可导致相邻碱性氨基酸侧链之间的排斥,多肽链的空间结构解离,使多肽链从凝胶状态转变溶液态,同时胰岛素释放,用以降低血糖,此水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性,将其经皮下注射于糖尿病小鼠后观察到,其可有效的控制血糖,发挥治疗作用。 2.2.3 光响应性水凝胶 局部的按需给药系统可对药物的释放行为进行精确的控制,其可根据患者的病情变化进行精确化的治疗。光敏性的水凝胶在局部按需给药系统的研究中引起了很多的关注,因为其具有高度的时间和空间的可控性,可远程且无创的控制治疗药物在局部的释放量[36-37]。光敏性水凝胶大多通过将光热传感性材料整合入热敏性的水凝胶内,通过将光照转化为热量促进水凝胶结构的改变,促进水凝胶内的药物的释放,达到按需给药的目的[38-40]。壳聚糖可与聚异丙基丙烯酰胺接枝形成复合物,然后通过甲基丙烯酰基乙酰化和并包埋光热碳的方法可合成一种新型紫外交联光响应性壳聚糖水凝胶。该智能型水凝胶的甲基丙烯酰基具有紫外可交联性,使其通过紫外线照射可实现凝胶化,聚异丙基丙烯酰胺为热响应单元,其赋予了壳聚糖水凝胶与温度相关的可逆性溶胀/去溶胀性质,而其中的光热碳可使水凝胶对近红外激光辐照产生温度升高的应答,从而触发凝胶体积的缩小。将阿霉素负载于其中发现,凝胶经近红外光照后,药物释放量升高了40倍[41]。但是单一功能区的光敏性的水凝胶也可能会出现光照时凝胶形态被破坏而降解的问题。Luo等[42]以琼脂糖/藻酸盐为基础联合光热材料聚吡咯纳米组成双层多功能室水凝胶。其光敏性原理为聚吡咯在接受近紫外光照后可产生热量,促进琼脂糖凝胶的降解,从而使负载于琼脂糖内的药物释放出来。该组合型多功能室凝胶相比于无藻酸盐的单一琼脂凝胶网络稳定性更强,在近紫外光照时仍具有良好的形态及机械性能。 2.2.4 氧化还原响应性水凝胶 在肿瘤组织内常会有氧化还原物质的堆积如谷胱甘肽,因此利用这一特点设计氧化还原应答性的水凝胶将为肿瘤的局部药物释放治疗提供有意义的方法[43]。水凝胶材料内二硫键的形成,是设计氧化还原反应性水凝胶的常用策略之一。这些氧化还原应答性材料中通常具有通过二硫键结合的亲水性基团如二谷氨酸基团,这些基团的存在赋予了水凝胶亲水性。谷胱甘肽是人体内主要的抗氧化剂,当谷胱甘肽的存在时,二硫键降解,亲水性降低,水凝胶结构将产生改变[44,45]。Ji等[46]将苯丙氨酸衍生物胶凝剂和含二硫键的4,4′-二吡啶二硫化物组合,制作了一种超分子氧化还原性水凝胶。该水凝胶搭载药物后可在还原环境中发挥良好的药物释放效应,在抗肿瘤的局部药物释放治疗中具有很好的应用前景。 除了二硫键,含硒的化学键尤其是二硒键因为其独特的氧化还原特性成为了氧化还原响应性水凝胶设计的新的策略之一[47]。相比于二硫键,二硒键的键能更低,因此也更容易被降解。二硒键具有氧化及还原双响应性的特点,氧化剂或还原剂可分别将其转变为硒酸以及硒醇,材料也产生相应的结构特性改变[48-49]。用氨基磺酸酯官能化的4-臂聚乙二醇通过氨基磺酸反应被硒代半胱氨酸交联,形成可注射的高灵敏度的双氧化还原反应性含二硒键的聚乙二醇水凝胶。这种水凝胶可分别在双氧水以及谷胱甘肽所提供的环境中产生氧化及还原应答而发生降解,这是因为二硒键在氧化及还原环境中的分别被转变为更加具有亲水性的硒酸和硒醇,使得水凝胶结合更多的水而溶胀,水凝胶结构因此变得疏松并最终降解使负载于其中的药物释放。将罗丹明B负载于这一可注射水凝胶中发现,载药水凝胶可在氧化及还原环境中持续释放药物,这证明该注射性水凝胶可在肿瘤局部注射,发挥良好的抗肿瘤作用[50]。对于某些难降解的材料,在其结构中引入而二硫键或者二硒键是一种较为理想的改善方案。聚亚安酯是一种pH敏感性材料,但单纯的聚亚安酯的降解速度可能持续数周甚至数月,这限制了其在生物学领域的应用。而在聚亚安酯的骨架上引入二硫键或者二硒键可加速其降解,达到更好的局部药物释放治疗效果[10,51]。 2.2.5 酶响应性水凝胶 与氧化还原性水凝胶相似,酶响应水凝胶通常在其结构网中含有酯或肽键,并且可以被特定的酯酶和蛋白酶切割,从而发生构象的变化,释放出搭载于其网状结构的药物。但与氧化还原及pH响应性水凝胶所不同的是,酶响应性水凝胶应有更强的靶向性,可以根据酶的特异性,靶向性在特定的组织及细胞释放搭载药物,这对于某些毒性较强的化疗药物及半衰期短的药物的局部释放来说具有重要的意义[52]。Koetting等[53]将衣康酸和N-乙烯基吡咯烷酮组合成共聚合物形成水凝胶,并将一段胰蛋白酶及糜蛋白酶可降解的多肽链交联于凝胶内形成了酶响应性水凝胶。该水凝胶搭载鲑鱼降钙素经口服给药后可靶向性在小肠内释放,而在胃内无药物丢失,这使得口服的蛋白质药物在小肠内能有较高的生物利用度。 多肽序列甘氨酸-苯丙氨酸-亮氨酸-甘氨酸-赖氨酸(GFLGK)因其可被巯基蛋白酶尤其是组织蛋白酶B特异性降解而广泛应用于肿瘤靶向治疗。组织蛋白酶B在肺、卵巢和结肠直肠肿瘤细胞常有过量的表达,所以将此多肽链整合入水凝胶材料可以组合成酶响应性水凝胶用于肿瘤的靶向药物释放治疗。将聚乙二醇二丁醚和丙烯酸酯化的GFLGK相结合作组织蛋白酶B响应性载体,其负载链霉亲和素-CY5可形成良好的药物释放系统,可用于肿瘤的局部靶向治疗[54]。 2.2.6 其他 一氧化氮是一种具有多种生理功能的重要的信号分子,将其作为交联剂可制作治疗气体响应性水凝胶作为药物载体。这种气体响应性水凝胶可特异性响应细胞分泌或者酶联反应中产生的一氧化氮而不对其他气体有反应。并且其还可以转变为酶响应性的水凝胶,因为某些特异性的酶在通过级联反应后可产生一氧化氮[55]。上述刺激因素如pH值、温度及酶等多是静态的刺激因素,而除此之外,一些动态的机械动力如软骨和骨骼的压缩力、肌肉和肌腱的张力以及血管的剪切力也可以成为智能响应性水凝胶的刺激因素。有研究通过β环糊精和藻酸盐的交联制作了一种压力响应性水凝胶。其中交联剂β环糊精通过范德华力与搭载药物相连接,而其分子势能与空间结构距离的六次方成反比,所以外部环境的对其的轻微作用力即可改变β环糊精与所载药物间的亲和力,从而促进药物的释放。这种凝胶搭载5氟尿嘧啶后可外部作用力存在的情况下明显增加药物的释放量,增加肿瘤细胞的摄取量,发挥良好的药物效应[56]。 2.3 多重智能响应性水凝胶 响应性聚合物材料被设计成在暴露于物理、化学和生物刺激时可改变性质,它们已成为药物输送和组织工程的有力工具。通过功能组的整合,这些材料被设计为“感知”周围的生理环境,并能够按需将封装的治疗性货物释放到高度特定的目标中。然而,人体生理环境是复杂的,并且在一些情况下,具有单一响应性的聚合物材料不能在药物递送系统中实现期望的目标,因此对多重刺激响应的水凝胶的开发有望在药物递送应用中展现创新性。 2.3.1 双重响应性 在某些复杂的病理环境如肿瘤中,利用其病理环境的特征设计双重响应性水凝胶可能会达到更良好的药物释放效果。在双重响应性的水凝胶中,不同的刺激因素之间会产生互相的协同影响作用。乙二醇壳聚糖和二苯甲醛封端的共聚物材料可制作成pH值和温度双重响应性水凝胶。将小分子药物罗丹明B负载于这种水凝胶网络结构中进行释放研究发现,pH值越低,温度越高,水凝胶网络收缩越明显,药物释放速度越快,两者之间显示了明显的协同作用,这也与肿瘤局部微酸性以及散热较慢的微环境相适应[57]。Yang等[43]应用回流沉淀聚合法制作了一种pH值和氧化还原响应性聚丙烯 酸/聚4-乙烯基苯硼酸纳米水凝胶(P(AA-co-4-VPBA)),其羧基可与抗肿瘤药物阿霉素的胺基结合从而形成载药纳米水凝胶,将载药P(AA-co-4-VPBA)和抗血管生成药物四磷酸酯整合入一种由聚乙二醇单丁醚和聚二甲基硅氧烷共聚物组成的可注射性水凝胶内形成复合抗肿瘤载药体系。微酸以及还原环境可促进纳米水凝胶中阿霉素的缓慢释放,这也与肿瘤细胞周围的微酸性的环境以及肿瘤细胞内较高的谷胱甘肽浓度相契合,该系统可在较长时间内缓慢释放阿霉素,使其持续作用于肿瘤细胞,而位于可注射凝胶基质中的抗血管剂四磷酸酯则在较短时间内快速释放,从而更好的发挥其药理作用。该系统可明显的抑制MCF-7肿瘤细胞的增殖,并在对异种移植荷瘤小鼠单次注射后显示出了优异的抗肿瘤能力[43],见图3。有研究开发了一种对pH值和Ca2+反应性的可逆地膨胀或收缩的聚丙烯酸盐/聚丙烯酸水凝胶。因为聚丙烯酸的pKa值约为4.5,在pH<pKa时,聚丙烯酸的羧基被质子化,并通过氢键与聚乙二醇链相互作用。另一方面,在pH>pKa(pH为5-10)时,聚丙烯酸和聚乙二醇链之间的氢键被破坏,导致水凝胶中聚合物链之间的排斥,从而导致膨胀率增加。不同浓度的Ca2+离子也可以控制膨胀率,并与聚丙烯酸发生静电作用。当Ca2+浓度超过10 mmol/L时,水凝胶表现出较低的溶胀比和较高的储能模量。由于Ca2+的浓度在关节软骨的功能和组织中起着重要作用,该水凝胶系统在治疗膝关节骨关节炎的药物输送系统中具有潜力[58]。 "


在难愈性伤口中常有基质金属蛋白酶的过表达以及局部体表温度的天然刺激因素,利用这一特点设计温度及基质金属蛋白酶双重响应性水凝胶伤口敷料水,可使水凝胶呈胶状贴合于伤口局部并使药物在伤口局部释放,增强其生物利用度并降低其不良反应[59]。Liu等[60]用基质金属蛋白酶可降解的明胶微球负载姜黄色素纳米 粒子作为治疗剂,将其搭载于普朗尼克F127及F96混合物制作的温敏性水凝胶内,组成了基质金属蛋白酶和温度双重响应性水凝胶敷料用于糖尿病伤口的治疗。该伤口敷料可在伤口局部形成良好的药物释放,并增强了其伤口局部的生物利用度,提升了其抗氧化剂促进细胞迁移的药物作用,并能明显促进糖尿病小鼠伤口的愈合。 2.3.2 三重响应性 与双重响应性水凝胶相似,也有研究者通过将3种不同的智能材料进行组合,制作成三重响应性水凝胶用于局部药物释放。Wang等[61]应用季铵反应将pH敏感性聚甲基丙烯酸二甲氨基乙酯和溴封端的聚乙二醇组合成季铵化合物,将α-环糊精与之结合后,可形成温敏性超分子结构水凝胶。而氧化石墨烯是一种光敏性智能材料,将其自组装入超分子水凝胶后,组合成了一种新型三重响应性水凝胶,可同时对温度,pH值以及近红外光照产生相应的理化性质改变。搭载5氟尿嘧啶后,升高温度,降低pH值以及增加光照均可促进其药物的释放,是一种有潜力的新型药物释放系统。采用蒸馏沉淀法聚合甲基丙烯酸、聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺、2-羟乙基甲基丙烯酸酯和含二硫键的交联剂N,N '-双(丙烯酰)半胱氨酸可制备一种温度,pH值以及氧化还原三重响应性水凝胶用于肿瘤的靶向治疗。其通过交联搭载抗肿瘤药物阿霉素形成的载药系统可在血液循环中保持稳定性。当其在肿瘤组织附近聚集时,聚合甲基丙烯酸和聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺可分别对pH值和温度的变化做出应答,使复合水凝胶载体体积收缩,促进药物纳米粒子扩散入肿瘤组织。而在肿瘤细胞内,大量的谷胱甘肽清除复合药物粒子的二硫键,从而使药物在肿瘤细胞内释放出来而发挥抑制肿瘤的作用。这种三重响应性水凝胶提高了肿瘤靶向药物释放治疗的精确性,并明显增强了药物的利用度,提高了抗肿瘤的治疗效果[62]。 不同智能响应性水凝胶用于药物局部释放的研究,见表1。 "

| [1]Basak S, Nanda J, Banerjee A. Multi-stimuli responsive self-healing metallo-hydrogels: tuning of the gel recovery property. Chem Commun. 2014;50:2356-23569. [2]Wei Y, Zeng Q, Hu Q, et al. Self-cleaned electrochemical protein imprinting biosensor basing on a thermo-responsive memory hydrogel. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;99:136-141. [3]Bhattarai N, Gunn J, Zhang MQ. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2010; 62:83-99. [4]Hamidi M, Azadi A, Rafiei P. Hydrogel nanoparticles in drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2008;60:1638-1649. [5]Amsden B. Novel biodegradable polymers for local growth factor delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;97:318-328. [6]Tessmar JK, Gopferich AM. Matrices and scaffolds for protein delivery in tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2007;59: 274-291. [7]Pan Y, Wang J, Cai P, et al. Dual-responsive IPN hydrogel based on sugarcane bagasse cellulose as drug carrier. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118:132-140. [8]Shang J, Theato P. Smart composite hydrogel with pH-, ionic strength- and temperature-induced actuation. Soft Matter. 2018; 14:8401-8407. [9]Cao ZQ, Wang GJ. Multi-stimuli-responsive polymer materials:particles, films, and bulk gels. Chem Rec. 2016;16: 1398-435. [10]Cheng X, Jin Y, Sun T, et al. An injectable, dual pH and oxidation-responsive supramolecular hydrogel for controlled dual drug delivery. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;141: 44-52.[11]Yu MC, Chang CY, Chao YC, et al. pH-Responsive Hydrogel With an Anti-Glycation Agent for Modulating Experimental Periodontitis. J Periodontol. 2016;87:742-748.[12]Lee W, Park J. 3D patterned stem cell differentiation using thermo-responsive methylcellulose hydrogel molds. Sci Rep. 2016;6:29408.[13]Caldorera-Moore M, Maass K, Hegab R, et al. Hybrid responsive hydrogel carriers for oral delivery of low molecular weight therapeutic agents. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2015;30:352-359.[14]Das D, Ghosh P, Ghosh A, et al. Stimulus-Responsive, Biodegradable, Biocompatible, Covalently Cross-Linked Hydrogel Based on Dextrin and Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) for in Vitro/in Vivo Controlled Drug Release. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2015;7: 14338-14351.[15]Yun J, Lee DH, Im JS, et al. Improvement in transdermal drug delivery performance by graphite oxide/temperature-responsive hydrogel composites with micro heater. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2012;32:1564-1570.[16]Bhattacharya S, Eckert F, Boyko V, et al. Temperature-, pH-, and magnetic-field-sensitive hybrid microgels. Small. 2007;3:650-657.[17]Bilalis P, Efthimiadou EK, Chatzipavlidis A, et al. Multi-responsive polymeric microcontainers for potential biomedical applications: synthesis and functionality evaluation. Polym Int. 2012;61: 888-894.[18]Werzer O, Tumphart S, Keimel R, et al. Drug release from thin films encapsulated by a temperature-responsive hydrogel. Soft Matter. 2019;15:1853-1859.[19]Yun J, Lee DH, Im JS, et al. Improvement in transdermal drug delivery performance by graphite oxide/temperature-responsive hydrogel composites with micro heater. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2012;32:1564-1570.[20]Norouzi M, Nazari B, Miller DW. Injectable hydrogel-based drug delivery systems for local cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21:1835-1849.[21]Klouda L. Thermoresponsive hydrogels in biomedical applications: a seven-year update. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;97:338-349.[22]Kim T, Seol DR, Hahm SC, et al. Analgesic Effect of Intra-Articular Injection of Temperature-Responsive Hydrogel Containing Bupivacaine on Osteoarthritic Pain in Rats. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:812949.[23]Liu H, Li W, Liu C, et al. Incorporating simvastatin/ poloxamer 407 hydrogel into 3D-printed porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds for the promotion of angiogenesis, osseointegration and bone ingrowth. Biofabrication. 2016;8:045012.[24]Liu H, Cheng YL, Chen JJ, et al. Component effect of stem cell-loaded thermosensitive polypeptide hydrogels on cartilage repair. Acta Biomater. 2018;73:103-111.[25]Pourjavadi A, Jahromi PE, Seidi F, et al. Synthesis and swelling behavior of acrylatedstarch-g-poly (acrylic acid) and acrylated starch-g-poly (acrylamide) hydrogels. Carbohyd Polym. 2010;79: 933-940.[26]Kurdtabar M, Koutenaee RN, Bardajee GR. Synthesis and characterization of a novel pH-responsive nanocomposite hydrogel based on chitosan for targeted drug release. J Polym Res. 2018. DOI: 10.1007/s10965-018-1499-1.[27]Khan SA, Naveed. Highly Porous pH-Responsive Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Grafted-Poly (Acrylic Acid) Based Smart Hydrogels for 5-Fluorouracil Controlled Delivery and Colon Targeting. Int J Polym Sci. 2019. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6579239.[28]Cevik O, Gidon D, Kizilel S. Visible-light-induced synthesis of pH-responsive composite hydrogels for controlled delivery of the anticonvulsant drug pregabalin. Acta Biomater. 2015;11:151-161.[29]Park SH, Shin HS, Park SN. A novel pH-responsive hydrogel based on carboxymethyl cellulose/2-hydroxyethyl acrylate for transdermal delivery of naringenin. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;200:341-352.[30]Ueoka H, Shimomura O, Pica M, et al. Immobilization of Anti-Inflammatory Drug on Exfoliated alpha-Zirconium Phosphate as a pH-Responsive Carrier. Colloid Interfac Sci. 2019;28:29-33.[31]Jo SM, Lee HY, Kim JC. Glucose-sensitive liposomes incorporating hydrophobically modified glucose oxidase. Lipids. 2008;43:937-943.[32]Tai W, Mo R, Di J, et al. Bio-inspired synthetic nanovesicles for glucose-responsive release of insulin. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15:3495-3502.[33]Mo R, Jiang T, Di J, et al. Emerging micro- and nanotechnology based synthetic approaches for insulin delivery. Chem Soc Rev. 2014;43:3595-3629.[34]Luo J, Cao S, Chen X, et al. Super long-term glycemic control in diabetic rats by glucose-sensitive LbL films constructed of supramolecular insulin assembly. Biomaterials. 2012;33:8733-8742.[35]Li X, Fu M, Wu J, et al. pH-sensitive peptide hydrogel for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Acta Biomater. 2017;51: 294-303.[36]Li JZ, Chen GX, Zhou Z, et al. A high water-content and high elastic dual-responsive polyurethane hydrogel for drug delivery. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3:8401-8409.[37]Ko JW, Choi WS, Kim J, et al. Self-Assembled Peptide-Carbon Nitride Hydrogel as a Light-Responsive Scaffold Material. Biomacromolecules. 2017;18:3551-3556.[38]Ha W, Zhao XB, Jiang K, et al. A three-dimensional graphene oxide supramolecular hydrogel for infrared light-responsive cascade release of two anticancer drugs. Chem Commun (Camb). 2016;52:14384-14387.[39]Highley CB, Kim M, Lee D, et al. Near-infrared light triggered release of molecules from supramolecular hydrogel-nanorod composites. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2016;11:1579-1590.[40]Wang X, Wang C, Zhang Q, et al. Near infrared light-responsive and injectable supramolecular hydrogels for on-demand drug delivery. Chem Commun (Camb). 2016;52:978-981.[41]Wang L, Li BQ, Xu F, et al. UV-crosslinkable and thermo-responsive chitosan hybrid hydrogel for NIR-triggered localized on-demand drug delivery. Carbohyd Polym. 2017;174: 904-914.[42]Luo R, Cao Y, Shi P, et al. Near-infrared light responsive multi-compartmental hydrogel particles synthesized through droplets assembly induced by superhydrophobic surface. Small. 2014;10: 4886-4894.[43]Yang WJ, Zhou P, Liang LJ, et al. Nanogel-Incorporated Injectable Hydrogel for Synergistic Therapy Based on Sequential Local Delivery of Combretastatin-A4 Phosphate (CA4P) and Doxorubicin (DOX). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:18560-18573.[44]Lv L, Liu H, Chen X, et al. Glutathione-triggered formation of molecular hydrogels for 3D cell culture. Colloids surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;108: 352-357.[45]Romic MD, Klaric MS, Lovric J, et al. Melatonin-loaded chitosan/ Pluronic(R) F127 microspheres as in situ forming hydrogel: an innovative antimicrobial wound dressing. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016;107:67-79.[46]Ji W, Liu GF, Xu MX, et al. A Redox-Responsive Supramolecular Hydrogel for Controllable Dye Release. Macromol Chem Phys. 2015; 216:1945-1951.[47]Xu H, Cao W, Zhang X. Selenium-containing polymers: promising biomaterials for controlled release and enzyme mimics. Acc Chem Res. 2013;46:1647-1658.[48]Ma N, Li Y, Xu H, et al. Dual redox responsive assemblies formed from diselenide block copolymers. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:442-443.[49]Wang L, Cao W, Yi Y, et al. Dual redox responsive coassemblies of diselenide-containing block copolymers and polymer lipids. Langmuir. 2014;30:5628-5636.[50]Gong C, Shan M, Li B, et al. Injectable dual redox responsive diselenide-containing poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel. Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2017;105:2451-2460.[51]Cherng JY, Hou TY, Shih MF, et al. Polyurethane-based drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2013;450:145-162.[52]Xue B, Kozlovskaya V, Kharlampieva E. Shaped stimuli-responsive hydrogel particles: syntheses, properties and biological responses. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5:9-35.[53]Koetting MC, Guido JF, Gupta M, et al. pH-responsive and enzymatically-responsive hydrogel microparticles for the oral delivery of therapeutic proteins: Effects of protein size, crosslinking density, and hydrogel degradation on protein delivery. J Control Release. 2016;221: 18-25.[54]Glangchai LC, Caldorera-Moore M, Shi L, et al. Nanoimprint lithography based fabrication of shape-specific, enzymatically-triggered smart nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2008;125:263-272.[55]Park J, Pramanick S, Park D, et al. Therapeutic-Gas-Responsive Hydrogel. Adv Mater. 2017. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201702859.[56]Hosseinifar T, Sheybani S, Abdouss M, et al. Pressure responsive nanogel base on Alginate-Cyclodextrin with enhanced apoptosis mechanism for colon cancer delivery. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018; 106:349-359.[57]Zhang YL, Li YS, Wang K, et al. Synthesis of an injectable, self-healable and dual responsive hydrogel for drug delivery and 3D cell cultivation. Royal Soc Chem. 2017;8:537-544.[58]Zhou C, Qian SS, Li XJ, et al. Synthesis and characterization of well-defined PAA-PEG multi-responsive hydrogels by ATRP and click chemistry. Rsc Adv. 2014;4:54631-54640.[59]Neibert K, Gopishetty V, Grigoryev A, et al. Wound-healing with mechanically robust and biodegradable hydrogel fibers loaded with silver nanoparticles. Adv Healthc Mater. 2012;1:621-630.[60]Liu J, Chen Z, Wang J, et al. Encapsulation of curcumin nanoparticles with mmp9-responsive and thermos-sensitive hydrogel improves diabetic wound healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b03868.[61]Wang P, Huang C, Xing Y, et al. NIR-Light- and pH-Responsive Graphene Oxide Hybrid Cyclodextrin-Based Supramolecular Hydrogels. Langmuir. 2019;35:1021-1031.[62]Yu B, Song N, Hu H, et al. A degradable triple temperature-, pH-, and redox-responsive drug system for cancer chemotherapy. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106:3203-3210. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [3] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [5] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [6] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [7] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [8] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [9] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [10] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [11] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [12] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [13] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||