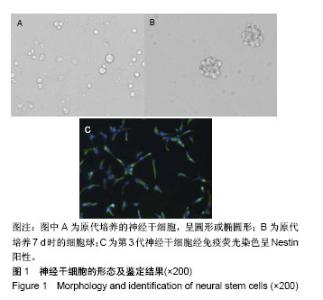
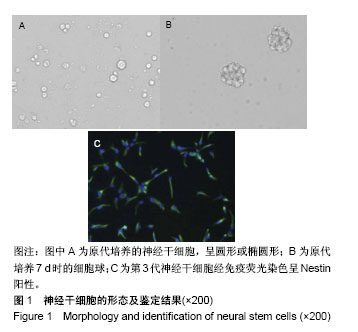
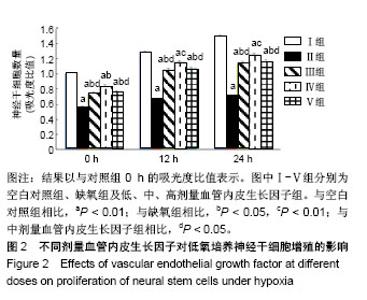
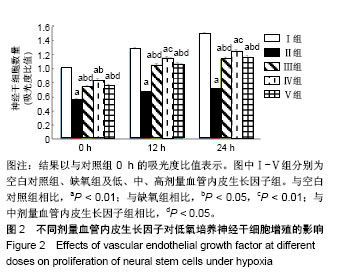
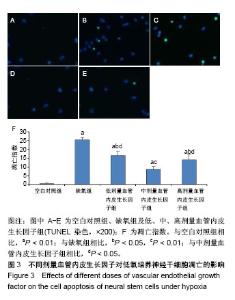
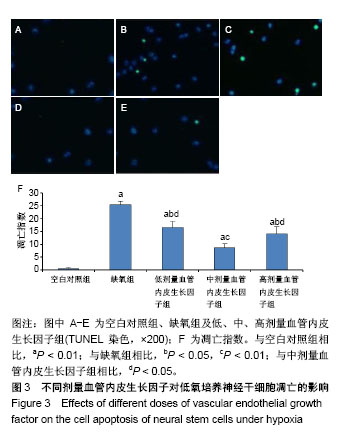
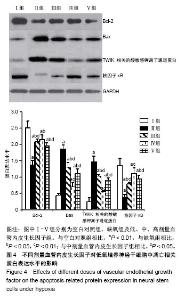
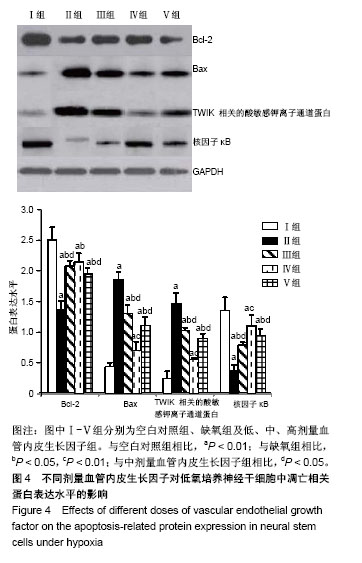
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (17): 2684-2689.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1709
Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effects of different doses of vascular endothelial growth factors on neural stem cells under hypoxic environment
Zhou Jingxia, Chen Lin, Chen Bocan, Xing Huaijie, Yan Limin, Zeng Chaosheng, Wu Hairong, Huang Yusheng, Chen Jiegui
- Department of Neurology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570031, Hainan Province, China
-
Revised:2019-01-16Online:2019-06-18Published:2019-06-18 -
Contact:Chen Lin, Master, Attending physician, Department of Neurology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570031, Hainan Province, China -
About author:Zhou Jingxia, Associate chief physician, Department of Neurology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570031, Hainan Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Project of Hainan Provincial Commission of Health and Family Planning, China, No. 1801032054A2011 (to ZJX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Jingxia, Chen Lin, Chen Bocan, Xing Huaijie, Yan Limin, Zeng Chaosheng, Wu Hairong, Huang Yusheng, Chen Jiegui . Protective effects of different doses of vascular endothelial growth factors on neural stem cells under hypoxic environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2684-2689.
share this article
| [1] 陈现乐.美国脑卒中中心认证制度及对我国的借鉴意义[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2016,23(2):115-116.[2] 王学义,马承君,王莹莹,等.亚低温治疗方案的临床应用[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2012,21(7):741-745.[3] 张儒有,郑永日,胡韶山,等.神经干细胞移植治疗脑卒中后遗症50例临床效果分析[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(9):138-139.[4] Sravanthi KN, Rao NR. Cerebroprotective activity of Pentapetes phoenicea on global cerebral ischemia in rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 2016;48(6):694-700.[5] Bai S, Sun Y, Wu L, et al. Tripotolide ameliorates inflammation and apoptosis induced by focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016;45(5): 493-500.[6] Gekht AB, Kanaeva LS, Avedisova AS, et al. Possible applications of rac-hopantenic acid in the treatment of anxiety and depressive disorders in patients with chronic cerebral ischemia. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2016; 116(11):45-57.[7] Gritti A, Vescovi AL, Galli R. Adult neural stem cells: plasticity and developmental potential. J Physiol Paris. 2002;96(1-2): 81-90.[8] 彭超华,戴冀斌,田毅浩,等.小鼠胚胎大脑皮质与中脑神经干细胞培养与分化比较的研究[J].解剖学报, 2005,36(6):660-664.[9] Laterza C, Wattananit S, Uoshima N, et al. Monocyte depletion early after stroke promotes neurogenesis from endogenous neural stem cells in adult brain. Exp Neurol. 2017;297:129-137.[10] Zhang F, Duan X, Lu L, et al. In Vivo Targeted MR Imaging of Endogenous Neural Stem Cells in Ischemic Stroke. Molecules. 2016;21(9): E1143.[11] Kokaia Z, Darsalia V. Human Neural Stem Cells for Ischemic Stroke Treatment. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2018;66:249-263.[12] Yu X, Wang X, Zeng S, et al. Protective effects of primary neural stem cell treatment in ischemic stroke models. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(3):2219-2228.[13] Bierer S, Herrmann E, Kopke T, et al. Lymphangiogenesis in kidney cancer: expression of VEGF-C, VEGF-D and VEGFR-3 in clear cell and papillary renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2008;20(4):721-725.[14] Zhao J, Li H, Wang M. Acute renal failure in a patient receiving anti-VEGF therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4(9):1185-1187.[15] Xu Z, Han K, Chen J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is neuroprotective against ischemic brain injury by inhibiting scavenger receptor A expression on microglia. J Neurochem. 2017;142(5):700-709.[16] Liu M, Wu Y, Liu Y, et al. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Protects Astrocytes Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Upregulating the Caveolin-1/VEGF Signaling Pathway. J Mol Neurosci. 2018;64(2):211-223.[17] 万鲁虹,张伟丽,孙凯,等.VEGF 2型受体基因多态与脑卒中易感性和脑卒中复发相关[J].中国分子心脏病学杂志, 2009,9(4): 204-208.[18] Anuncibay-Soto B, Santos-Galdiano M, Fernandez-Lopez A. Neuroprotection by salubrinal treatment in global cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(11):1744-1745.[19] Duan K, Wang X, Yang Z, et al. Therapeutic effect of GDNF gene-modified mesencephalic neural stem cell transplantation in a rat model of Parkinson disease. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2016;36(1):32-38.[20] McGinley LM, Kashlan ON, Bruno ES, et al. Human neural stem cell transplantation improves cognition in a murine model of Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14776.[21] Zhou CL, Zhao L, Shi HY, et al. Combined acupuncture and HuangDiSan treatment affects behavior and synaptophysin levels in the hippocampus of senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 after neural stem cell transplantation. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(3):541-548. [22] Chen M, Takano-Maruyama M, Pereira-Smith OM, et al. MRG15, a component of HAT and HDAC complexes, is essential for proliferation and differentiation of neural precursor cells. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87(7):1522-1531. [23] Bieberich E, MacKinnon S, Silva J, et al. Regulation of cell death in mitotic neural progenitor cells by asymmetric distribution of prostate apoptosis response 4 (PAR-4) and simultaneous elevation of endogenous ceramide. J Cell Biol. 2003;162(3):469-479. [24] Braga A, Maestá I, Rocha Soares R, et al. Apoptotic index for prediction of postmolar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215(3):336.e1-336.e12.[25] Szweda M, Rychlik A, Nowicki M, et al. The effect of budesonide on the expression of Ki-67 and PCNA and the apoptotic index in dogs with inflammatory bowel disease. Pol J Vet Sci. 2017;20(4):743-750.[26] Shi X, Yan C, Liu B, et al. miR-381 Regulates Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation via Regulating Hes1 Expression. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0138973. [27] Zheng J, Yi D, Liu Y, et al. Long nonding RNA UCA1 regulates neural stem cell differentiation by controlling miR-1/Hes1 expression. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(8):3696-3704. [28] Bao H, Song J. Treating Brain Disorders by Targeting Adult Neural Stem Cells. Trends Mol Med. 2018;24(12):991-1006.[29] Wang C, Lu CF, Peng J, et al.Roles of neural stem cells in the repair of peripheral nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017; 12(12):2106-2112.[30] Vogel S, Aswendt M, Nelles M, et al. Initial graft size and not the innate immune response limit survival of engrafted neural stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(3):784-793.[31] Thermet A, Robaczewska M, Rollier C, et al. Identification of antigenic regions of duck hepatitis B virus core protein with antibodies elicited by DNA immunization and chronic infection. J Virol. 2004;78(4):1945-1953.[32] 冯娜,戴冀斌,陈龙菊,等.不同低氧浓度对神经干细胞增殖与凋亡的影响[J].解剖学研究,2011,33(5):327-330.[33] Zhao C, Sun G, Li S, et al. MicroRNA let-7b regulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting nuclear receptor TLX signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107(5):1876-1881. [34] Edlich F. BCL-2 proteins and apoptosis: Recent insights and unknowns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500(1): 26-34.[35] Cianciulli A, Porro C, Calvello R, et al. Resistance to apoptosis in Leishmania infantum-infected human macrophages: a critical role for anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein and cellular IAP1/2. Clin Exp Med. 2018;18(2):251-261.[36] Peña-Blanco A, García-Sáez AJ. Bax, Bak and beyond - mitochondrial performance in apoptosis. FEBS J. 2018; 285(3):416-431.[37] Schwingshackl A, Lopez B, Teng B, et al. Hyperoxia treatment of TREK-1/TREK-2/TRAAK-deficient mice is associated with a reduction in surfactant proteins. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017;313(6):L1030-L1046.[38] Pan L, Yang F, Lu C, et al. Effects of sevoflurane on rats with ischemic brain injury and the role of the TREK-1 channel. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(4):2937-2942.[39] QiNan W, XiaGuang G, XiaoTian L, et al. Par-4/NF-κB Mediates the Apoptosis of Islet β Cells Induced by Glucolipotoxicity. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:4692478.[40] Zhang DX, Ma DY, Yao ZQ, et al. ERK1/2/p53 and NF-κB dependent-PUMA activation involves in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016; 20(11):2435-2442. [41] Zhuang C, Huo H, Fu W, et al. Aluminum chloride induced splenic lymphocytes apoptosis through NF-κB inhibition. Chem Biol Interact. 2016;257:94-100. |
| [1] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [2] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [3] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [4] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [5] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [6] | Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi. Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718. |
| [7] | Zhang Wenwen, Jin Songfeng, Zhao Guoliang, Gong Lihong. Mechanism by which Wenban Decoction reduces homocysteine-induced apoptosis of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 723-728. |
| [8] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [9] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [10] | Su Liping, Lu Ziyang, Liu Li, Zhang Wei, Su Tianyuan, Hu Xiayun, Pu Hongwei, Han Dengfeng. C-jun, Cytc and Caspase-9 in the apoptosis of cerebellar granule neurons induced by diacetylmorphine in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3943-3948. |
| [11] | Zuo Zhenkui, Han Jiarui, Ji Shuling, He Lulu. Pretreatment with ginkgo biloba extract 50 alleviates radiation-induced acute intestinal injury in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3666-3671. |
| [12] | Zhang Liang, Ma Xiaoyan, Wang Jiahong. Regulatory mechanism of Shenshuai Yin on cell apoptosis in the kidney of chronic renal failure rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3672-3677. |
| [13] | Xie Yang, Lü Zhiyu, Zhang Shujiang, Long Ting, Li Zuoxiao. Effects of recombinant adeno-associated virus mediated nerve growth factor gene transfection on oligodendrocyte apoptosis and myelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3678-3683. |
| [14] | Huang Maomao, Hu Yue, Wang Binchuan, Zhang Chi, Xie Yujie, Wang Jianxiong, Wang Li, Xu Fangyuan. Bibliometric and visual analysis of international literature addressing ischemic stroke rehabilitation in recent 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3725-3733. |
| [15] | Xu Bin, Yang Xiushu, Liu Xuan, Wang Zhenxing. Changes of intestinal epithelial cells and their apoptotic factors Caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 under urinary environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3173-3177. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||