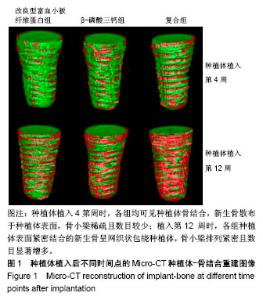
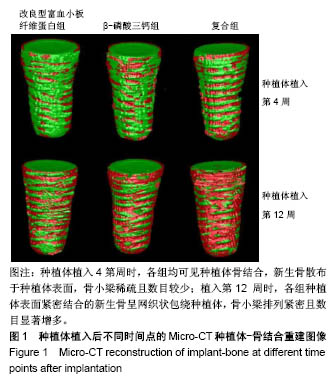
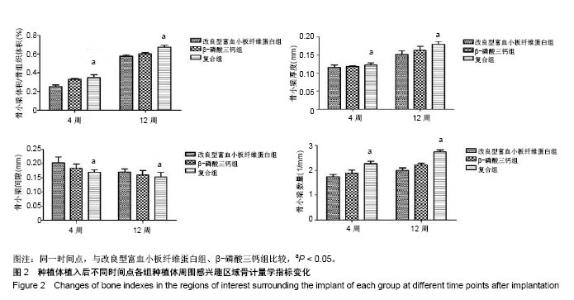
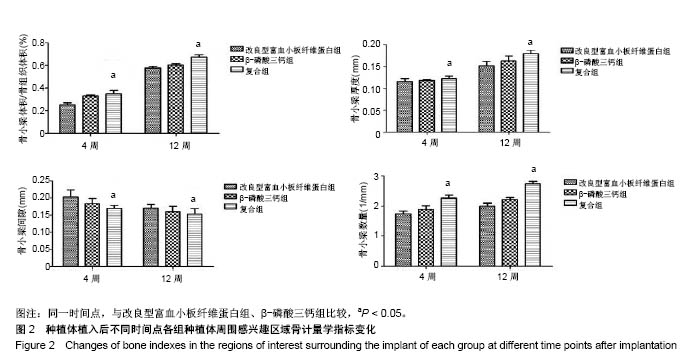
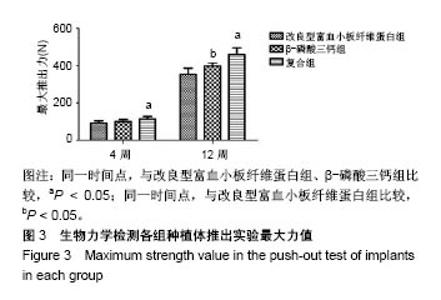
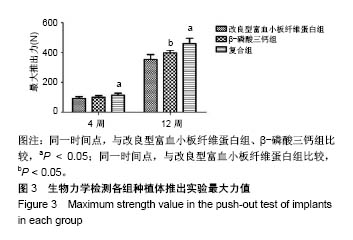
| [1] Branemark PI. Osseointegration and its experimental background.J Prosthet Dent. 1983;50(50):399-410.[2] Elnayef B,Monje A,Gargallo-Albiol J,et al.Vertical Ridge Augmentation in the Atrophic Mandible: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017;32(2): 291-312.[3] 马士卿,张旭,孙迎春,等.引导骨组织再生膜的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(3):308-310.[4] Masoudi Rad M,Nouri Khorasani S,Ghasemi-Mobarakeh L,et al.Fabrication and characterization of two-layered nanofibrous membrane for guided bone and tissue regeneration application. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;80:75-87. [5] Arunjaroensuk S, Panmekiate S, Pimkhaokham A. The Stability of Augmented Bone Between Two Different Membranes Used for Guided Bone Regeneration Simultaneous with Dental Implant Placement in the Esthetic Zone. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(1):206-216.[6] Benic GI,Bernasconi M,Jung RE,et al.Clinical and radiographic intra-subject comparison of implants placed with or without guided bone regeneration: 15-year results.J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44(3):315-325. [7] 陈卓凡,刘泉,Matinlinna JP.口腔种植中磷酸钙类骨替代材料的应用(英文)[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2016,26( 1):1-12.[8] Ghanaati S,Booms P,Orlowska A,et al.Advanced platelet-rich fibrin: a new concept for cell-based tissue engineering by means of inflammatory cells. J Oral Implantol. 2014;40(6): 679-689. [9] 焦志立,谢晓玲,付冬梅,等.改良型富血小板纤维蛋白在兔颅骨诱导成骨中的组织学观察[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(14): 2208-2214[10] 毛俊丽,孙勇,赵峰,等.兔PRF、A-PRF制备方法的筛选[J].西南国防医药,2016,26(6):593-596.[11] Hoshino A, Hanada S, Yamada H, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis escapes from the phagosomes of infected human osteoclasts reprograms osteoclast development via dysregulation of cytokines and chemokines.Pathog Dis. 2014;70(1):28-39.[12] 何通文,徐庚池,韩耀辉,等.构建兔颅顶骨临界骨缺损模型:确立颅顶临界骨缺损的参考值[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(18): 2789-2794.[13] 韦从云.重组人骨形成蛋白-2结合胶原骨粉/无胶原骨粉在兔股骨远端标准骨缺损模型中成骨效能的研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2010.[14] 邓威,郑欣,谌业帅,等. 3D打印多孔钛材料修复兔股骨髁骨缺损的实验研究[J].实验动物与比较医学, 2017,37(4):266-272.[15] 刘伟,陈杰,胡开进,等.负载CGRP及SP的明胶缓释微球用于修复家兔骨质疏松模型骨缺损的研究[J].口腔医学研究, 2016, 32(3):228-233.[16] Walsh WR,Oliver RA,Christou C,et al.Critical Size Bone Defect Healing Using Collagen-Calcium Phosphate Bone Graft Materials.PloS One.2017;12(1):e0168883.[17] 焦志立,谢晓玲,付冬梅,等.改良型富血小板纤维蛋白在兔颅骨诱导成骨中的组织学观察[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(14): 2208-2214.[18] Jacobsson M, Tjellström A, Thomsen P, et al. Integration of titanium implants in irradiated bone. Histologic and clinical study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1988;97(4 Pt 1):337-340.[19] He T,Cao C,Xu Z,et al.A comparison of micro-CT and histomorphometry for evaluation of osseointegration of PEO-coated titanium implants in a rat model. Sci Rep.2017; 7(1):16270.[20] Goldberg M, Marchadier A, Vidal C, et al. Differential effects of fibromodulin deficiency on mouse mandibular bones and teeth: a micro-CT time course study.Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;194(2-4):205-210. [21] 王军,毕龙,白建萍,等.显微CT与组织切片技术在骨形态计量研究中的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(5):381-384.[22] Abduljabbar T,Kellesarian SV,Vohra F,et al.Effect of Growth Hormone Supplementation on Osseointegration: A Systematic Review and Meta-analyses.Implant Dent. 2017; 26(4):613-620. [23] Pan W, Wei Y, Zhou L,et al. Comparative in vivo study of injectable biomaterials combined with BMP for enhancing tendon graft osteointegration for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(7):1015-1021. [24] 王程越,赵远,杨曼,等.组织工程化骨修复兔下颌骨缺损同期种植体植入的实验研究[J].口腔医学, 2016,36(1):12-17.[25] Degidi M, Daprile G, Piattelli A, et al. Development of a New Implant Primary Stability Parameter: Insertion Torque Revisited. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2013;15(5):637-644.[26] Öncü E,Bayram B,Kantarci A,et al.Positive effect of platelet rich fibrin on osseointegration. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2016;21(5):e601-607.[27] 邵磊,赵宝红.钛种植体骨结合界面组织学研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2014,7(7):440-445.[28] Masuki H,Okudera T,Watanebe T,et al.Growth factor and pro-inflammatory cytokine contents in platelet-rich plasma (PRP), plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF), advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), and concentrated growth factors (CGF). Int J Implant Dent.2016;2(1):19.[29] Thuaksuban N,Pannak R,Boonyaphiphat P,et al.In vivo biocompatibility and degradation of novel Polycaprolactone- Biphasic Calcium phosphate scaffolds used as a bone substitute. Biomed Mater Eng. 2018;29(2):253-267.[30] Matsuki K,Sugaya H,Takahashi N,et al.Degradation of Cylindrical Poly-Lactic Co-Glycolide/Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Biocomposite Anchors After Arthroscopic Bankart Repair: A Prospective Study. Orthopedics. 2018;41(3): e348-e353.[31] Del RC,Rodríguez-Évora M,Reyes R,et al. BMP-2, PDGF-BB, and bone marrow mesenchymal cells in a macroporous β-TCP scaffold for critical-size bone defect repair in rats. Biomed Mater. 2015;10(4):45008.[32] 尚文博.锰掺杂β-磷酸三钙多孔仿骨材料性能研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2016.[33] 周骁,钱玉芬.组织工程骨修复骨缺损的稳定性:材料降解与新骨形成[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(12):1938-1942. |