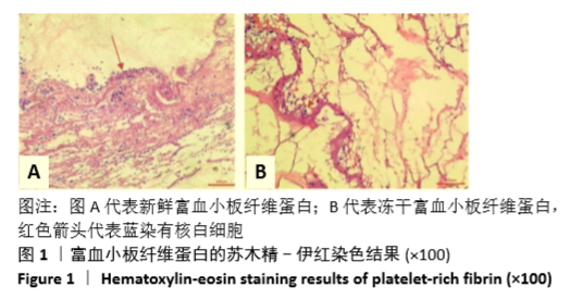
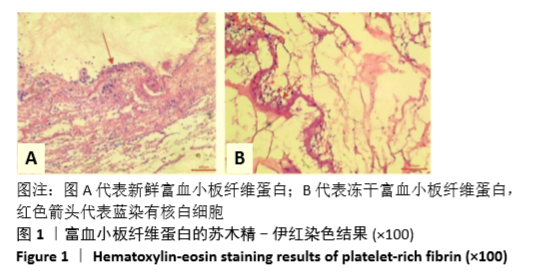
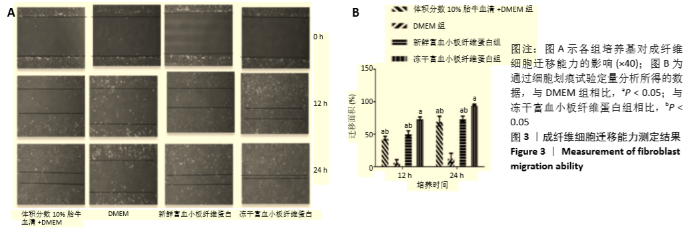
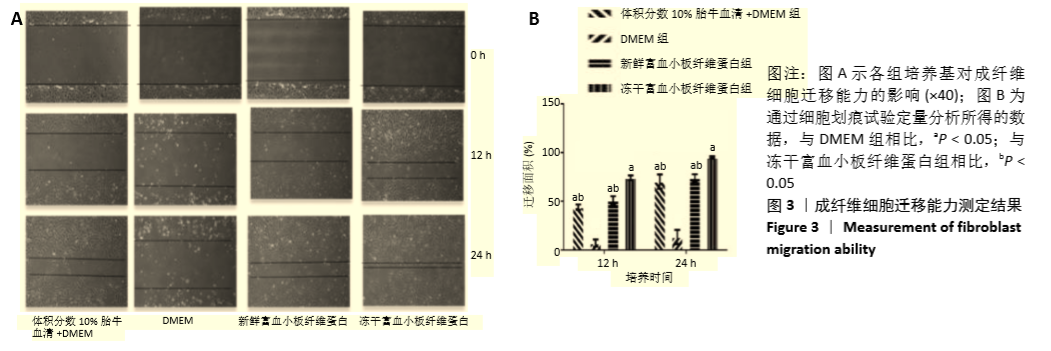
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (31): 4995-4999.doi: 10.12307/2021.142
Previous Articles Next Articles
Changes in biological characteristics of platelet-rich fibrin by freeze-drying technology
Liu Lei, Di Haiping, Guo Haina, Cao Dayong, Niu Xihua, Xia Chengde
- Department of Burn, First People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou City, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2020-06-10Revised:2020-06-16Accepted:2020-08-25Online:2021-11-08Published:2021-04-25 -
Contact:Xia Chengde, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Burn, First People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou City, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Liu Lei, Master, Department of Burn, First People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou City, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Lei, Di Haiping, Guo Haina, Cao Dayong, Niu Xihua, Xia Chengde. Changes in biological characteristics of platelet-rich fibrin by freeze-drying technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4995-4999.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
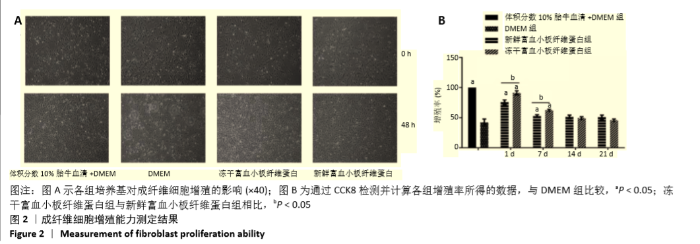
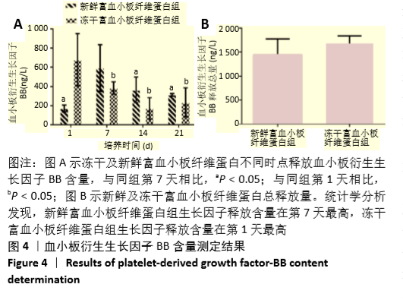
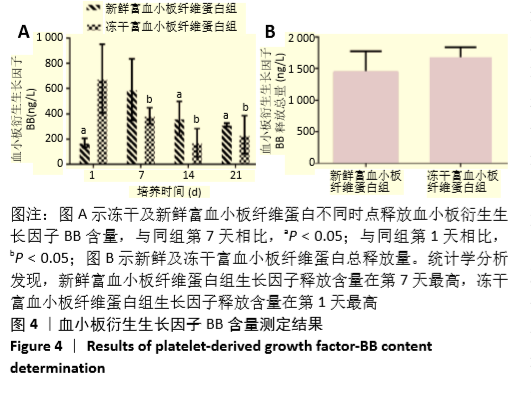
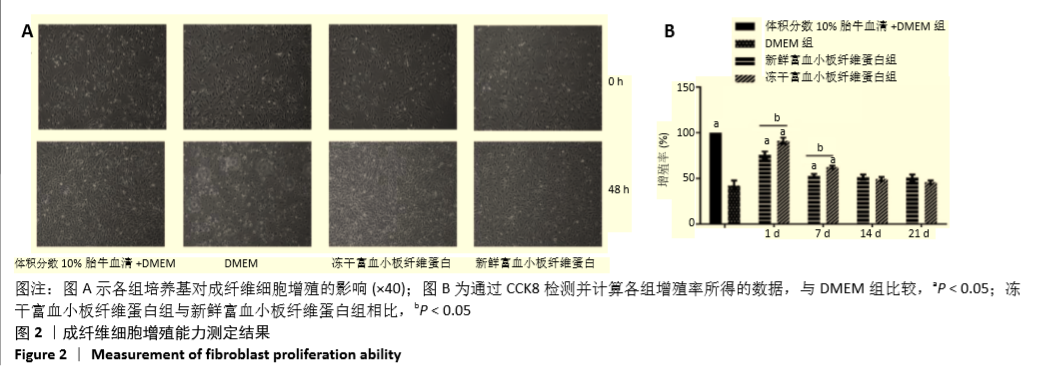
2.2 成纤维细胞增殖能力测定 成纤维细胞培养48 h后,在显微镜下进行细胞形态学观察,含有冻干PRF析出液和新鲜PRF析出液培养的成纤维细胞,形态良好,细胞数目明显增多,与含体积分数10%胎牛血清完全培养基培养的成纤维细胞数目相比无明显差别。而无血清培养基培养48 h,细胞形态变圆,脱落,细胞数目明显减少(图2A)。成纤维细胞培养48 h,CCK8进行增增殖能力测定,结果表明,与无血清基础培养基相比,第1天和第7天收集的新鲜及冻干PRF析出液明显促进成纤维细胞增殖(P < 0.05),其余各个时间点收集的两组析出液促进细胞增殖能力与无血清培养基组相比无差异,第1天及第7天两组析出液对成纤维细胞的增殖能力相比,冻干PRF析出液更能促进成纤维细胞增殖(P < 0.05),见图2B。结果表明,低温冷冻干燥不影响PRF中血小板释放生长因子的活力。"
| [1] ROY S, DRIGGS J, ELGHARABLY H, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin matrix improves wound angiogenesis via inducing endothelial cell proliferation. Wound Repair Regen. 2011;19(6):753-766. [2] CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, SIMONPIERI A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF):a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part V: histologic evaluations of PRF effects on bone allograft maturation in sinus lift.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3):299-303. [3] 雷朝锋,王英博,徐屹. 富血小板纤维蛋白在牙周植骨手术中的临床观察[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2017,27(9):525-528. [4] MIRON RJ, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, BISHARA M, et al. Platelet-rich fi-brin and soft tissue wound healing: a systematic review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23(1):83-99. [5] 孙洁, 张剑明, 李彦秋. 富血小板纤维蛋白超微结构的观察与探讨[J] .口腔医学研究,2010;26(1):98-101. [6] CHOI CW, KIM BS, SEO JH, et al. Long-term engraftment stability of peripheral blood stem cells cryopreserved using the dump-freezing method in a −80 °C mechanical freezer with 10% dimethyl sulfoxide. Int J Hematol. 2001;73(1):245-250. [7] HAUGH MG, MURPHY CM, O’BRIEN FJ. Novel freeze-drying methods to produce a range of collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds with tailored mean pore sizes. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(5):887-894. [8] ANITUA E, SÁNCHEZ M, ORIVE G, et al. The potential impact of the preparation rich in growth factors (PRGF) in different medical fields. Biomaterials. 2007;28(31): 4551-4560. [9] PIETRAMAGGIORI G, KAIPAINEN A, CZECZUGA JM, et al. Freeze-dried platelet-rich plasma shows beneficial healing properties in chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2006;14(5):573-580. [10] LI Q, REED DA, MIN L, et al. Lyophilized Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) Promotes Craniofacial Bone Regeneration through Runx2. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:8509-8525. [11] CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, SIMONPIERI A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part V: histologic evaluations of PRF effects on bone allograft maturation in sinus lift.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3):299-303. [12] 黎晓莉,张雁 ,吴宏. 包皮成纤维细胞的生物学特性研究[J]. 重庆医科大学学报,2009,34(1):41. [13] HAUGH MG, MURPHY CM, O’BRIEN FJ. Novel freeze-drying methods to produce arrange of collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds with tailored mean pore sizes. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(5):887-894. [14] ZHANG J, QI X, LUO X, et al. Clinical and immunohistochemical performance of lyophilized platelet-rich fibrin (Ly-PRF) on tissue re-generation. Clin Implant Dent Rela Res. 2017;19(3):466-477. [15] TSAI CH, SHEN SY, ZHAO JH, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin modulates cell proliferatation of human periodontally related cells in vitro. J Dent Sci. 2009;4(3):103-135. [16] DANGARIA SJ, ITO Y, LUAN X, et al. Successful periodontal ligament regeneration by periodontal progenitor preseeding on natural tooth root surfaces. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(10):1659-1668. [17] TEMMERMAN A, VANDESSEL J, CASTRO A, et al. The use of leucocyte and platelet-rich fibrin in socket management and ridge preserva-tion: a split-mouth, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2016; 43(11): 990-999. [18] 王澜,刘 刚,王杨,等.富血小板纤维蛋白在合并潜行皮下窦道的慢性创面治疗中的临床应用[J].中华烧伤杂志,2018,34(9):637-642. [19] DOHAN DM, DISS A, ODIN G, et al. In vitro effects of Choukroun’s PRF (Platelet-rich fibrin) on human gingival fibroblasts, dermal prekeratinocytes, preadipocytes, and maxillofacial osteoblasts in primary cultures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108(3):341-352. [20] LIAO HT, MARRA KG, RUBIN PJ. Application of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Fat Grafting: Basic Science and Literature Review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013;20(4):267-276. [21] NAIK B, KARUNAKAR P, JAYADEV M, et al. Role of Platelet rich fibrin in wound healing: A critical review. J Conserv Dent. 2013;16(4):284-293. [22] SCLAFANI AP, SAMAN M. Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrix for Facial Plastic Surgery. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2012;20(2):177-186. [23] SHARMA A , PRADEEP AR . Treatment of 3-Wall Intrabony Defects in Patients With Chronic Periodontitis With Autologous Platelet-Rich Fibrin: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J Periodontol. 2011; 82(12):1705-1712. [24] 周延民,付丽.富血小板纤维蛋白在口腔软硬组织再生中的作用—回顾与展望[J]. 口腔医学,2018,38(11):961-965. [25] LIN C, CHEN Z, PAN W, et al. Effect of platelet-rich fibrin on ridge preservation in perspective of bone healing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019; 34(4):845-854 [26] MIRON RJ, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, BISHARA M, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin and soft tissue wound healing: a systematic review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23(1):83-99. [27] TEMMERMAN A, VANDESSEL J, CASTRO A, et al. The use of leucocyte and platelet-rich fibrin in socket management and ridge preservation: a split-mouth, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2016;43(11):990-999. [28] 杨波,王少根.富血小板纤维蛋白在骨再和创面修复中的应用及机制的研究进展[J].安徽医药,2019,23(9):1705-1710. [29] 武钰翔,司少艳,许樟荣,等.富白细胞血小板纤维蛋白促进创面愈合的优势[J].中国组织程研究,2018,22(34):5484-5489. [30] BOSS WK, USAL H, CHERNOFF G, et al. Autologous cultured fibroblasts as cellular therapy in plastic surgery. Clin Plast Surg. 2000;27(4):613-626. [31] SEYHUN S, TUNC T, SINEM EC. The effect of cultured autologous fibroblasts on longevity of cross -linked hyaluronic acid used as a filler. Ann Plast Surg. 2008; 28(4):412 [32] LEASK A,ABRAHAM DJ. The role of connective tissue growth factor, multifunctional matricellu-lar protein,in fibroblast biology. Biochem Cell Biol. 2003;81(6):355. [33] 周剑虹,邢新,任常群,等. 血小板源生长因子受体α和β在瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞中表达的差异性研究[J]. 中国美容医学,2009,18(6): 814. [34] TABLIN F, WALKER NJ, HOGLE SE, et al. Assessment of platelet growth factors in supernatants from rehydrated freeze-dried equine platelets and their effects on fibroblasts in vitro. Am J Vet Res. 2008;69(11): 1512-1519. [35] MCCARREL T, FORTIER L. Temporal growth factor release from platelet-rich plasma, trehalose lyophilized platelets, and bone marrow aspirate and their effect on tendon and ligament gene expression. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(8):1033-1042. |
| [1] | Mei Jingyi, Liu Jiang, Xiao Cong, Liu Peng, Zhou Haohao, Lin Zhanyi. Proliferation and metabolic patterns of smooth muscle cells during construction of tissue-engineered blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1043-1049. |
| [2] | Wang Xinmin, Yan Wenkai, Song Yahui, Liu Fei. Leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin with autologous hamstring tendon for traumatic patella dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 404-410. |
| [3] | Wang Qian, Lu Ziang, Li Lihe, Lyu Chaoliang, Wang Meng, Zhang Cunxin. Sinomenine effectively inhibits interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 224-230. |
| [4] | Sun Jing, Liao Jian, Sun Jiangling, Cheng Ping, Feng Hongchao. Recombinant human growth hormone promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 56-61. |
| [5] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [6] | Tang Yuting, He Xi, Wan Yu, Wang Jianjun, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Shikonin inhibits fibrosis of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts via MicroRNA-382-5p [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5642-5648. |
| [7] | Huang Qian, Hao Liying, He Longlong, Du Liangzhi. Graphene oxide-chitosan composite coating affects the biological behavior of osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5430-5435. |
| [8] | Zhou Yuebin, Guo Honggang. Construction of tissue-engineered bone composite scaffolds by loading rabbit-derived bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on magnesium-based alloy scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5491-5496. |
| [9] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [10] | Duan Jiahao, Tan Xuyi, Lu Min, Kuang Gaoyan, Fang Chuanlong, Xiao Man. Effects of Sanhua Jiegu San on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3230-3235. |
| [11] | Luo Wenhao, Feng Le, Huang Haixia, Liu Min, Wang Pin. Effect of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibitor Tideglusib on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under high glucose microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(19): 2968-2974. |
| [12] | Zhang Yuwei, Liu Chuanchuan, Mao Jiaqi, Zhang Qingqing, Liu Hong, Chen Ying, Ma Lan. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes treated with hypoxic preconditioning inhibits proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(19): 2986-2992. |
| [13] | Zhao Yan, Xia Qiuqiu, Xiang Shaojie, Mao Qiming, Kong Weijun, Du Qian, Liao Wenbo, Xin Zhijun. Exosomal miRNA in the repair mechanism of degenerative diseases of the spine and joints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(19): 3040-3051. |
| [14] | Zhu Can, He Jiaheng, Chen Chichi, Liu Bo, Luo Zongping, Sun Jie, Shi Qin. Chlorogenic acid promotes osteogenic differentiation of osteoblast precursor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2170-2175. |
| [15] | Lu Yangyang, Yan Ruihong, Qiu Zhongpeng, Dai Yi, Wang Zixin, Wang Weishan, Shi Chenhui, Du Xinhui, Li Gang. Intervention with platelet-rich fibrin in rabbit models after microvascular anastomosis surgery of the femoral artery: changes in vascular structure and soft tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1659-1668. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||