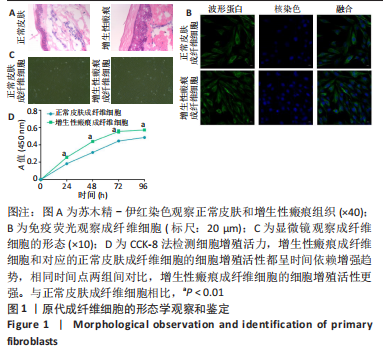
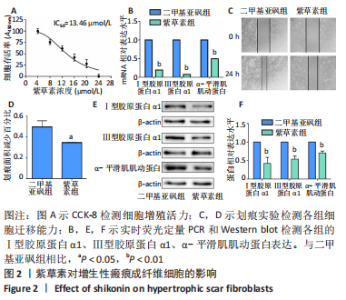
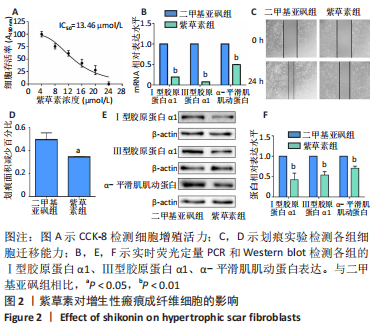
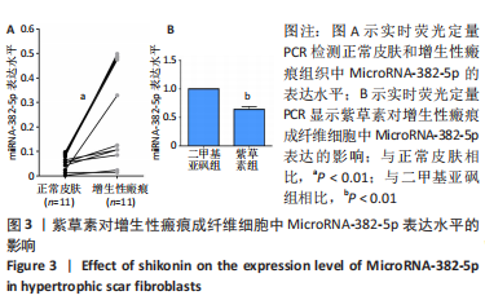
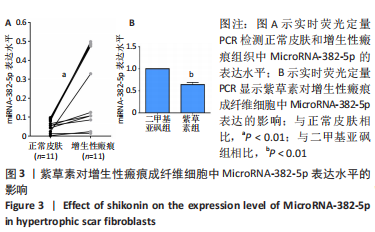
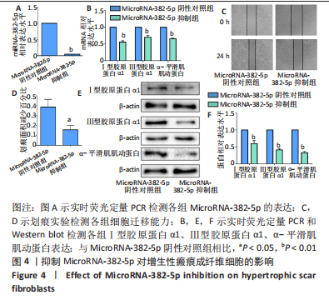
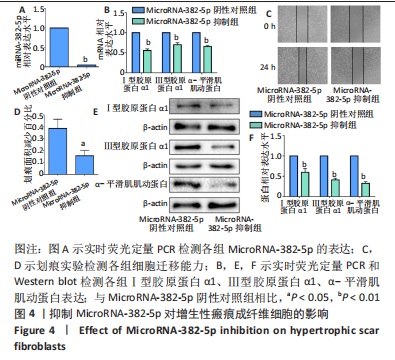
[1] ZHANG J, LI Y, BAI X, et al. Recent advances in hypertrophic scar. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(1):27-39.
[2] OGAWA R, DOHI T, TOSA M, et al. The Latest Strategy for Keloid and Hypertrophic Scar Prevention and Treatment: The Nippon Medical School (NMS) Protocol. J Nippon Med Sch. 2021;88(1):2-9.
[3] LEE HJ, JANG YJ. Recent Understandings of Biology, Prophylaxis and Treatment Strategies for Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):711.
[4] KAFKA M, COLLINS V, KAMOLZ LP, et al. Evidence of invasive and noninvasive treatment modalities for hypertrophic scars: A systematic review. Wound Repair Regen. 2017;25(1):139-144.
[5] BI M, SUN P, LI D, et al. Intralesional Injection of Botulinum Toxin Type A Compared with Intralesional Injection of Corticosteroid for the Treatment of Hypertrophic Scar and Keloid: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:2950-2958.
[6] ZHANG H, WANG HY, WANG DL, et al. Effect of pressure therapy for treatment of hypertrophic scar. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(26): e16263.
[7] LIANG YY, SHEN JC, LI W. Evolution of compressive mechanical properties of early hypertrophic scar during laser treatment. J Biomech. 2021;129:110783.
[8] OGAWA R. Keloid and Hypertrophic Scars Are the Result of Chronic Inflammation in the Reticular Dermis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):606.
[9] OGAWA R. The Most Current Algorithms for the Treatment and Prevention of Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids: A 2020 Update of the Algorithms Published 10 Years Ago. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022;149(1): 79e-94e.
[10] HONG M, WANG N, TAN HY, et al. MicroRNAs and Chinese Medicinal Herbs: New Possibilities in Cancer Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2015;7(3): 1643-1657.
[11] GUO C, HE J, SONG X, et al. Pharmacological properties and derivatives of shikonin-A review in recent years. Pharmacol Res. 2019;149:104463.
[12] WANG Q, WANG J, WANG J, et al. Molecular mechanism of shikonin inhibiting tumor growth and potential application in cancer treatment. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021;10(6):1077-1084.
[13] FAN C, XIE Y, DONG Y, et al. Investigating the potential of Shikonin as a novel hypertrophic scar treatment. J Biomed Sci. 2015;22(1):70.
[14] 彭旦明, 蔡紫光, 张瑾楠, 等. 紫草素对增生性瘢痕中VEGF亚型mRNA表达的影响[J]. 实用中西医结合临床,2010,10(2):1-2+4.
[15] DENG X, CHEN Q, QIANG L, et al. Development of a Porcine Full-Thickness Burn Hypertrophic Scar Model and Investigation of the Effects of Shikonin on Hypertrophic Scar Remediation. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:590.
[16] OGAWA R, AKAISHI S, KURIBAYASHI S, et al. Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars Can Now Be Cured Completely: Recent Progress in Our Understanding of the Pathogenesis of Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars and the Most Promising Current Therapeutic Strategy. J Nippon Med Sch. 2016;83(2):46-53.
[17] MARTIN P, NUNAN R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of repair in acute and chronic wound healing. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173(2):370-378.
[18] FOSTER DS, JANUSZYK M, YOST KE, et al. Integrated spatial multiomics reveals fibroblast fate during tissue repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(41):e2110025118.
[19] BAINBRIDGE P. Wound healing and the role of fibroblasts. J Wound Care. 2013;22(8):407-408,410-412.
[20] FAN C, EL ANDALOUSSI S, LEHTO T, et al. Smad‑binding decoy reduces extracellular matrix expression in human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(6):4589-4600.
[21] DEKONINCK S, BLANPAIN C. Stem cell dynamics, migration and plasticity during wound healing. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(1):18-24.
[22] TREPAT X, CHEN Z, JACOBSON K. Cell migration. Compr Physiol. 2012; 2(4):2369-2392.
[23] JIANG D, GUO B, LIN F, et al. miR-205 inhibits the development of hypertrophic scars by targeting THBS1. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(21): 22046-22058.
[24] YAN L, WANG LZ, XIAO R, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-21-5p reduces keloid fibroblast autophagy and migration by targeting PTEN after electron beam irradiation. Lab Invest. 2020;100(3):387-399.
[25] 李战, 农晓琳, 李佳荃, 等. 青蒿琥酯对增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞的抑制作用及机制探讨[J]. 中国药理学通报,2014,30(7):947-951.
[26] 王莎丽, 杨琳, 刘勇, 等. 积雪草苷对博莱霉素诱导小鼠皮肤瘢痕形成的抑制作用[J]. 医药导报,2017,36(12):1363-1366.
[27] 王雷, 马园园, 李亚玲, 等. 芍药苷对增殖性瘢痕成纤维细胞增殖抑制作用及机制研究[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2017,27(11):38-43.
[28] ZHOU L, WANG J, ZHAO J, et al. Shikonin promotes osteogenesis and suppresses osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(12): 8099-8110.
[29] ZHANG X, CUI JH, MENG QQ, et al. Advance in Anti-tumor Mechanisms of Shikonin, Alkannin and their Derivatives. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018; 18(2):164-172.
[30] TSAI MF, CHEN SM, ONG AZ, et al. Shikonin Induced Program Cell Death through Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species in Renal Cancer Cells. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(11):1831.
[31] LIU C, XUAN LQ, LI K, et al. Shikonin Inhibits Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Line QBC939 by Regulating Apoptosis, Proliferation, and Invasion. Cell Transplant. 2021;30:963689720979162.
[32] WANG H, ZUO J. Shikonin Inhibits Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer H1299 Cell Growth through Survivin Signaling Pathway. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021;2021:6435393.
[33] LIU T, XU L, WANG C, et al. Alleviation of hepatic fibrosis and autophagy via inhibition of transforming growth factor-β1/Smads pathway through shikonin. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34(1):263-276.
[34] WEI Q, SU J, DONG G, et al. Glycolysis inhibitors suppress renal interstitial fibrosis via divergent effects on fibroblasts and tubular cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019;316(6):F1162-F1172.
[35] NING X, WIRAJA C, CHEW WTS, et al. Transdermal delivery of Chinese herbal medicine extract using dissolvable microneedles for hypertrophic scar treatment. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(9):2937-2944.
[36] LI Y, ZHANG J, LEI Y, et al. MicroRNA-21 in Skin Fibrosis: Potential for Diagnosis and Treatment. Mol Diagn Ther. 2017;21(6):633-642.
[37] LIN CA, DUAN KY, WANG XW, et al. Study on the role of Hsa-miR-382-5p in epidural fibrosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(12):3663-3668.
[38] GUO L, XU K, YAN H, et al. MicroRNA expression signature and the therapeutic effect of the microRNA‑21 antagomir in hypertrophic scarring. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(3):1211-1221. |