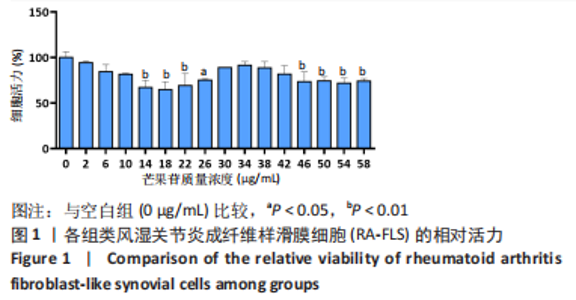
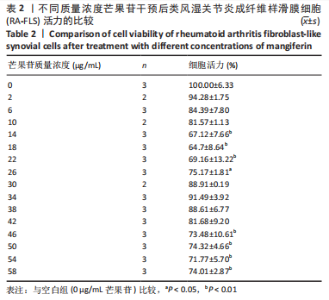
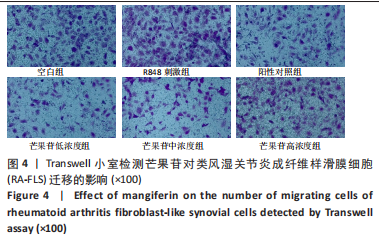
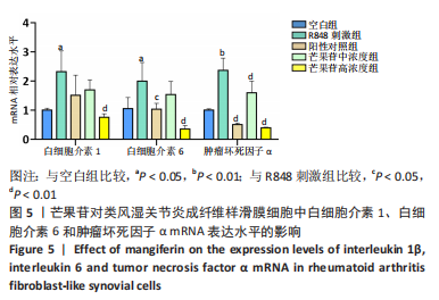
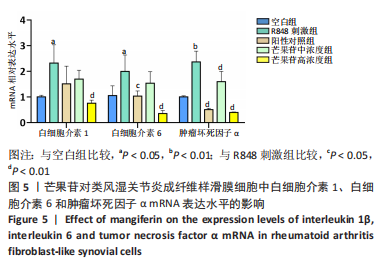
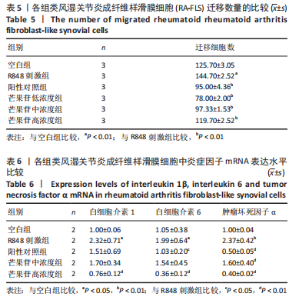
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (11): 1690-1695.doi: 10.12307/2024.203
Previous Articles Next Articles
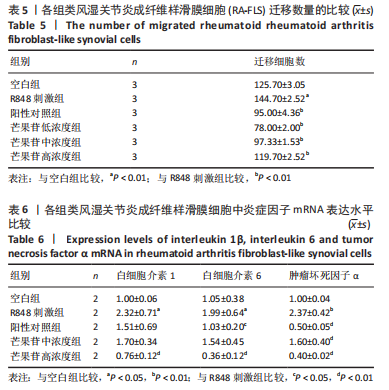
Mangiferin inhibits proliferation, migration and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
Hu Mengfan1, Yan Qiuhui2, Deng Mengran2, Liang Meimei2, Liang Liang1, 3, 4, Yi Sisi1, 3, 4, Deng Jiagang5, Yun Chenxia1, 3, 4
- 1School of Basic Medicine, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Key Laboratory of Integrative Translational Medicine of Guangxi High Incidence Infectious Diseases, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 4Key Laboratory of Guangxi Characteristic Experimental Animal Disease Model, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 5Guangxi Collaborative Innovation Center for Research on Functional Components of Crop Waste, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China