Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (19): 2968-2974.doi: 10.12307/2023.620
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibitor Tideglusib on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under high glucose microenvironment
Luo Wenhao1, 2, Feng Le2, 3, Huang Haixia1, 2, Liu Min1, 2, Wang Pin1, 2
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 3Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Panzhihua University, Panzhihua 617000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2022-06-25Accepted:2022-08-01Online:2023-07-08Published:2022-11-28 -
Contact:Wang Pin, Master, Attending physician, Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Luo Wenhao, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Medical Research Project of Sichuan Province, No. S19023 (to LM); Science and Technology Plan Project of Luzhou City, No. 2021-JYJ-68 (to HHX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Wenhao, Feng Le, Huang Haixia, Liu Min, Wang Pin. Effect of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibitor Tideglusib on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under high glucose microenvironment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(19): 2968-2974.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
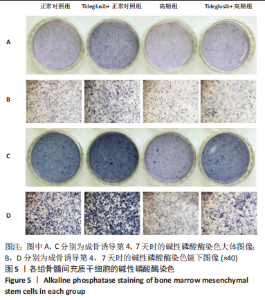
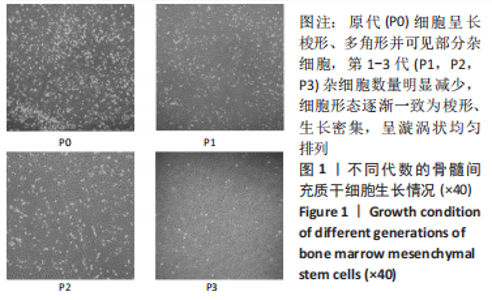
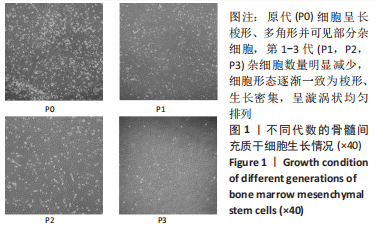
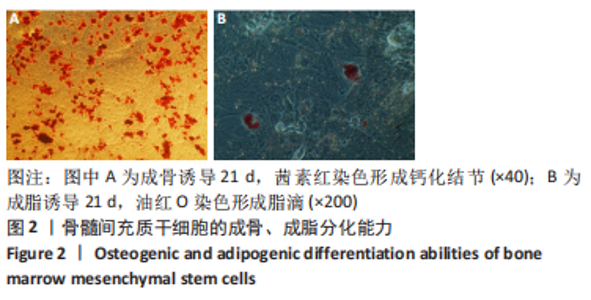
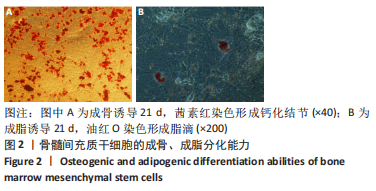
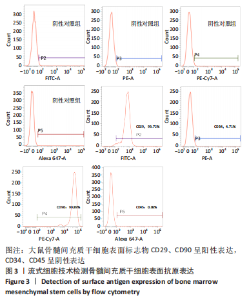
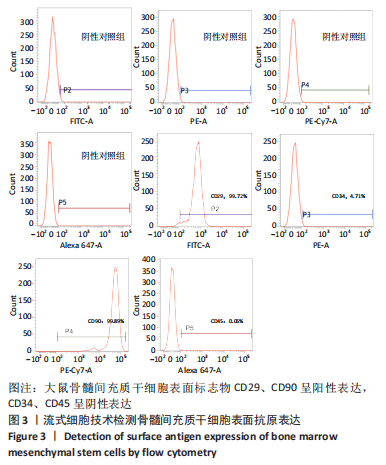
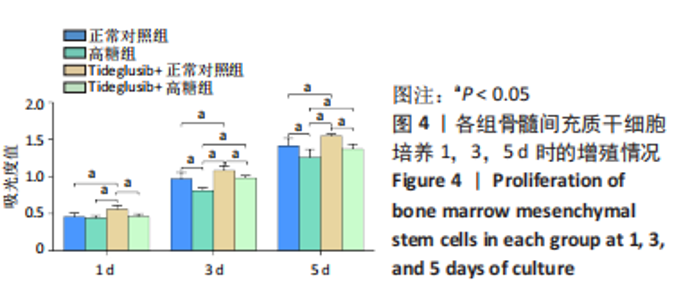
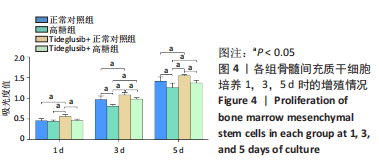
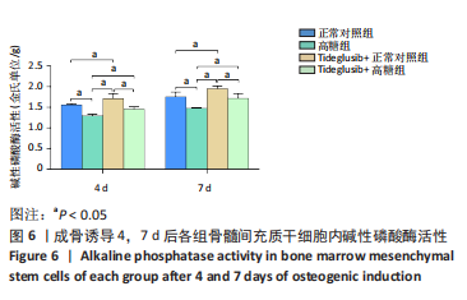
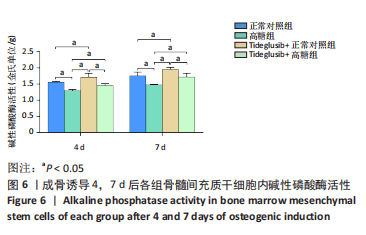
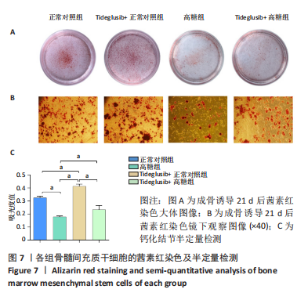
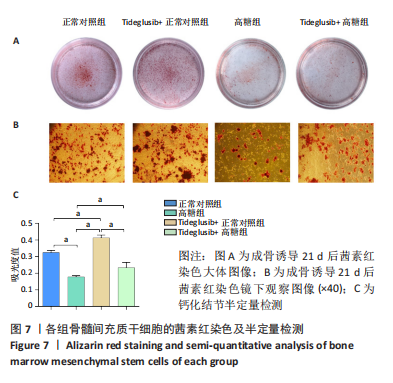
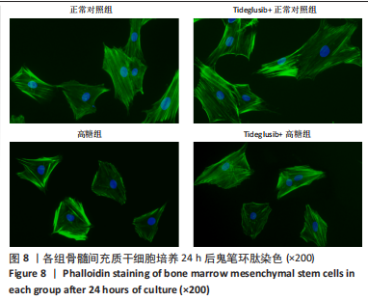
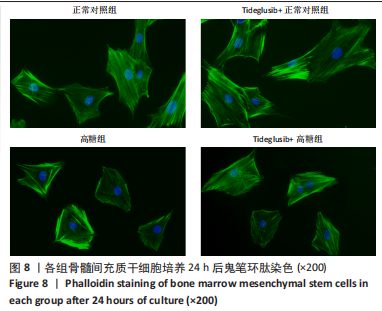
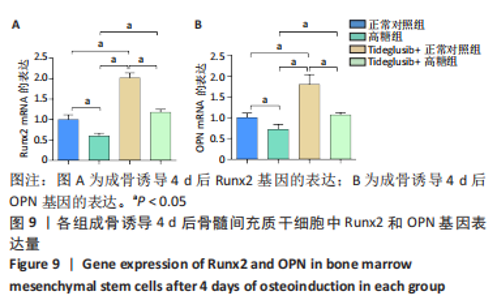
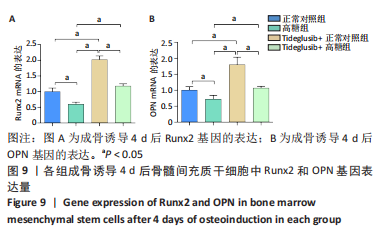
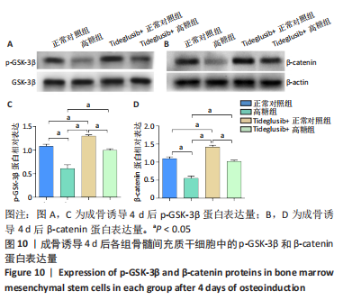
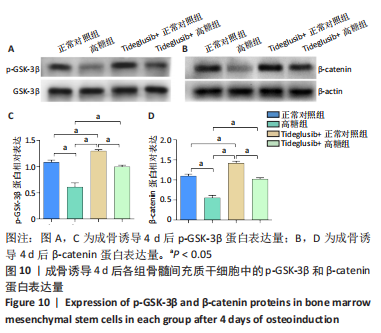
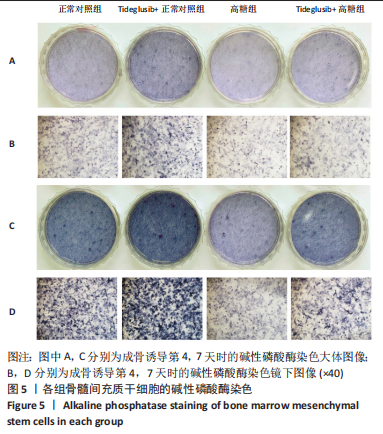
2.4 Tideglusib减轻高糖微环境下大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化障碍 各组成骨诱导4 d和7 d后,碱性磷酸酶染色显示:Tideglusib+正常对照组的碱性磷酸酶染色程度最深,高糖组的碱性磷酸酶染色程度低于正常对照组,Tideglusib+高糖组的碱性磷酸酶染色程度优于高糖组,见图5。碱性磷酸酶活性定量测定显示:在第4,7天时,Tideglusib+正常对照组的碱性磷酸酶活性高于其他各组(P < 0.05);高糖组的碱性磷酸酶活性低于其他各组(P < 0.05);Tideglusib+高糖组的碱性磷酸酶活性高于高糖组(P < 0.05),见图6。成骨诱导21 d后,茜素红染色显示:Tideglusib+正常对照组茜素红特异性红染的钙化结节较多,染色较深,红染斑块面积较大,钙化结节形成能力较强;正常对照组的红染钙化结节数量低于Tideglusib+正常对照组,且红染斑块面积小于Tideglusib+正常对照组;Tideglusib+高糖组的红染结节少于正常对照组,且斑块较小;高糖组的红染结节数量和面积最小。钙化结节半定量检测结果显示,Tideglusib+正常对照组的钙化结节数量最多,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),高糖组的钙化结节数量最低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),Tideglusib+高糖组的钙化结节数量大于高糖组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图7。"
| [1] Monje A, Catena A, Borgnakke WS. Association between diabetes mellitus/hyperglycaemia and peri-implant diseases: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44(6):636-648. [2] Park SY, Choi KH, Jun JE, et al. Effects of Advanced Glycation End Products on Differentiation and Function of Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(37):e239. [3] Kaur J, Khosla S, Farr JN. Effects of diabetes on osteocytes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2022;29(4):310-317. [4] Kasperk C, Georgescu C, Nawroth P. Diabetes Mellitus and Bone Metabolism. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2017;125(4):213-217. [5] Murray CE, Coleman CM. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Bone Health. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4873. [6] 董刚,徐欣,田燕,等.2型糖尿病患者血糖控制水平与种植牙愈合的关系[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2013,39(1):143-147. [7] Al Zahrani S, Al Mutairi AA. Crestal Bone Loss Around Submerged and Non-Submerged Dental Implants in Individuals with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 7-Year Prospective Clinical Study. Med Princ Pract. 2019;28(1):75-81. [8] King S, Klineberg I, Levinger I, et al. The effect of hyperglycaemia on osseointegration: a review of animal models of diabetes mellitus and titanium implant placement. Arch Osteoporos. 2016;11(1):29. [9] Neves VC, Babb R, Chandrasekaran D, et al. Promotion of natural tooth repair by small molecule GSK3 antagonists. Sci Rep. 2017;7:39654. [10] Zaugg LK, Banu A, Walther AR, et al. Translation Approach for Dentine Regeneration Using GSK-3 Antagonists. J Dent Res. 2020;99(5):544-551. [11] Comeau-Gauthier M, Tarchala M, Luna JLR, et al. Unleashing β-catenin with a new anti-Alzheimer drug for bone tissue regeneration. Injury. 2020;51(11):2449-2459. [12] Lektemur Alpan A, Çalişir M, Kizildağ A, et al. Effects of a Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Inhibitor Tideglusib on Bone Regeneration With Calvarial Defects. J Craniofac Surg. 2020;31(5):1477-1482. [13] Sun Y, Zhu Y, Liu X, et al. Morroniside attenuates high glucose-induced BMSC dysfunction by regulating the Glo1/AGE/RAGE axis. Cell Prolif. 2020; 53(8):e12866. [14] Li Y, Wang X. Chrysin Attenuates High Glucose-Induced BMSC Dysfunction via the Activation of the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:165-182. [15] Liu S, Yang X, Zhong X, et al. Involvement of miR-337 in high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via negative regulation of Rap1A. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2021;57(3):350-358. [16] Li Z, Zhao H, Chu S, et al. miR-124-3p promotes BMSC osteogenesis via suppressing the GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway in diabetic osteoporosis rats. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020;56(9):723-734. [17] Zhang B, Liu N, Shi H, et al. High glucose microenvironments inhibit the proliferation and migration of bone mesenchymal stem cells by activating GSK3β. J Bone Miner Metab. 2016;34(2):140-150. [18] 陈杨. Runx2对高糖环境下干细胞成骨分化作用和机制的初步研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2017. [19] Fairfield H, Falank C, Harris E, et al. The skeletal cell-derived molecule sclerostin drives bone marrow adipogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233(2):1156-1167. [20] Jin P, Zhang X, Wu Y, et al. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat-derived bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells have impaired abilities in proliferation, paracrine, antiapoptosis, and myogenic differentiation. Transplant Proc. 2010;42(7):2745-2752. [21] del Ser T, Steinwachs KC, Gertz HJ, et al. Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease with the GSK-3 inhibitor tideglusib: a pilot study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33(1):205-215. [22] Atila D, Chen CY, Lin CP, et al. In vitro evaluation of injectable Tideglusib-loaded hyaluronic acid hydrogels incorporated with Rg1-loaded chitosan microspheres for vital pulp regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;278: 118976. [23] 孙佳辰,刘馨竹,申传安,等.小分子药物Tideglusib促进大鼠创面愈合的机制研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2021,16(3):224-231. [24] 胡洋,张媛媛,李芳,等.中药有效成分调节细胞骨架功能的研究进展[J].药学研究,2018,37(4):187-193. [25] Duan P, Bonewald LF. The role of the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in formation and maintenance of bone and teeth. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016;77(Pt A):23-29. [26] 姜朝阳,谢兴文,徐世红,等.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化相关信号通路[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2020,13(5):473-478. [27] Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985-999. [28] Maeda K, Kobayashi Y, Koide M, et al. The Regulation of Bone Metabolism and Disorders by Wnt Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5525. [29] 史卫东. AGEs、GSK3β、TRPM2对高糖环境下成骨细胞增殖影响的机制研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2019. [30] Cheng J, Xu HY, Liu MM, et al. Catalpol Promotes the Proliferation and Differentiation of Osteoblasts Induced by High Glucose by Inhibiting KDM7A. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:705-712. [31] Chen Y, Chen L, Huang R, et al. Investigation for GSK3β expression in diabetic osteoporosis and negative osteogenic effects of GSK3β on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under a high glucose microenvironment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;534:727-733. [32] Antika LD, Lee EJ, Kim YH, et al. Dietary phlorizin enhances osteoblastogenic bone formation through enhancing β-catenin activity via GSK-3β inhibition in a model of senile osteoporosis. J Nutr Biochem. 2017;49:42-52. |
| [1] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [2] | Zhao Lu, Zhao Yifei, Gao Da, Liu Yanfang, Fu Tingting, Xu Jiangyan. Expression of suppressor of Zeste 12 in kidney tissues of rats with diabetic nephropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1179-1186. |
| [3] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [4] | Li Xinyue, Li Xiheng, Mao Tianjiao, Tang Liang, Li Jiang. Three-dimensional culture affects morphology, activity and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 846-852. |
| [5] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [6] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [7] | Yuan Wei, Liu Jingdong, Xu Guanghui, Kang Jian, Li Fuping, Wang Yingjie, Zhi Zhongzheng, Li Guanwu. Osteogenic differentiation of human perivascular stem cells and its regulation based on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 866-871. |
| [8] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [9] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [10] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [11] | Dai Xianglin, Zhang Wenfeng, Yao Xijun, Shang Jiaqi, Huang Qiujin, Ren Yifan, Deng Jiupeng. Barium titanate/polylactic acid piezoelectric composite film affects adhesion, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 367-373. |
| [12] | Li Rui, Liu Zhen, Guo Zige, Lu Ruijie, Wang Chen. Aspirin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and polydopamine modified titanium sheets improve osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 374-379. |
| [13] | Duan Jiahao, Tan Xuyi, Lu Min, Kuang Gaoyan, Fang Chuanlong, Xiao Man. Effects of Sanhua Jiegu San on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3230-3235. |
| [14] | Wang Buyu, Zhang Yong, Li Feifei, Dong Xiaoyu, Deng Jiang, Ruan Shiqiang. Role and application of bone morphogenetic protein 2 in the repair of osteochondral defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3259-3265. |
| [15] | Wu Shuangshuang, Zhang Ying, Kou Xianjuan. Treadmill exercise improves cognitive dysfunction in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 208-215. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||