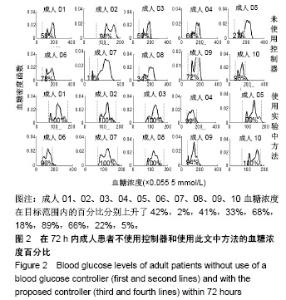
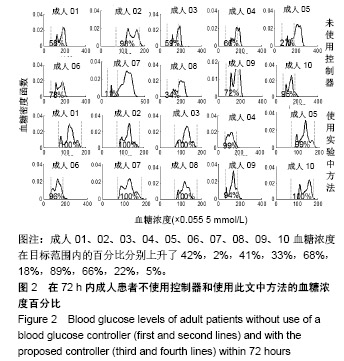
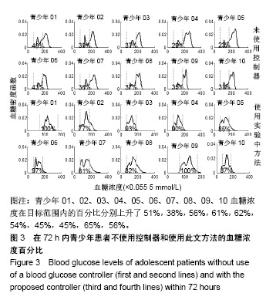
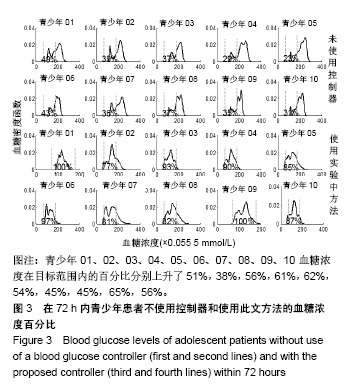
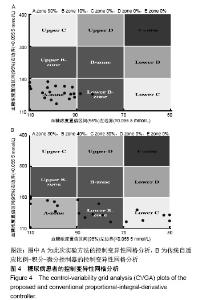
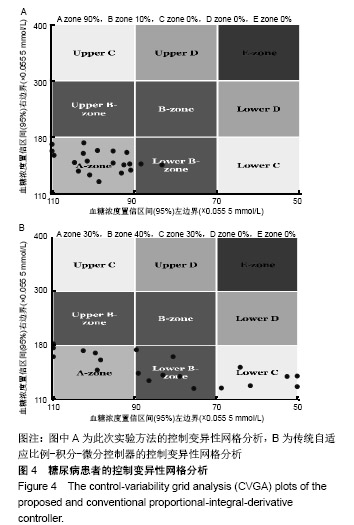
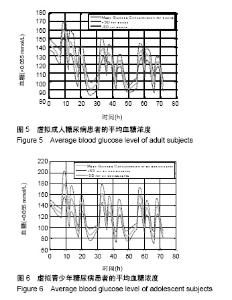
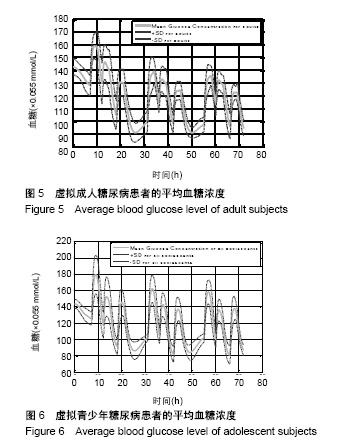
| [1]Liu WP, Zhang GP, Yu LL, et al. Improved GPC Algorithm for Blood Glucose Control of Type 1 Diabetes. Artif Organs.2019;43(4):386-398. [2]Hirsch IB.Clinical review: Realistic expectations and practical use of continuous glucose monitoring for the endocrinologist.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2009;94(7):2232-2238. [3]Cobelli C, Renard E, Kovatchev B. Artificial pancreas: past, present, future. Diabetes. 2011; 60: 2672-2682.[4]Davey RJ, Low C,Jones TW,et al.Contribution of an intrinsic lag of continuous glucose monitoring systems to differences in measured and actual glucose concentrations changing at variable rates in vitro.J Diabetes Sci Technol.2010;4(6):1393-1399.[5]Bagis A,Senberber H.ABC algorithm based PID controller design for higher order oscillatory systems.Elektron Elektrotech.2017;23(6):3-9.[6]Soylu S,Danisman K.In silico testing of optimized Fuzzy P+D controller for artificial pancreas. Biocybern Biomed Eng.2018;38(2):399-408.[7]Gondhalekar R,Dassau E,Doyle FJ 3rd.MPC design for rapid pump-attenuation and expedited hyperglycemia response to treat T1DM with an artificial pancreas.Proc Am Control Conf.2014;2014:4224-4230.[8]Turksoy K,Quinn L,Littlejohn E,et al.Multivariable adaptive identification and control for artificial pancreas systems.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2014;61:883-891.[9]Turksoy K,Cinar A. Adaptive control of artificial pancreas systems-a review. J Healthc Eng. 2014; 5:1-22.[10]Abbes IB,Richard PY,Lefebvre MA,et al.A closed-loop artificial pancreas using a proportional integral derivative with double phase lead controller based on a new nonlinear model of glucose metabolism.J Diabetes Sci Technol.2013;7:699-707.[11]Steil GM,Rebrin K,Janowski R,et al.Modeling beta-cell insulin secretion–implications for closed-loop glucose homeostasis.Diabetes Technol Ther.2003;5(6):953-964.[12]Eren M.Adaptive control strategy for regulation of blood glucose levels in patients with type 1 diabetes.J Proc Control.2009;19:1333-1346.[13]Kovatchev B,Cobelli C,Renard E,et al.Multinational study of subcutaneous model-predictive closed-loop control in type 1 diabetes mellitus: summary of the results.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010;4(6): 1374-1381.[14]Mauseth R,Hirsch IB, Bollyky J,et al.Use of a "fuzzy logic" controller in a closed-loop artificial pancreas.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013;15(8): 628-633.[15]Khooban MH, Abadi DNM, Alfi A, et al.Swarm optimization tuned Mamdani fuzzy controller for diabetes delayed model.Turk J Elec Eng Comp Sci.2013;21:2110-2126.[16]Man CD, Micheletto F, Lv D,et al.The UVA/PADOVA Type 1 Diabetes Simulator: New Features.J Diabetes Sci Technol.2014;8(1):26-34.[17]Visentin R,Man CD,Cobelli C.One-Day Bayesian Cloning of Type 1 Diabetes Subjects: Toward a Single-Day UVA/Padova Type 1 Diabetes Simulator.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2016;63(11):2416-2424. [18]闫朝峰.基于个体化参数的血糖控制策略设计[D].北京:北京化工大学,2014.[19]Turksoy K,Samadi S,Feng J,et al.Meal-Detection in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A New Module for The Multivariable Adaptive Artificial Pancreas Control System.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2016;20(1): 47-54. |