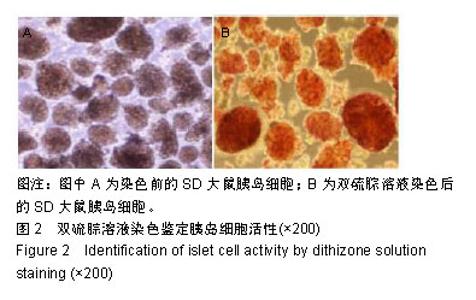
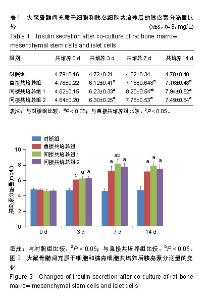
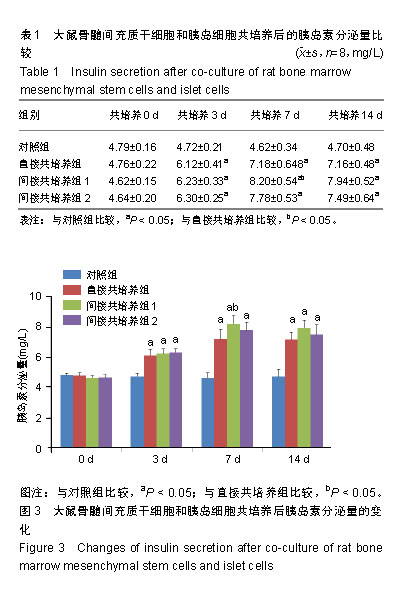
| [1]梁梦璐,胡永华.1型糖尿病病因流行病学研究进展[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2013,17(4):349-353.[2]Kharroubi AT, Darwish HM. Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World J Diabetes. 2015;6(6):850-867.[3]Kim JY, Lee JI, Jeong JH, et al. Functional evaluation of chondrocyte sheeting immunodelusive immunoisolated bioartificial pancreas. Transplant Proc. 2010;42(3):903-906.[4]Jin SM, Kim KW. Is islet transplantation a realistic approach to curing diabetes. Korean J Intern Med. 2017;32(1):62-66.[5]Dunn TB, Wilhelm JJ, Bellin MD, et al. Autologous islet transplantation: challenges and lessons. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2017;22(4):364-371.[6]张德国,谭雪莹,唐楠,等.人脂肪间充质干细胞尾静脉移植治疗大鼠急性肝衰竭[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(9):1416-1421.[7]Rawal S, Williams SJ, Ramachandran K, et al. Integration of mesenchymal stem cells into islet cell spheroids improves long-term viability, but not islet function. Islets. 2017;9(5): 87-98.[8]刘红静,王慧丰,韦雅淑.胰腺组织裂解液诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为胰岛样结构的鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(13): 2088-2093.[9]Gabr MM, Zakaria MM, Refaie AF, et al. Insulin-producing cells from adult human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells control streptozotocin-induced diabetes in nude mice. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(1):133-145.[10]Xie H, Wang Y, Zhang H, et al. Role of injured pancreatic extract promotes bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells efficiently differentiate into insulin-producing cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e76056.[11]Kim JW, Vang S, Luo JZQ, et al. Human Islet Co-Cultured with Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in 3D Scaffolding May Augment Pancreatic Beta Cell Function. Journal of biomaterials and tissue engineering. 2017;7(3):203-209.[12]Unsal IO, Ginis Z, Pinarli FA, et al. Comparison of therapeutic characteristics of islet cell transplantation simultaneous with pancreatic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in rats with Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Stem Cell Rev. 2015;11(3):526-532.[13]Wen D, Peng Y, Liu D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell and derived exosome as small RNA carrier and Immunomodulator to improve islet transplantation. J Control Release. 2016;238: 166-175.[14]Corradi-Perini C, Santos TM, Camara NOS, et al. Co-transplantation of Xenogeneic Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviates Rejection of Pancreatic Islets in Non-obese Diabetic Mice. Transplant Proc. 2017; 49(4):902-905.[15]徐昕博.糖尿病治疗的研究现状及进展[J].养生保健指南,2019 (7):213-214.[16]Moravej H, Salehi A, Shamsedini A, et al. Complementary and Alternative Medicine to Treat Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 in Southern Iran. Iran J Med Sci. 2016;41(1):71-72.[17]Heller T, Kloos C, Lehmann T, et al. Mortality and its Causes in a German Cohort with Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 after 20 Years of Follow-Up: The JEVIN Trial. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2018;126(6):387-393.[18]Kramer G, Kuniss N, Kloos C, et al. Principles and frequency of self-adjustment of insulin dose in people with diabetes mellitus type 1 and correlation with markers of metabolic control. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016;116:299-305.[19]Bro?ová J, ?echurová D, Lacigová S. Metabolic syndrome in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1, prevalence, impact on morbidity and mortality. Vnitr Lek. 2016;62(11 Suppl 4):S8-14.[20]Pathak S, Regmi S, Nguyen TT, et al. Polymeric microsphere-facilitated site-specific delivery of quercetin prevents senescence of pancreatic islets in vivo and improves transplantation outcomes in mouse model of diabetes. Acta Biomater. 2018;75:287-299.[21]Tchokonte-Nana V, Manda JK. Early islets and mesenchyme from an injured adult pancreas improve syngeneic engraftments and islet graft function in diabetic rats. Acta Histochem. 2018;120(4):356-362.[22]He Y, Zhang D, Zeng Y, et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Islet Grafts Against Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis During the Early Stage After Transplantation. Stem Cells. 2018;36(7): 1045-1061.[23]Carlsson PO, Espes D, Sedigh A, et al. Transplantation of macroencapsulated human islets within the bioartificial pancreas βAir to patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Am J Transplant. 2018;18(7):1735-1744.[24]Cao XK, Li R, Sun W, et al. Co-combination of islets with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes angiogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;78:156-164.[25]Wang H, Strange C, Nietert PJ, et al. Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cell and Islet Cotransplantation: Safety and Efficacy. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(1):11-19. [26]He Y, Zhang D, Zeng Y, et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Islet Grafts Against Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis During the Early Stage After Transplantation. Stem Cells. 2018;36(7): 1045-1061.[27]Li HT, Jiang FX, Shi P, et al. In vitro reprogramming of rat bmMSCs into pancreatic endocrine-like cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2017;53(2):157-166.[28]Cantarelli E, Citro A, Pellegrini S, et al. Transplant Site Influences the Immune Response After Islet Transplantation: Bone Marrow Versus Liver. Transplantation. 2017;101(5): 1046-1055.[29]李宏图,林学文,李彩虹,等.负向调节因子重编程诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向胰岛内分泌细胞分化的研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2016,45(1):1-6.[30]Westenfelder C, Gooch A, Hu Z, et al. Durable Control of Autoimmune Diabetes in Mice Achieved by Intraperitoneal Transplantation of "Neo-Islets," Three-Dimensional Aggregates of Allogeneic Islet and "Mesenchymal Stem Cells" Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(7):1631-1643. |