Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (7): 1109-1114.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0572
Previous Articles Next Articles
Risk factors for multi-drug resistant organisms infection after liver transplantation
Liu Mengyuan1, Fang Fang2
- (1School of Nursing, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200080, China; 2Shanghai Central Hospital, Shanghai 200080, China)
-
Received:2018-07-29Online:2019-03-08Published:2019-03-08 -
Contact:Fang Fang, Master, Chief nurse, Shanghai Central Hospital, Shanghai 200080, China -
About author:Liu Mengyuan, Master candidate, School of Nursing, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200080, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Program of Health Bureau of Shanghai, No. 20134135; the Important Weak Discipline Construction Project of Shanghai, No. 2015ZB0304
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Mengyuan1, Fang Fang2. Risk factors for multi-drug resistant organisms infection after liver transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1109-1114.
share this article
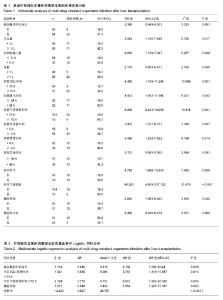
2.1 参与者数量分析 共收集第一人民医院及仁济医院符合纳入标准的肝移植患者128例,排除术后24 h内死亡的患者3例,转院及研究期间失访的患者5例,病历资料不完整的患者6例,得到可供分析的患者共114例(第一人民医院54例,仁济医院60例)。 2.2 两组患者一般资料 共收集第一人民医院及仁济医院符合纳入标准、可供分析的肝移植患者114例,平均年龄(51.88±10.16)岁。多重耐药菌感染组共28例,其中男19例,女9例,原发病为肝细胞癌8例,乙肝肝硬化10例,胆汁性肝硬化2例,酒精性肝硬化2例,其他6例;非多重耐药菌感染组共86例,其中男63例,女23例,原发病为肝细胞癌31例,乙肝肝硬化34例,胆汁性肝硬化6例,酒精性肝硬化4例,其他11例。肝移植术后多重耐药菌感染组的死亡率(5例,17.9%)明显高于非感染组(6例,7.0%)。见表1。 2.3 肝移植后多重耐药菌的感染率及菌株分布情况 根据院内多重耐药菌感染的诊断标准,两肝移植中心共28例患者发生多重耐药菌感染,肝移植后患者多重耐药菌感染率为24.6%。 在两肝移植中心总患者中,多重耐药革兰阴性菌感染20例(71.4%),其中第一人民医院多重耐药革兰阴性菌感染14例(77.8%),仁济医院多重耐药革兰阴性菌感染6例(60.0%),均以多重耐药鲍曼不动杆菌最常见。多重耐药革兰阳性菌感染8例(28.6%)。其中第一人民医院多重耐药革兰阳性菌感染4例(22.2%),在仁济医院10例患者中,多重耐药革兰阳性菌感染4例(40.0%),均以金黄色葡萄球菌最常见。 在两肝移植中心总患者中,肺部感染占57.0%。其次是血流感染占25.0%。其中第一人民医院多重耐药菌感染患者中最常见的感染部位是肺部12例(66.7%),其次是血流感染(11.1%);在仁济医院最常见的血流感染(50.0%),其次是肺部感染(40%)。 2.4 肝移植后多重耐药菌感染危险因素的单因素分析 首先对数据进行正态性检验,结果显示年龄、体质量指数、血清白蛋白水平及手术时间4个变量基本符合正态分布 (P > 0.05)外,其余各变量均不符合正态分布(P < 0.05)。统计分析结果发现12个因素是肝移植术后发生多重耐药菌感染的潜在危险因素,包括失血量≥3 L、红细胞输入量> 8 U、术中尿量≥1 L、留置ICU时间≥10 d、机械通气时间>24 h、留置气管插管时间≥72 h、留置导尿管时间≥ 5 d、留置胃管时间≥4 d、恢复饮食、再次手术、胸腔穿刺和腹腔内出血。而年龄、性别、腹水、上消化道出血、糖尿病、高血压、血清肌酐、血胆红素、胆道并发症及留置深静脉导管时间≥14 d等差异无显著性意义(P > 0.1)。具体见表1。 2.5 肝移植后多重耐药菌感染多元Logistic回归分析 将以上单因素分析中P < 0.1的变量(凝血酶原时间延长、失血量≥3 L、红细胞输入量>8 U、术中尿量≥1 L、留置ICU时间≥10 d、机械通气时间>24 h、留置气管插管时间≥ 72 h、留置导尿管时间≥5 d、留置胃管时间≥4 d、恢复饮食、再次手术、胸腔穿刺和腹腔内出血)纳入非条件Logistic回归中进行分析。结果显示,以下4个因素:凝血酶原时间延长(OR:3.102,95%CI 0.066-9.024,P=0.038)、ICU留置时间≥10 d(OR:3.745,95%CI 1.313-10.687,P=0.014)、气管插管时间≥72 h(OR:8.972,95%CI 1.983-40.582,P=0.004)、胸腔穿刺(OR:3.564,95%CI 1.223-10.387,P=0.020)是影响肝移植后多重耐药菌感染的独立危险因素。具体见表2。"
| [1] 夏穗生.肝移植进展[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2005,12(2):97-99.[2] 黄勋,邓子德,倪语星,等.多重耐药菌医院感染预防与控制中国专家共识[J].中国感染控制杂志,2015,14(1):1-9.[3] 中华人民共和国卫生部.多重耐药菌医院感染预防与控制技术指南(试行)[J].中国危重病急救医学, 2011,23(2):65.[4] Shukla A,Vadeyar H,Rela M,et al. Liver Transplantation: East versus West.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2013,3(3):243-253.[5] Wang FS,Fan JG,Zhang Z,et al.The global burden of liver disease: the major impact of China. Hepatology. 2014;60(6):2099-2108.[6] Li C,Wen TF,Mi K,et al.Analysis of infections in the first 3-month after living donor liver transplantation.World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(16):1975-1980.[7] Linares L,Garcia-Goez JF,Cervera C,et al.Early bacteremia after solid organ transplantation.Transplant Proc.2009;41(6): 2262-2264.[8] Kim SI.Bacterial infection after liver transplantation.World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(20):6211-6220.[9] Santoro-Lopes G,de Gouvea EF.Multidrug-resistant bacterial infections after liver transplantation: an ever-growing challenge.World J Gastroenterol.2014,20(20):6201-6210.[10] 李明霞,彭贵主,王忍,等.肝移植术后感染研究进展[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2015,21(7):494-497.[11] 杨富,陈兰,方芳,等.肝移植术后多重耐药菌感染危险因素的系统评价[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2015,35(7):1015-1022.[12] [Magiorakos AP,Srinivasan A,Carey RB, et al.Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance.Clin Microbiol Infect.2012;18(3):268-281.[13] Shields RK,Clancy CJ,Gillis LM,et al.Epidemiology, clinical characteristics and outcomes of extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections among solid organ transplant recipients.PLoS One.2012;7(12):e52349.[14] 中华人民共和国卫生部. 医院感染诊断标准(试行)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2001,81(5):314-320.[15] 陈佰义,何礼贤,胡必杰,等.中国鲍曼不动杆菌感染诊治与防控专家共识[J].中国医药科学,2012,2(8):3-8.[16] Kim SI,Kim YJ,Jun YH,et al.Epidemiology and risk factors for bacteremia in 144 consecutive living-donor liver transplant recipients.Yonsei Med J.2009;50(1):112-121.[17] Friedrich-Rust M, Wanger B, Heupel F, et al. Influence of antibiotic- regimens on intensive-care unit-mortality and liver-cirrhosis as risk factor.World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(16):4201-4210.[18] 谢秀华,孔心涓,饶伟.肝移植术后感染并发症的研究现状及进展[J].实用器官移植电子杂志, 2017,5(1):61-64.[19] Netsvyetayeva I,Sikora M,Golas M,et al.Acinetobacter baumannii multidrug-resistant strain occurrence in liver recipients with reference to other high-risk groups.Transplant Proc. 2011;43(8): 3116-3120.[20] Hand J,Patel G.Multidrug-resistant organisms in liver transplant: Mitigating risk and managing infections.Liver Transpl.2016;22(8): 1143-1153.[21] Reddy P,Zembower TR,Ison MG,et al.Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections after organ transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis.2010;12(1):87-93.[22] Sun HY, Cacciarelli TV, Singh N. Impact of pretransplant infections on clinical outcomes of liver transplant recipients.Liver Transpl.2010;16(2):222-228.[23] Bellier C,Bert F,Durand F,et al.Risk factors for Enterobacteriaceae bacteremia after liver transplantation.Transpl Int.2008;21(8): 755-763.[24] Siniscalchi A,Aurini L,Benini B,et al.Ventilator associated pneumonia following liver transplantation: Etiology, risk factors and outcome.World J Transplant.2016;6(2):389-395.[25] Lim S, Kim E J, Lee T B, et al. Predictors of postoperative infectious complications in liver transplant recipients: experience of 185 consecutive cases. Korean J Intern Med. 2018 Feb 23. [26] 杨富,方芳,陈兰,等.肝移植术后多重耐药菌感染风险预测评分模型的建立与评价[J].护理研究,2017,31(17):2076-2080.[27] Desai D, Desai N, Nightingale P, et al. Carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is associated with an increased risk of infection after liver transplantation.Liver Transpl. 2003,9(7):754-759.[28] Hashimoto M,Sugawara Y,Tamura S,et al.Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection after living-donor liver transplantation in adults.Transpl Infect Dis.2008;10(2):110-116.[29] Avkan-Oguz V,Ozkardesler S,Unek T,et al.Risk factors for early bacterial infections in liver transplantation.Transplant Proc.2013; 45(3):993-997.[30] 谢秀华,姜英俊,解曼,等.肝移植后早期受者发生感染的危险因素及病原学分析[J].中华器官移植杂志, 2017,38(4):200-205.[31] Shi SH,Kong HS,Jia CK,et al.Risk factors for pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli among liver recipients. Clin Transplant.2010;24(6):758-765.[32] 浦燕萍,顾燕,杨富,等.肝移植患者术后多重耐药鲍曼不动杆菌感染影响因素[J].中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志, 2016,5(3):158-162.[33] Zhong L,Men TY, Li H,et al.Multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections after liver transplantation - spectrum and risk factors.J Infect.2012;64(3):299-310.[34] Alonso JC.Pleural effusion in liver disease.Semin Respir Crit Care Med.2010;31(6):698-705.[35] 聂深钰,时宇,高普均.难治性肝性胸水的治疗[J].中国老年学杂志, 2015,35(11):3171-3173.[36] Machicao VI,Balakrishnan M,Fallon MB.Pulmonary complications in chronic liver disease. Hepatology.2014;59(4):1627-1637.[37] Singh A,Bajwa A,Shujaat A.Evidence-based review of the management of hepatic hydrothorax. Respiration. 2013;86(2): 155-173.[38] 杨富.肝移植术后多重耐药菌感染风险预测模型的构建[D].上海:上海交通大学,2015. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [4] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [5] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [6] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [7] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [8] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [9] | Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Zhao Qiao, Chen Shuo, Bai Yiguang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and properties of copper-loaded antibacterial functional film on titanium surface [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [10] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [11] | Shi Xiaoxiu, Mao Shilong, Liu Yang, Ma Xingshuang, Luo Yanfeng. Comparison of tantalum and titanium (alloy) as orthopedic materials: physical and chemical indexes, antibacterial and osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 593-599. |
| [12] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [13] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [14] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [15] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||