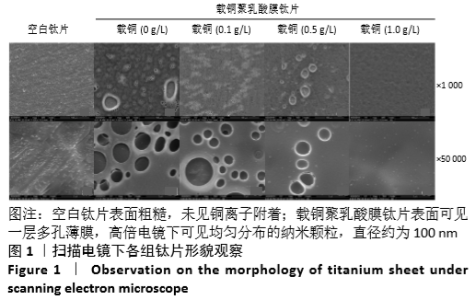
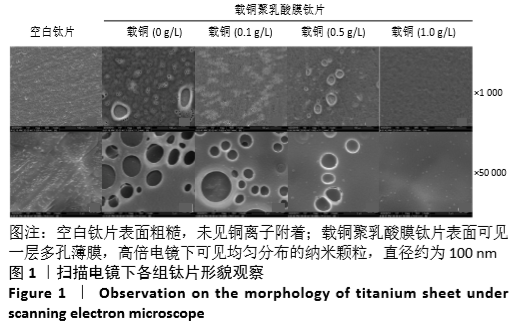
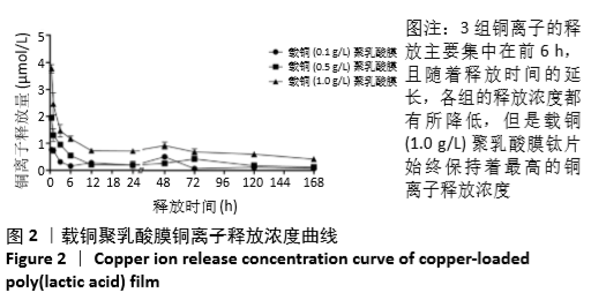
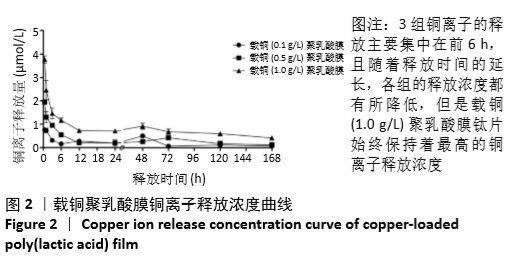
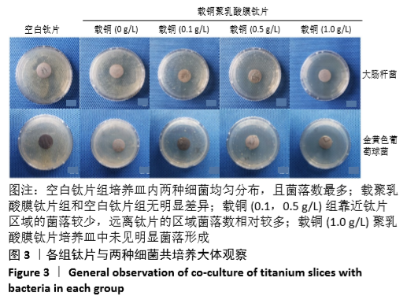
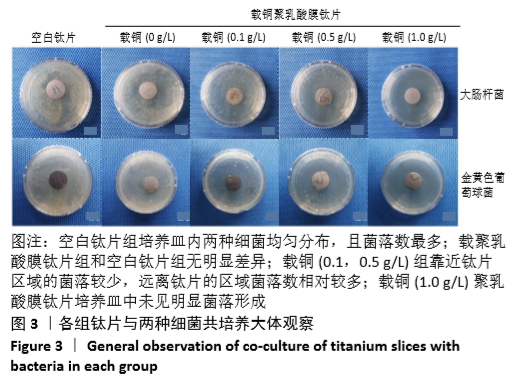
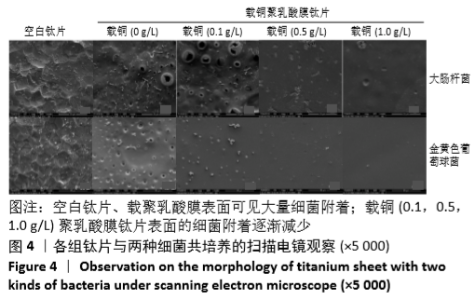
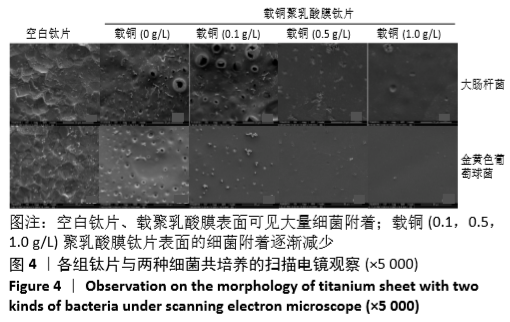
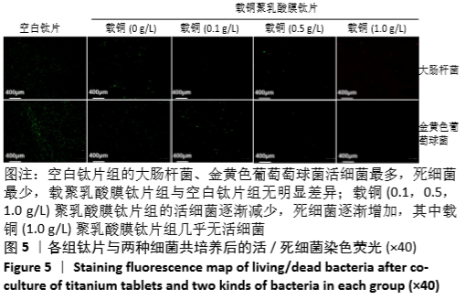
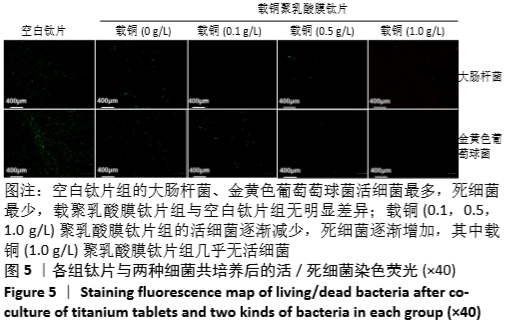
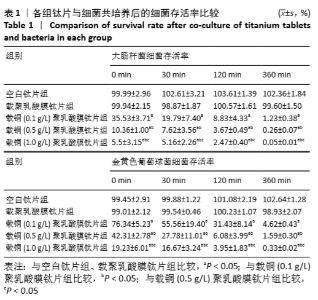
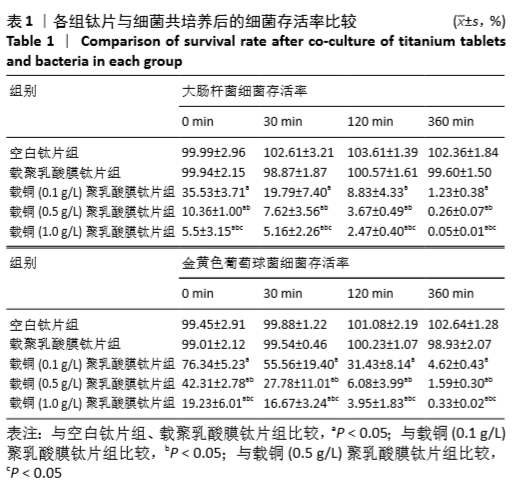
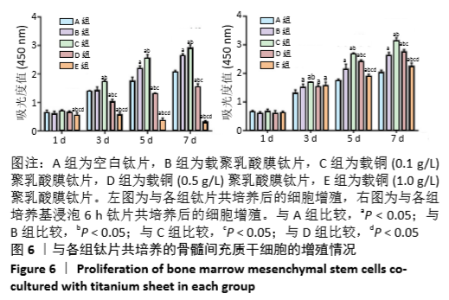
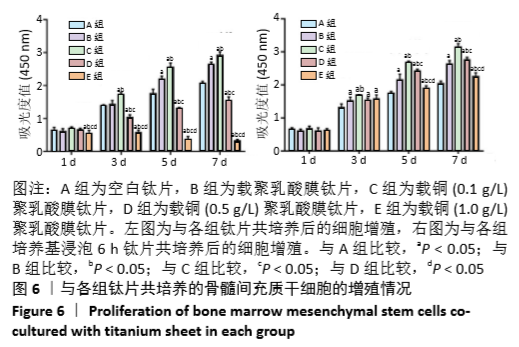
[1] DONATI D, ZOLEZZI C, TOMBA P, et al. Bone grafting: historical and conceptual review, starting with an old manuscript by Vittorio Putti.Acta Orthop.2007;78(1):19-25.
[2] LEŠIĆ A, ZAGORAC S, BUMBAŠIREVIĆ V, et al. The development of internal fixation: Historical overview.Acta Chirurgica Iugoslavica.2012;59(3):9.
[3] WANG J, WU G, LIU X, et al. A decomposable silica-based antibacterial coating for percutaneous titanium implant.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12: 371-379.
[4] RAJ RM, PRIYA P, RAJ V. Gentamicin-Loaded Ceramic-Biopolymer Dual Layer Coatings on the Ti with Improved Bioactive and Corrosion Resistance Properties for Orthopedic Applications.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2018; 82:299-309.
[5] 徐晶,刘蕊,曲冠霖,等.SLM含铜钴基合金的抗菌性能及细胞相容性的初步探索[J].表面技术, 2019,48(7):296-301,315.
[6] 陈阳,王亮亮,张慧明,等.钛阳极氧化载铜层的抗菌及生物相容性研究[J].材料保护, 2018,51(12):55-58,94.
[7] ANDREW NP, BUMGARDNER JD. Biomaterial and antibiotic strategies for peri-implantitis: a review.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2011;26(3):553-560.
[8] WOJCIESZAK D, MAZUR M, KALISZ M, et al. Influence of Cu, Au and Ag on structural and surface properties of bioactive coatings based on titanium.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;71(2):1115-1121.
[9] 李琪,代明江,韦春贝,等.钛合金表面MoS_2-Ti/Cu-Ni-In多层固体润滑膜的制备及其抗微动磨损性能[J].表面技术,2017,46(1):111-117.
[10] HUANG Q, OU Y, TAN Y, et al. Activating macrophages for enhanced osteogenic and bactericidal performance by Cu ion release from micro/nano-topographical coating on a titanium substrate.Acta Biomater.2019; 100:415-426.
[11] KUBIAK A, SIWIŃSKA CK, GOSCIANSKA J, et al. Hydrothermal-assisted synthesis of highly crystalline titania-copper oxide binary systems with enhanced antibacterial properties.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2019;104:109839.
[12] KELLY P, ARNELL R. Magnetron sputtering:a review of recent developments and applications. Vacuum.2000;56(3):159-172.
[13] 凃松,罗欣,刘芳超,等.骨科患者手术部位感染相关因素分析[J].中国社会医学杂志,2019,36(2):203-206.
[14] 宝龙华.骨科手术部位感染分析[J].世界最新医学信息文摘(电子版), 2014(27):127-127.
[15] JOHN-JAIRO AC, DOADRIO AL, ANA C, et al. Antibiotic release from F-doped nanotubular oxide layer on TI6AL4V alloy to decrease bacterial viability.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2018;29(8):118-129.
[16] WARNES SL, KEEVIL CW. Mechanism of copper sur face toxicity invancom ycin—resistant enterococci follow ing w et or dry surface contact.Appl Environ M icrobiol.2011;77(17):6049-6059.
[17] IBRAHIM M, WANG F, LOU M, et al. Copper as an antibacterial agent for human pathogenic multidrug resistant Burkholderia cepacia complex bacteria. J Biosci Bioeng.2011;112(6):570-576.
[18] YUAN X, WANG J, ZHU X, et al. Effect of copper on levels of collagen and alkaline phosphatase activity from chondrocytes in newborn piglets in vitro. Biol Trace Elem Res.2011;144(1-3):597-605.
[19] ŁUCJA R, TIAINEN H, CIBOR U, et al. Ceramic scaffolds enriched with gentamicin loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microparticles for prevention and treatment of bone tissue infections. Mater Sci Eng C.2016;69:856-864. |