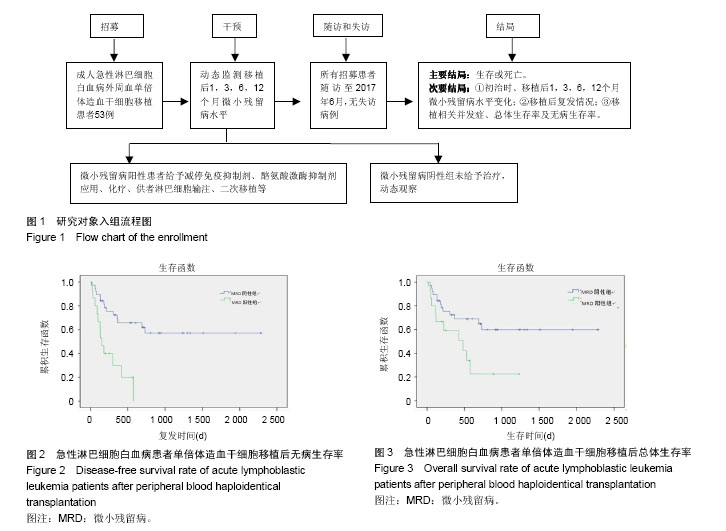
| [1] Hart DP, Peggs KS. Current status of allogeneic stem cell transplantation for treatment of hematologic malignancies. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82(3):325-329.[2] 王健民. 急性白血病异基因造血干细胞移植后复发的机制及防治策略[J]. 中华血液学杂志,2013,34(8):649-650.[3] 吴穗晶,杜欣,翁建宇,等. 异基因造血干细胞移植后复发的临床分析[J]. 实用医学杂志,2011,27(14):2614-2615.[4] 邱阳,刘越坚,郭慧淑,等. 流式细胞术在159例急性白血病免疫分型中的应用[J]. 中国实验诊断学,2009,13(1):103-105.[5] 张之南,沈悌. 血液病诊断及疗效标准[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2007.[6] 中华医学会血液学分会干细胞应用学组. 中国异基因造血干细胞移植治疗血液系统疾病专家共识(Ⅰ)——适应证、预处理方案及供者选择(2014年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志,2014,35(8):775-780.[7] Huang XJ, Liu DH, Liu KY, et al. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T-cell depletion for the treatment of hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006;38(4):291-297.[8] Ji SQ, Chen HR, Wang HX, et al. G-CSF-primed haploidentical marrow transplantation without ex vivo T cell depletion: an excellent alternative for high-risk leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;30(12):861-866.[9] 万鼎铭,康轶青,孙慧,等. 改良BU/CY预处理方案行异基因造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病的临床研究[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2009,29(7):648-649.[10] 施继敏,景晶,罗依,等. 异基因造血干细胞移植后并发出血性膀胱炎的高危因素和防治措施[J]. 中华器官移植杂志,2011, 32(3): 148-151.[11] 万鼎铭,周雪芳,谢新生,等. 异基因造血干细胞移植后肠球菌相关性腹泻的临床分析[J]. 郑州大学学报:医学版,2014,49(2): 284-287.[12] 万鼎铭,张诚,谢新生,等. 单倍体相合造血干细胞移植治疗高危白血病[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(19): 3485-3488.[13] 窦青瑜,许兰平,刘代红,等. 四色流式细胞术检测造血干细胞移植后急性B淋巴细胞白血病相关免疫表型及临床意义分析[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2008,28(9):729-731.[14] Chinese Society Of Hematology Chinese Medical Ass,中华医学会血液学分会干细胞应用学组. 中国异基因造血干细胞移植治疗血液系统疾病专家共识(Ⅱ)——移植后白血病复发(2016年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志,2016,37(10):846-851.[15] Lee S, Kim DW, Cho B, et al. Risk factors for adults with Philadelphia-chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in remission treated with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: the potential of real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. Br J Haematol. 2003;120(1):145-153.[16] 舒晓艳,闫侠芳,董磊,等. 异基因造血干细胞移植后白血病复发的危险因素分析和治疗[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志,2016,24(4): 1137-1142.[17] Yan CH, Xu LP, Wang FR, et al. Causes of mortality after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and the comparison with HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51(3): 391-397.[18] 石连霞. 急性淋巴细胞白血病微小残留病诊断研究进展[J]. 临床检验杂志,2016,34(9):682-685.[19] Terwey TH, Hemmati PG, Nagy M, et al. Comparison of chimerism and minimal residual disease monitoring for relapse prediction after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(10):1522-1529.[20] Bar M, Wood BL, Radich JP, et al. Impact of minimal residual disease, detected by flow cytometry, on outcome of myeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Res Treatment. 2014;2014: 421723.[21] Zhao XS, Liu YR, Zhu HH, et al. Monitoring MRD with flow cytometry: an effective method to predict relapse for ALL patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol. 2012;91(2):183-192.[22] 周立昕,宫蔷,陈洁平. 异基因造血干细胞移植后伊马替尼维持治疗对Ph+ALL疗效的Meta分析[J]. 重庆医学,2014,43(34): 4584-4588.[23] Wassmann B, Pfeifer H, Stadler M, et al. Early molecular response to posttransplantation imatinib determines outcome in MRD+ Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL). Blood. 2005;106(2):458-463.[24] 刘启发,周淑芸. 供者淋巴细胞输注对异基因造血干细胞移植后白血病复发的防治作用[J]. 中华血液学杂志,2002,23(4): 220-222.[25] Yan CH, Liu DH, Liu KY, et al. Risk stratification-directed donor lymphocyte infusion could reduce relapse of standard-risk acute leukemia patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;119(14): 3256-3262.[26] Freytes CO, Lazarus HM. Second hematopoietic SCT for lymphoma patients who relapse after autotransplantation: another autograft or switch to allograft. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009;44(9):559-569.[27] Dhédin N, Huynh A, Maury S, et al. Role of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with Ph-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2015;125(16):2486-2496.[28] Beldjord K, Chevret S, Asnafi V, et al. Oncogenetics and minimal residual disease are independent outcome predictors in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2014;123(24):3739-3749.[29] Kern W, Schoch C, Haferlach T, et al. Monitoring of minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005;56(2):283-309.[30] Craig FE, Foon KA. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping for hematologic neoplasms. Blood. 2008;111(8):3941-3967.[31] 张博,赵晓甦,秦亚溱,等. 急性T淋巴细胞白血病异基因造血干细胞移植后WT1基因表达及其与预后关系[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2015,36(8):642-646.[32] Zhao XS, Yan CH, Liu DH, et al. Combined use of WT1 and flow cytometry monitoring can promote sensitivity of predicting relapse after allogeneic HSCT without affecting specificity. Ann Hematol. 2013;92(8):1111-1119.[33] Nishiwaki S, Miyamura K, Kato C, et al. Impact of post-transplant imatinib administration on Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Anticancer Res. 2010;30(6):2415-2418. |