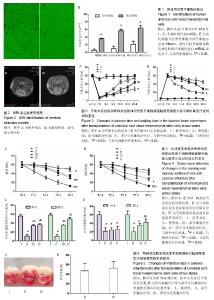
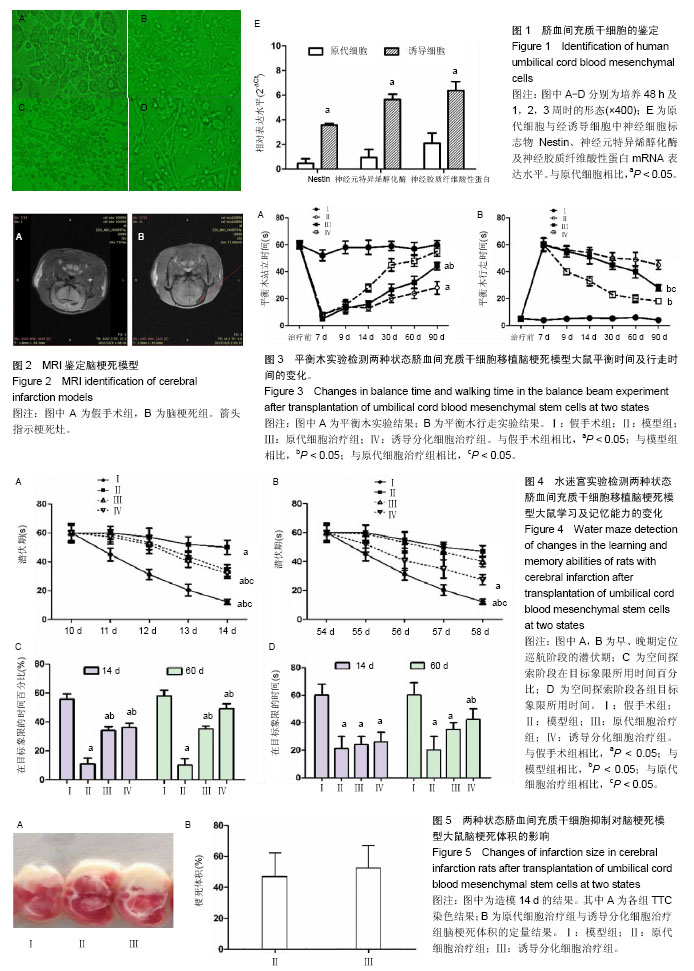
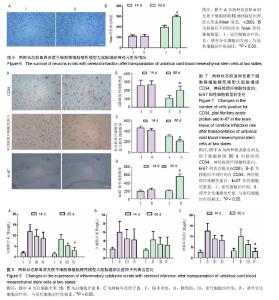
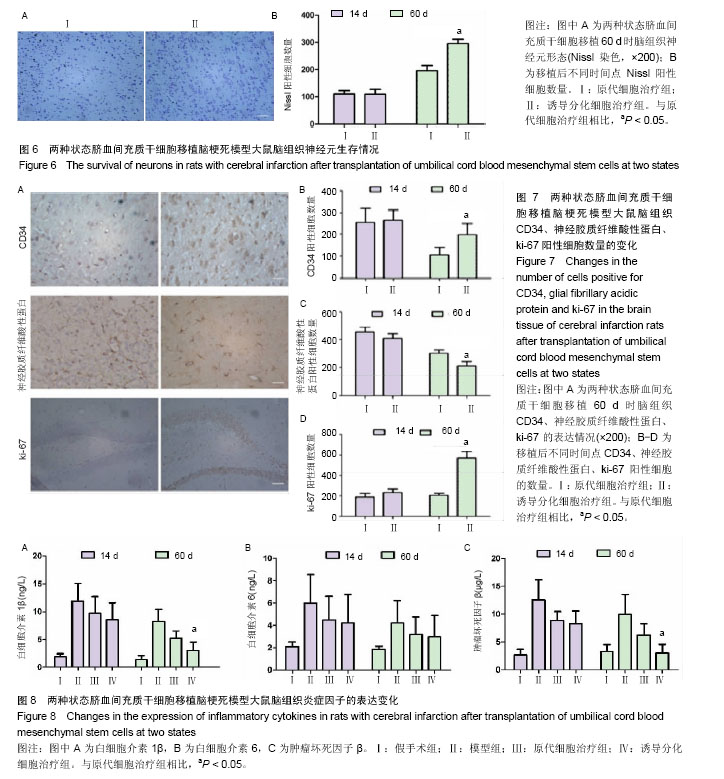
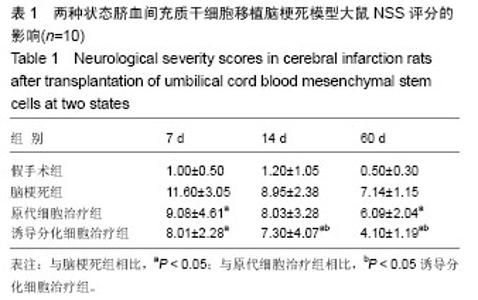
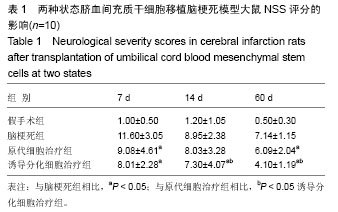
| [1] 王志敏,王雷,徐程华.卒中单元超早期康复治疗对急性脑出血患者的疗效观察及治疗费用评价[J].中华老年医学杂志,2009,28(11):908-911.[2] 吕莹.卒中单元超早期康复治疗对急性脑梗死患者的临床疗效分析[J].黑龙江医学,2017,41(5):397-399.[3] Przybyt E, Harmsen MC. Mesenchymal stem cells: promising for myocardial regeneration? Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;8(4): 270-277.[4] 张丹,秦书俭.脐血间充质干细胞多向分化能力的研究进展[J].河北联合大学学报(医学版),2006,8(4):457-459.[5] Zhang Y, Yu LK, Xia N. Evaluation of serum and pleural levels of endostatin and vascular epithelial growth factor in lung cancer patients with pleural effusion. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012;5(3): 239-242. [6] 陈津,郭子宽,王立生,等.大规模间充质干细胞培养技术评估报告[J].中国医药生物技术,2013,8(4):274-284.[7] 何津,张毅,江小霞,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞对脐血T淋巴细胞转化的影响[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2003,11(1):11-14.[8] 鞠秀丽,黄志伟,时庆,等.体外扩增脐血间充质干细胞的生物学特性和诱导分化能力的研究[J].中华儿科杂志,2005,43(7):499-502.[9] 赵林娜,李建斌,单泓,等.四联袋分离脐血干细胞效果的初步研究[J].中国现代医生,2008,46(17):70-71. [10] 薛静,高培毅,孙崇然,等,用于神经干细胞移植的大鼠脑梗死模型的建立[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2006,3(1):34-37.[11] 金成日,姜奥,张小卿.电针对脑缺血再灌注大鼠行为学影响实验研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2017,(8):108-110.[12] Hara H, Friedlander RM, Gagliardini V, et al. Inhibition of interleukin 1beta converting enzyme family proteases reduces ischemic and excitotoxic neuronal damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(5): 2007-2012.[13] 向军,王西樵,刘英开,等.烧伤后瘢痕组织中成纤维细胞ET-1表达及血管新生和胶原分布研究[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2010,30(7): 839-842.[14] 贾明,胡波飞,魏素菊.细胞增殖标志物Ki-67与乳腺癌[J].国际肿瘤学杂志,2011,38(5):364-366.[15] 刘军朋,姜文学.骨髓间充质干细胞旁分泌促血管生成的研究进展[J].天津医科大学学报,2011,17(1):130-133,139.[16] Welzel M, Appari M, Bramswig N, et al. Transcriptional response of peripheral blood mononuclear cells to recombinant human growth hormone in a routine four-days IGF-I generation test. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2011;21(6):336-342. [17] Haiyan W, Qi Z, Huo F. General anesthesia-associated DNA damage in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of surgical patients. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2011;4(9):686-688. [18] Shin SW, Oh TJ, Park SM, et al. Asthma-predictive genetic markers in gene expression profiling of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011;3(4):265-272. [19] [Costa-Rodrigues J, Fernandes A, Fernandes MH. Spontaneous and induced osteoclastogenic behaviour of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and their CD14(+) and CD14(-) cell fractions. Cell Prolif. 2011;44(5):410-419. [20] 支中文,杨龙,杜波,等.Necrostatin-1对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后小胶质细胞和炎症因子的影响[J].中华神经医学杂志,2015,14(8):757-763. [21] França CM, Barros FM, Lotufo MA, et al. Response of peripheral blood mononuclear cells to conditioned medium from cultured oral squamous cell carcinomas. Braz Oral Res. 2011;25(5):414-420.[22] Ji J, Kinders RJ, Zhang Y, et al. Modeling pharmacodynamic response to the poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase inhibitor ABT-888 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(10): e26152. [23] Parekh VS, Joglekar MV, Hardikar AA. Differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mononuclear cells to endocrine pancreatic lineage. Differentiation. 2009;78(4):232-240.[24] Yan X, Yang Y, Liu W, et al. Differentiation of neuron-like cells from mouse parthenogenetic embryonic stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(4):293-300. [25] [Gnecchi M, Danieli P, Cervio E. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for heart disease. Vascul Pharmacol. 2012;57(1):48-55. [26] Chen BY, Wang X, Wang ZY, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells, possibly by triggering the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Neurosci Res. 2013;91(1):30-41.[27] 曹勇,杨波,宋来君,等.脐血间质干细胞移植对肌萎缩侧索硬化患者血浆和脑脊液中谷氨酸浓度的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2006,41(2): 236-238. [28] 刘玉府,王利红,尚闯,等.人脐带血衍生间质干细胞改善大鼠急性期缺血性脑卒中模型神经功能[J].中华实验外科杂志,2015,32(3):534-537.[29] Alaimo G, Cozzoli E, Marfe G, et al. Blood-derived stem cells (BDSCs) plasticity: in vitro hepatic differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(6):1249-1254. |