Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (13): 2002-2008.doi: 10.12307/2024.169
Previous Articles Next Articles
Radioprotective effect of 1,2-propanediol combined with hepatocyte growth factor-modified dental pulp stem cell exosomes on human skin cells
Liu Yun1, 2, Jin Jiayan3, Liu Yubin2, Li Qiang2, Ren Boyuan2, Liu He3, Wu Zuze2, Zhou Gangqiao2, Jin Jide2
- 1School of Medicine, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China; 2Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine, Beijing 100850, China; 3School of Basic Medical Science, Air Force Medical University, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-04-22Accepted:2023-06-06Online:2024-05-08Published:2023-08-28 -
Contact:Zhou Gangqiao, PhD, Doctoral supervisor, Researcher, Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine, Beijing 100850, China Jin Jide, PhD, Master’s supervisor, Associate researcher, Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine, Beijing 100850, China -
About author:Liu Yun, Master candidate, School of Medicine, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China; Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine, Beijing 100850, China -
Supported by:Scientific Research Project of Military Logistics, No. AWS21J003 (to JJD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Yun, Jin Jiayan, Liu Yubin, Li Qiang, Ren Boyuan, Liu He, Wu Zuze, Zhou Gangqiao, Jin Jide. Radioprotective effect of 1,2-propanediol combined with hepatocyte growth factor-modified dental pulp stem cell exosomes on human skin cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2002-2008.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
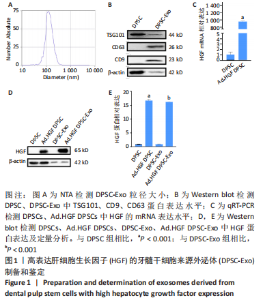
2.1 Ad.HGF修饰提高DPSC-Exo中HGF表达 提取的DPSC-Exo粒径均一,集中在30-150 nm之间,符合外泌体大小特征,见图1A。CD9、CD63和TSG101产生于细胞中,定位于膜结构附近,参与外泌体囊泡的形成和分泌过程[17],是外泌体表面特异性标记蛋白。Western blot结果显示,DPSC-Exo 中CD9、CD63、TSG101表达均呈阳性,见图1B。DPSCs用携带人HGF的重组腺病毒(Ad.HGF)进行感染,感染后48 h用qRT-PCR检测细胞中HGF的mRNA表达水平,结果显示,与未感染的DPSCs相比,感染后的DPSCs中HGF mRNA表达水平显著上调(P < 0.001),见图1C。Western blot检测结果显示,未感染的DPSCs及其外泌体中HGF基本没有表达,而Ad.HGF DPSCs以及Ad.HGF DPSC-Exo中HGF表达水平显著上调,见图1D,E。"
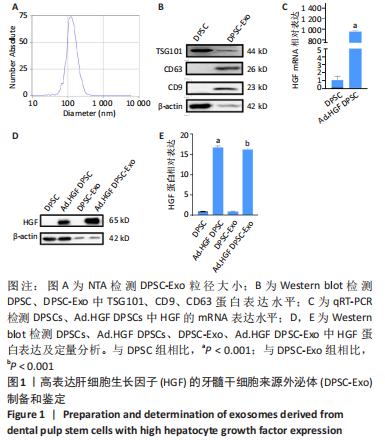
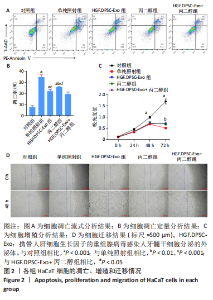
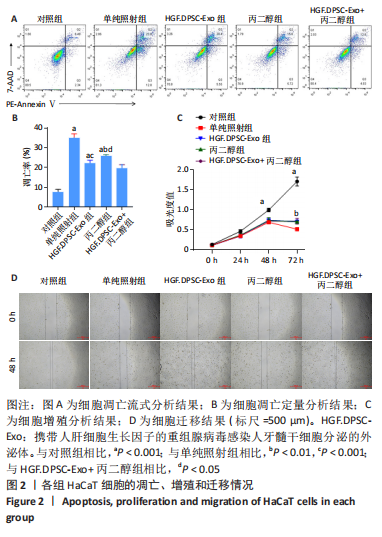
2.2 HGF修饰的DPSC-Exo联合丙二醇减轻放射诱导的HaCaT细胞增殖抑制和凋亡,促进细胞迁移 通过流式细胞术检测各组HaCaT细胞凋亡情况,见图2A,B,在暴露于10 Gy的X射线下,HGF. DPSC-Exo组、丙二醇组、HGF.DPSC-Exo+丙二醇组细胞凋亡率均显著降低,而HGF.DPSC-Exo+丙二醇组降低最为明显,细胞凋亡减少了19%。细胞增殖结果显示,HGF. DPSC-Exo组、丙二醇组、HGF.DPSC-Exo+丙二醇组对于HaCaT细胞的增殖有显著保护作用(P < 0.01)。但是3个处理组之间没有显著性差异,见图2C。迁移实验结果显示,照射后HaCaT细胞迁移能力明显受到抑制,而HGF. DPSC-Exo组、丙二醇组、HGF.DPSC-Exo+丙二醇组HaCaT细胞的迁移能力显著改善,其中HGF.DPSC-Exo+丙二醇组最为显著,恢复到接近未受照水平,见图2D。"
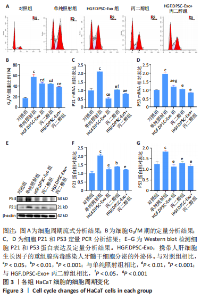
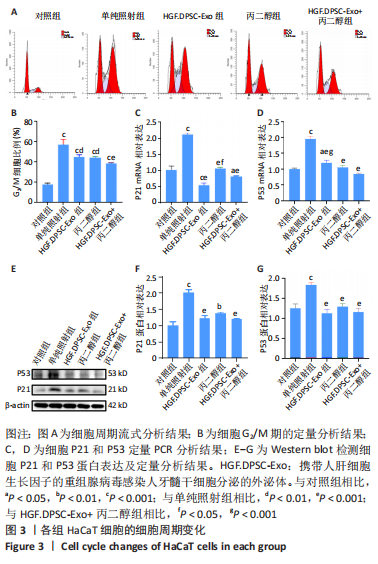
2.3 HGF修饰的DPSC-Exo联合丙二醇减轻HaCaT细胞的G2/M阻滞,降低细胞周期基因表达 研究表明,受到电离辐射的细胞会通过启动G2/M期阻滞信号通路等途径来修复辐射对细胞造成的损伤。细胞周期分析结果见图3A,B,照射后48 h,单纯照射组G2/M期细胞比例显著升高(P < 0.001),丙二醇组、HGF.DPSC-Exo组以及HGF.DPSC-Exo+丙二醇组的G2/M期细胞比例显著低于单纯照射组(P < 0.01),表明放射能够诱导HaCaT发生细胞周期的G2/M期阻滞,而HGF.DPSC-Exo、丙二醇以及二者联合处理都能减轻放射诱导的细胞G2/M期阻滞,其中联合处理作用效果最为显著。 研究表明,上调P21和P53基因表达会导致细胞周期阻滞,从而影响细胞增殖等过程。PCR和Western blot结果显示,照射后48 h,HaCaT细胞中P21、P53基因表达均明显上调(P < 0.001),而丙二醇组、HGF.DPSC-Exo组以及HGF.DPSC-Exo+丙二醇组的P21、P53基因表达显著低于单纯照射组(P < 0.01),表明放射能诱导HaCaT细胞P21、P53的表达上调,从而阻滞细胞于G2/M期,以进行DNA的损伤修复,而HGF.DPSC-Exo、丙二醇以及二者联合处理细胞P21、P53基因表达均处于正常水平,说明处理后细胞的DNA等大分子没有受到严重损伤,不需要启动P53和P21的上调表达,以阻止细胞分裂,进行修复,见图3C-G。"
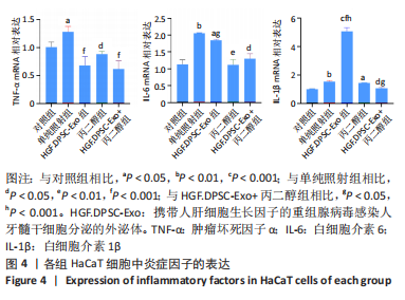
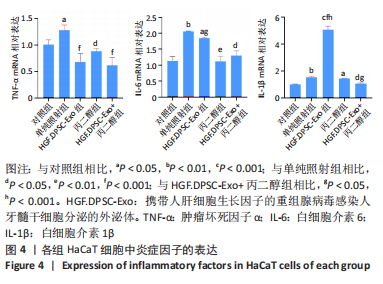
2.4 HGF修饰的DPSC-Exo与丙二醇联合处理降低HaCaT细胞炎性因子的表达 在照射后48 h,用qRT-PCR检测HaCaT细胞炎症因子表达水平,结果显示,与对照组相比,照射后HaCaT细胞中促炎因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α表达均显著上调。3个不同处理组肿瘤坏死因子α表达均恢复到正常水平,丙二醇组和HGF.DPSC-Exo+丙二醇组的白细胞介素6也恢复到正常水平。但白细胞介素1β在HGF.DPSC-Exo组中表达水平显著增加,高于其他组(P < 0.001),而HGF.DPSC-Exo+丙二醇组明显降低,并恢复到正常水平。实验结果表明,丙二醇与HGF.DPSC-Exo联合作用抑制炎症的效果优于二者单独应用,见图4。"
| [1] ROSENTHAL A, ISRAILEVICH R, MOY R. Management of acute radiation dermatitis: A review of the literature and proposal for treatment algorithm. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81(2):558-567. [2] BRAND RM, EPPERLY MW, STOTTLEMYER JM, et al. A Topical Mitochondria-Targeted Redox-Cycling Nitroxide Mitigates Oxidative Stress-Induced Skin Damage. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137(3):576-586. [3] NYSTEDT KE, HILL JE, MITCHELL AM, et al. The standardization of radiation skin care in British Columbia: a collaborative approach. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2005;32(6):1199-1205. [4] HYMES SR, STROM EA, FIFE C. Radiation dermatitis: clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and treatment 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54(1):28-46. [5] ZASADZIŃSKI K, SPAŁEK MJ, RUTKOWSKI P. Modern Dressings in Prevention and Therapy of Acute and Chronic Radiation Dermatitis-A Literature Review. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(6):1204. [6] YAO C, ZHOU Y, WANG H, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells alleviate radiation-induced dermatitis by suppressing apoptosis and downregulating cathepsin F expression. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):447. [7] YI L, TIAN M, PIAO C, et al. The protective effects of 1,2-propanediol against radiation-induced hematopoietic injury in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;114: 108806. [8] CRENSHAW MD, TEFFT ME, BUEHLER SS, et al. Determination of nicotine, glycerol, propylene glycol and water in electronic cigarette fluids using quantitative 1 H NMR. Magn Reson Chem. 2016;54(11):901-904. [9] CARRER V, ALONSO C, PONT M, et al. Effect of propylene glycol on the skin penetration of drugs. Arch Dermatol Res. 2020;312(5):337-352. [10] WANG PW, CHENG YC, HUNG YC, et al. Red Raspberry Extract Protects the Skin against UVB-Induced Damage with Antioxidative and Anti-inflammatory Properties. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:9529676. [11] WU P, ZHANG B, SHI H, et al. MSC-exosome: A novel cell-free therapy for cutaneous regeneration. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(3):291-301. [12] RAJENDRAN P, RENGARAJAN T, THANGAVEL J, et al. The vascular endothelium and human diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9(10):1057-1069. [13] SANADA F, TANIYAMA Y, AZUMA J, et al. Therapeutic Angiogenesis by Gene Therapy for Critical Limb Ischemia: Choice of Biological Agent. Immunol Endocr Metab Agents Med Chem. 2014;14(1):32-39. [14] MOON SH, LEE CM, PARK SH, et al. Effects of hepatocyte growth factor gene-transfected mesenchymal stem cells on dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Growth Factors. 2019;37(3-4):105-119. [15] PARK BW, JUNG SH, DAS S, et al. In vivo priming of human mesenchymal stem cells with hepatocyte growth factor-engineered mesenchymal stem cells promotes therapeutic potential for cardiac repair. Sci Adv. 2020;6(13):eaay6994. [16] WEN Q, ZHANG S, DU X, et al. The Multiplicity of Infection-Dependent Effects of Recombinant Adenovirus Carrying HGF Gene on the Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(3):734. [17] CHEN J, CHOPP M. Exosome Therapy for Stroke. Stroke. 2018;49(5):1083-1090. [18] YANG X, REN H, GUO X, et al. Radiation-induced skin injury: pathogenesis, treatment, and management. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(22):23379-23393. [19] NONAKA D, FUJIWARA R, HIRATA Y, et al. Metabolic engineering of 1,2-propanediol production from cellobiose using beta-glucosidase-expressing E. coli. Bioresour Technol. 2021;329:124858. [20] MASSARSKY A, ABDEL A, GLAZER L, et al. Neurobehavioral effects of 1,2-propanediol in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurotoxicology. 2018;65:111-124. [21] ZENG Z, LI S, BOEREN S, et al. Anaerobic Growth of Listeria monocytogenes on Rhamnose Is Stimulated by Vitamin B12 and Bacterial Microcompartment-Dependent 1,2-Propanediol Utilization. mSphere. 2021;6(4):e0043421. [22] 中国人民解放军军事科学院军事医学研究院.丙二醇在制备用于预防肠型放射病及放射性肠炎的药物中的应用:CN201910230933.2[P]. 2019-05-28. [23] SHAEFFER J, SCHELLENBERG KA. Polyethylene glycol as a protector against head and neck irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984;10(12):2329-2333. [24] MACHTAY M, SCHERPEREEL A, SANTIAGO J, et al. Systemic polyethylene glycol-modified (PEGylated) superoxide dismutase and catalase mixture attenuates radiation pulmonary fibrosis in the C57/bl6 mouse. Radiother Oncol. 2006;81(2): 196-205. [25] LIU D, KONG F, YUAN Y, et al. Decorin-Modified Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Attenuate Radiation-Induced Lung Injuries via Regulating Inflammation, Fibrotic Factors, and Immune Responses. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;101(4):945-956. [26] SUN J, ZHANG Y, SONG X, et al. The Healing Effects of Conditioned Medium Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Radiation-Induced Skin Wounds in Rats. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(1):105-115. [27] WEN S, DOONER M, CHENG Y, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles rescue radiation damage to murine marrow hematopoietic cells. Leukemia. 2016;30(11):2221-2231. [28] PIRYANI SO, JIAO Y, KAM AYF, et al. Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Mitigate Radiation-Induced Hematopoietic Injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;104(2):291-301. [29] LIN Z, WU Y, XU Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in cancer therapy resistance: recent advances and therapeutic potential. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):179. [30] ZHAO H, LI Z, WANG Y, et al. Bioengineered MSC-derived exosomes in skin wound repair and regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1029671. [31] HU P, YANG Q, WANG Q, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells-exosomes: a promising cell-free therapeutic tool for wound healing and cutaneous regeneration. Burns Trauma. 2019;7:38. [32] LU K, LI HY, YANG K, et al. Exosomes as potential alternatives to stem cell therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration: in-vitro study on exosomes in interaction of nucleus pulposus cells and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):108. [33] LEI X, HE N, ZHU L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Radiation-Induced Lung Injury via miRNA-214-3p. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021;35(11):849-862. [34] CZYZ M. HGF/c-MET Signaling in Melanocytes and Melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(12):3844. [35] ZHAO Y, YE W, WANG YD, et al. HGF/c-Met: A Key Promoter in Liver Regeneration. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:808855. [36] NAKAMURA T, MIZUNO S. The discovery of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its significance for cell biology, life sciences and clinical medicine. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2010;86(6):588-610. [37] CHEN W, WANG S, XIANG H, et al. Microvesicles derived from human Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate acute lung injury partly mediated by hepatocyte growth factor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;112:114-122. [38] YARNOLD J, BROTONS MC. Pathogenetic mechanisms in radiation fibrosis. Radiother Oncol. 2010;97(1):149-161. [39] DONG X, KONG F, LIU C, et al. Pulp stem cells with hepatocyte growth factor overexpression exhibit dual effects in rheumatoid arthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):229. [40] MENG HF, JIN J, WANG H, et al. Recent advances in the therapeutic efficacy of hepatocyte growth factor gene-modified mesenchymal stem cells in multiple disease settings. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(18):4745-4755. [41] WANG H, SUN RT, LI Y, et al. HGF Gene Modification in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduces Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury by Modulating Immunity. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0124420. [42] GENG P, ZHANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. HGF-Modified Dental Pulp Stem Cells Mitigate the Inflammatory and Fibrotic Responses in Paraquat-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:6662831. [43] USUNIER B, BROSSARD C, L’HOMME B, et al. HGF and TSG-6 Released by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Colon Radiation-Induced Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1790. [44] CUI HS, JOO SY, CHO YS, et al. Effect of Combining Low Temperature Plasma, Negative Pressure Wound Therapy, and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells on an Acute Skin Wound Healing Mouse Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3675. [45] JIAO Y, CAO F, LIU H. Radiation-induced Cell Death and Its Mechanisms. Health Phys. 2022;123(5):376-386. [46] PISTRITTO G, TRISCIUOGLIO D, CECI C, et al. Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies. Aging (Albany NY). 2016;8(4):603-619. [47] LUO J, ZHANG M, HUANG H, et al. Matrilin-2 regulates proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle during radiation-induced injury in HPAEpiC cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;485(3):577-583. [48] SU X, UPADHYAY A, TRAN SD, et al. Cell-Free Therapies: The Use of Cell Extracts to Mitigate Irradiation-Injured Salivary Glands. Biology (Basel). 2023;12(2):305. [49] CHEN H, CUI Z, LU W, et al. Association between serum manganese levels and diabetes in Chinese adults with hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2022; 24(7):918-927. [50] ZHANG Y, DENG H, YANG Z, et al. Treatment of Radiation Bone Injury with Transplanted hUCB-MSCs via Wnt/β-Catenin. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:5660927. |
| [1] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [2] | Bai Chen, Yang Wenqian, Meng Zhichao, Wang Yuze. Strategies for repairing injured anterior cruciate ligament and promoting graft healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1457-1463. |
| [3] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [4] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [5] | Qiu Xiaoyan, Li Bixin, Li Jingdi, Fan Chuiqin, Ma Lian, Wang Hongwu. Differentiation of insulin-producing cells from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells infected by MAFA-PDX1 overexpressed lentivirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1000-1006. |
| [6] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [7] | Wang Shanshan, Shu Qing, Tian Jun. Physical factors promote osteogenic differentiation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [8] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [9] | Xu Canli, He Wenxing, Wang Lei, Wu Fangting, Wang Jiahui, Duan Xuelin, Zhao Tiejian, Zhao Bin, Zheng Yang. Bibliometric analysis of researches on liver organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1099-1104. |
| [10] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| [11] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [12] | Sun Yukang, Song Lijuan, Wen Chunli, Ding Zhibin, Tian Hao, Ma Dong, Ma Cungen, Zhai Xiaoyan. Visualization analysis of stem cell therapy for myocardial infarction based on Web of Science in recent ten years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1143-1148. |
| [13] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [14] | Shen Ziqing, Xia Tian, Shan Yibo, Zhu Ruijun, Wan Haoxin, Ding Hao, Pan Shu, Zhao Jun. Vascularized tracheal substitutes constructed by exosome-load hydrogel-modified 3D printed scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 697-705. |
| [15] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||