Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (32): 5232-5237.doi: 10.12307/2023.842
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of hypoxia environment on microvessels and bone metabolism and bone repair in chronic periodontitis
Shan Chao1, 2, Wu Zeyu1, 2, Zhao jin1, 2
- 1Department of Dentistry and Pulp, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2School of Stomatology, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-11-23Accepted:2022-12-14Online:2023-11-18Published:2023-03-23 -
Contact:Zhao Jin, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Dentistry and Pulp, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; School of Stomatology, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Shan Chao, Master, Department of Dentistry and Pulp, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; School of Stomatology, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Regional Collaborative Innovation Special Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Science and Technology Aid Program), No. 2021E01069 (to ZJ)
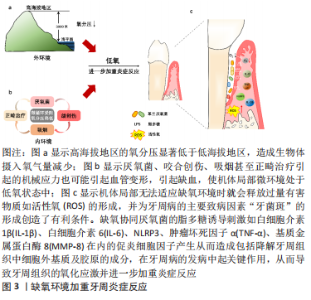
2.1 缺氧环境可加重炎症反应 2.1.1 体外氧分压与牙周炎的相关性 缺氧和炎症通常在许多疾病中同时发生,包括缺血性疾病、慢性炎症性疾病和肿瘤。而无论是机体所处的大环境还是组织细胞所生存的微环境中,缺氧所造成的影响往往是一致的。高海拔水平氧分压较低,流行病学研究报告指出牙周病的发病率往往与大气氧水平呈负相关,当移居至高海拔地区时,如移居8个月至4年时发病率为23.5%,随着移居时间延长发病率也明显上升,移居4-10年时发病率上升为77.1%[8]。佘建祯等[9]对1 800余名官兵进行口腔疾病检查时也发现地处高海拔地区的官兵更易患有牙周疾病。因此有理由推测低氧大环境是导致牙周炎的危险因素之一。 2.1.2 低氧微环境加重炎症反应 除了外部因素所造成的缺氧环境外,厌氧菌、咬合创伤、吸烟甚至咀嚼、研磨或正畸治疗引起的机械应力也可能引起血管变形,引起缺血和低氧状态。当机体局部无法适应缺氧环境时就会释放过量有害物质如活性氧的形成,从而导致牙周组织发生氧化应激[10]。加上龈下微生物的大量增殖,缺氧同时也创造了有利于牙周厌氧致病菌定植与生存的微环境,并为牙周病的主要致病因素“牙菌斑”的形成创造了有利条件[11-12]。因此,氧浓度对维持牙周组织的稳态与平衡至关重要。 已知缺氧和促炎细胞因子如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α均能引起转录因子缺氧诱导因子1 (hypoxia inducible factor 1,HIF-1)的积累和激活。HIF-1是一种异二聚体转录因子,由2个亚基组成HIF-1α和HIF-1β。HIF-1α位于胞质溶中,主要受细胞氧张力调节。在常氧条件下脯氨酰羟化酶(proline hydroxylase,PHDs)或天冬酰胺羟化酶FIH羟化HIF-1α在特定脯氨酸和天冬酰胺上的残基从而启动蛋白的降解。相比之下,HIF-1β是组成性表达的,位于细胞核中起到稳定HIF-1α的作用[13]。缺氧又反过来刺激如白细胞介素1β和基质金属蛋白酶8在内的促炎细胞因子产生从而造成包括降解牙周组织中细胞外基质及胶原的成分,在牙周病的发病中起关键作用[14]。AGIS等[15]在缺氧条件下培养人牙周膜细胞的研究中发现血管内皮生长因子和白细胞介素6的浓度增加。JIAN等[16]发现缺氧协同P.g脂多糖可诱导牙周膜细胞中的肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6表达,表明缺氧至少部分通过增强脂多糖诱导的促炎细胞因子的表达而加剧了牙周炎症;与单独使用脂多糖组相比,缺氧联用脂多糖可使核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)表达增加,但骨保护素(osteoprotegerin,OPG)表达没有显著变化;这些结果表明,缺氧可能至少部分调节RANKL/OPG系统,从而加剧脂多糖引起的牙周炎与骨吸收。ZHU等[10]通过用缺氧模拟剂氯化钴处理人牙周膜细胞(HPDLCs)建立了细胞缺氧模型,发现缺氧可诱导人牙周膜细胞中活性氧的过量产生和积累,并诱导硫氧还蛋白相互作用蛋白(thioredoxin- interacting protein,TXNIP)、NLRP3炎症小体相关因子和白细胞介素1β 的异常表达,说明缺氧诱导的活性氧可激活TXNIP/NLRP3炎症小体信号通路,从而导致人牙周膜细胞中炎症因子的表达增加。因此缺氧可导致牙周组织的氧化应激和凋亡。 2.1.3 低氧与牙周炎症的体内实验 低氧影响牙周炎的体内研究也发现缺氧会加重实验性牙周炎大鼠的牙槽骨丢失以及牙周炎发病过程中一些重要的炎症递质的水平,如NO和肿瘤坏死因子α[16-17]。武曦等[18]在低氧环境下研究兔牙周炎模型时,发现抗氧化应激标志物之一的超氧化物岐化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)活性降低,进而使活性氧在牙周组织中蓄积,并加重牙周炎症水平。TERRIZZI等[19-20]发现两种类型的缺氧(持续性与间歇性)都会在大鼠的下颌骨皮质骨的舌侧引起牙槽骨丢失;当存在牙周炎时,低氧应激会导致矿物质特性降低,并加剧牙周损伤大鼠的皮质骨吸收。以上研究结果提示,无论是低氧大环境还是局部的低氧微环境都是牙周炎症的危险因素,与此同时缺氧也可加重原有的牙周炎症的发生和发展,见图3。"


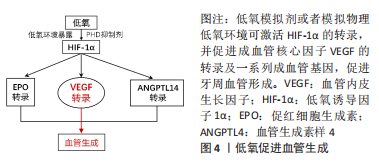
2.2 低氧:促进牙周微环境血管生成 由创伤、炎症或缺血性疾病引起的牙周组织损伤,进一步导致微环境的局部缺氧以及缺乏血管现象,特别是在愈合的早期阶段,在组织损伤和建立血运时牙槽骨血管的侵入生长是牙周组织骨代谢过程中的关键因素,骨血管不仅为骨组织提供营养物质,同时也提供骨细胞活动所必需的氧气。当各种因素造成骨血管的营养及氧气灌注不足时,骨组织形成的低氧微环境就会诱导维持细胞内稳态的核心转录因子HIF-1α的表达。骨血管的生长与骨代谢平衡是相互偶联的过程,骨血管运输促进骨形成必需的营养物质并及时转运出代谢废物,而骨细胞在成骨过程中也能分泌促血管生成细胞因子以调控血管增殖并促进血管化[12]。 2.2.1 低氧促进核心成血管因子的转录 目前血管生成与低氧的联系已经建立,低氧被认为可以有效刺激血管生成。血管内皮生长因子和HIF-1通路是成血管过程的核心调控因子,其中血管内皮生长因子作为血管生成的主要标志,也是HIF-1α主要的下游靶基因。低氧状态下HIF-1α积累后作为转录因子与血管内皮生长因子的启动子区域结合,启动血管内皮生长因子及促红细胞生成素(erythropoietin,EPO)、血管生成素样4 (angiopoietin-like 4,ANGPTL4) 等下游成血管基因的转录[21],从而促进血管增殖并加强营养与氧气向缺氧骨组织内的输送[22]。而牙槽骨的再生必将伴随血管的侵入,为成骨提供必要的营养与微环境。与健康的牙周组织相比,炎症及缺氧状态下牙周组织中血管内皮生长因子和HIF-1α出现明显增加[23],进一步说明缺氧在牙周炎组织血管再生中起关键作用。OISHI等[24]通过对SD大鼠暴露于间歇性低氧(IH)下3周,评估下颌第一磨牙远端根部的牙槽骨固有结构并测量牙周组织中HIF-1α和血管内皮生长因子的表达,通过测量碱性磷酸酶(ALP)和骨形态发生蛋白2 (BMP-2) 的mRNA水平来评估成骨作用,发现间歇性低氧暴露后所有这些标记物的表达增加,表明间歇性低氧在动物模型中通过牙周血管生成增强了下区域的成骨反应。KIFUNE等[25]发现暴露于缺氧24 h后,牙周膜细胞中血管内皮生长因子的基因及蛋白表达显著升高,表明低氧水平能够刺激上调牙周膜细胞中血管内皮生长因子的合成并促进血管生成。 2.2.2 低氧模拟剂促进血管生成 脯氨酰羟化酶(PHD)抑制剂作为缺氧以及HIF的激动剂自产生以来长期应用于口腔,如颌面外科及牙周硬组织修复,其具有优秀的促血管生成以及骨骼再生能力,特别是炎症状态下[15,26]。脯氨酰羟化酶通过抑制常氧及低氧下HIF-1α的降解从而促进牙周组织内血管内皮生长因子的生成并促进血管生成反应,以促进伤口愈合和骨质再生。比如在破骨与成骨细胞中应用脯氨酰羟化酶抑制剂可促进血管生成[27]。AGIS等[15]在牙周膜细胞中应用脯氨酰羟化酶抑制剂,结果发现其可稳定HIF-1α并增加了血管内皮生长因子的产生,并且在存在促炎因子白细胞介素1的情况下也不影响成血管反应,表明脯氨酰羟化酶抑制剂的局部应用并不会引起显著的促炎或抗炎反应,见图4。"
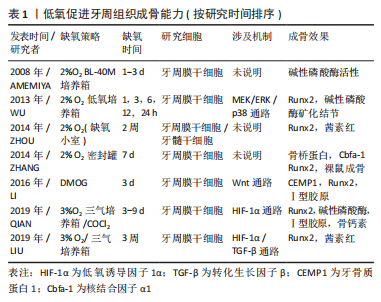
低氧在牙周炎中促进血管生成的作用已毋庸置疑,一方面它可以通过血管生成促进细胞因子炎性因子的释放从而加重炎症反应,而另一方面炎症过后的组织新生以及骨质的再生又离不开血管的侵入与伴行;因此,如何理性客观地分析缺氧在牙周炎血管新生中的双重角色,并且如何将它的这一特性更好地为牙周炎的组织再生所服务就显得至关重要了。 2.3 低氧:对牙槽骨代谢的影响 与其他组织相比,牙槽骨也处于相对低氧的微环境中[28],牙槽骨的稳态是由牙周膜干细胞、成骨细胞与破骨细胞等骨调节细胞之间的平衡所保证,任何病理改变都可能破坏骨骼系统的平衡。目前已经进行了多种类型的牙周组织骨代谢细胞与缺氧的体外研究,以阐明缺氧反应在生理和病理情况中的作用,相对于体内实验缺氧会加重牙周炎症的结果普遍被人接受而言,体外研究对牙槽骨形成的影响虽然并不一致,但结论在缺氧促进成骨的同时也促进破骨的现象上往往一致。 2.3.1 低氧对牙周膜干细胞增殖的影响 已知干细胞的生理氧张力低至1%-2%,这表明缺氧对干细胞维持有明显影响。人牙周膜干细胞(HPDLSCs)拥有良好的增殖能力与分化潜力,如成脂、成骨及成软骨能力,具有再生牙周组织的潜能,是牙齿组织再生中的候选种子细胞。目前越来越多的研究也探讨缺氧对牙周膜干细胞的影响,了解缺氧对维持牙周膜干细胞的干性和分化能力的作用非常重要。ZHOU等[29]研究发现,缺氧对牙周膜干细胞的增殖没有负面影响,而其多能性标记物和成骨分化潜能均显著增加。AMEMIYA等[30]从大鼠门牙中分离出牙周膜成纤维细胞,缺氧培养后发现细胞的增殖率呈时间依赖性增加;同时缺氧组的碱性磷酸酶活性、骨唾液酸蛋白以及血管内皮生长因子显著高于对照组和再氧合组。目前越来越多的证据表明,在短期低氧条件下可促进干细胞增殖,而长时间低氧则相反地抑制其增殖。LI等[31]研究发现低氧与牙周细胞增殖作用存在时间依赖性关系,在(1%O2)条件下培养人牙周膜干细胞,增殖速率在前6 h升高,但从6-72 h增殖速率显著下降;他们在缺氧条件下的人牙周膜干细胞蛋白组学研究也发现与细胞呼吸相关的蛋白水平发生显著变化,这些代谢变化为细胞适应性反应提供了必需的能量,也可以部分解释干细胞增殖变化的原因;随着低氧的持续刺激,人牙周膜干细胞会改变自己的能量代谢模式,从有氧呼吸转变为无氧糖酵解,以此维持自身的干性并适应低氧微环境,并且在这一过程中多种信号通路被激活以便细胞适应低氧环境。 2.3.2 低氧对牙周膜干细胞成骨分化能力的影响 已有大量研究证实了低氧对成骨的促进作用,XU 等[32]发现缺氧可诱导牙周膜干细胞和牙周组织中血管内皮生长因子和RUNX2 的表达,并且促进成骨。ZHANG等[33]将牙周膜干细胞(第3代)暴露于正常氧气(21% O2)或缺氧(2%O2)条件下7 d评估细胞成骨能力,并将每个细胞组与羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙载体一起孵育,皮下移植到免疫受损小鼠的背部,以研究体内移植差异;结果发现缺氧培养下显示出更高的成骨分化潜力;移植12周后,缺氧处理的人牙周膜干细胞分化为成骨细胞样细胞,形成骨样结构,表明缺氧在体内及体外均有较强的刺激成骨能力;在这一过程中多条信号通路被激活以便细胞适应低氧环境。Wnt/β-catenin信号通路是骨发育过程中经典的通路,其对成骨细胞的作用广泛且复杂,在骨组织的矿化和代谢中具有双重作用[34]。LI等[35]在缺氧条件下研究了牙周膜干细胞的成骨和成牙骨质分化,发现Wnt信号的激活抑制了牙骨质生成,而单独的缺氧并不影响牙周膜细胞的分化;随后发现缺氧逆转了Wnt信号过表达引起的牙骨质生成的抑制作用。转化生长因子β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β) 属于TGF-β超家族,调节细胞生长和分化,在成骨分化中起到关键作用[22]。TGF-β1可以通过对Smad3磷酸化来诱导HIF-1α的稳定化。LIU等[36]发现TGF-β1可以在非缺氧条件下诱导牙周膜干细胞中HIF-1α的稳定,HIF-1α可以负调节牙周膜干细胞中的TGF-β信号通路,降低早期Runx-2基因的表达和牙周膜干细胞的最终矿化,并与TGF-β1协同抑制牙周膜干细胞的成骨。WU等[37]建立人牙周膜干细胞与人脐静脉内皮细胞的非接触共培养系统,研究了不同缺氧时间(2%O2)对共培养的人牙周膜干细胞成骨潜能、矿化和旁分泌功能的影响。发现人牙周膜干细胞暴露于缺氧可显著激活MEK/ERK和p38 MAPK信号级联,并刺激转录因子Runx2和Sp7的表达,进而上调成骨调控基因碱性磷酸酶、前列腺素E2和血管内皮生长因子,最终形成长期矿化结节。HE等[38]在5%O2条件下培养牙周膜干细胞14 d,发现缺氧条件下牙周膜干细胞增殖能力提高;低氧牙周膜干细胞中的p38和ERK1/2磷酸化明显增强,因此,缺氧通过激活p38/MAPK和ERK/MAPK信号通路来增强牙周膜干细胞的增殖,但未检测成骨指标。低氧促进牙周成骨能力的研究汇总,见表1。"
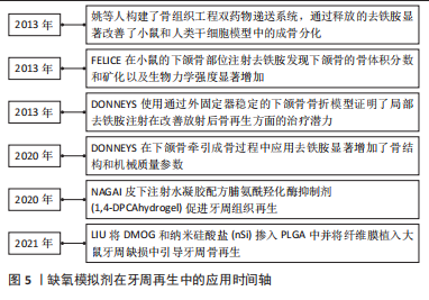
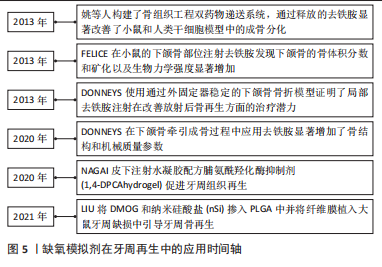
牙周组织所处的低氧微环境由细胞间相互作用,HIF-1α以及下游的信号通路等积极响应。在体外实验中,牙周组织相关细胞所处的微环境往往均衡而稳定,由人为控制,如无特殊要求时,多数体外环境是大气中的“常氧”,要远远高于体内微环境的氧气环境。研究者们往往聚焦于细胞因子和信号通路的表达变化,忽视了氧气浓度的影响。近年来随着细胞环境研究的深入,研究者热衷于用体内微环境的氧浓度或者一些缺氧模拟剂来替换大气中的氧浓度来培养细胞[39]。虽然低氧培养牙周组织细胞往往有利于其增殖和成骨,但也不乏一些抑制其干性及活性的结果。由此可见,未来的体外研究仍需尽量模仿和复制体内的环境以达到更准确的结果,目前并没有绝对的证据证明低氧对于成骨是一种绝对的有利性因素。 2.4 低氧:通过HIF通路促进骨再生 牙周硬组织再生是一系列复杂生理反应和多种信号通路调控的共同结果。研究再生过程中各种调节因子的表达和相关蛋白质的合成是组织工程技术和再生医学研究的基础。牙周组织再生有四大要素:具有成骨与成牙周膜潜能的干细胞;起到支持作用的支架与材料;生长因子;充足的血供[40]。新的再生手段中就包括模拟缺氧以诱导组织缺损中缺氧诱导因子的产生,以及药理学和基因诱导的缺氧信号以刺激口腔组织再生,这意味着将间充质干细胞等细胞暴露在缺氧条件下加速其增殖及分化能力,以刺激促血管生成因子的产生并应用于缺损部位[41]。然而,缺氧也会导致增殖率下降,因此需要密切观察培养环境。在过去的几年中,新的治疗概念包括缺氧预处理和药理学模拟缺氧环境,以诱导组织缺损中促血管生成因子及成骨基因的产生。与使用单一促血管生成因子相比,HIF-1作为调节血管生成的最上游信号分子,触发了一系列级联反应, HIF-1α通路的生物学效应还可以诱导种子细胞成骨分化,调节细胞代谢以适应缺氧条件,提高细胞存活率[42]。 低氧模拟剂在牙周再生中的应用:低氧模拟剂(hypoxia mimetic agents,HMA)被提倡作为骨科再生手术和牙周病学的工具,可以支持伤口愈合和骨再生。例如:REZAEI等[43]研究发现将脯氨酰羟化酶(PHD)抑制剂二甲基草酰甘氨酸(DMOG)和氯化钴(CoCl2)加载到成骨细胞中可以逆转高血糖对骨结节形成的抑制。LIU等[44]将DMOG和纳米硅酸盐(nSi)掺入聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物(PLGA)中并将纤维膜植入大鼠牙周缺损中,发现DMOG/nSi-PLGA纤维膜在牙周骨缺损修复过程中发挥保护作用,并引导牙周骨再生。NAGAI等[45]应用了可注射的水凝胶配方脯氨酰羟化酶抑制剂(1,4-DPCA/hydrogel)促进牙周组织再生,与用载体对照处理的小鼠相比,皮下注射 1,4-DPCA的小鼠显示出HIF-1α水平显著提高、骨再生增加与成骨基因表达升高、促炎细胞因子基因表达降低。目前尚不清楚含有上调HIF-1α蛋白水平的1,4DPCA的局部应用可否直接用于治疗人类牙周炎,但仍值得研究。在药理学上,使用已知的脯氨酰羟化酶抑制剂去铁胺(DFO)来激活HIF信号通路也可获得相似的结果。DONNEYS 等[46]在下颌骨牵引成骨过程中应用去铁胺显著增加了骨结构和机械质量参数,例如骨体积分数(BVF)、骨矿物质密度(BMD)和极限负荷(UL)。有研究者构建了骨组织工程双药物递送系统,通过释放的去铁胺显著改善了小鼠和人类干细胞模型中的成骨分化[47]。FELICE等[48]在小鼠的下颌骨部位注射去铁胺,经过40 d的愈合时间后,发现经去铁胺处理下颌骨的骨体积分数和矿化以及生物力学强度显著增加,骨体积分数和矿物质密度值实际上显示出显著更高的结果。DONNEYS 等[49]使用通过外固定器稳定的下颌骨骨折模型证明了局部去铁胺注射在改善放射后骨再生方面的治疗潜力。缺氧模拟剂在牙周组织再生工程中的应用情况,见图5。"
| [1] 吴梦鑫,梁文红,杨琨,等.牙周膜干细胞促进牙周组织再生的影响因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(30):4912-4920. [2] YANG B, PANG X, LI Z, et al. Immunomodulation in the Treatment of Periodontitis: Progress and Perspectives. Front Immunol. 2021;12:781378. [3] GRAVES DT, CORRÊA JD, SILVA TA. The Oral Microbiota Is Modified by Systemic Diseases. J Dent Res. 2019;98:148-156. [4] PLACHOKOVA AS, ANDREU-SÁNCHEZ S, NOZ MP, et al. Oral Microbiome in Relation to Periodontitis Severity and Systemic Inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(11):5876. [5] FANDREY J, SCHÖDEL J, ECKARDT KU, et al. Now a Nobel gas: oxygen. Pflugers Arch. 2019;471:1343-1358. [6] MANRESA MC, SMITH L, CASALS-DIAZ L, et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-hydroxylases ameliorates allergic contact dermatitis. Allergy. 2019;74:753-766. [7] HUANG Y, WANG X, LIN H. The hypoxic microenvironment: a driving force for heterotopic ossification progression. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18:20. [8] 李婧.高原地理环境与牙周炎的关系研究进展[J].全科口腔医学杂志(电子版),2020,7(1):26,36. [9] 佘建祯,冯帆,周兴田,等.驻高原与驻平原空军官兵口腔健康现状调查[J].西南军医,2016,18(2):101-103. [10] ZHU R, MI X, LI Y. Effects of Hypoxic Environment on Periodontal Tissue through the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022: 7690960. [11] SCHRÖDER A, BARSCHKIES L, JANTSCH J, et al. Role of Oxygen Supply in Macrophages in a Model of Simulated Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:5802435. [12] WERLE SB, CHAGASTELLES P, PRANKE P, et al. The effects of hypoxia on in vitro culture of dental-derived stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2016;68:13-20. [13] MCGETTRICK AF, O’NEILL LAJ. The Role of HIF in Immunity and Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2020;32:524-536. [14] SONG ZC, ZHOU W, SHU R, et al. Hypoxia induces apoptosis and autophagic cell death in human periodontal ligament cells through HIF-1α pathway. Cell Prolif. 2012;45:239-248. [15] AGIS H, WATZEK G, GRUBER R. Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors increase the production of vascular endothelial growth factor by periodontal fibroblasts. J Periodontal Res. 2012;47:165-173. [16] JIAN C, LI C, REN Y, et al. Hypoxia augments lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine expression in periodontal ligament cells. Inflammation. 2014;37:1413-1423. [17] TERRIZZI AR, FERNANDEZ-SOLARI J, LEE CM, et al. Alveolar bone loss associated to periodontal disease in lead intoxicated rats under environmental hypoxia. Arch Oral Biol. 2013;58:1407-1414. [18] 武曦,黄镜静,张纲,等.高原低氧环境对兔牙周炎模型血清和牙龈组织中超氧化物歧化酶活力的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2012,30(3):247-250. [19] TERRIZZI AR, CONTI MI, MARTÍNEZ MP, et al. The Process of Acclimation to Chronic Hypoxia Leads to Submandibular Gland and Periodontal Alterations: An Insight on the Role of Inflammatory Mediators. Mediators Inflamm. 2018; 2018:6794508. [20] TERRIZZI AR, RUGOLO G, BOZZINI C, et al. Mandibular biomechanical behavior of rats submitted to chronic intermittent or continuous hypoxia and periodontitis. S Sleep Breath. 2021;25:519-527. [21] DE HEER EC, JALVING M, HARRIS AL. HIFs, angiogenesis, and metabolism: elusive enemies in breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:5074-5087. [22] QIN Q, LIU Y, YANG Z, et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors Signaling in Osteogenesis and Skeletal Repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):11201. [23] VASCONCELOS RC, COSTA ADE L, FREITAS RDE A, et al. Immunoexpression of HIF-1α and VEGF in Periodontal Disease and Healthy Gingival Tissues. Braz Dent J. 2016;27:117-122. [24] OISHI S, SHIMIZU Y, HOSOMICHI J, et al. Intermittent Hypoxia Influences Alveolar Bone Proper Microstructure via Hypoxia-Inducible Factor and VEGF Expression in Periodontal Ligaments of Growing Rats. Front Physiol. 2016;7:416. [25] KIFUNE T, ITO H, ISHIYAMA M, et al. Hypoxia-induced upregulation of angiogenic factors in immortalized human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Oral Sci. 2018; 60:519-525. [26] MAMALIS AA, COCHRAN DL. The therapeutic potential of oxygen tension manipulation via hypoxia inducible factors and mimicking agents in guided bone regeneration. A review. Arch Oral Biol. 2011;56:1466-1475. [27] EDELMAYER M, AL-HABBAL D, PENSCH M, et al. Effect of prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor-loaded collagen barrier membranes on osteoclastogenesis and osteoblastogenesis. J Biomater Appl. 2017;31:1370-1379. [28] TAO J, MIAO R, LIU G, et al. Spatiotemporal correlation between HIF-1α and bone regeneration. FASEB J. 2022;36:e22520. [29] ZHOU Y, FAN W, XIAO Y. The effect of hypoxia on the stemness and differentiation capacity of PDLC and DPC. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:890675. [30] AMEMIYA H, MATSUZAKA K, KOKUBU E,et al. Cellular responses of rat periodontal ligament cells under hypoxia and re-oxygenation conditions in vitro. J Periodontal Res. 2008;43:322-327. [31] LI Q, LUO T, LU W, et al. Proteomic analysis of human periodontal ligament cells under hypoxia. Proteome Sci. 2019;17:3. [32] XU Q, LIU Z, GUO L, et al. Hypoxia Mediates Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2 Expression via Induction of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Mol Cells. 2019;42:763-772. [33] ZHANG QB, ZHANG ZQ, FANG SL, et al. Effects of hypoxia on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells: an in vitro and in vivo study. GMR. 2014;13:10204-10214. [34] MAEDA K, KOBAYASHI Y, KOIDE M, et al. The Regulation of Bone Metabolism and Disorders by Wnt Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5525. [35] LI S, SHAO J, ZHOU Y, et al. The impact of Wnt signalling and hypoxia on osteogenic and cementogenic differentiation in human periodontal ligament cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14:4975-4982. [36] LIU Z, GUO L, LI R, et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 and hypoxia inducible factor-1α synergistically inhibit the osteogenesis of periodontal ligament stem cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105834. [37] WU Y, CAO H, YANG Y, et al. Effects of vascular endothelial cells on osteogenic differentiation of noncontact co-cultured periodontal ligament stem cells under hypoxia. J Periodontal Res. 2013;48:52-65. [38] HE Y, JIAN CX, ZHANG HY, et al. Hypoxia enhances periodontal ligament stem cell proliferation via the MAPK signaling pathway. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(4). doi: 10.4238/gmr15048965. [39] MOHYELDIN A, GARZÓN-MUVDI T, QUIÑONES-HINOJOSA A. Oxygen in stem cell biology: a critical component of the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7:150-161. [40] 闫福华,李丽丽.牙周再生治疗研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2018,34(3):217-222. [41] FENG Y, HAN Z, JIANG W, et al. Promotion of osteogenesis in BMSC under hypoxia by ATF4 via the PERK-eIF2α signaling pathway. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022 Nov 15. doi: 10.1007/s11626-022-00732-4. [42] LI L, LI A, ZHU L, et al. Roxadustat promotes osteoblast differentiation and prevents estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss by stabilizing HIF-1α and activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17:286. [43] REZAEI A, LI Y, TURMAINE M, et al. Hypoxia mimetics restore bone biomineralisation in hyperglycaemic environments. Sci Rep. 2022;12:13944. [44] LIU ZQ, SHANG LL, GE SH. Immunomodulatory effect of dimethyloxallyl glycine/nanosilicates-loaded fibrous structure on periodontal bone remodeling. J Dent Sci. 2021;16:937-947. [45] NAGAI K, IDEGUCHI H, KAJIKAWA T, et al. An injectable hydrogel-formulated inhibitor of prolyl-4-hydroxylase promotes T regulatory cell recruitment and enhances alveolar bone regeneration during resolution of experimental periodontitis. FASEB J. 2020;34:13726-13740. [46] DONNEYS A, DESHPANDE SS, TCHANQUE-FOSSUO CN, et al. Deferoxamine expedites consolidation during mandibular distraction osteogenesis. Bone. 2013;55:384-390. [47] YAO Q, LIU Y, SELVARATNAM B, et al. Mesoporous silicate nanoparticles/3D nanofibrous scaffold-mediated dual-drug delivery for bone tissue engineering. J Control Release. 2018;279:69-78. [48] FELICE PA, AHSAN S, DONNEYS A, et al. Deferoxamine administration delivers translational optimization of distraction osteogenesis in the irradiated mandible. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946). 2013;132:542e-548e. [49] DONNEYS A, AHSAN S, PEROSKY JE, et al. Deferoxamine restores callus size, mineralization, and mechanical strength in fracture healing after radiotherapy. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946). 2013;131:711e-719e. |
| [1] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [2] | Sun Jiajia, Zhu Haidi, Lu Yun, Zhang Kai. Comparison of bone metabolism markers between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [3] | Li Mengfei, Zhang Hong, Zhao Shaojian, Yin Guanghao, Wang Qibao. Expression of forkhead box protein 3 in refractory periapical periodontitis in rats with Enterococcus faecalis infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1187-1192. |
| [4] | Xu Yan, Li Ping, Lai Chunhua, Zhu Peijun, Yang Shuo, Xu Shulan. Piezoelectric materials for vascularized bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [5] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [6] | Shao Zichen, Li Huanan, Gu Bing, Zhang Xiaoyun, Sun Weikang, Liu Yongqian, Gan Bin. MicroRNA, long non-coding RNA and circular RNA mediate the mechanism of decreasing uric acid, anti-inflammation and regulating bone metabolism in gout [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 765-771. |
| [7] | Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 787-792. |
| [8] | Liu Yuan. Effect of hypoxic training on the oxygen sensing pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 793-798. |
| [9] | Han Jie, Lin Zhiyu, Xu Zhiwei, Zhang Xiaoyun, Shang Yuzhi, Liu Hao. Interventional effect of microRNA on osteonecrosis of the femoral head through bone metabolism mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5238-5248. |
| [10] | Liu Guanjuan, Xia Qianxi, Song Na, Huo Hua, Hong Wei, Liao Jian. Role of pyruvic acid in osteoclast differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5015-5021. |
| [11] | Liu Huan, Li Han, Ma Yunhao, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu. Osteogenic capacity of partially demineralized dentin particles in the maxillary sinus lift [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 354-359. |
| [12] | Zong Mingrui, Liu Haiyan, Li Bing, Wu Xiuping. Application of carboxymethyl chitosan in tissue engineering of stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 447-452. |
| [13] | Su Hui, Yan Binghan, Wang Ruochong, Xue Haipeng, Tan Guoqing, Xu Zhanwang. Effect of Bushen Zhuanggu Fang on bone metabolism and bone mineral density in rats with ovariectomized osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4507-4512. |
| [14] | Xiong Bo, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Lu Guanyu, Chen Cai, Huang Yue, Chen Lihua. Roles of N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 in regulating bone metabolism and related diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4566-4570. |
| [15] | Zhao Zirui, Hu Qiaoyu, Qi Xia, Liu Qing. Metabolomics evaluation of periodontitis: biomarkers, pathological mechanism and systemic relationship [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4239-4245. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 252
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 377
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

