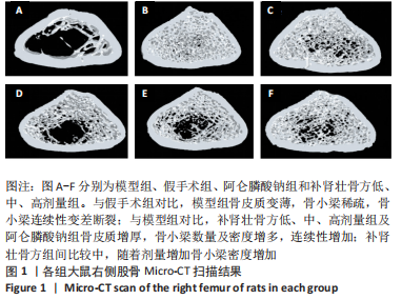
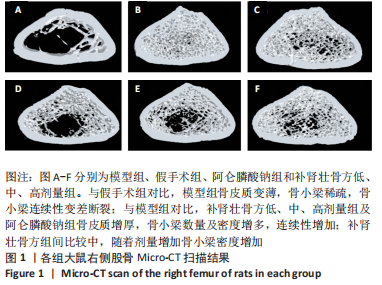
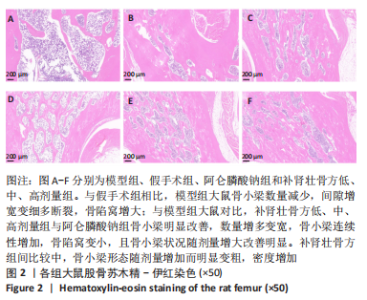
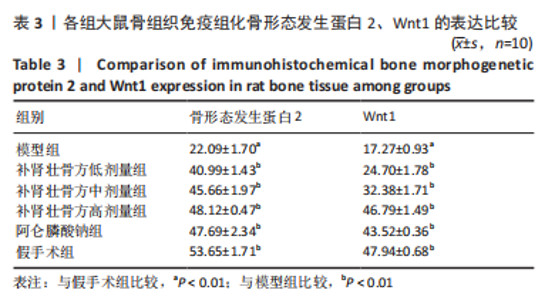
[1] ENSRUD KE, CRANDALL CJ. Osteoporosis. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167(3): ITC17-ITC32.
[2] ANTHAMATTEN A, PARISH A. Clinical Update on Osteoporosis. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2019;64(3):265-275.
[3] 郑蹦蹦,王佳明,余迎奇,等.绝经后骨质疏松症的药物防治研究进展[J].医学综述,2021,27(18):3675-3681.
[4] 夏荣林.中医药防治老年骨质疏松骨折的研究进展[J].内蒙古中医药,2022,41(4):135-137.
[5] 杜丽坤,李佳睿.骨质疏松症的中医认识及防治[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(2):296-299.
[6] 王庆谚,李佳,郑洪新.从“肾虚络病,瘀阻骨络”探讨原发性骨质疏松症中医病机[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(2):756-759.
[7] 彭斯伟,宋敏,范凯,等.单味中药治疗肾虚型骨质疏松症机制研究状况[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2022,38(1):76-80.
[8] 刘达,王昆鹏,王宇峰.中药组方论治老年性骨质疏松症的临床评价研究[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(97):381+386.
[9] 陈沙,王桂云,李荣慧,等.雌性大鼠手术去势骨质疏松症模型建立及评价[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2020,40(11):1315-1319.
[10] 孙岩,陈冉,王小琦,等.恒古骨伤愈合剂对去势雌性大鼠骨质疏松模型的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(12):1513-1515+1539.
[11] LATT RH, 郑月华.实验动物的药物剂量[J].上海实验动物科学, 1984(3):178-182.
[12] 中成药治疗骨质疏松症临床应用指南(2021年)[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2022,42(4):393-404.
[13] 杜丽坤,李佳睿.骨质疏松症的中医认识及防治[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(2):296-299.
[14] 王新祥,张允岭,黄启福.对骨质疏松症中医主要病机和现代病因学的认识与探讨[J].中西医结合学报,2010,8(12):1119-1123.
[15] 杜晓萌,甘可.从脾虚论治原发性骨质疏松症[J].河北中医,2018, 40(8):1256-1259.
[16] 张沛,杜源,金祺,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折手术患者的临床特征分析[J].临床骨科杂志,2022,25(2):175-178.
[17] 张芸,薛景才,郑平原,等.血瘀型骨质疏松症的方药配伍规律探讨[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(7):1036-1041.
[18] 梁文娜,李西海,李灿东.绝经后骨质疏松的核心病机——骨痿[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(18):5333-5335
[19] 李攀,胡志俊,唐占英,等.中药从肾论治骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].长春中医药大学学报,2022,38(4):461-466.
[20] 叶丙霖,李盛华,王想福,等.补肾壮骨类中药治疗绝经期骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].西部中医药,2018,31(3):136-139.
[21] 张峻玮,李琰,薛海鹏,等.骨碎补经骨髓间充质干细胞调节OPG/RANKL/RANK通路抑制破骨细胞的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2019,25(5):617-624.
[22] 李琰,李志航,陈云刚,等.骨碎补水煎液经Wnt/β-catenin通路对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(2):279-284+518-520.
[23] 高海垚,史杭楚,王昌兴.唑来膦酸配合补肾壮骨方促进绝经后骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折术后骨愈合疗效观察[J].浙江中医杂志, 2022,57(5):353-354.
[24] 李智奎,孔俊博,赵王林.补肾壮骨方辅助治疗对绝经后骨质疏松患者炎性因子及骨代谢指标的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(9): 1901-1904.
[25] 孟玥,任艳玲,孙月娇,等.左归丸、右归丸及其拆方对去卵巢骨质疏松症模型大鼠肾脏碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素表达的影响[J].中医杂志,2016,57(5):423-427.
[26] 黄广平,陈民,李腾辉.原发性骨质疏松患者中医证型与Runx2基因多态性的相关性研究[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2018,39(10): 1120-1123.
[27] 徐众华,莫雨晴,周驰.基于BMP/Runx2/Osx信号通路研究淫羊藿总黄酮改善绝经后骨质疏松模型大鼠的作用机制[J].中国药房, 2020,31(19):2333-2338.
[28] 谢忠建.从OPG-RANKL-RANK通路到骨质疏松症分子靶向治疗[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2022,15(2):126-134.
[29] 宋敏,王凯,文皓楠,等.基于“脾主肉,肾主骨”理论探讨OPG/RANK/RANKL信号通路与老年性骨质疏松的相关性[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2020,27(5):1-4.
[30] 卜寒梅,王世坤,李远栋,等.补肾中药基于OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路对原发性骨质疏松症作用机制的研究进展[J].中草药,2022, 53(10):3209-3217.
[31] 唐尤超,汤炜,田卫东,等. BMP-2在骨质疏松症胫骨骨折愈合中的表达[C]//.第四届中国国际暨第七次全国口腔颌面外科学术会议论文集,2005:260-261.
[32] 张拔山,李荣,王文锋,等.成骨不全XV型WNT1基因突变影响成骨细胞分化的机制[J].分子诊断与治疗杂志,2021,13(4):526-530.
[33] 梁帅,曲华,凌树宽,等.中药防治骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].北京中医药,2021,40(10):1169-1173.
[34] 乔小万,邓强,李中锋,等.基于“肾虚髓枯”理论探讨骨质疏松症的病机及中药治疗[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(5):760-765+780. |