Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (35): 5734-5740.doi: 10.12307/2023.841
A systemic review of the effectiveness and safety of fractional CO2 laser combined with platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of atrophic acne scars
Song Li, Lu Mao, Tang Yi, Liu Yanlin
- Department of Dermatology, First Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu 610500, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-17Accepted:2022-11-21Online:2023-12-18Published:2023-06-05 -
Contact:Song Li, Department of Dermatology, First Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu 610500, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Song Li, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Dermatology, First Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu 610500, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Project of Sichuan Provincial Health Bureau, No. 120480 (to SL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Li, Lu Mao, Tang Yi, Liu Yanlin. A systemic review of the effectiveness and safety of fractional CO2 laser combined with platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of atrophic acne scars[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(35): 5734-5740.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

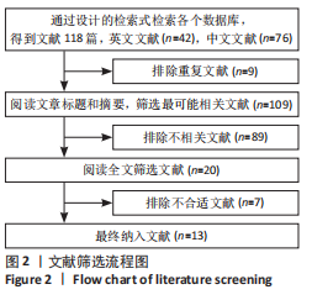
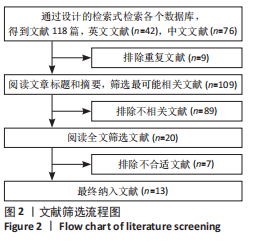
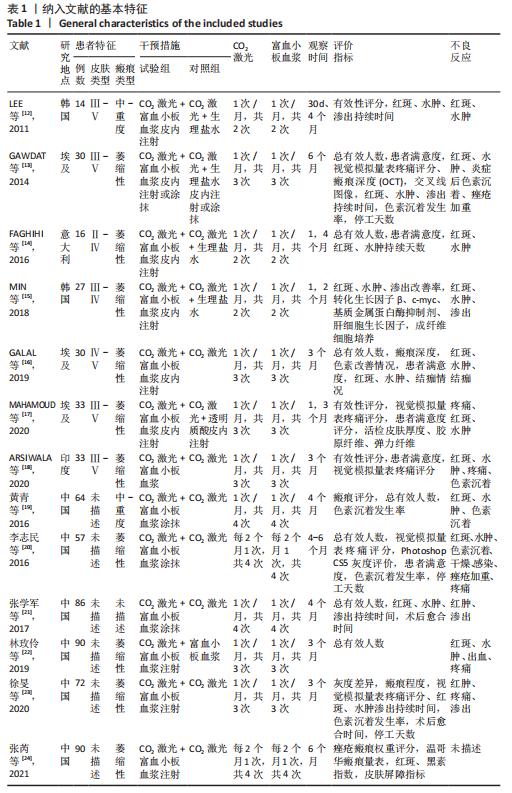
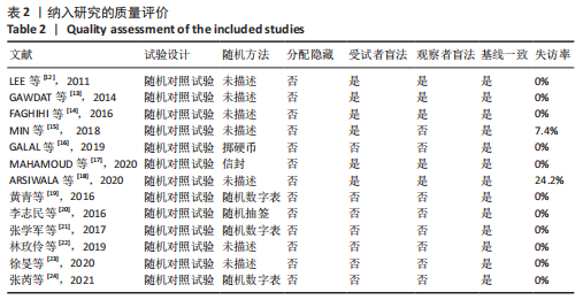
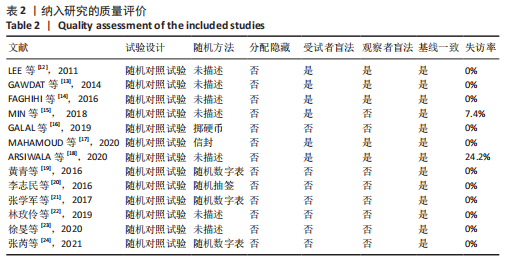
2.3.1 随机方法 纳入的13个研究中[12-24],均为随机对照试验。其中7个研究为半脸自身对照[12-18],另外6个研究纳入不同的患者作为对照组[19-24]。6个研究描述了随机方法[16-17,19-21,24],分别为掷硬币、抽签、随机数字表、信封法。所有研究都未采取分配隐藏。 2.3.2 盲法 5个研究为观察者及受试者双盲[12-14,17-18],1个研究为观察者单盲[15],7个研究没有采取盲法[16,19-24]。 2.3.3 基线一致 7个研究为半脸自身对照[12-18],另外6个研究纳入不同的患者作为对照组[19-24]。所有研究描述了试验组与对照组的基线情况,均具有可比性。 2.3.4 随访情况 全部研究进行了随访,随访时间最长为6个月。2个研究有患者失访[15,18],失访率分别为7.4%[15],24.2%[18],都采取将失访患者排除结果统计。 2.4 纳入临床试验偏倚分析 偏倚风险评价结果表明,纳入的13个研究中[12-24],只有6个研究描述了随机方法[16-17,19-21,24],全部没有采用分配隐藏,其中5个采用了双盲[12-14,17-18],1个采用了单盲,没有研究采用三盲。2个研究有一定比例的失访[15,18],均将失访案例排除试验数据统计。所有研究都清楚的报告了研究结果,见图3。"

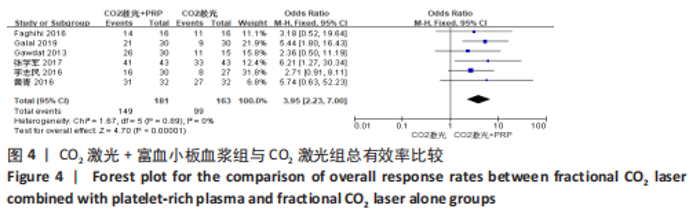
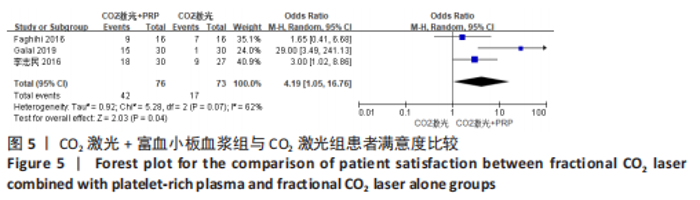
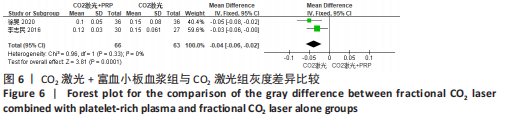
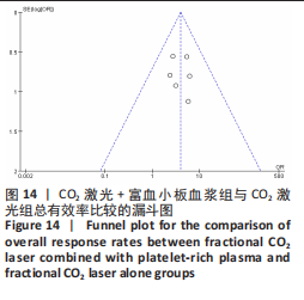
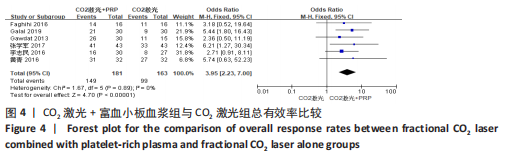
2.5 Meta分析结果 2.5.1 主要指标(总有效率) 采取治疗前后拍摄患者面部照片的方法,将瘢痕的改善程度采用四分法分类:0分,无效;1分,< 25%,改善不佳;2分,≥25%,但< 50%,稍微改善;3分,≥50%,但< 75%,有效改善;4分,≥75%,显著改善。统计有效及显著改善人数,计算总有效率。7个研究通过计算有效人数统计了总有效率[13-14,16,19-22],其中6个研究为点阵CO2激光联合富血小板血浆组与点阵CO2激光组相比[13,14,16,19-21],研究间无临床异质性,无统计学异质性[Chi2=1.67,df=5(P=0.89),I2=0%],采用固定效应模式进行Meta分析,结果显示点阵CO2激光联合富血小板血浆组总有效率高于点阵CO2激光组,差异有显著性意义(OR=3.95,95%CI=2.23-7.00,P < 0.000 01),见图4。另外1个研究对照组为富血小板血浆,故没有纳入数据合并[22]。"

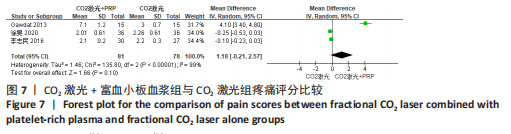
(3)疼痛评分:5个研究报道了患者对疼痛的评价[13,17-18,20,23],均采用视觉模拟量表评分,但只有3个研究分别报道了治疗组及对照组疼痛评分分数[13,20,23]。3个研究均为点阵CO2激光联合富血小板血浆组与点阵CO2激光组相比,研究间无临床异质性,有统计学异质性[Tau2=1.46,Chi2=135.80,df=2(P < 0.000 01),I2=99%],采用随机效应模式进行Meta分析。结果显示点阵CO2激光联合富血小板血浆组疼痛评分稍高于点阵CO2激光组,但差异无显著性意义(MD=1.18,95%CI=-0.21至2.57,P=0.10),见图7。异质性检验结果显示 I2=99%,表示存在较高异质性。"
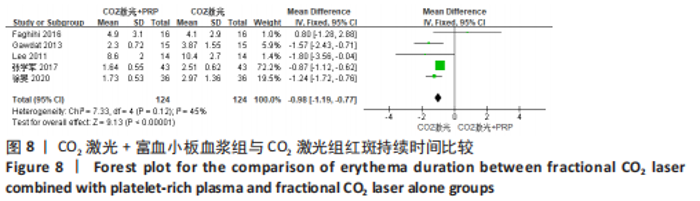
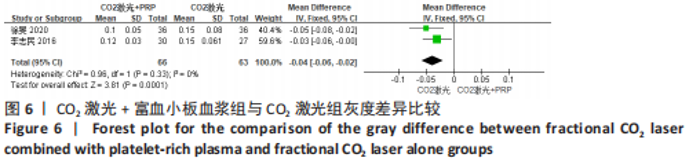
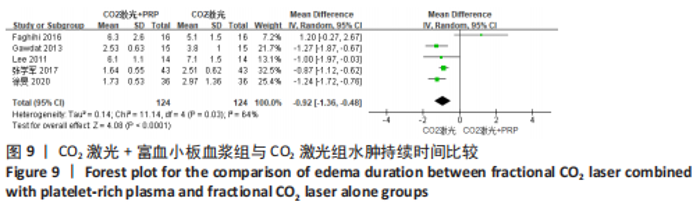
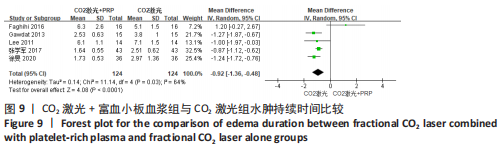
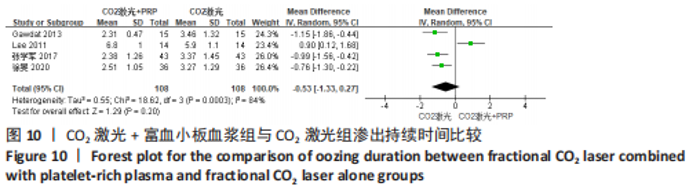
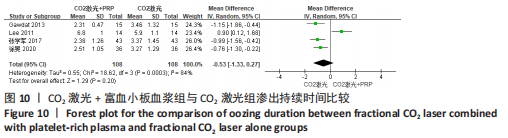
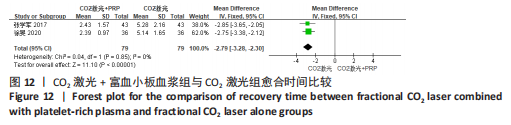
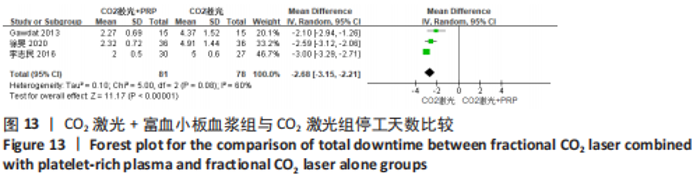
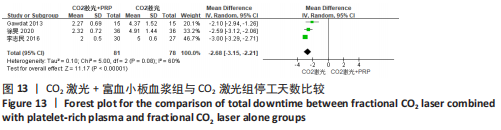
为了探究异质性的来源,采用了敏感性分析的方法,发现去除GAWDAT等[13]后,总的效应量变为MD=-0.13,95%CI=-0.25至-0.01,P=0.04,且 I2=0%,与未去除前相比异质性变化较大,表明GAWDAT等[13]这篇研究可能是异质性的来源。 (4)红斑、水肿、渗出持续时间:6个研究报道了治疗后红斑持续时间[12-14,16,21,23] ,其中5个研究报道了治疗组与对照组的红斑持续天数[12-14,21,23]。6个研究报道了治疗后水肿持续时间[12-14,16,21,23] ,其中5个研究报道了治疗组与对照组的水肿持续天数[12-14,21,23]。5个研究报道了治疗后渗出或结痂时间[12-13,16,21,23],其中4个研究报道了治疗组与对照组的渗出或结痂持续天数[12-13,21,23]。研究均为点阵CO2激光联合富血小板血浆组与点阵CO2激光组相比。 针对红斑的研究间无临床异质性,无统计学异质性[Chi2=7.33,df=4(P=0.12),I2=45%],采用固定效应模式进行Meta分析。针对水肿的研究间无临床异质性,有统计学异质性[Tau2=0.14,Chi2=11.14,df=4(P=0.03),I2=64%],采用随机效应模式进行Meta分析。针对渗出的研究间无临床异质性,有统计学异质性[Tau2=0.55,Chi2=18.62,df=3(P=0.000 3),I2=84%],采用随机效应模式进行Meta分析。结果显示点阵CO2激光联合富血小板血浆组术后红斑、水肿持续时间均短于点阵CO2激光组,差异均有显著性意义(MD=-0.98,95%CI=-1.19至-0.77,P < 0.000 01,MD=-0.92,95%CI=-1.36至-0.48,P < 0.000 1);点阵CO2激光联合富血小板血浆组术后渗出持续时间稍短于点阵CO2激光组,但差异无显著性意义(MD=-0.53,95%CI=-1.33至0.27,P=0.20),分别见图8-10。"

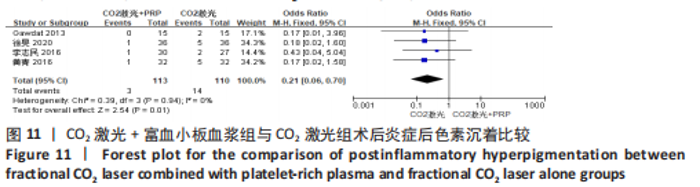
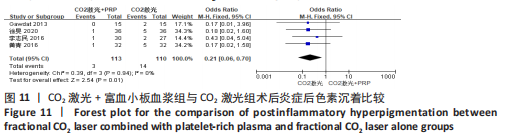
关于渗出及结痂时间的4个研究异质性检验结果显示 I2=84%,表示存在较高异质性[12-13,21,23]。为了探究异质性的来源,采用了敏感性分析的方法,发现去除LEE等[12]后,总的效应量变为MD=-0.94,95%CI=-1.28至-0.59,P < 0.000 1,且 I2= 0%,与未去除前相比异质性变化较大,表明LEE等[12]这篇研究可能是异质性的来源。 (5)术后色素沉着发生率:4个研究分别报道了治疗组及对照组术后色素沉着发生率[13,19-20,23],均为点阵CO2激光联合富血小板血浆组与点阵CO2激光组相比,研究间无临床异质性,无统计学异质性[Chi2=0.39,df=3(P=0.94),I2=0%],采用固定效应模式进行Meta分析。结果显示点阵CO2激光联合富血小板血浆组术后色素沉着发生率低于点阵CO2激光组,差异有显著性意义(OR=0.21,95%CI=0.06-0.70,P=0.01),见图11。"
| [1] GONZÁLEZ N, GOLDBERG DJ. Update on the Treatment of Scars. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18(6):550-555. [2] BOEN M, JACOB C. A Review and Update of Treatment Options Using the Acne Scar Classification System. Dermatol Surg. 2019; 45(3):411-422. [3] 中华医学会医学美学与美容学分会激光美容学组,中华医学会皮肤性病学分会美容激光学组,中国医师协会美容与整形医师分会激光学组. 中国痤疮瘢痕治疗专家共识(2021)[J].中华皮肤科杂志, 2021,54(9):747-756. [4] DRÉNO B, TAN J, KANG S, et al. How People with Facial Acne Scars are Perceived in Society: an Online Survey. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2016;6(2):207-218. [5] XU S, ZHU Y, HU H, et al. The analysis of acne increasing suicide risk. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(24):e26035. [6] DRENO B, AMICI JM, DEMESSANT-FLAVIGNY AL, et al. The Impact of Acne, Atopic Dermatitis, Skin Toxicities and Scars on Quality of Life and the Importance of a Holistic Treatment Approach. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021;14:623-632. [7] 贾彦敏,丁媛,康晓静.痤疮凹陷性瘢痕的治疗进展[J].中国医疗美容,2018,8(1): 102-106. [8] 鞠强.中国痤疮治疗指南(2019修订版)[J].临床皮肤科杂志,2019,48(9):583-588. [9] MANINDER K, RICHA R, DINESH AP, et al. Factors affecting the outcome of fractional carbon dioxide laser resurfacing of various types of scars in skin of color. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21(9):3842-3847. [10] 庄化迪,冯杰,刘顺英,等.富血小板血浆联合CO2点阵激光治疗萎缩性痤疮瘢痕疗效和安全性Meta分析[J].中国麻风皮肤病杂志,2020,36(2):75-79. [11] GOODMAN GJ, BARON JA. Postacne scarring: a qualitative global scarring grading system. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32(12):1458-1466. [12] LEE JW, KIM BJ, KIM MN, et al. The efficacy of autologous platelet rich plasma combined with ablative carbon dioxide fractional resurfacing for acne scars: a simultaneous split-face trial. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37(7):931-938. [13] GAWDAT HI, HEGAZY RA, FAWZY MM, et al. Autologous platelet rich plasma: topical versus intradermal after fractional ablative carbon dioxide laser treatment of atrophic acne scars. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40(2):152-161. [14] FAGHIHI G, KEYVAN S, ASILIAN A, et al. Efficacy of autologous platelet-rich plasma combined with fractional ablative carbon dioxide resurfacing laser in treatment of facial atrophic acne scars: A split-face randomized clinical trial. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82(2):162-168. [15] MIN S, YOON JY, PARK SY, et al. Combination of platelet rich plasma in fractional carbon dioxide laser treatment increased clinical efficacy of for acne scar by enhancement of collagen production and modulation of laser-induced inflammation. Lasers Surg Med. 2018;50(4):302-310. [16] GALAL O, TAWFIK AA, ABDALLA N, et al. Fractional CO2 laser versus combined platelet-rich plasma and fractional CO2 laser in treatment of acne scars: Image analysis system evaluation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18(6):1665-1671. [17] MAHAMOUD WA, EL BARBARY RA, IBRAHIM NF, et al. Fractional carbon dioxide laser combined with intradermal injection of autologous platelet-rich plasma versus noncross-linked hyaluronic acid in the treatment of atrophic postacne scars: A split face study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;19(6): 1341-1352. [18] ARSIWALA NZ, INAMADAR AC, ADYA KA. A Comparative Study to Assess the Efficacy of Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser and Combination of Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser with Topical Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma in Post-acne Atrophic Scars. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2020;13(1):11-17. [19] 黄青,洪婷,彭胜男,等.PRP联合CO2点阵激光治疗面部痤疮瘢痕的临床疗效观察[J].医学理论与实践2016,29(13):1686-1687. [20] 李志民,谢培煜,吴丽惠,等.点阵CO2激光联合自体富血小板血浆治疗面部痤疮瘢痕的临床效果[J].中华医学美学美容杂志,2016,22(5):293-295. [21] 张学军.点阵CO2激光联合自体富血小板血浆对面部痤疮瘢痕患者瘢痕区皮肤创面愈合时间的影响[J].中国医疗美容, 2017,7(7):37-39. [22] 林玫伶,谢君,林德基,等.以富血小板血浆(PRP)为基础的联合疗法治疗痤疮萎缩性瘢痕的疗效观察[J].中国医疗美容, 2019,9(12):78-82. [23] 徐旻,吕君,陈尚周,等.超脉冲CO2点阵激光联合PRP治疗面部痤疮凹陷性瘢痕疗效分析[J].中国美容医学,2020,29(5): 41-44. [24] 张芮,闵伟.局灶点阵激光联合自体富血小板血浆对痤疮凹陷性瘢痕患者瘢痕情况及皮肤屏障功能的影响[J].中国医疗美容,2021,11(6):67-70. [25] 卞媛媛,于浩,高兴华.富血小板血浆联合剥脱性CO2点阵激光治疗面部痤疮后瘢痕临床疗效研究[J].临床军医杂志, 2019,47(3):297-298. [26] GAWDAT HI, EL-HADIDY YA, ALLAM RSHM, et al. Autologous platelet-rich plasma ‘fluid’ versus ‘gel’ form in combination with fractional CO2 laser in the treatment of atrophic acne scars: a split-face randomized clinical trial. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33(5): 2654-2663. [27] AL TAWEEL AI, AL REFAE AA, HAMED AM, et al. Comparative study of the efficacy of Platelet-rich plasma combined with carboxytherapy vs its use with fractional carbon dioxide laser in atrophic acne scars. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18(1):150-155. [28] ABDEL AAL AM, IBRAHIM IM, SAMI NA, et al. Evaluation of autologous platelet-rich plasma plus ablative carbon dioxide fractional laser in the treatment of acne scars. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2018;20(2):106-113. [29] KAR BR, RAJ C. Fractional CO2 Laser vs Fractional CO2 with Topical Platelet-rich Plasma in the Treatment of Acne Scars: A Split-face Comparison Trial. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2017;10(3):136-144. [30] ABDEL-MAGUID EM, AWAD SM, HASSAN YS, et al. Efficacy of stem cell-conditioned medium vs. platelet-rich plasma as an adjuvant to ablative fractional CO2 laser resurfacing for atrophic post-acne scars: a split-face clinical trial. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32(2):242-249. [31] SHARMA S, KAUR J, KAUR T, et al. Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser versus Combined Fractional Carbon Dioxide Laser with Platelet-rich Plasma in the Treatment of Atrophic Post-acne Scars: A Split-face Comparative Study. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2021;14(1):41-46. [32] KIM SA, RYU HW, LEE KS, et al. Application of platelet-rich plasma accelerates the wound healing process in acute and chronic ulcers through rapid migration and upregulation of cyclin A and CDK4 in HaCaT cells. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7(2):476-480. [33] BARAN U, LI Y, CHOI WJ, et al. High resolution imaging of acne lesion development and scarring in human facial skin using OCT-based microangiography. Lasers Surg Med. 2015;47(3):231-238. [34] 崔佳,姚庆君,韩维鑫,等.面部痤疮凹陷性瘢痕的治疗方法及趋势[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2021,32(3):191-200. [35] 阚厚铭,范利君,陈学泰,等.富血小板血浆在神经病理性疼痛中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(8):1286-1292. [36] KAPOOR P, KUMAR S, BRAR BK, et al. Comparative Evaluation of Therapeutic Efficacy of Intralesional Injection of Triamcinolone Acetonide versus Intralesional Autologous Platelet-rich Plasma Injection in Alopecia Areata. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2020;13(2):103-111. [37] TAN J, FREY MP, KNEZEVIC S, et al. The Relationship Between Dermatologist- and Patient-Reported Acne Severity Measures and Treatment Recommendations. J Cutan Med Surg. 2015;19(5):464-469. |
| [1] | Zhong Jun, Wang Wen. Network meta-analysis of different anatomical repair strategies to improve chronic lateral ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1470-1476. |
| [2] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [3] | Feng Ruiqin, Han Na, Zhang Meng, Gu Xinyi, Zhang Fengshi. Combination of 1% platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 985-992. |
| [4] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [5] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [6] | Hu Zhixing, Li Qun, Yang Chao, Wang Xiaoxiao, Fang Luochangting, Hou Wuqiong, Lin Na, Chen Weiheng, Liu Chunfang, Lin Ya. Network meta-analysis of the modeling effects of different factors on rabbit models of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 976-984. |
| [7] | Yu Zhaoyu, Tan Lixin, Sun Kai, Lu Yao, Li Yong. Meta-analysis of cement-augmented pedicle screw for thoracolumbar degenerative diseases with osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 813-820. |
| [8] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [9] | Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Maimaitimin·Abulimiti, Tuerhongjiang·Abudurexiti. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of terlipatide and bisphosphate in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 639-645. |
| [10] | Bai Xiaotian, Chen Zhaoying, Song Yiling, Wang Ye, Liu Jingmin. Effect of minimalist shoes on foot muscle morphology: systematic evaluation and Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 646-650. |
| [11] | Wang Juan, Wang Ling, Zuo Huiwu, Zheng Cheng, Wang Guanglan, Chen Peng. Rehabilitative efficacy of kinesio taping following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 651-656. |
| [12] | Dong Kuan, Xu Chengli, Tian Jing, Xu Changchun. Effects of endurance training with blood flow restriction on aerobic capacity, lower limb muscle strength, and sports performance: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3766-3772. |
| [13] | Dai Xinyu, Yan Jihong, Hua Lingjun, Zheng Xiaohong. Resistance exercise improves body composition in overweight and obese people: an umbrella review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 267-271. |
| [14] | Li Chengming, Xue Dongling, Yang Xinyu, Xiao Chi, Cui Daping. Mechanism of Chinese medicine for promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis combined with platelet-rich plasma to improve steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 288-294. |
| [15] | Chang Wanpeng, Zhang Zhongwen, Yang Yulin, Zi Yang, Yang Mengqi, Du Bingyu, Wang Nan, Yu Shaohong. Efficacy of rehabilitation exoskeleton robots on post-stroke lower limb motor dysfunction: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 321-328. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||