Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (23): 3766-3772.doi: 10.12307/2024.398
Effects of endurance training with blood flow restriction on aerobic capacity, lower limb muscle strength, and sports performance: a Meta-analysis
Dong Kuan1, Xu Chengli2, Tian Jing2, Xu Changchun3
- 1School of Physical Education, Myongji University, Yongin 17113, South Korea; 2School of Physical Education, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China; 3Shandong Province Physical Training Centre, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-05-31Accepted:2023-07-15Online:2024-08-18Published:2023-09-14 -
Contact:Tian Jing, Master’s supervisor, Associate professor, School of Physical Education, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Dong Kuan, PhD candidate, School of Physical Education, Myongji University, Yongin 17113, South Korea
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dong Kuan, Xu Chengli, Tian Jing, Xu Changchun. Effects of endurance training with blood flow restriction on aerobic capacity, lower limb muscle strength, and sports performance: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3766-3772.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
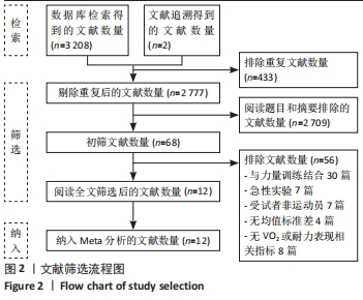
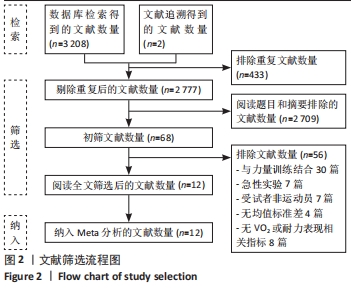
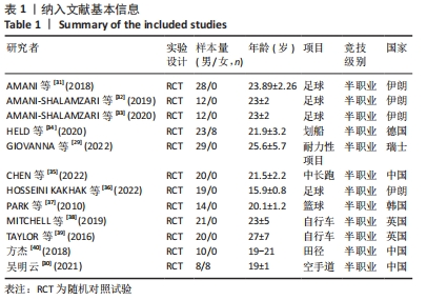
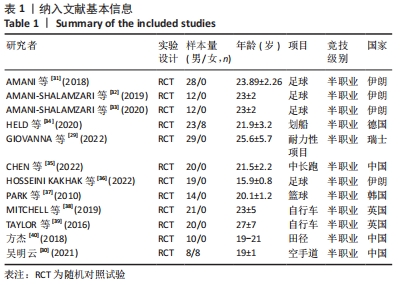
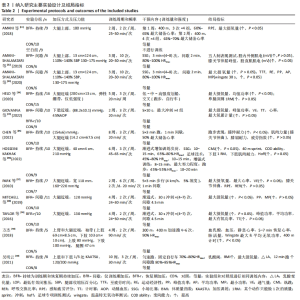
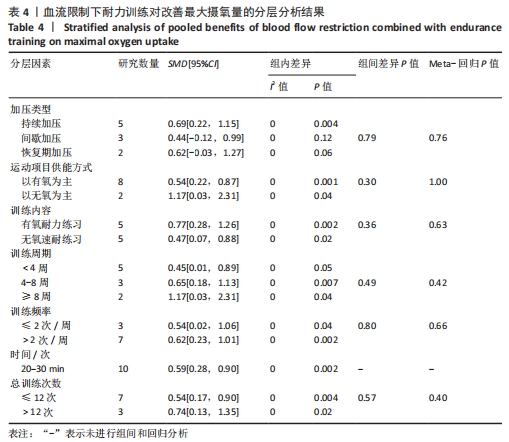
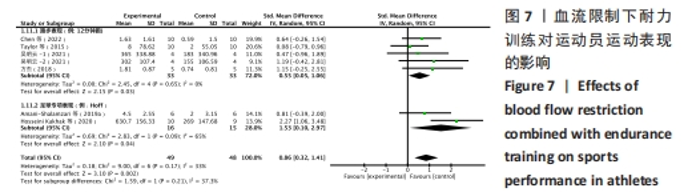
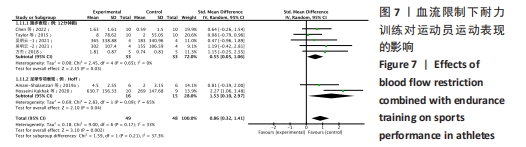
纳入研究中,仅含有3臂设计2份,其余均为双臂设计。持续加压、间歇加压和恢复期加压分别为8份、4份和2份。对照组均进行等量耐力练习,此外一项3臂设计试验中还含有空白对照组。训练内容以有氧练习为主7份,以无氧速度耐力练习为主7份。训练周期2-10周不等,频率2-6次/周不等。结局指标方面:最大摄氧量10份,运动表现7份,下肢肌力8份。1份研究未提供计时赛均值和标准差,见表2。 2.2 纳入研究的质量评价 按照PEDro量表,纳入研究的质量评价结果见表3。12项研究中,2项研究未明确描述随机化,1项研究报告中明确了盲法。2项研究被评定为5分,1项研究被评定为7分,9项研究被评定为6分,所以纳入的研究被评定为中高质量。"
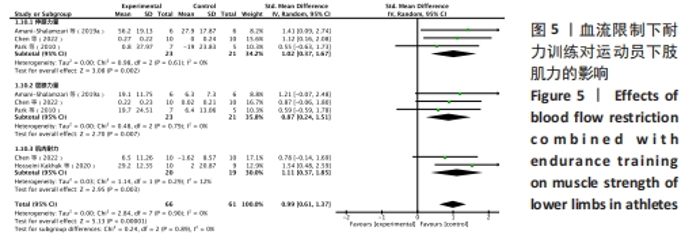
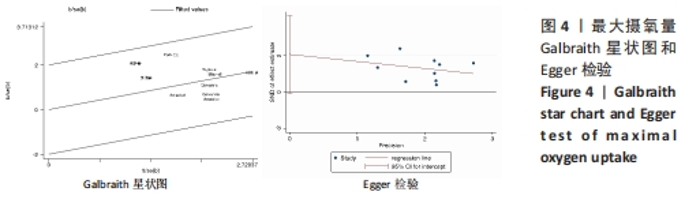
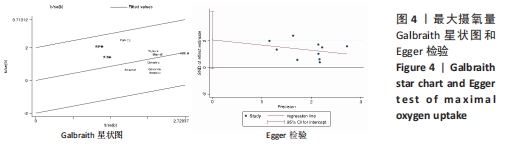
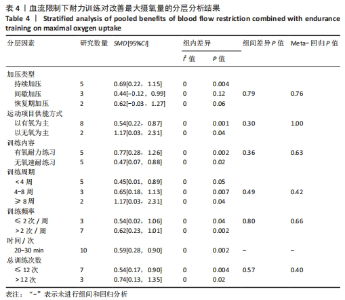
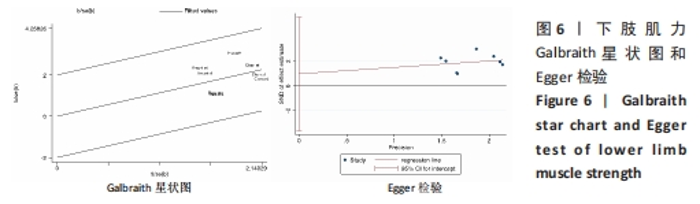
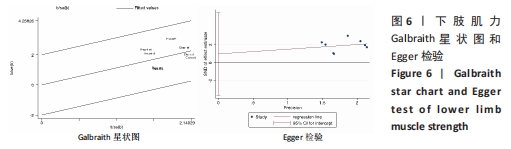
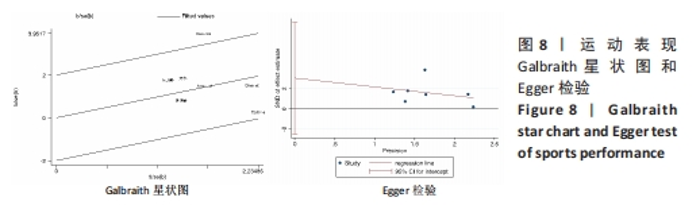
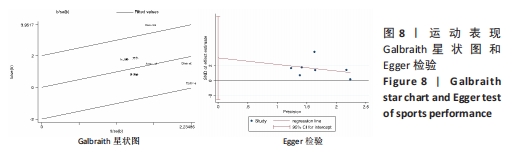
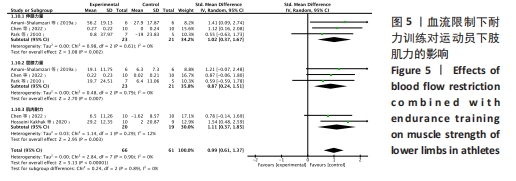
(2)将各训练因素作为协变量进行Meta回归,发现也均未对合并效应量造成影响(P > 0.05),见表4。 2.3.2 下肢肌力效应量的Meta分析结果及发表偏倚评价 共8份研究报告数据纳入分析[32,35-37]。Meta分析结果见图5,合并研究的总效应量及95%CI为0.99[0.61,1.37]。研究间不存在异质性,且具有统计学意义(I2=0,P < 0.05)。采用Galbraith星状图法,均落在平行线之间,同质性较好,见图6。同时Egger检验表明,纳入研究无明显发表偏倚(P > 0.05),见图6。亚组分析结果显示肌肉耐力提升效果最好(SMD=1.11;95%CI:0.37-1.85),其次为伸膝力量(SMD=1.02,95%CI:0.37-1.67)、屈膝力量(SMD=0.87,95%CI:0.24-1.51)。肌肉耐力分析结果显示存在较低的异质性。之后进行敏感性分析,剔除HOSSEINI KAKHAK等[36]研究后,合并研究总效应量及95%CI为0.91[0.51,1.32],无明显变化,故仍保留该研究合并分析。"
| [1] SATO Y. The history and future of KAATSU Training. Int J KAATSU Train Res. 2005;1(1):1-5. [2] DEPHILLIPO NN, KENNEDY MI, AMAN ZS, et al. The Role of Blood Flow Restriction Therapy Following Knee Surgery: Expert Opinion. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(8):2506-2510. [3] 魏佳,李博,杨威,等.血流限制训练的应用效果与作用机制[J].体育科学,2019,39(4): 71-80. [4] PIGNANELLI C, CHRISTIANSEN D, BURR JF. Blood flow restriction training and the high-performance athlete: science to application. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021;130(4):1163-1170. [5] SCOTT BR, SLATTERY KM, SCULLEY DV, et al. Hypoxia and resistance exercise: a comparison of localized and systemic methods. Sports Med. 2014;44(8):1037-1054. [6] YASUDA T, LOENNEKE JP, THIEBAUD RS, et al. Effects of blood flow restricted low-intensity concentric or eccentric training on muscle size and strength. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52843. [7] LOENNEKE JP, FAHS CA, ROSSOW LM, et al. The anabolic benefits of venous blood flow restriction training may be induced by muscle cell swelling. Med Hypotheses. 2012; 78(1):151-154. [8] 徐飞,王健.加压力量训练:释义及应用[J].体育科学,2013,33(12):71-80. [9] TAKARADA Y, NAKAMURA Y, ARUGA S, et al. Rapid increase in plasma growth hormone after low-intensity resistance exercise with vascular occlusion. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2000; 88(1):61-65. [10] FRY CS, GLYNN EL, DRUMMOND MJ, et al. Blood flow restriction exercise stimulates mTORC1 signaling and muscle protein synthesis in older men. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010;108(5):1199-1209. [11] COOK SB, CLARK BC, PLOUTZ-SNYDER LL. Effects of exercise load and blood-flow restriction on skeletal muscle function. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(10):1708-1713. [12] HORIUCHI M, ENDO J, THIJSSEN DH. Impact of ischemic preconditioning on functional sympatholysis during handgrip exercise in humans. Physiol Rep. 2015;3(2):e12304. [13] ENKO K, NAKAMURA K, YUNOKI K, et al. Intermittent arm ischemia induces vasodilatation of the contralateral upper limb. J Physiol Sci. 2011;61(6):507-513. [14] HUGHES L, ROSENBLATT B, HADDAD F, et al. Comparing the Effectiveness of Blood Flow Restriction and Traditional Heavy Load Resistance Training in the Post-Surgery Rehabilitation of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Patients: A UK National Health Service Randomised Controlled Trial. Sports Med. 2019;49(11):1787-1805. [15] INCOGNITO AV, BURR JF, MILLAR PJ. The Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning on Human Exercise Performance. Sports Med. 2016;46(4):531-544. [16] KILDUFF LP, FINN CV, BAKER JS, et al. Preconditioning strategies to enhance physical performance on the day of competition. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2013;8(6):677-681. [17] LOENNEKE JP, YOUNG KC, WILSON JM, et al. Rehabilitation of an osteochondral fracture using blood flow restricted exercise: a case review. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2013;17(1):42-45. [18] WORTMAN RJ, BROWN SM, SAVAGE-ELLIOTT I, et al. Blood Flow Restriction Training for Athletes: A Systematic Review. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(7):1938-1944. [19] 李志远,赵之光,王明波,等.4周加压训练对男子手球运动员身体成分和最大力量的影响[J].中国体育科 技,2019,55(5):37-43. [20] FERGUSON RA, MITCHELL EA, TAYLOR CW, et al. Blood-flow-restricted exercise: Strategies for enhancing muscle adaptation and performance in the endurance-trained athlete. Exp Physiol. 2021;106(4):837-860. [21] CASTILLA-LÓPEZ C, MOLINA-MULA J, ROMERO-FRANCO N. Blood flow restriction during training for improving the aerobic capacity and sport performance of trained athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Exerc Sci Fit. 2022;20(2):190-197. [22] SILVA JCG, DOMINGOS-GOMES JR, FREITAS EDS, et al. Physiological and Perceptual Responses to Aerobic Exercise With and Without Blood Flow Restriction. J Strength Cond Res. 2021;35(9):2479-2485. [23] ABE T, KEARNS CF, SATO Y. Muscle size and strength are increased following walk training with restricted venous blood flow from the leg muscle, Kaatsu-walk training. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006;100(5):1460-1466. [24] BENNETT H, SLATTERY F. Effects of Blood Flow Restriction Training on Aerobic Capacity and Performance: A Systematic Review. J Strength Cond Res. 2019;33(2):572-583. [25] TZVETKOV S.Indicators of effectiveness and economy in evaluation of functional working capability of elite athletes. Act Phys Educ Sport. 2017;7(1):95-99. [26] NUÑEZ J, SUAREZ-ARRONES L, DE HOYO M, et al. Strength Training in Professional Soccer: Effects on Short-sprint and Jump Performance. Int J Sports Med. 2022;43(6):485-495. [27] MOSELEY AM, HERBERT RD, SHERRINGTON C, et al. Evidence for physiotherapy practice: a survey of the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro). Aust J Physiother. 2002;48(1):43-49. [28] HOPKINS WG, MARSHALL SW, BATTERHAM AM, et al. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41(1):3-13. [29] GIOVANNA M, SOLSONA R, SANCHEZ AMJ, et al. Effects of short-term repeated sprint training in hypoxia or with blood flow restriction on response to exercise. J Physiol Anthropol. 2022;41(1):32. [30] 吴明云.加压有氧训练对空手道组手运动员有氧能力的影响[D].上海:上海体育学院, 2021. [31] AMANI AR, SADEGHI H, AFSHARNEZHAD T. Interval Training With Blood Flow Restriction On Aerobic Performance Among Young Soccer Players At Transition Phase. Monten J Sports Sci Med. 2018;7(2):5-10. [32] AMANI-SHALAMZARI S, FARHANI F, RAJABI H, et al. Blood Flow Restriction During Futsal Training Increases Muscle Activation and Strength. Front Physiol. 2019;10:614. [33] AMANI-SHALAMZARI S, SARIKHANI A, PATON C, et al. Occlusion Training During Specific Futsal Training Improves Aspects of Physiological and Physical Performance. J Sports Sci Med. 2020;19(2):374-382. [34] HELD S, BEHRINGER M, DONATH L. Low intensity rowing with blood flow restriction over 5 weeks increases V̇O2max in elite rowers: A randomized controlled trial. J Sci Med Sport. 2020;23(3):304-308. [35] CHEN YT, HSIEH YY, HO JY, et al. Running Training Combined With Blood Flow Restriction Increases Cardiopulmonary Function and Muscle Strength in Endurance Athletes. J Strength Cond Res. 2022;36(5):1228-1237. [36] HOSSEINI KAKHAK SA, KIANIGUL M, HAGHIGHI AH, et al. Performing Soccer-Specific Training With Blood Flow Restriction Enhances Physical Capacities in Youth Soccer Players. J Strength Cond Res. 2022;36(7):1972-1977. [37] PARK S, KIM JK, CHOI HM, et al. Increase in maximal oxygen uptake following 2-week walk training with blood flow occlusion in athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010;109(4):591-600. [38] MITCHELL EA, MARTIN NRW, TURNER MC, et al. The combined effect of sprint interval training and postexercise blood flow restriction on critical power, capillary growth, and mitochondrial proteins in trained cyclists. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(1):51-59. [39] TAYLOR CW, INGHAM SA, FERGUSON RA. Acute and chronic effect of sprint interval training combined with postexercise blood-flow restriction in trained individuals. Exp Physiol. 2016;101(1):143-154. [40] 方杰.加压血流阻滞训练对无氧耐力及400米跑运动成绩的影响研究[D].广州:广州体育学院,2018. [41] PATON CD, ADDIS SM, TAYLOR LA. The effects of muscle blood flow restriction during running training on measures of aerobic capacity and run time to exhaustion. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117(12):2579-2585. [42] AMANI-SHALAMZARI S, RAJABI S, RAJABI H, et al. Effects of Blood Flow Restriction and Exercise Intensity on Aerobic, Anaerobic, and Muscle Strength Adaptations in Physically Active Collegiate Women. Front Physiol. 2019; 10:810. [43] SLYSZ JT, BURR JF. Impact of 8 weeks of repeated ischemic preconditioning on running performance. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019;119(6): 1431-1437. [44] FARUP J, DE PAOLI F, BJERG K, et al. Blood flow restricted and traditional resistance training performed to fatigue produce equal muscle hypertrophy. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(6):754-763. [45] MANIMMANAKORN A, HAMLIN MJ, ROSS JJ, et al. Effects of low-load resistance training combined with blood flow restriction or hypoxia on muscle function and performance in netball athletes. J Sci Med Sport. 2013;16(4): 337-342. [46] ABE T, FUJITA S, NAKAJIMA T, et al. Effects of Low-Intensity Cycle Training with Restricted Leg Blood Flow on Thigh Muscle Volume and VO2MAX in Young Men. J Sports Sci Med. 2010;9(3):452-458. [47] MERTZ KH, REITELSEDER S, BECHSHOEFT R, et al. The effect of daily protein supplementation, with or without resistance training for 1 year, on muscle size, strength, and function in healthy older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;113(4):790-800. [48] RODRÍGUEZ-ROSELL D, FRANCO-MÁRQUEZ F, MORA-CUSTODIO R, et al. Effect of High-Speed Strength Training on Physical Performance in Young Soccer Players of Different Ages. J Strength Cond Res. 2017;31(9):2498-2508. [49] STEINER T, WEHRLIN JP. Does hemoglobin mass increase from age 16 to 21 and 28 in elite endurance athletes? Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(9):1735-1743. [50] KOMI PV, GOLLHOFER A. Stretch Reflexes Can Have an Important Role in Force Enhancement During SSC Exercise. J Appl Biomech.1997;13(4):451-460. [51] TAUBE W, LEUKEL C, GOLLHOFER A. How neurons make us jump: the neural control of stretch-shortening cycle movements. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2012;40(2):106-115. [52] CORMIE P, MCGUIGAN MR, NEWTON RU. Developing maximal neuromuscular power: part 2 - training considerations for improving maximal power production. Sports Med. 2011;41(2):125-146. [53] MARKOVIC G, MIKULIC P. Neuro-musculoskeletal and performance adaptations to lower-extremity plyometric training. Sports Med. 2010;40(10):859-895. [54] BOBBERT MF. Drop jumping as a training method for jumping ability. Sports Med. 1990; 9(1):7-22. [55] MALISOUX L, FRANCAUX M, NIELENS H, et al. Stretch-shortening cycle exercises: an effective training paradigm to enhance power output of human single muscle fibers. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006;100(3):771-779. [56] LAURSEN PB, SHING CM, PEAKE JM, et al. Influence of high-intensity interval training on adaptations in well-trained cyclists. J Strength Cond Res. 2005;19(3):527-533. [57] THOMAS K, GOODALL S, STONE M, et al. Central and peripheral fatigue in male cyclists after 4-, 20-, and 40-km time trials. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(3):537-546. [58] CHRISTIANSEN D, EIBYE KH, RASMUSSEN V, et al. Cycling with blood flow restriction improves performance and muscle K+ regulation and alters the effect of anti-oxidant infusion in humans. J Physiol. 2019;597(9):2421-2444. [59] GREEN H, DAHLY A, SHOEMAKER K, et al. Serial effects of high-resistance and prolonged endurance training on Na+-K+ pump concentration and enzymatic activities in human vastus lateralis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1999;165(2):177-184. [60] SUNDE A, STØREN O, BJERKAAS M, et al. Maximal strength training improves cycling economy in competitive cyclists. J Strength Cond Res. 2010;24(8):2157-2165. [61] HOFF J, GRAN A, HELGERUD J. Maximal strength training improves aerobic endurance performance. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2002; 12(5):288-295. [62] RØNNESTAD BR, HANSEN J, HOLLAN I, et al. Strength training improves performance and pedaling characteristics in elite cyclists. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(1):e89-98. [63] LOENNEKE JP, FAHS CA, ROSSOW LM, et al. Effects of cuff width on arterial occlusion: implications for blood flow restricted exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(8):2903-2912. [64] SIELJACKS P, KNUDSEN L, WERNBOM M, et al. Body position influences arterial occlusion pressure: implications for the standardization of pressure during blood flow restricted exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018;118(2):303-312. [65] 郜卫峰,冯鑫,顾大成.同期耐力与力量训练对长跑运动员跑步经济性及耐力表现相关指标影响的Meta分析[J].体育科学, 2019,39(9):68-81. |
| [1] | Zhong Jun, Wang Wen. Network meta-analysis of different anatomical repair strategies to improve chronic lateral ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1470-1476. |
| [2] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [3] | Zhang Zeyi, Yang Yimin, Li Wenyan, Zhang Meizhen. Effect of foot progression angle on lower extremity kinetics of knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 968-975. |
| [4] | Hu Zhixing, Li Qun, Yang Chao, Wang Xiaoxiao, Fang Luochangting, Hou Wuqiong, Lin Na, Chen Weiheng, Liu Chunfang, Lin Ya. Network meta-analysis of the modeling effects of different factors on rabbit models of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 976-984. |
| [5] | Yu Zhaoyu, Tan Lixin, Sun Kai, Lu Yao, Li Yong. Meta-analysis of cement-augmented pedicle screw for thoracolumbar degenerative diseases with osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 813-820. |
| [6] | Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Maimaitimin·Abulimiti, Tuerhongjiang·Abudurexiti. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of terlipatide and bisphosphate in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 639-645. |
| [7] | Bai Xiaotian, Chen Zhaoying, Song Yiling, Wang Ye, Liu Jingmin. Effect of minimalist shoes on foot muscle morphology: systematic evaluation and Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 646-650. |
| [8] | Wang Juan, Wang Ling, Zuo Huiwu, Zheng Cheng, Wang Guanglan, Chen Peng. Rehabilitative efficacy of kinesio taping following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 651-656. |
| [9] | Kong Jianda, Xie Yingao, Chen Shijuan, Zhu Lei. Blood flow restriction training interventions for sarcopenia in older adults: biological mechanisms and proposed application protocols [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3743-3750. |
| [10] | Qi Yuqing, Liu Xiaoran. Mechanisms of exercise-regulated telomere length and health promotion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3759-3765. |
| [11] | Xie Enli, Tao Huimin. Application trends of blood flow restriction training in clinical rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 258-262. |
| [12] | Chang Wanpeng, Zhang Zhongwen, Yang Yulin, Zi Yang, Yang Mengqi, Du Bingyu, Wang Nan, Yu Shaohong. Efficacy of rehabilitation exoskeleton robots on post-stroke lower limb motor dysfunction: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 321-328. |
| [13] | Zhang Guoxu, Zeng Jianbo, Li Jing, Xie Qijun, Zhou Guanbin, Guan Jianhao, Chen Wenchuang, Chen Haiyun. Meta-analysis of efficacy of orthopedic robot-assisted versus freehand percutaneous sacroiliac screw fixation for posterior pelvic ring fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2932-2938. |
| [14] | Wang Ke, Zhang Zeyi, Zhang Liwen, Zhang Meizhen. Biomechanics characteristics during sitting up in knee osteoarthritis patients of different ages: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2939-2946. |
| [15] | Zhang Yue, Guo Yingjie, Cheng Yang, Yang Tingting. Effect of blood flow restriction training on the fitness benefit of upper limb muscles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2248-2253. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||