Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (29): 4736-4744.doi: 10.12307/2023.486
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and mechanism by which long non-coding RNAs regulate subchondral bone homeostasis in knee osteoarthritis
Wei Zongbo1, Su Yunyu2, Zhang Xiaoyun1, Huang Wei1, Xu Hang1, Liu Rongfa1
- 1Ruikang Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Qinzhou First People’s Hospital, Qinzhou 535000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-07-21Accepted:2022-08-18Online:2023-10-18Published:2022-12-02 -
Contact:Su Yunyu, Chief physician, Qinzhou First People’s Hospital, Qinzhou 535000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wei Zongbo, Master candidate, Ruikang Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Guangxi Natural Science Foundation for the Youth, No. 2020GXNSFBA159053 (to ZXY); Huang Yourong TCM Master Training Project, No. [2022]6; Guangxi Key Clinical Specialty (Trauma Surgery) Construction Project, No. {2021}17
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Zongbo, Su Yunyu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Huang Wei, Xu Hang, Liu Rongfa. Role and mechanism by which long non-coding RNAs regulate subchondral bone homeostasis in knee osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4736-4744.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
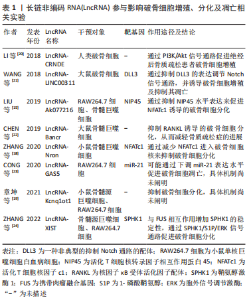
2.1 膝骨关节炎中软骨下骨的稳态破坏特点 软骨下骨是一种动态骨组织,主要存在于关节软骨下方,在正常情况下可随机械应力的变化及代谢的需求而改变,通过骨重塑维持所谓的骨稳态,即由成骨细胞和破骨细胞共同协调骨形成与骨吸收之间所达成的一种动态平衡[4]。因此,成骨细胞和破骨细胞在维持软骨下骨的稳态中发挥着关键作用。当成骨细胞功能缺陷或破骨细胞过度活跃时,骨重塑发生异常,骨形成与骨吸收的骨转换平衡发生变化,软骨下骨的骨稳态遭到破坏。然而,软骨下骨的骨异常重塑在膝骨关节炎的病理过程中表现并非一成不变。在膝骨关节炎发展初期,软骨下骨中的破骨细胞过度生成和骨吸收活性增强[5-6],骨重塑伴骨周转率增加,此时软骨下骨的骨量减少,呈现骨质疏松结构,软骨下骨板变薄,为维持正常生物力学特性,软骨下骨开始发生代偿性骨形成,同时伴骨异常高转换引起新生骨组织矿化不全;到膝骨关节炎晚期,以骨形成为主,骨量增加,软骨下骨板显著增厚[7],这也是骨端边缘骨赘形成的原因。此外,软骨下骨异常骨重塑会诱发异常的血管新生,血管直接侵入软骨下骨及软骨组织,同时伴随着周边炎症因子浸润,进一步破坏软骨和软骨下骨稳态。随着膝骨关节炎病程的进展,软骨下骨结构因稳态失衡发生改变,同时也会导致软骨完整性破坏及软骨基质退化,从而进一步恶化膝骨关节炎病变。 2.2 LncRNA对影响软骨下骨稳态各因素的调控 国外学者首次报道了LncRNA在骨关节炎患者软骨下骨中表达,研究显示共有2 816个LncRNAs在软骨下骨中表达良好,其中仅233个LncRNAs在膝骨关节炎软骨下骨中表达,进一步分析发现21个LncRNAs呈差异性表达[8],并指出LncRNA AC005165.1可作为膝骨关节炎软骨下骨调控的潜在治疗靶点。随着研究的不断深入,骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞与破骨细胞的增殖分化异常、血管新生以及炎症细胞因子浸润被认为是软骨下骨稳态失常的重要影响因素,而LncRNA在上述生物学过程中发挥着重要的调节作用。 2.2.1 LncRNA对破骨细胞的调控作用 破骨细胞是软骨下骨中唯一负责骨吸收的功能细胞,其活性异常会解耦软骨下骨中骨重塑的动态平衡[9],从而引发膝骨关节炎。BERTUGLIA等[10]在马腕骨关节炎中证实了软骨细胞核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)将破骨细胞大量募集到软骨下板,通过释放基质金属蛋白酶和组织蛋白酶K促进软骨下骨的退化。因此,软骨下骨中的破骨细胞可能是未来膝骨关节炎治疗的靶点。越来越多研究发现,LncRNA在破骨细胞分化到骨吸收的过程中起到表观遗传调节剂的作用,其在骨吸收过程中调节并参与了破骨细胞功能基因的转录。 目前,已有多个研究表明LncRNAs可通过直接或间接调控活性T细胞核因子c1(Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cell C1,NFATC1)来促进破骨细胞分化。NAFTc1在破骨细胞分化过程发挥了关键作用[11],其被RANKL激活从细胞质转移至细胞核中,并促进破骨细胞相关基因转录,例如TRAP、Ctsk、CTR、Oscar等,进而影响破骨细胞活性,发挥骨吸收作用。LEE等[12]微阵列分析鉴定水合尿酸钠诱导破骨细胞系RAW264.7分化过程中存在差异表达的LncRNA,发现LncRNA-Jak3表达显著上调;经更深入的研究发现,LncRNA-Jak3通过上调NFATc1促进了Ctsk的表达,从而增强水合尿酸钠诱导的破骨细胞分化能力。NFAT相互作用蛋白45(NFAT interacting protein of 45 k Da,NIP45)被认为是NFATc1上游的负反馈因子,通过抑制前者表达可促进后者诱导的破骨细胞分化和骨吸收[13-14]。LIU等[15]研究发现在去卵巢小鼠骨髓和脾脏组织中Lnc-AK077216和NFATc1过表达,而NIP45的表达下调;随后根据TRAP染色和qPCR验证显示,Lnc-AK077216的上调和下调分别促进和抑制破骨细胞分化和骨吸收,而NIP45的调控作用刚好与之相反。由此可见,此研究证实了NIP45与NFATc1存在负向调节关系,且Lnc-AK077216可能通过抑制NIP45表达来促进NFATc1诱导的破骨细胞分化。此外,LncRNA还能通过对miRNA的海绵吸附作用促进破骨细胞分化[16]。RANKL和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(macrophage colony-stimulating factor,M-SFC)是破骨细胞发生中的2个重要调控因子,一项研究将小鼠股骨分离出来的骨髓巨噬细胞与RANKL和M-CSF一起培养生成破骨细胞,通过对破骨细胞LncRNAs进行生物信息学分析,发现LncRNA MIRG和NFATc1水平具有高表达且呈正相关[17];进一步探索发现LncRNA MIRG通过靶向吸附miR-1897间接促进NFATc1的表达,从而正向调控破骨细胞分化。 LncRNA不仅能诱导破骨细胞增殖,还能抑制破骨细胞分化,从而抑制骨吸收。ZHANG等[18]通过对比过表达和敲除基因LncRNA Nron的两组小鼠模型后,发现LncRNA Nron与牙槽骨骨量丢失呈负相关,过表达LncRNA Nron通过减少NFATc1进入破骨细胞核来抑制破骨细胞分化,从而减弱牙槽骨丢失能力。章坤等[19]在骨髓巨噬细胞和RAW264.7细胞诱导破骨细胞过程中利用小干扰RNAs沉默了LncRNA Kcnq1ot1的表达,通过荧光实时定量PCR结果发现沉默LncRNA Kcnq1ot1的表达可促进破骨相关基因Ctsk和Oscar的表达;TRAP染色结果进一步证实LncRNA Kcnq1ot1显著抑制破骨细胞分化,虽然该实验未阐明具体机制,但指出LncRNA Kcnq1ot1有可能成为调控骨吸收作用的潜在靶点。 总而言之,LncRNA在破骨细胞增殖、分化及凋亡方面影响骨吸收的研究虽取得初步成效,但在调控软骨下骨中的破骨细胞具体机制尚不明确,缺少相关方面的研究,因此,后续研究可将上述潜在靶点的LncRNA作为调控软骨下骨中骨吸收作用来防治膝骨关节炎的研究重点。LncRNAs参与影响破骨细胞增殖、分化及凋亡相关实验汇总,见表1。"
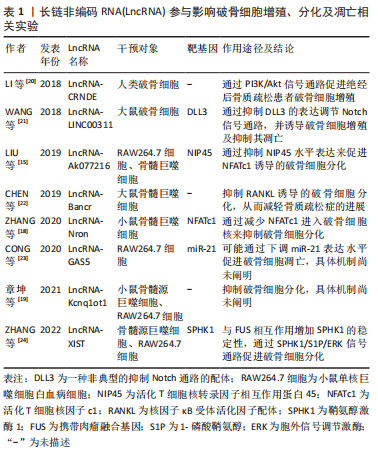

2.2.2 LncRNA对骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞的调控作用 骨髓间充质干细胞具有多向分化和无限增殖的潜能使其作为种子细胞广泛应用于骨组织工程领域。路冬冬等[25]应用3D生物打印技术将骨髓间充质干细胞装载到甲基丙烯酸酐化明胶(GelMA)水凝胶支架上,发现其能有效重现软骨下骨的骨小梁微结构,并促进软骨下骨修复。成骨细胞主要由骨髓间充质干细胞分化而成,是软骨下骨稳态中对抗骨吸收作用的骨形成细胞。越来越多的证据表明成骨细胞分化功能异常与膝骨关节炎发病机制密切相关,成骨细胞分化过程中多个基因的异位表达是导致软骨下骨异常骨重塑和矿化减少的原因。因此,软骨下骨异常骨形成主要与骨髓间充质干细胞及成骨细胞分化相关。近年多项研究报道,LncRNAs广泛参与表观遗传因子调节骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞介导的骨形成,通过总结LncRNA对骨髓间充质干细胞及成骨细胞分化的影响,有助于更好找到防治软骨下骨异常骨形成的潜在靶点。 有研究表明,miRNA可以通过下调成骨分化来阻止软骨下骨硬化。WANG等[26]通过微阵列表达谱检测膝骨关节炎患者血液,鉴定出48个miRNA差异表达,其中以miR-582-5p和miR-424-5p最为显著;随后通过qRT-RCR组织特异性验证,发现miR-582-5p和miR-424-5p在软骨下骨中的表达显著降低,提示这两种miRNA可能参与了软骨下骨硬化的发病机制;经进一步研究证实,miR-582-5p可靶向RUNX2来抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。因此,在膝骨关节炎软骨下骨中miR-582-5p的表达降低,抑制成骨分化的能力也随之相应减弱,最终导致软骨下骨硬化形成。ZHENG等[27]研究发现LncRNA SNHG5过表达可使miR-582-5p海绵化以上调RUNX3来促进人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,表明下调SNHG5/miR-582-5p/RUNX3反馈环可抑制软骨下骨异常骨形成,SNHG5可能是改善软骨下骨硬化的新靶点。LncRNA H19被认为在促进骨形成中发挥重要作用。一方面,LncRNA H19可通过调控下游miRNA介导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,如上调下游的miR-675表达[28],促使成骨相关基因RUNX2在miR-675/转化生长因子β1(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β1)和miR-675/Smad3/HDAC两条途径中上调,从而促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化。另一方面,LncRNA H19还可作为miRNA海绵介导成骨细胞基质矿化,如吸附并抑制miR-185-5p水平表达[29],进而使成骨分化增殖相关因子胰岛素样生长因子1(IGF1)和矿化相关基因碱性磷酸酶(ALP)、骨钙素(OCN)和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白上调,最终诱导体外成骨细胞矿化。此外,还有学者发现,组蛋白去乙酰化酶4(histone deacetylase 4,HDAC4)的表达上调会造成成骨细胞分化过程中关键转录因子RUNX2和Osterix表达下调,从而不利于成骨细胞形成[30]。一项体外研究显示,miRNA-29a可通过阻断HDAC4表达来促进软骨下骨中的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[31],且miRNA-29a已被证实为LncRNA H19下游靶基因[32],其被LncRNA H19海绵化后无法阻断HDAC4的表达,从而抑制了软骨下骨中骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,延缓了软骨下骨硬化进程。作者认为,虽然已初步探索LncRNA H19在体外调节成骨细胞,但还需进一步体内实验来验证LncRNA H19作为未来研究中抑制软骨下骨骨形成的潜在靶点。 ALNAJJAR等[2]发现LncRNA MALAT1在膝骨关节炎患者软骨下骨中高度表达,通过使用锁定核酸(LNA)对MALAT1靶向敲低进行了软骨下骨成骨细胞功能研究,利用RNAseq技术鉴定出成骨细胞转录组有155个转录物差异表达。然而,此次研究MALAT1敲低对骨保护素(OPG)、碱性磷酸酶等关键成骨基因没有任何影响,这与之前研究发现MALAT1能介导成骨细胞骨保护素的产生及促进成骨分化过程中碱性磷酸酶活性和矿化大相径庭[33]。作者认为,造成这种情况可能与选择不同部位的骨组织及骨组织本身病变程度有关,后续研究可针对现有不足进行更深入的了解。LncRNAs参与影响骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞增殖、分化及凋亡相关实验汇总,见表2。"
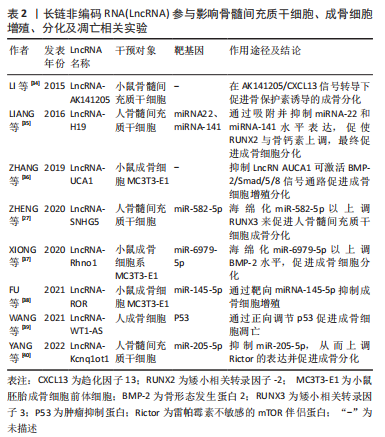
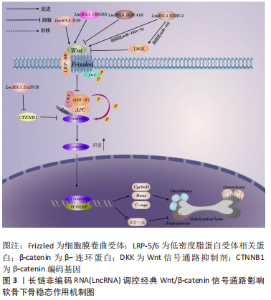
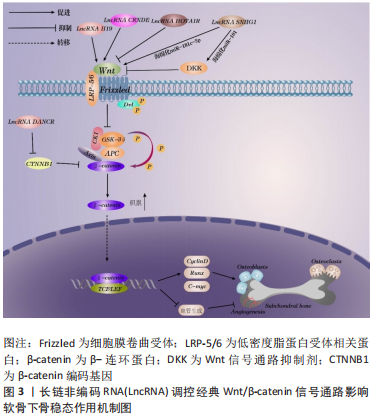
2.2.3 LncRNA对软骨下骨血管新生的潜在影响 在膝骨关节炎患者中,软骨下骨血管生成异常增多,血管进一步突破潮位线(钙化软骨和非钙化软骨层之间的边界)进入关节软骨是软骨下骨异常骨重塑的重要病理特征之一[41]。SU等[42]实验研究发现早期膝骨关节炎参与骨重塑的破骨细胞活性异常增加,导致过量分泌的血小板衍生生长因子BB(PDGF-BB)不仅刺激血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)过度生成[43-44],还可通过激活周细胞中的PDGF-B/PDGFR-β信号诱导软骨下骨异常血管生成,新生成的血管促使软骨下骨中类骨质胰岛形成,结构发生改变。由此可见,控制血管新生对维持软骨下骨的稳态及延缓疾病进展具有重要意义。VEGF被认为是血管生成的关键因素,大量研究已证明其可以调节肥大软骨的重塑、骨化和软骨下骨的血管侵袭[45]。LncRNA MEG3是位于人类染色体14q32.3上的一种母系遗传的印记基因,在促进血管生成中发挥重要的调控作用。SU等[46]研究发现在骨关节炎软骨中MEG3与 VEGF mRNA的表达呈负相关,表明骨关节炎软骨组织中增强的血管新成可能是因MEG3失活所致,而骨关节炎软骨中的血管是由软骨下骨异常骨重塑后血管侵入而成,故通过上调MEG3的表达可能对软骨下骨血管新生起抑制作用,但具体机制尚不明确。已有研究表明P53通过与VEGFA启动子上的转录因子SP1或E2F位点结合来负调控VEGF的转录[47],而MEG3能刺激p53介导的转录激活[48],表明MEG3表达下调可能导致p53活性降低和VEGFA转录增加。因此,推测通过P53途径上调LncRNA MEG3可抑制软骨和软骨下骨血管生成。综上所述,调控LncRNA MEG3有望成为软骨下骨血管新生的干预措施,但目前关于LncRNA与软骨下骨血管新生的相关文献报道少之又少,研究有待深入。 2.2.4 LncRNA调控细胞因子对膝骨关节炎软骨下骨的影响 研究表明,白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α等是膝骨关节炎发生、进展过程中重要的炎症细胞因子,与软骨下骨异常骨重建密切相关。膝骨关节炎软骨下骨中成骨细胞和破骨细胞通过释放多种蛋白酶及上述炎症因子刺激各种信号通路,例如Wnt/β-catenin、TGF-β1/骨形态发生蛋白(bone morphogenetic protein,BMP),促使基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)家族酶过表达,从而引起上层软骨细胞凋亡,软骨基质降解,受损的软骨和软骨基质进一步释放炎症细胞因子和破骨细胞刺激因子又可使软骨下骨的骨吸收增强。因此,调控炎症细胞因子是维持软骨下骨稳态平衡的重要措施。多效生长因子(pleiotrophin,PTN)受体主要分布在软骨下骨细胞中,有研究发现在骨关节炎Ahlback分级Ⅱ、Ⅲ度的患者中,软骨及软骨下骨的PTN表达显著增加[49], 表明PTN是软骨下骨潜在的重要靶点。内皮素1是血管内皮产生的一种损伤因子,其也参与到骨关节炎软骨下骨形成的过程中,并可诱导软骨细胞基质金属蛋白酶1、基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,降解软骨基质,进一步加重骨关节炎发展[50]。PAN等[51]研究证实,LncRNA MALAT1通过上调miR-19b抑制了小鼠软骨细胞中炎性因子白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,降低了炎症给软骨及软骨下骨带来的损伤,为膝骨关节炎的诊断和治疗提供了可能靶点。黑色素瘤细胞黏附分子(melanoma cell adhesion molecule,MCAM)在细胞生长、迁移和血管生成等生物过程中发挥着重要作用,MCAM的下调可导致人脐血来源间充质干细胞的成骨分化潜能降低。而有项研究表明,LncRNA NONHSAT119105.2受PTN影响可调节MCAM在内的多个靶基因,从而促进牙髓干细胞成骨分化,这揭示了LncRNA NONHSAT119105.2与软骨下骨中的PTN具有某种必然联系,为LncRNA下调PTN的表达来抑制软骨下骨硬化提供了理论依据[52]。LncRNA调控内皮素1促进血管生成在心肌肥厚、高血压等疾病已有研究报道[53],然而其在调控软骨下骨中的血管新生仍未有研究报道,这将是未来研究治疗膝骨关节炎的一个突破点。 2.3 LncRNA调控信号通路对影响软骨下骨稳态各因素的作用机制 近年来研究发现,软骨下骨的稳态失衡与信号通路调控异常存在密切的联系。根据相关实验研究表明,目前LncRNA在调控成骨细胞与破骨细胞分化、抑制炎症因子表达等过程中有多条信号通路参与,常见的信号通路以Wnt/β-catenin、TGF-β/BMPs为主,其他信号通路如磷脂酰肌醇激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(AKT)、基质细胞衍生因子1(stromal cell derived factor1,SDF-1)/CXCR4等也有报道。各种信号通路之间相互串扰,通过平衡骨形成与骨吸收,抑制炎症因子表达及血管生成,从而起到保护软骨下骨的作用。 2.3.1 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路是目前研究最为广泛且高度保守的一条经典信号通路,已有研究证实此通路水平改变影响软骨下骨破坏与重塑,并与骨赘形成相关。在经典途径中,Wnt蛋白配体首先由细胞膜表面的低密度脂蛋白相关蛋白5和6(low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6,LRP-5/6)介导与属于Frizzled(FZD)家族的7-跨膜区特异性受体结合成复合体,以促进Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活。而当胞外存在Wnt信号通路抑制剂DKK时,Wnt蛋白配体与其受体LRP和FZD结合受到抑制,此时Wnt/β-catenin信号通路处于关闭状态。当该通路激活后,LRP-5/6和FZD的膜内部分接受信号传导,引诱散乱蛋白(Dvl)磷酸化,从而使由糖原合成酶激酶GSK-3β、支架蛋白(Axin)、结肠腺瘤性息肉病蛋白(APC)、酪氨酸蛋白激酶Ⅰ以及β-catenin组成的降解复合体失活,游离β-catenin在胞质内大量堆积,最终进入胞核内与T细胞因子/淋巴样增强因子(TCF/LEF)结合成复合体,从而激活下游相关靶基因转录,进一步促进骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞增殖和成骨分化,这对改善早期软骨下骨过度骨吸收引起的骨量减少具有参考价值。WANG等[54]通过研究骨质疏松动物模型发现LncRNA DANCR过表达抑制编码β-catenin基因CTNNB1的表达,从而使Wnt/β-catenin通路失活,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。XIANG等[55]研究通过生物信息学和荧光素酶测定证实了LncRNA SNHG1与miR-101之间相互作用,即SNHG1海绵化miR-101以促进DKK1的表达,从而抑制Wnt信号,下游的RUNX2、骨钙素和骨保护素表达受到抑制,表明SNHG1/miR-101在Wnt/β-catenin信号通路上负调节骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。此外,YU等[56]发现LncRNA SNGH1还能通过调控下游抗血管生成靶标miR-181c-5p激活Wnt信号来抑制小鼠骨髓内皮细胞的血管生成、迁移和增殖。LncRNA HOTAIR在大鼠骨质疏松模型中亦被证明能抑制Wnt蛋白,从而使下游的β-catenin、CyclinD、C-myc 和Runx2的蛋白质水平下调,最终HOTAIR过表达的大鼠显示出更差的骨形态[57]。而LncRNA CRNDE和LncRNA H19都被证明通过刺激Wnt/β-catenin通路正向调节成骨分化,促进骨形成[35,58]。 由此可见,上述LncRNAs激活或是抑制 Wnt/β-catenin信号传导途径能对成骨细胞分化及骨形成、抑制血管新生等影响软骨下骨稳态等因素产生影响,对防治软骨下骨硬化具有重要意义,具体机制见图3。"

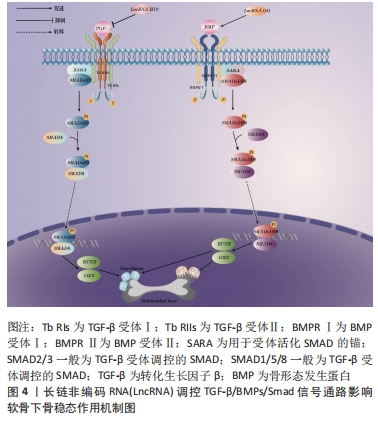
2.3.2 TGF-β/BMPs/Smad信号通路 TGF-β和BMPs是重要的骨生长因子,TGF-β/BMPs信号通路在成骨细胞和破骨细胞的分化增殖、骨及软骨下骨修复过程中发挥重要作用。实际上,TGF-β是个配体的超家族,其包括TGF-β、BMPs、Activin、Nodal等。以TGF-β配体为例,TGF-β与胞膜上2个TGF-βⅠ和Ⅱ型受体结合形成四聚体,Ⅰ型受体在结合后被Ⅱ型受体磷酸化激活,此时结合在受体活化的Smad锚定蛋白(The SMAD anchor for receptor activation,SARA)上的受体调控SMAD(receptor-regulated SMADs,R-SMAD)会停泊到被磷酸化的Ⅰ型受体上,接着Ⅰ型受体磷酸化R-SMAD,使之从SARA上脱落下来;游离的R-SMAD结合到辅助结合SMAD(cosSMAD)上形成二聚体,最终二聚体进入胞核内协同其他因子激活或抑制下游相关靶基因转录与表达,对相关骨病起到调控作用。HUANG等[59]研究发现LncRNA H19与其编码衍生的miR-675通过抑制TGF-β表达来阻断Smad3磷酸化,进而阻止了Smad3磷酸化后募集的HDAC4/5与RUNX2启动子区竞争性结合,从而使RUNX2得以正常转录调控成骨相关基因骨钙素的表达,发挥成骨分化作用。SHEN等[60]发现LncRNA OG在异质核核糖核蛋白hnRNPK调控下能够促进BMP家族蛋白BMP-2、BMP-4、BMP-6的表达并显著影响 Smad1/5/8 磷酸化水平,进而提高下游RUNX2、骨钙素水平,促进了小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。由此可见,LncRNA H19和LncRNA OG都通过介导TGF-β/BMPs/Smad信号通路促进骨形成,通过沉默上述两种LncRNA有可能抑制软骨下骨板增厚、硬化,为平衡晚期膝骨关节炎软骨下骨稳态提供新思路,具体机制见图4。"
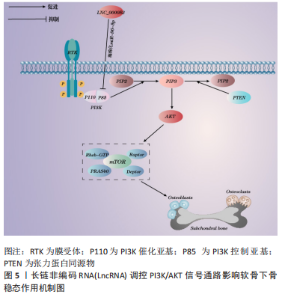
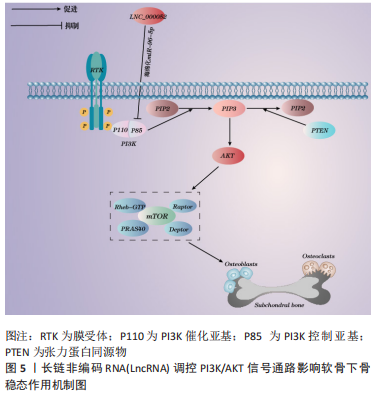
2.3.3 PI3K/AKT信号通路 PI3K/AKT通路广泛存在于多种组织炎症反应、细胞增殖、分化和凋亡过程中。 PI3K/AKT信号通路上的膜受体RTK结合生长因子后自动磷酸化激活PI3K,其又促进胞膜上的磷脂酰肌醇4,5(phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate,PIP2)转化成第二信使磷脂酰肌醇3,4,5-三磷酸(phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-bisphosphate,PIP3),进一步激活AKT。AKT在信号传导下激活下游效应因子mTORC,最终调节并激活更多的下游激酶工作,影响细胞的增殖、分化和代谢,从而对相关骨病起到调控作用。LIN等[61]研究发现,PI3K/AKT信号通路在骨性关节炎小鼠模型中被显著激活,这与小鼠内侧半月板失稳后胫骨软骨下骨异常骨形成有关,通过阻断此通路能够阻止异常骨形成和减轻软骨下骨及软骨的退变。林创鑫[62]通过切断小鼠膝关节内侧副韧带和内侧半月板胫骨韧带构建了内侧半月板的失稳骨关节炎模型,4周后,发现膝关节软骨下骨PI3K/AKT信号通路活化,进而提高了软骨下骨成骨细胞增殖和分化能力,软骨下骨骨量异常增多,骨质硬化;因此,可以推测出膝关节软骨下骨骨量增多、骨硬化是因PI3K/AKT信号通路活化促进成骨细胞增殖和分化导致的,通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路活化可阻止软骨下骨硬化,从而延缓膝骨关节炎发病进程。另有一项研究发现了一种新的LncRNA,即LNC_000052,敲除此基因后可促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、迁移和成骨,并抑制细胞凋亡;通过进一步研究发现,LNC_000052通过海绵吸附miR-96-5p来下调下游靶点PIK3R1(p85α)的表达,从而抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路,抑制成骨分化[63]。由此可见,促进LNC_000052在PI3K/AKT信号通路上的表达可能会是防治软骨下骨硬化的潜在靶点。具体机制见图5。"
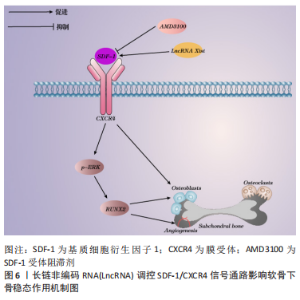
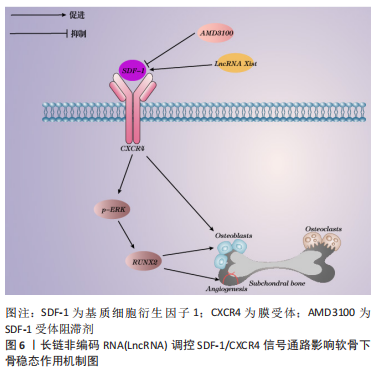
2.3.4 SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路 SDF-1又称趋化因子2(CXCL12),其广泛参与了对细胞外基质、炎症因子及软骨下骨稳态的调控,SDF-1还可以激活同源CXC受体CXCR4促进成骨细胞增殖分化,在骨关节炎中发挥重要作用。QIN等[64]研究通过显微外科技术横断前交叉韧带来构建ACLT小鼠模型,与正常组相比,发现模型小鼠胫骨软骨下骨中SDF-1高表达,高水平的SDF-1显著诱导骨髓间充质干细胞迁移,并通过上调p-ERK水平促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化和H血管内皮标志物CD31/Emcn显著增加,导致软骨下骨异常增多的骨形成和血管生成;随后使用SDF-1受体阻滞剂AMD3100,发现软骨下骨中RUNX2水平降低,TRAP阳性破骨细胞数量降至正常,血管生成减少,表明抑SDF-1受体阻滞剂制SDF-1/CXCR4轴可减少骨髓间充质干细胞募集、成骨分化和骨吸收,使软骨下骨异常成骨正常化及减少异常血管生成。因此,SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路活化是软骨下骨稳态失衡的重要因素。段亚妮等[65]研究发现LncRNA Xist通过下调SDF-1/CXCR4的表达,抑制了大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖、迁移能力,其机制可能是通过抑制膜受体CXCR4的表达来实现,不足的是该实验未进行过表达实验对比,对骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移能力没有在体外模拟缺氧环境下进行,缺乏准确性,有待进一步的研究。具体机制见图6。"
| [1] ZHOU J, ZHONG P, LIAO Y, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates subchondral bone deterioration and inhibits cartilage degeneration in ovariectomised rats. Acupunct Med. 2018;36(1):37-43. [2] ALNAJJAR FA, SHARMA-Oates A, WIJESINGHE SN, et al. The Expression and Function of Metastases Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript-1 Long Non-Coding RNA in Subchondral Bone and Osteoblasts from Patients with Osteoarthritis. Cells. 2021;10(4):786. [3] WANG J, SUN Y, LIU J, et al. Roles of long non coding RNA in osteoarthritis (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(1):133. [4] GOLDRIN MB, GOLDRING SR. Articular cartilage and subchondral bone in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192: 230-237. [5] CABAHUG-ZUCKEERMAN P, FRIKHA-BENAYDE D, MAJESKA RJ, et al. Osteocyte Apoptosis Caused by Hindlimb Unloading is Required to Trigger Osteocyte RANKL Production and Subsequent Resorption of Cortical and Trabecular Bone in Mice Femurs. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(7):1356-1365. [6] PLOTKIN LI, GORTAZAR AR, DAVIS HM, et al. Inhibition of osteocyte apoptosis prevents the increase in osteocytic receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL) but does not stop bone resorption or the loss of bone induced by unloading. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(31):18934-18942. [7] JAKAITE L, SCHETININ V, HLADUVKA J, et al. Deep learning for early detection of pathological changes in X-ray bone microstructures: case of osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):2294. [8] TUERLINGS M, VAN HOOLWERFF M, VAN BOKKUM JM, et al. Long non-coding RNA expression profiling of subchondral bone reveals AC005165.1 modifying FRZB expression during osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022;61(7):3023-3032. [9] IKEBUCHI Y, AOKI S, HONMA M, et al. Coupling of bone resorption and formation by RANKL reverse signalling. Nature. 2018;561(7722):195-200. [10] BERTUGLIA A, LACOURT M, GIRARD C, et al. Osteoclasts are recruited to the subchondral bone in naturally occurring post-traumatic equine carpal osteoarthritis and may contribute to cartilage degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(3):555-566. [11] TAKAYANAGI H, KIM S, KOGA T,et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002;3(6):889-901. [12] LEE CP, HUANG YN, NITHIYANANTHAM S, et al. LncRNA-Jak3:Jak3 coexpressed pattern regulates monosodium urate crystal-induced osteoclast differentiation through Nfatc1/Ctsk expression. Environ Toxicol. 2019;34(2):179-187. [13] BRYCE PJ, OYOSHI MK, KAWAMOTO S, et al. TRAF1 regulates Th2 differentiation, allergic inflammation and nuclear localization of the Th2 transcription factor, NIP45. Int Immunol. 2006;18(1):101-111. [14] SHANMUGARAJAN S, HAYCRAFT CJ, REDDY SV, et al. NIP45 negatively regulates RANK ligand induced osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(4):1274-1281. [15] LIU C, CAO Z, BAI Y, et al. LncRNA AK077216 promotes RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via NFATc1 by inhibition of NIP45. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(2):1606-1617. [16] HANSEN TB, JENSEN TI, CLAUSEN BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384-388. [17] LING L, HU HL, LIU KY, et al. Long noncoding RNA MIRG induces osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in osteoporosis through negative regulation of miR-1897. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 23(23):10195-10203. [18] ZHANG R, LI J, LI G, et al. LncRNA Nron regulates osteoclastogenesis during orthodontic bone resorption. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):14. [19] 章坤,时哲敏,任怡,等.长链非编码RNA Kcnqlot1促进成骨细胞分化和抑制破骨细胞分化[J].南方医科大学学报,2021,41(1):31-38. [20] LI W, ZHU HM, XU HD, et al. CRNDE impacts the proliferation of osteoclast by estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(18):5815-5821. [21] WANG Y, LUO TB, LIU L, et al. LncRNA LINC00311 Promotes the Proliferation and Differentiation of Osteoclasts in Osteoporotic Rats Through the Notch Signaling Pathway by Targeting DLL3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(6):2291-2306. [22] CHEN RS, ZHANG XB, ZHU XT, et al. LncRNA Bmncr alleviates the progression of osteoporosis by inhibiting RANML-induced osteoclast differentiation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(21):9199-9206. [23] CONG C, TIAN J, GAO T, et al. lncRNA GAS5 Is Upregulated in Osteoporosis and Downregulates miR-21 to Promote Apoptosis of Osteoclasts. Clin Interv Aging. 2020;15:1163-1169. [24] ZHANG DW, WANG HG, ZHANG KB, et al. LncRNA XIST facilitates S1P-mediated osteoclast differentiation via interacting with FUS. J Bone Miner Metab. 2022;40(2):240-250. [25] 路冬冬,朱天峰,张一健,等.3D生物打印甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶支架促进软骨下骨缺损的修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(34):5454-5460. [26] WANG P, DONG R, WANG B, et al. Genome-wide microRNA screening reveals miR-582-5p as a mesenchymal stem cell-specific microRNA in subchondral bone of the human knee joint. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(12):21877-21888. [27] ZHENG J, GUO H, QIN Y, et al. SNHG5/miR-582-5p/RUNX3 feedback loop regulates osteogenic differentiation and apoptosis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2020. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29527. [28] HUANG G, KANG Y, HUANG Z, et al. Identification and Characterization of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(3):1037-1050. [29] WU Y, JIANG Y, LIU Q, et al. lncRNA H19 promotes matrix mineralization through up-regulating IGF1 by sponging miR-185-5p in osteoblasts. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1):48. [30] ZHU J, SHIMIZU E, ZHANG X, et al. EGFR signaling suppresses osteoblast differentiation and inhibits expression of master osteoblastic transcription factors Runx2 and Osterix. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(7): 1749-1760. [31] LIAN WS, WU RW, LEE MS, et al. Subchondral mesenchymal stem cells from osteoarthritic knees display high osteogenic differentiation capacity through microRNA-29a regulation of HDAC4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017;95(12):1327-1340. [32] YANG Q, YAO Y, ZHAO D, et al. LncRNA H19 secreted by umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells through microRNA-29a-3p/FOS axis for central sensitization of pain in advanced osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(3):1245-1256. [33] XIAO X, ZHOU T, GUO S, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 sponges miR-204 to promote osteoblast differentiation of human aortic valve interstitial cells through up-regulating Smad4. Int J Cardiol. 2017;243:404-412. [34] LI H, ZHANG Z, CHEN Z, et al. Osteogenic growth peptide promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells mediated by LncRNA AK141205-induced upregulation of CXCL13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;466(1):82-88. [35] LIANG WC, FU WM, WANG YB, et al. H19 activates Wnt signaling and promotes osteoblast differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20121. [36] ZHANG RF, LIU JW, YU SP, et al. LncRNA UCA1 affects osteoblast proliferation and differentiation by regulating BMP-2 expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(16):6774-6782. [37] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YAN C, et al. The lncRNA Rhno1/miR-6979-5p/BMP2 Axis Modulates Osteoblast Differentiation. Int J Biol Sci. 2020; 16(9):1604-1615. [38] FU Y, HU X, GAO Y, et al. LncRNA ROR/miR-145-5p axis modulates the osteoblasts proliferation and apoptosis in osteoporosis. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):7714-7723. [39] WANG C, XIE Q, SUN W, et al. lncRNA WT1-AS is upregulated in osteoporosis and regulates the apoptosis of osteoblasts by interacting with p53. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(1):734. [40] YANG JJ, PENG WX, ZHANG MB. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes osteogenic differentiation via miR-205-5p/RICTOR axis. Exp Cell Res. 2022;415(1):113119. [41] BURR DB, GALLANT MA. Bone remodelling in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(11):665-673. [42] SU W, LIU G, LIU X, et al. Angiogenesis stimulated by elevated PDGF-BB in subchondral bone contributes to osteoarthritis development. JCI Insight. 2020;5(8):e135446. [43] XIE H, CUI Z, WANG L, et al. PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nat Med. 2014;20(11):1270-1278. [44] SUFEN G, XIANGHONG Y, YONGXIA C, et al. bFGF and PDGF-BB have a synergistic effect on the proliferation, migration and VEGF release of endothelial progenitor cells. Cell Biol Int. 2011;35(5):545-551. [45] GERBER HP, VU TH, RYAN AM, et al. VEGF couples hypertrophic cartilage remodeling, ossification and angiogenesis during endochondral bone formation. Nat Med. 1999;5(6):623-628. [46] SU W, XIE W, SHANG Q, et al. The Long Noncoding RNA MEG3 Is Downregulated and Inversely Associated with VEGF Levels in Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:356893. [47] FARHANG GHAHREMANI M, GOOSSENS S, NITTNER D, et al. p53 promotes VEGF expression and angiogenesis in the absence of an intact p21-Rb pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20(7):888-897. [48] ZHOU Y, ZHONG Y, WANG Y, et al. Activation of p53 by MEG3 non-coding RNA. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(34):24731-24742. [49] KASPIRIS A, MIKELIS C, HEROULT M, et al. Expression of the growth factor pleiotrophin and its receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta in the serum, cartilage and subchondral bone of patients with osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2013;80(4):407-413. [50] SIN A, TANG W, WEN CY, et al. The emerging role of endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of subchondral bone disturbance and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;3(4):516-524. [51] PAN L, LIU D, ZHAO L, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury by upregulating microRNA-19b in murine chondrogenic ATDC5 cells. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(12):10165-10175. [52] JIN L, GAO F, ZHANG L, et al. Pleiotropin enhances the osteo/dentinogenic differentiation potential of dental pulp stem cells. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(5):495-507. [53] ZHUO X, WU Y, YANG Y, et al. LncRNA AK094457 promotes AngII-mediated hypertension and endothelial dysfunction through suppressing of activation of PPARγ. Life Sci. 2019;233:116745. [54] WANG CG, HU YH, SU SL, et al. LncRNA DANCR and miR-320a suppressed osteogenic differentiation in osteoporosis by directly inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp Mol Med. 2020; 52(8):1310-1325. [55] XIANG J, FU HQ, XU Z, et al. lncRNA SNHG1 attenuates osteogenic differentiation via the miR 101/DKK1 axis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(5):3715-3722. [56] YU X, RONG PZ, SONG MS, et al. lncRNA SNHG1 induced by SP1 regulates bone remodeling and angiogenesis via sponging miR-181c-5p and modulating SFRP1/Wnt signaling pathway. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):141. [57] SHEN JJ, ZHANG CH, CHEN ZW, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR inhibited osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(17):7232-7246. [58] DING Q, MO F, CAI X, et al. LncRNA CRNDE is activated by SP1 and promotes osteosarcoma proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(5-6):3358-3371. [59] HUANG Y, ZHENG Y, JIA L, et al. Long Noncoding RNA H19 Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation Via TGF-β1/Smad3/HDAC Signaling Pathway by Deriving miR-675. Stem Cells. 2015;33(12):3481-3492. [60] SHEN H. LncRNA-OG Promotes the Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Under the Regulation of hnRNPK. Stem Cells. 2019;37(2):270-283. [61] LIN C, SHAO Y, ZENG C, et al. Blocking PI3K/AKT signaling inhibits bone sclerosis in subchondral bone and attenuates post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(8):6135-6147. [62] 林创鑫. 软骨下骨PI3K/AKT/mTORC1信号通路活性在骨关炎发病中的作用及机制研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2018. [63] LI M, CONG R, YANG L, et al. A novel lncRNA LNC_000052 leads to the dysfunction of osteoporotic BMSCs via the miR-96-5p-PIK3R1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):795. [64] QIN H, ZHAO X, HU YJ, et al. Inhibition of SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis to Alleviate Abnormal Bone Formation and Angiogenesis Could Improve the Subchondral Bone Microenvironment in Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8852574. [65] 段亚妮,木拉提·阿比来列提,朱雁秋,等.LncRNA Xist通过调控SDF-1/CXCR4轴促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖与迁移[J].中山大学学报(医学版),2020,41(1):37-43. |
| [1] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [2] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [3] | Long Guiyue, Li Dongdong, Liao Hongbing. Calcium phosphate cement/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) degradation products promote osteoclast differentiation of mouse monocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1193-1198. |
| [4] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [5] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [6] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [7] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [8] | Long Yanming, Xie Mengsheng, Huang Jiajie, Xue Wenli, Rong Hui, Li Xiaojie. Casein kinase 2-interaction protein-1 regulates the osteogenic ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 878-882. |
| [9] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [10] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [11] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [12] | Hu Xinming, Qiao Yanhua, Wang Xiaofan, Li Linyu, Zhao Bing. Mechanism of long non-coding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 involved in pelvic organ prolapse [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 669-675. |
| [13] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [14] | Shao Zichen, Li Huanan, Gu Bing, Zhang Xiaoyun, Sun Weikang, Liu Yongqian, Gan Bin. MicroRNA, long non-coding RNA and circular RNA mediate the mechanism of decreasing uric acid, anti-inflammation and regulating bone metabolism in gout [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 765-771. |
| [15] | Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 787-792. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||