Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (14): 2222-2228.doi: 10.12307/2023.430
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and application of melatonin in prevention and treatment of osteoporosis
Yan Liyan, Han Xiaonan, Kou Hongwei, Shang Guowei, Leng Zikuan, Liu Hongjian, Cheng Tian
- Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-06-01Accepted:2022-07-18Online:2023-05-18Published:2022-09-30 -
Contact:Cheng Tian, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Yan Liyan, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Province Health Commission Joint Youth Project, No. SB201902001 (to CT); Henan Provincial Department of Human Resources and Social Affairs Independent Project for Overseas Students, No. 2020034 (to CT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yan Liyan, Han Xiaonan, Kou Hongwei, Shang Guowei, Leng Zikuan, Liu Hongjian, Cheng Tian. Role and application of melatonin in prevention and treatment of osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2222-2228.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
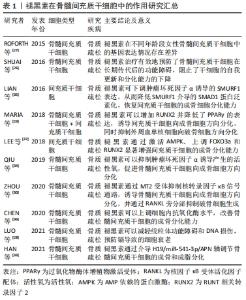
2.1 褪黑素的受体及其作用特点 目前为止,在哺乳动物中鉴定出了以下几种褪黑素受体:MT1(Mel1a),MT2(Mel1b)以及核结合位点RORα和RZR[18]。褪黑素受体最初于1994年在非洲爪蟾中发现,最初命名为Mel1a和Mel1b[14-15],后根据IUPHAR官方命名法改为MT1和MT2。人类MT1由350个氨基酸组成,MT2由362个氨基酸组成,总体氨基酸同源性为55%,跨膜结构域内的同源性为70%[19]。 MT1和MT2均观察到侧向配体的存在,在其他的亲脂性G蛋白偶联受体中也观察到类似的侧向配体结构,这可能是褪黑素容易穿过生物膜的原因[20]。MT1受体介导褪黑素调节昼夜节律的功能,机制为通过激活上交叉核和边缘系统区域中的MT1受体,减少神经元放电[21-22]。在MT1受体敲除小鼠中,昼夜节律对TREK-1通道的调控作用消失[23]。MT2受体可能在调节组织损伤后氧化应激反应中发挥一定作用。LI等[24]报道了褪黑素通过激活MT2受体,从而降低缺血性脑卒中小鼠的Nox2和Nox4的表达,降低活性氧水平,减轻炎症反应。 2.2 褪黑素治疗骨质疏松症细胞水平的研究 2.2.1 褪黑素对骨髓间充质干细胞的调控作用 骨髓间充质干细胞是一种多能干细胞,可以向成骨细胞、脂肪细胞、软骨细胞等多种细胞分化,在组织再生和疾病治疗方面有巨大的应用潜力。 细胞衰老以不可逆的细胞周期阻滞为特征,是骨量丢失的一个关键病理因素[25]。在骨髓间充质干细胞的长期体外传代中,可出现干细胞性缺失,这一现象限制了干细胞的应用。SHUAI等[26]在干细胞的体外培养中使用褪黑素,结果表明褪黑素对干细胞的集落形成和增殖没有影响,干细胞在体外培养15代后,仍然表现出良好的自我更新和分化能力。在一项针对年轻女性(平均28.7岁)和老年女性(平均73.3岁)的骨髓间充质干细胞的基因表达分析中,RNA测序结果鉴定出褪黑素、雷帕霉素信号通路、蛋白合成及降解的表达水平之间存在显著差异,这表明褪黑素可能在干细胞的衰老中发挥相应的生物学效应[27]。另外,流行病学表明,镉作为一种重金属毒性物质,可以增加骨质疏松症和自发性骨折的风险。LUO等[28]研究发现镉通过激活核转录因子κB信号通路,诱导骨髓间充质干细胞衰老,产生衰老相关分泌表型细胞,引起细胞周期阻滞和p21/p53/p16蛋白表达上调、线粒体形态不规则排列并出现线性结构,最终导致细胞质量下降伴功能障碍。但是,在褪黑素预处理后可以有效恢复线粒体形态和功能。 成骨细胞的骨形成和破骨细胞的骨吸收之间的平衡在整个生命周期维持骨骼质量中起着至关重要的作用。在骨老化过程中,间充质干细胞向成骨细胞的分化减少,骨髓脂肪生成逐渐增加。MARIA等[29]在间充质干细胞和单核细胞共培养模型中加入褪黑素,发现褪黑素可以增加RUNX2的表达,抑制过氧化物酶体增殖剂激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors,PPARγ)和核因子κ B受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand,RANKL)的表达,提示褪黑素可以调控间充质干细胞的分化方向,促进干细胞向成骨细胞分化,抑制其向脂肪细胞分化。另一项研究发现生理浓度的褪黑素即可促进干细胞的成骨分化。但是,在使用慢病毒转染敲除MT1和MT2受体后,这一成骨作用减弱,褪黑素受体下游的核转录因子κB信号通路被激活,RANKL分泌增加,进而促进破骨细胞形成,导致骨稳态失衡[30]。 LncRNA H19是LncRNA家族的一员,研究表明上调H19可通过miR-149促进基质细胞衍生因子1促进骨髓间质干细胞的成骨分化[31]。此外,H19通过调控miR-1405p/SATB2轴增强骨髓间质干细胞的成骨分化[32]。在另一研究中,褪黑素过表达H19促进褪黑素介导的骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨分化,抑制成脂分化,而下调H19或过表达miR-541-3p则相反。此外,褪黑素可以激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,降低骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化,促进成骨分化,这一效应可被MT2选择性抑制剂4-P-PDOT逆转[33]。 骨质疏松患者的骨髓间质干细胞存在骨生成减少和氧化应激增加的现象,肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的活性氧累积可显著抑制骨髓间质干细胞的成骨分化,进而导致骨代谢失衡,最终导致骨质疏松症。QIU等[34]发现褪黑素可以抑制p65蛋白的磷酸化,阻断IkBα蛋白的降解,上调抗氧化酶的表达,进而拮抗肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的骨髓间质干细胞的成骨抑制作用。CHEN等[36]从骨质疏松大鼠中分离出骨髓间质干细胞,使用褪黑素处理后基质矿化水平和成骨特异性基因表达增加,同时,细胞内抗氧化酶如超氧化物歧化酶2、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶1显著上调。AMP依赖的蛋白激酶(Adenosine 5‘-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase,AMPK)可保护细胞线粒体,抑制内质网氧化应激反应,FOXO3a和RUNX2是氧化应激和成骨表型之间联系的主要因子[37]。 一方面,褪黑素可以有效维持干细胞的活性,在干细胞多次增殖传代后仍具有良好的自我更新能力,从而避免因细胞衰老导致的骨量丢失。另一方面,褪黑素可以通过抑制PPARγ和RANKL的表达、调控SATB2轴等多种方式增强干细胞的成骨分化,抑制其向脂肪细胞和破骨细胞方向分化。褪黑素在骨髓间充质干细胞中的作用研究汇总见表1。 "
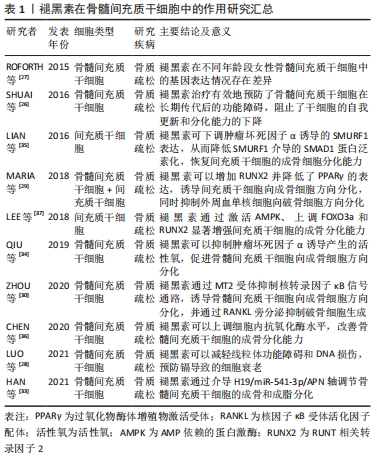
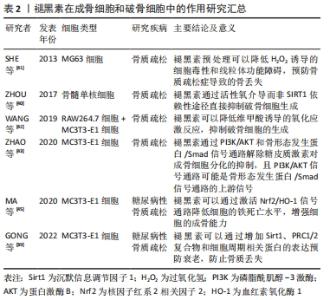
2.2.2 褪黑素对成骨细胞、破骨细胞的调控作用 破骨细胞介导的骨吸收和成骨细胞介导的骨形成维持骨转换的动态平衡,修复骨组织细小裂缝,愈合骨折,形成正常骨骼。 Sirt1是一种NAD+依赖的与衰老密切相关的酶,能够阻止葡萄糖诱导的内皮细胞衰老[38]。GONG等[39]使用褪黑素处理高糖环境中培养的MC3T3-E1细胞,发现褪黑素促进Sirt1,PRC1/2复合物和细胞周期相关蛋白的表达,进而抑制衰老,防止可能出现的骨丢失。值得关注的是,在转染MT1或MT2特异性的shRNA后,Sirt1表达显著降低,褪黑素的抗衰老作用消失。ZHOU等[40]用褪黑素预培养破骨细胞,发现TRAP阳性细胞数和破骨细胞特异性标志物的基因表达在褪黑素治疗的骨髓单核细胞中下调,在使用Sirt1抑制剂后并不影响破骨细胞的分化,但加入H2O2后,被褪黑素抑制的破骨细胞可发生部分恢复。由此推断褪黑素是通过活性氧而非Sirt1独立途径直接抑制骨髓单核细胞的破骨细胞分化。 有研究表明,骨质疏松症与活性氧诱导的细胞毒性有关,线粒体功能障碍可能参与活性氧诱导细胞毒性的机制。SHE等[41]使用H2O2处理MG63成骨样细胞,结果表明H2O2显著降低细胞活力,增加活性氧和丙二醛水平,细胞线粒体电位破坏,线粒体DNA拷贝数减少;而褪黑素可以有效降低氧化应激诱导的细胞毒性损伤,维持线粒体稳定。WANG等[42]使用维甲酸培养MC3T3-E1和RAW264.7细胞,细胞的氧化应激水平增加,破骨细胞分化加强,但褪黑素通过ERK/SMAD和核转录因子κB信号通路降低体内和体外氧化水平,逆转了视黄酸导致的骨生理紊乱。 铁死亡是最近发现的一种依赖铁和活性氧的调节性细胞死亡方式[44]。MA等[45]将MC3T3-E1细胞暴露在高糖中,结果表明谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4和SLC7A11表达下调,过氧化物聚集;使用褪黑素处理后,Nrf2/HO-1通路被激活,显著提高了MC3T3-E1细胞的成骨能力。近年来,氧化应激反应是骨质疏松症的重要发病机制之一已经逐渐成为共识。褪黑素可以通过激活多条信号通路增强细胞的抗氧化能力,维持线粒体稳定,抑制细胞凋亡,从而减少细胞毒性损伤,加强细胞的成骨分化和矿化能力,抑制破骨细胞的分化。褪黑素在成骨细胞和破骨细胞中的作用研究汇总见表2。 "
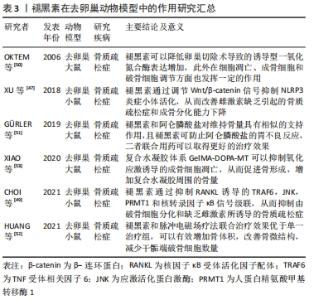
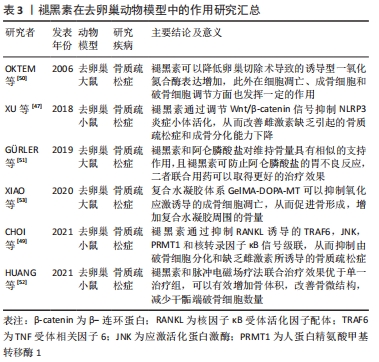
2.3 褪黑素调节骨代谢在动物水平的研究 2.3.1 褪黑素与去卵巢动物模型 雌激素可诱导成骨细胞分化并降低破骨细胞活性,在调节骨代谢中发挥重要作用。绝经后女性雌激素缺乏导致骨吸收过度、新骨形成不足,进而导致骨密度显著降低和骨质疏松[46]。绝经后骨质疏松症由于雌激素缺乏、新骨形成不足引起,影响全世界数百万妇女。 XU等[47]使用褪黑素治疗去卵巢小鼠,结果显示褪黑素以剂量依赖的方式减轻骨丢失,增加碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素,增强成骨细胞分化,减少破骨细胞标志物抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶。此外,使用Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制剂和敲除NLRP3炎症小体证实褪黑素通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制NLRP3炎症小体的激活,进而改善去卵巢引起的骨质疏松和成骨分化潜能受损。蛋白精氨酸甲基转移酶1(Protein arginine methyltransferase 1,PRMT1)是RANKL诱导破骨细胞发生的重要中介物[48]。在CHOI等[49]的研究中,褪黑素可以抑制PRMT1、不对称二甲基精氨酸(Asymmetric dimethylarginine,ADMA)以及RANKL下游的肿瘤坏死因子相关受体6(TNF receptor associated factor 6,TRAF6)和JNK的磷酸化的表达,有效阻断了去卵巢小鼠体内RANKL诱导的破骨细胞形成。 诱导型一氧化氮合酶在骨质疏松症的发病机制中起着重要作用。诱导型一氧化氮合酶产生一氧化氮,一氧化氮作为一种自由基,在雌激素缺乏引起的骨形成和骨吸收失衡中发挥重要作用。OKTEM等[50]对去卵巢大鼠椎体区域的成骨细胞和破骨细胞进行定量分析,发现卵巢切除可增加髓核的骨骺软骨中诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达和凋亡细胞的数量,但在4周的褪黑素处理后可以降低这两种效应,表明褪黑素在诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达、细胞凋亡、破骨细胞和成骨细胞的平衡之间发挥相应的生物学效应。 抗分解代谢的阿仑膦酸被认为是绝经后骨质疏松症的一线治疗药物,但是长期使用可导致胃黏膜损伤。GüRLER等[51]的研究表明,阿仑膦酸与褪黑素联合用药在维持骨量方面优于单用阿仑膦酸或者褪黑素,且褪黑素可以防止阿仑膦酸的胃不良反应,这一组合成为治疗绝经期骨质疏松症的一种可行治疗方法。HUANG等[52]使用脉冲电磁场疗法和褪黑素联合治疗去卵巢骨质疏松症小鼠,脉冲电磁场疗法和褪黑素联合治疗使骨体积分数-骨表面/骨体积比(BS/BV)较去卵巢组提高2.2倍,Ⅰ型胶原蛋白提高1.9倍,BS/BV降低40%,并减少了干骺端破骨细胞的数量,且效果优于脉冲电磁场疗法或褪黑素单独治疗组。另外,基于褪黑素的分布和代谢特点,如果全身用药则需要大剂量的褪黑素,会增加发生药物不良反应的概率,因此局部用药可能比全身用药更有效。XIAO等[53]等构建了一个包裹褪黑素的复合水凝胶体系(GelMA-DOPA-MT),实现了褪黑素在局部的持续释放,在去卵巢大鼠植入体周围氧化应激反应被抑制,成骨细胞凋亡明显减少,骨量增加。 因此,卵巢切除后骨量不断丢失,褪黑素可以部分逆转雌激素缺乏导致的成骨细胞减少及成骨细胞分化潜能受损,同时,通过抑制炎症小体NLRP3,RANKL以及自由基的表达,减少骨组织中破骨细胞的数量,恢复骨代谢的稳定。另一方面,褪黑素可以与其他疗法联合使用,在减轻药物不良反应的同时可以获得更好的治疗效果,具有较好的应用前景。褪黑素在去卵巢动物模型中的作用研究汇总见表3。 "
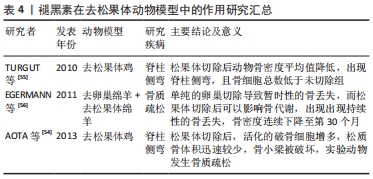
2.3.2 去松果体动物模型 松果体来源于神经外胚层,位置相当于第三脑室顶部,作为一种神经腺体,可以调节多种激素的合成与释放,从而影响全身的代谢情况。 AOTA等[54]的研究发现,松果体切除肉鸡的松质骨体积迅速减少,小梁结构严重破坏,在软骨-骨交界处,活化的破骨细胞吞噬变性的软骨细胞,进而失去形成骨的支架,软骨内骨化受损,导致脊柱侧弯。在另一项松果体切除肉鸡的研究中,去松果体组肉鸡的椎体骨密度显著降低,几乎所有实验对象均发生脊柱侧弯,值得特别关注的是,去松果体组肉鸡骨细胞和成骨细胞总数高于未去松果体组,但是椎体骨细胞总数显著低于未去松果体组,表明褪黑素对骨形成具有重要的诱导作用[55]。EGERMANN等[56]分别使用卵巢切除、松果体切除、卵巢联合松果体切除处理雌性绵羊,3组均出现松质骨体积下降,且联合组下降最为显著;不同的是,单纯卵巢切除在经历一段时间的骨丢失后,骨密度会持续增加到基线水平,但卵巢联合松果体切除后会导致持续性的骨丢失,表明松果体可能影响骨代谢,松果体切除可诱导持续性骨丢失。 骨细胞是由包埋于骨基质中的成骨细胞转化而来,松果体切除后成骨细胞数量未见明显减少,但是骨组织变形严重且发生较长时间的骨量丢失,由此推断褪黑素可能在成骨细胞分泌骨基质中发挥了重要作用。在松果体切除后,骨形成过程被阻断,因此骨吸收和骨形成逐渐失衡,发生骨质疏松。但是,目前关于去松果体的文献数量有限,仍有待进一步的研究。褪黑素在去松果体动物模型中的作用研究汇总见表4。 "

2.3.3 褪黑素与其他动物模型 衰老被认为在糖尿病骨质疏松的病理生理机制中发挥重要作用,越来越多的证据表明褪黑素具有抗衰老作用。GONG等[39]使用褪黑素治疗1型糖尿病模型小鼠,micro-CT表明褪黑素可以防止小鼠骨丢失,组织检测发现细胞周期蛋白的表达增加,这项研究表明褪黑素可能通过抑制衰老来保护1型糖尿病诱导的骨丢失。JING等[57]使用有氧运动和褪黑素治疗2型糖尿病模型大鼠,发现有氧运动和褪黑素均可增加骨密度,改善糖尿病型骨质疏松,且联合治疗效果更佳。组织检测发现对照组超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶显著降低,说明褪黑素干预糖尿病骨质丢失可能与抑制氧化应激有关。 2.4 褪黑素的临床应用研究 随着年龄的增长,褪黑素水平下降,可能导致骨骼代谢进一步失衡。在一项双盲随机对照试验中,使用褪黑素治疗绝经后骨质疏松女性,褪黑素可呈剂量依赖性增加骨密度,且骨密度变化的部位与褪黑素使用剂量有关,低剂量褪黑素增加股骨颈的骨密度,高剂量褪黑素则增加脊柱的骨密度,褪黑素对其他部位骨密度或骨转换标志物没有显著影响[58]。在另一项对褪黑素不良反应的研究评估中,与安慰剂组相比,褪黑素不会引起宿醉效应,且对肌肉功能没有影响,因此降低了患者跌倒和骨折风险,此外,对于睡眠质量较差的女性来说,低剂量的褪黑素可以显著改善睡眠质量[59]。神经性厌食症的年轻女性和女童会出现褪黑素分泌异常,尤其是在夜间阶段,与此相对应的是大量的骨量丢失和骨代谢异常。一项纳入57例女童患者的研究表明,神经性厌食症患者骨代谢异常与夜间褪黑素水平变化有关,RANKL可能在这一机制中起重要作用。褪黑素夜间和早晨水平之间的振幅增加可能对患者的骨组织产生不利影响,这种影响很可能是由于干扰了骨保护素/RANKL平衡[60]。血液透析患者骨质疏松发生率为40%-60%,严重影响其生活质量[61]。在一项临床研究中,REN等[62]发现血液透析的骨质疏松患者褪黑素水平低于对照组,氧化应激指标血清高级氧化蛋白产物、丙二醛水平高于对照组;Pearson相关分析显示血清高级氧化蛋白产物、丙二醛与骨密度呈负相关,而褪黑素与骨密度呈正相关,提示褪黑素参与抑制氧化应激反应、维持骨代谢平衡的过程。总之,褪黑素可以呈剂量依赖性治疗骨质疏松,增加骨密度,且可能参与多种疾病的发病机制。"

| [1] CLARKE B. Normal bone anatomy and physiology. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3(Suppl 3):S131-S139. [2] NOH JY, YANG Y, JUNG H. Molecular mechanisms and emerging therapeutics for osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7623. [3] TUMAY S, LALE O, NURSEL CB. An overview and management of osteoporosis. Eur J Rheumatol. 2017;4(1):46. [4] MARAKA S, KENNEL KA. Bisphosphonates for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. BMJ. 2015;351:h3783. [5] LIM SY, BOLSTER MB. Current approaches to osteoporosis treatment. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27(3):216-224. [6] BINKLEY N, BOLOGNESE M, SIDOROWICZ‐BIALYNICKA A, et al. A phase 3 trial of the efficacy and safety of oral recombinant calcitonin: the Oral Calcitonin in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis (ORACAL) trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(8):1821-1829. [7] LIU Z, GAN L, LUO D, et al. Melatonin promotes circadian rhythm‐induced proliferation through C lock/histone deacetylase 3/c‐M yc interaction in mouse adipose tissue. J Pineal Res. 2017;62(4):e12383. [8] SONG C, WANG J, KIM B, et al. Insights into the role of circadian rhythms in bone metabolism: a promising intervention target? Biomed Res Int. 2018. doi: 10.1155/2018/9156478. [9] ALBERTI C. Melatonin: the first hormone isolated from the pineal body.Farmaco Sci. 1958;13(8):604-605. [10] MCISAAC WM, KHAIRALLAH PA, PAGE IH.10-Methoxyharmalan, a potent serotonin antagonist which affects conditioned behavior. Science. 1961; 134(3480):674-675. [11] AXELROD J, WURTMAN RJ, CHU EW. Effects of melatonin, a pineal substance, on the rat ovary. Science. 1963;140(3565):378. [12] COHEN M, ROSELLE D, CHABNER B, et al. Evidence for a cytoplasmic melatonin receptor. Nature. 1978;274(5674):894-895. [13] SANDYK R, ANASTASIADIS PG, ANNINOS PA, et al. Is postmenopausal osteoporosis related to pineal gland functions? Int J Neurosci. 1991;62(3-4): 215-225. [14] EBISAWA T, KARNE S, LERNER MR, et al. Expression cloning of a high-affinity melatonin receptor from Xenopus dermal melanophores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91(13):6133-6137. [15] REPPERT SM, GODSON C, MAHLE CD, et al. Molecular characterization of a second melatonin receptor expressed in human retina and brain: the Mel1b melatonin receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(19):8734-8738. [16] ROTH JA, KIM BG, LIN WL, et al. Melatonin promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(31):22041-22047. [17] KOTLARCZYK MP, LASSILA HC, O’NEIL CK, et al. Melatonin osteoporosis prevention study (MOPS): a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study examining the effects of melatonin on bone health and quality of life in perimenopausal women. J Pineal Res. 2012;52(4):414-426. [18] HARDELAND R. Melatonin: signaling mechanisms of a pleiotropic agent. Biofactors. 2009;35(2):183-192. [19] CECON E, LIU L, JOCKERS R. Melatonin receptor structures shed new light on melatonin research.J Pineal Res. 2019;67(4):e12606. [20] HANSON MA, ROTH CB, JO E, et al. Crystal structure of a lipid G protein–coupled receptor.Science. 2012;335(6070):851-855. [21] LIU C, WEAVER DR, JIN X, et al. Molecular dissection of two distinct actions of melatonin on the suprachiasmatic circadian clock. Neuron. 1997;19(1): 91-102. [22] JIN X, GALL CV, PIESCHL RL, et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse mel1b melatonin receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(3):1054-1060. [23] GIANNONI‐GUZMÁN MA, KAMITAKAHARA A, MAGALONG V, et al. Circadian photoperiod alters TREK‐1 channel function and expression in dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons via melatonin receptor 1 signaling. J Pineal Res. 2021; 70(2):e12705. [24] LI HY, WANG Y, FENG DX, et al. Alterations in the time course of expression of the Nox family in the brain in a rat experimental cerebral ischemia and reperfusion model: effects of melatonin. J Pineal Res. 2014;57(1):110-119. [25] BOROS K, FREEMONT T. Physiology of ageing of the musculoskeletal system. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017;31(2):203-217. [26] Shuai Y, Liao L, Su X, et al. Melatonin treatment improves mesenchymal stem cells therapy by preserving stemness during long-term in vitro expansion.Theranostics. 2016;6(11):1899-1917. [27] ROFORTH MM, FARR JN, FUJITA K, et al. Global transcriptional profiling using RNA sequencing and DNA methylation patterns in highly enriched mesenchymal cells from young versus elderly women. Bone. 2015;76:49-57. [28] LUO H, GU R, OUYANG H, et al. Cadmium exposure induces osteoporosis through cellular senescence, associated with activation of NF-κB pathway and mitochondrial dysfunction. Environ Pollut. 2021;290:118043. [29] MARIA S, SAMSONRAJ RM, MUNMUN F, et al. Biological effects of melatonin on osteoblast/osteoclast cocultures, bone, and quality of life: implications of a role for MT 2 melatonin receptors, MEK 1/2, and MEK 5 in melatonin‐mediated osteoblastogenesis. J Pineal Res. 2018;64(3):e12465. [30] ZHOU Y, WANG C, SI J, et al. Melatonin up‐regulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic action but suppresses their mediated osteoclastogenesis via MT2‐inactivated NF‐κB pathway. Br J Pharmaco. 2020;177(9):2106-2122. [31] LI G, YUN X, YE K, et al. Long non‐coding RNA‐H19 stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the microRNA‐149/SDF‐1 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(9):4944-4955. [32] BI H, WANG D, LIU X, et al. Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating microRNA-140-5p/SATB2 axis. J Biosci. 2020;45(1):1-13. [33] HAN H, TIAN T, HUANG G, et al. The IncRNA H19/miR-541-3p/Wnt/-catenin axis plays a vital role in melatonin-mediated osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. doi: 10. 18632/aging. 203267 [34] QIU X, WANG X, QIU J, et al. Melatonin rescued reactive oxygen species-impaired osteogenesis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the presence of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019: 6403967. [35] LIAN C, WU Z, GAO B, et al. Melatonin reversed tumor necrosis factor‐alpha‐inhibited osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by stabilizing SMAD 1 protein. J Pineal Res. 2016;61(3):317-327. [36] CHEN W, CHEN X, CHEN AC, et al. Melatonin restores the osteoporosis-impaired osteogenic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by preserving SIRT1-mediated intracellular antioxidant properties. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;146:92-106. [37] LEE S, LE NH, KANG D. Melatonin alleviates oxidative stress-inhibited osteogenesis of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through AMPK activation. Int J Med Sci. 2018;15(10):1083. [38] LIU J, CHEN S, BISWAS S, et al. Glucose‐induced oxidative stress and accelerated aging in endothelial cells are mediated by the depletion of mitochondrial SIRTs. Physiol Rep. 2020;8(3):e14331. [39] GONG Z, DA W, TIAN Y, et al. Exogenous melatonin prevents type 1 diabetes mellitus–induced bone loss, probably by inhibiting senescence. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(2):453-466. [40] ZHOU L, CHEN X, YAN J, et al. Melatonin at pharmacological concentrations suppresses osteoclastogenesis via the attenuation of intracellular ROS. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(12):3325-3337. [41] SHE F, WANG W, WANG Y, et al. Melatonin protects MG63 osteoblast-like cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity by maintaining mitochondrial function. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(2):493-498. [42] WANG X, LIANG T, ZHU Y, et al. Melatonin prevents bone destruction in mice with retinoic acid–induced osteoporosis. Mol Med. 2019;25(1):1-14. [43] ZHAO R, TAO L, QIU S, et al. Melatonin rescues glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of osteoblast differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells via the PI3K/AKT and BMP/Smad signalling pathways. Life Sci. 2020;257:118044. [44] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072. [45] MA H, WANG X, ZHANG W, et al. Melatonin suppresses ferroptosis induced by high glucose via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:1-18. [46] KRASSAS GE, PAPADOPOULOU P. Oestrogen action on bone cells. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2001;2(2):143-152. [47] XU L, ZHANG L, WANG Z, et al. Melatonin suppresses estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis and promotes osteoblastogenesis by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;103(4):400-410. [48] CHOI JH, JANG AR, KIM D, et al. PRMT1 mediates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and contributes to bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(8):1-15. [49] CHOI JH, JANG AR, PARK MJ, et al. Melatonin inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone loss in ovariectomized mice by regulating PRMT1-mediated signaling. Endocrinology. 2021;162(6):bqab057. [50] OKTEM G, USLU S, VATANSEVER SH, et al. Evaluation of the relationship between inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activity and effects of melatonin in experimental osteoporosis in the rat. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006; 28(2):157-162. [51] GÜRLER EB, ÇILINGIR‐KAYA ÖT, PEKER EYÜBOGLU I, et al. Melatonin supports alendronate in preserving bone matrix and prevents gastric inflammation in ovariectomized rats. Cell Biochem Funct. 2019;37(2):102-112. [52] HUANG J, LI Y, WANG L, et al. Combined effects of low‐frequency pulsed electromagnetic field and melatonin on ovariectomy‐induced bone loss in mice. Bioelectromagnetics. 2021;42(8):616-628. [53] XIAO L, LIN J, CHEN R, et al. Sustained release of melatonin from GelMA liposomes reduced osteoblast apoptosis and improved implant osseointegration in osteoporosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020(4):1-20. [54] AOTA Y, TERAYAMA H, SAITO T, et al. Pinealectomy in a broiler chicken model impairs endochondral ossification and induces rapid cancellous bone loss. Spine J. 2013;13(11):1607-1616. [55] TURGUT M, SÜLEYMAN KAPLAN, TURGUT A T, et al. Morphological, stereological and radiological changes in pinealectomized chicken cervical vertebrae. J Pineal Res. 2010;39(4):392-399. [56] EGERMANN M, GERHARDT C, BARTH A, et al. Pinealectomy affects bone mineral density and structure-an experimental study in sheep. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12(1):1-9. [57] JING HF, WANG XM. Effects of aerobic exercise combined with melatonin on osteoporosis of type II diabetic rats. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2017;33(3):252-256. [58] AMSTRUP AK, SIKJAER T, HEICKENDORFF L, et al. Melatonin improves bone mineral density at the femoral neck in postmenopausal women with osteopenia: a randomized controlled trial. J Pineal Res. 2015;59(2):221-229. [59] AMSTRUP AK, SIKJAER T, MOSEKILDE L, et al. The effect of melatonin treatment on postural stability, muscle strength, and quality of life and sleep in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial. Nutr J. 2015;14(1):1-8. [60] OSTROWSKA Z, ZIORA K, KOS-KUDŁA B, et al. Melatonin, the RANKL/RANK/OPG system, and bone metabolism in girls with anorexia nervosa. Endokrynol Pol. 2010;61(1):117-123. [61] SHIGEMATSU T, MURAOKA R, SUGIMOTO T, et al. Risedronate therapy in patients with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease with osteoporosis: post-hoc analysis of data from the risedronate phase III clinical trials. BMC Nephrol. 2017;18(1):1-8. [62] REN H, SUN R, WANG J. Relationship of melatonin level, oxidative stress and inflammatory status with osteoporosis in maintenance hemodialysis of chronic renal failure. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(6):5183-5188. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [4] | Du Xueting, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Yanjun, Wang Mei, Chen Wubiao, Huang Wenhua. Application of compressed sensing technology in two-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle joint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1396-1402. |
| [5] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [6] | Jiang Xiaocheng, Shi Lu, Wang Yinbin, Li Qiujiang, Xi Chuangzhen, Ma Zefeng, Cai Lijun. Systematical evaluation of bone fusion rate after interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis and lumbar degenerative disease treated with teriparatide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1427-1433. |
| [7] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [8] | Liang Jiaqi, Liu Hengxu, Yang Jinxin, Yang Yi, Deng Xuhui, Tan Mingjian, Luo Jiong. Health benefit relationship between exercise and intestinal bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [9] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [10] | Sun Jiajia, Zhu Haidi, Lu Yun, Zhang Kai. Comparison of bone metabolism markers between type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with hip fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1156-1160. |
| [11] | Long Guiyue, Li Dongdong, Liao Hongbing. Calcium phosphate cement/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) degradation products promote osteoclast differentiation of mouse monocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1193-1198. |
| [12] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [13] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [14] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [15] | Xue Ting, Zhang Xinri, Kong Xiaomei. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for pneumoconiosis using nanomaterials combined with multi-modal molecular imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1133-1140. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||