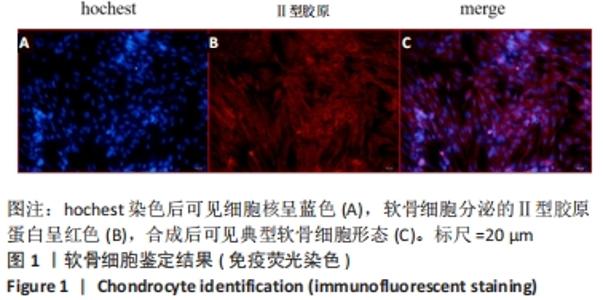
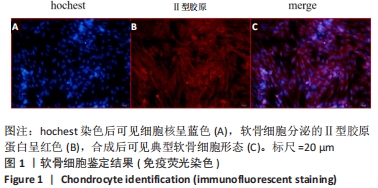
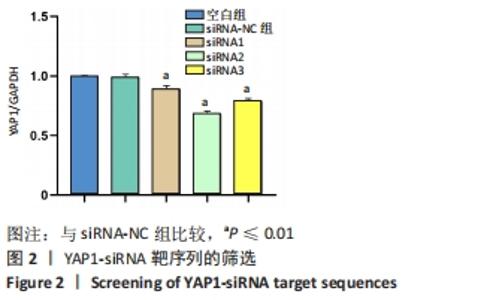
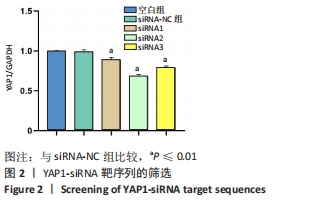
[1] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715.
[2] SAFIRI S, KOLAHI AA, SMITH E, et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):819-828.
[3] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组,中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨关节炎学组,国家老年疾病临床医学研究中心(湘雅医院),等.中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2021年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2021, 41(18):1291-1314.
[4] ZHANG JF, SONG LH, WEI JN, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for the occurrence of symptomatic osteoarthritis in rural regions of Shanxi Province, China. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(8):781-789.
[5] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311.
[6] LUO Y, SINKEVICIUTE D, HE Y, et al. The minor collagens in articular cartilage. Protein Cell. 2017;8(8):560-572.
[7] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019; 393(10182):1745-1759.
[8] MOYA IM, HALDER G. Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling in organ regeneration and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(4):211-226.
[9] WANG S, ZHOU L, LING L, et al. The Crosstalk Between Hippo-YAP Pathway and Innate Immunity. Front Immunol. 2020;11:323.
[10] IBAR C, IRVINE KD. Integration of Hippo-YAP Signaling with Metabolism. Dev Cell. 2020;54(2):256-267.
[11] CHUANG LSH, ITO Y. The Multiple Interactions of RUNX with the Hippo-YAP Pathway. Cells. 2021;10(11):2925.
[12] 袁永刚.Yes相关蛋白(YAP)通过细胞外基质力学调节非小细胞肺癌生长的研究[D].济南:山东大学,2015.
[13] DENG Y, LU J, LI W, et al. Reciprocal inhibition of YAP/TAZ and NF-κB regulates osteoarthritic cartilage degradation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1): 4564.
[14] WANG F, QIAN H, KONG L, et al. Accelerated Bone Regeneration by Astragaloside IV through Stimulating the Coupling of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(7):1821-1836.
[15] JIANG C, ZHOU Z, LIN Y, et al. Astragaloside IV ameliorates steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by repolarizing the phenotype of pro-inflammatory macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;93:107345.
[16] LI M, WANG W, GENG L, et al. Inhibition of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through the suppression of the ERK signaling pathway by astragaloside IV and attenuation of titanium-particle-induced osteolysis. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(5):1335-1344.
[17] HAN J, SHEN X, ZHANG Y, et al. Astragaloside IV suppresses transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in glioma U251 cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2020;84(7):1345-1352.
[18] 赵永见,薛纯纯,王利波,等.黄芪甲苷对关节不稳诱导型小鼠膝骨关节炎的保护作用[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2015,21(6):668-670.
[19] 余素姣,谭慧.黄芪甲苷通过炎症小体活化影响软骨细胞炎性因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(11):1652-1656.
[20] LIU J, MENG Q, JING H, et al. Astragaloside IV protects against apoptosis in human degenerative chondrocytes through autophagy activation. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(3):3269-3275.
[21] RAHMATI M, NALESSO G, MOBASHERI A, et al. Aging and osteoarthritis: Central role of the extracellular matrix. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;40:20-30.
[22] CHARLIER E, DEROYER C, CIREGIA F, et al. Chondrocyte dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165:49-65.
[23] YANG Y, LIN H, SHEN H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular matrix enhances chondrogenic phenotype of and cartilage formation by encapsulated chondrocytes in vitro and in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2018;69:71-82.
[24] 刘建红,孟庆刚,胡佳卉,等.黄芪甲苷对早期骨关节炎软骨细胞基质金属蛋白酶-1表达的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2017,37(3):532-534.
[25] CUI N, HU M, KHALIL RA. Biochemical and Biological Attributes of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2017;147:1-73.
[26] TOMASZEWSKA E, RUDYK H, ŚWIETLICKA I, et al. Trabecular Bone Parameters, TIMP-2, MMP-8, MMP-13, VEGF Expression and Immunolocalization in Bone and Cartilage in Newborn Offspring Prenatally Exposed to Fumonisins. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12528.
[27] SAW S, AIKEN A, FANG H, et al. Metalloprotease inhibitor TIMP proteins control FGF-2 bioavailability and regulate skeletal growth. J Cell Biol. 2019;218(9):3134-3152.
[28] AHARONOV A, SHAKKED A, UMANSKY KB, et al. ERBB2 drives YAP activation and EMT-like processes during cardiac regeneration. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(11):1346-1356.
[29] WANG J, LIU S, HEALLEN T, et al. The Hippo pathway in the heart: pivotal roles in development, disease, and regeneration. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15(11):672-684.
[30] SUN X, REN Z, CUN Y, et al. Hippo-YAP signaling controls lineage differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells through modulating the formation of super-enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(13):7182-7196.
[31] LI C, JIN Y, WEI S, et al. Hippo Signaling Controls NLR Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3 Activation and Governs Immunoregulation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Mouse Liver Injury. Hepatology. 2019;70(5): 1714-1731.
[32] ZHOU X, LI Y, WANG W, et al. Regulation of Hippo/YAP signaling and Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma progression by an E3 ubiquitin ligase PARK2. Theranostics. 2020;10(21):9443-9457.
[33] LIU H, DU S, LEI T, et al. Multifaceted regulation and functions of YAP/TAZ in tumors (Review). Oncol Rep. 2018;40(1):16-28.
[34] LUO H, YAO L, ZHANG Y, et al. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics analysis reveals chondroprotective effects of astragaloside IV in interleukin-1β-induced SW1353 chondrocyte-like cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;91:796-802.
[35] WANG L, WANG S, SHI Y, et al. YAP and TAZ protect against white adipocyte cell death during obesity. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):5455.
|