Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (14): 2243-2251.doi: 10.12307/2022.490
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism by which antler glue treats avascular necrosis of the femoral head induced by retinoic acid in rats: a serum proteomics study
Hu Yanan1, Wang Ping2, 3, Du Haitao2, Jing Tianyuan1, Wang Chengcheng1
- 1School of Pharmacy, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Shandong Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 3State Key Laboratory of Precision Testing Technology and Instruments, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
-
Received:2021-06-02Revised:2021-06-04Accepted:2021-07-14Online:2022-05-18Published:2021-12-22 -
Contact:Wang Ping, Master, Researcher, Shandong Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; State Key Laboratory of Precision Testing Technology and Instruments, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China -
About author:Hu Yanan, Master candidate, School of Pharmacy, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2020MH386 (to WP); Shandong Provincial Major Science and Technology Innovation Project, No. 2018CXGC1310 and 2020CXGC010505-04 (to WP); the National Key Research and Development Program of China, No. 2019YFE0117800; grants from the Collaborative Innovation Center for the Quality Control of Traditional Chinese Medicine and the Construction of the Whole Industry Chain in Shandong Provincial Universities, Nos. CYLXTCX2021-01 and CYLXTCX2020-04 (to WP); the Central Government-Guided Local Project, No. YDZX20203700002055 (to WP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Yanan, Wang Ping, Du Haitao, Jing Tianyuan, Wang Chengcheng. Mechanism by which antler glue treats avascular necrosis of the femoral head induced by retinoic acid in rats: a serum proteomics study[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2243-2251.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
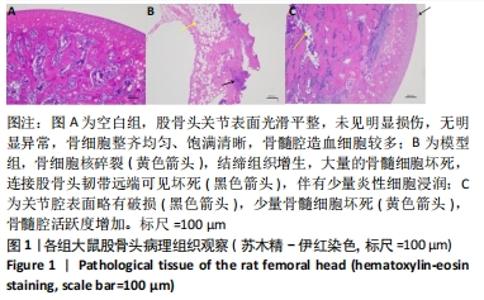
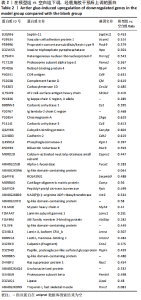
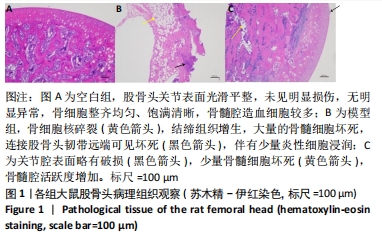
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用大鼠36只,分为3组,每组10只进入结果分析。 2.2 大体观察及骨组织病理学检查结果 ①空白组正常大鼠饮食正常,状态活跃;股骨头骨质较硬,骨头表面光滑;病理组织观察可见股骨头内骨细胞整齐均匀、饱满清晰;②模型组大鼠食量减少,体质量明显下降,精神萎靡,出现跛脚现象;股骨头骨质变软易折,关节表面较为粗糙;病理组织观察可见骨陷窝空缺较多,骨细胞核碎裂,结缔组织增生,大量的骨髓细胞坏死,连接股骨头韧带远端可见坏死,同时伴有少量炎性细胞浸润,说明造模成功;③鹿角胶组大鼠造模期间体质量下降,出现跛脚现象,经鹿角胶灌胃后,食量明显增多,体质量增加,活动量增减,跛脚现象逐渐减轻,股骨头表面轻度凹陷,病理组织观察显示股骨头关节腔表面略有破损,少量骨髓细胞坏死,骨髓腔活跃增加,说明股骨头坏死现象有所改善,见图1。"
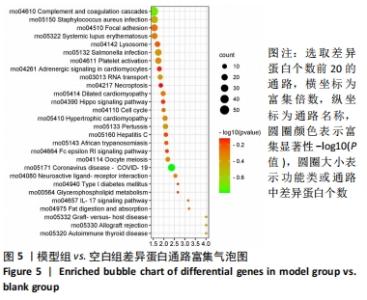
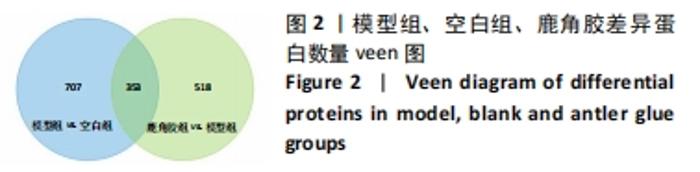
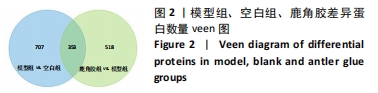
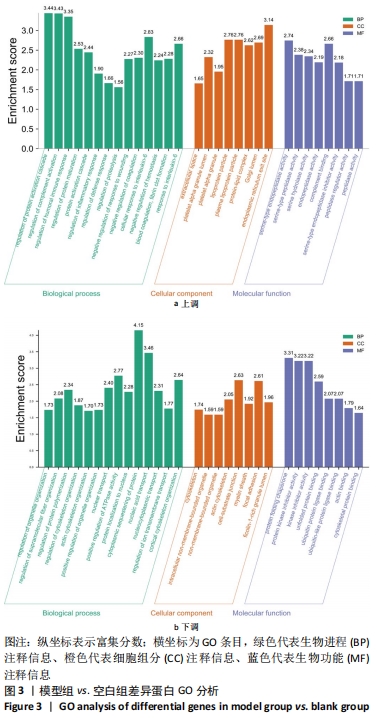
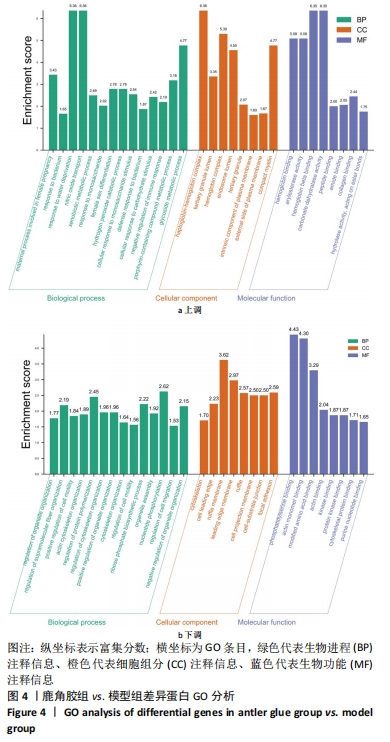
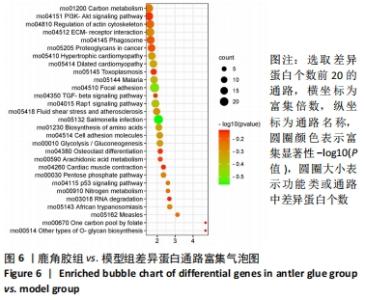
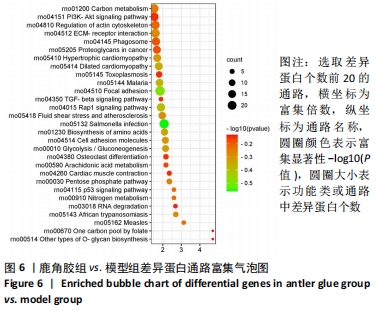
其中BP涉及cellular process、biological regulation、response to stimulus、multicellular organismal process、metabolic process、localization、developmental process、immune system process、signaling等过程;CC包括cell、intracellular、protein-contaiing complex;MF涉及catalytic activity、molecular function regulator、structural molecule activity、molecular transducer activity、transporter activity等。 2.5 差异蛋白通路富集结果 利用KEGG信息数据库对空白组、模型组和鹿角胶组差异蛋白涉及的通路进行分析,见图5,6。"
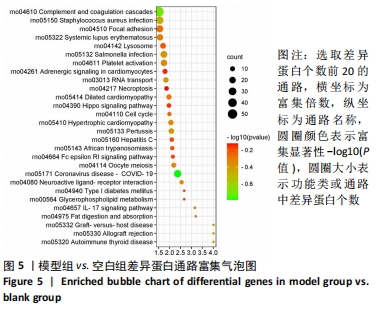
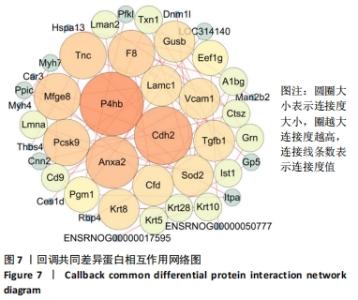
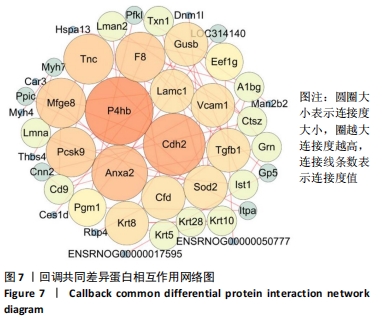
模型组与正常组比较,主要富集通路包括补体和凝血级联、甘油磷脂代谢、卵母细胞减数分裂、坏死性凋亡、心肌细胞中的肾上腺素能信号、血小板活化、百日咳、白细胞介素17等通路。鹿角胶组与模型组主要富集通路包括糖酵解/糖异生、戊糖磷酸途径、PI3-Akt、花生四烯酸代谢、RAP1、破骨细胞分化、ECM-受体相互作用、细胞黏附分子、肌动蛋白细胞骨架的调控、转化生长因子β等通路。 2.6 共同差异蛋白互作网络分析 为更好揭示鹿角胶干预股骨头坏死大鼠作用机制,对模型组vs.空白组、鹿角胶组vs.模型组共同涉及的回调蛋白做蛋白互作网络分析。 发现蛋白质二硫键异构酶(P4HB)、钙黏蛋白2(CDH2)、膜联蛋白A2(ANXA2)、枯草杆菌前蛋白转换酶/可信9型(PCSK9)、乳脂球-表皮生长因子8(MFGE8)、腱生蛋白(TNC)、层粘连蛋白亚基γ-1(LAMC1)、血管细胞黏附蛋白1(VCAM1)、转化生长因子β1蛋白(TGFB1)等连接度较高,分别为9,8,7,6,6,6,6,5,5,5,见图7。"
| [1] MONT MA, CHERIAN JJ, SIERRA RJ, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today? A Ten-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(19):1604-1627. [2] ZHAO DW, YU M, HU K, et al. Prevalence of Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head and its Associated Risk Factors in the Chinese Population: Results from a Nationally Representative Survey. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(21):2843-2850. [3] 王平, 张会敏, 李刚.鹿角多肽对骨髓间充质干细胞的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(12):5644-5647. [4] RICHTER JF, SCHMAUDER R, KRUG SM, et al. A novel method for imaging sites of paracellular passage of macromolecules in epithelial sheets. J Control Release. 2016;229:70-79. [5] WANG P, SUN T, LI G, et al. The Separation of Antler Polypeptide and Its Effects on the Proliferation and Osteogenetic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:1294151. [6] 国家药典委员会. 中国药典[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020. [7] 陈方,吴铁,崔燎.维甲酸致小鼠骨质疏松模型的量效关系及骨药理作用探讨[J].中国药理学通报,2002,18(6):681-684. [8] 孙铁锋,王平. 鹿角胶-壳聚糖细胞支架修复大鼠股骨头缺血性坏死[J].中成药,2015,37(11):2337-2341. [9] 杨帆,刘红梅,吉红玉.鹿角胶临床应用及其用量探究[J].长春中医药大学学报,2021,37(3):512-515. [10] 黄思敏,吴雨蒙,张丽,等.甘草附子汤对大鼠骨关节炎及关节软骨蛋白质组学的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2021,46(3):661-669. [11] YUN C, QIAN W, WU J, et al. Pilose antler peptide promotes osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and mineralization via the insulin signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(2):923-930. [12] 刘小元,李蕾,张凯,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞膜片复合3D打印马鹿角粉/丝素蛋白/聚乙烯醇支架的体内成骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(34):5420-5426. [13] CHEN R, MIAN M, FU M, et al. Degeneration By Inhibition Of TGF-beta Signaling In A Mouse Model Of Osteoarthritis. Am J Pathol. 2015; 185(11):2875-2885. [14] CHEN G, DENG C, LI YP, et al. TGF-beta and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(2):272-288. [15] SHI L, SUN W, GAO F, et al. Heterotopic ossification related to the use of recombinant human BMP-2 in osteonecrosis of femoral head. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(27):e7413. [16] 杨武斌. 鹿角胶对hBMP7基因转染的骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨性诱导[D]. 济南:山东中医药大学, 2015. [17] LEMMA S, SBOARINA M, PORPORATO P, et al. Energy metabolism in osteoclast formation and activity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016;79: 168-180. [18] WANG C, SILVERMAN RM, SHEN J, et al. Distinct metabolic programs induced by TGF-β1 and BMP2 in human articular chondrocytes with osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2018;12:66-73. [19] CHEN L, HUANG M, TAN J, et al. PI3K/AKT pathway involvement in the osteogenic effects of osteoclast culture supernatants on preosteoblast cells.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(19-20):2226-2232. [20] ZHANG D, WANG J, ZHOU C, et al. Zebrafish akt2 is essential for survival, growth, bone development, and glucose homeostasis. Mech Dev. 2017;143:42-52. [21] PARK HH, HAN MH, CHOI H, et al. Mitochondria damaged by Oxygen Glucose Deprivation can be Restored through Activation of the PI3K/Akt Pathway and Inhibition of Calcium Influx by Amlodipine Camsylate. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15717. [22] ZHANG Z, ZHANG X, ZHAO D, et al. TGFβ1 promotes the osteoinduction of human osteoblasts via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K1 signalling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(5):3505-3518. [23] 瞿麟平. ATP在高糖引起肾脏系膜细胞TGF-β1增加中的作用[D].上海:复旦大学,2008. [24] 吴惠春,李曼,周振华,等. PI3K/PKB信号通路在TGF-β_1诱导人肝星状细胞表达骨桥蛋白中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015, 31(1):93-97. [25] LINDERT U, CABRAL WA, AUSAVARAT S, et al. MBTPS2 mutations cause defective regulated intramembrane proteolysis in X-linked osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11920. [26] LI L, ZHAO D, ZHENG W, et al. A novel missense mutation in P4HB causes mild osteogenesis imperfecta. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(4): BSR20182118. [27] ZENG Y , ZHANG L , ZHU W , et al. Network based subcellular proteomics in monocyte membrane revealed novel candidate genes involved in osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(10):3033-3042. [28] DUBON MJ, YU J, CHOI S,et al. Transforming growth factor β induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell migration via noncanonical signals and N-cadherin. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(1):201-213. [29] 王永会. 钙粘蛋白与胶原微环境对MSC成软骨早期分化的影响[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2019. [30] XIANG L, ZHENG J, ZHANG M, et al. FOXQ1 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling by binding with ANXA2.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):403. [31] ZHOU X, WU LF, WANG WY, et al. Anxa2 attenuates osteoblast growth and is associated with hip BMD and osteoporotic fracture in Chinese elderly. PLoS One. 2018;13(3):e0194781. [32] MIDWOOD KS, CHIQUET M, TUCKER RP, et al.Tenascin-C at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2016;129(23):4321-4327. [33] 刘洋. 不同界面处理对腱-骨愈合影响及TNC作用机制初步研究[D].重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2017. [34] GUO Y, YAN B, GUI Y, et al. Physiology and role of PCSK9 in vascular disease: Potential impact of localized PCSK9 in vascular wall. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(4):2333-2351. [35] DEMERS A, SAMAMI S, LAUZIER B, et al. PCSK9 induces CD36 degradation and affects long-chain fatty acid uptake and triglyceride metabolism in adipocytes and in mouse liver. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35(12):2517-2525. [36] JANG YJ, AN SY, KIM JH. Identification of MFGE8 in mesenchymal stem cell secretome as an anti-fibrotic factor in liver fibrosis. BMB Rep. 2017; 50(2):58-59. [37] 祝皓. 痹肿消汤及其有效成分阿魏酸干预胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠的定量蛋白质组学研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2014. [38] Gemert VY, Kozijn AE, Pouwer MG, et al. Novel high-intensive cholesterol-lowering therapies do not ameliorate knee OA development in humanized dyslipidemic mice.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;S1063-4584. [39] 李晶, 李娜, 律广富, 等. 鹿角胶对环磷酰胺所致血虚模型小鼠的影响[J].吉林中医药,2014,34(10):973-975. [40] 李辉, 陈俊宇, 杨擎, 等.鹿角胶对脑缺血大鼠脑组织的保护作用及机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(16):3895-3897. |
| [1] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [2] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [3] | Liu Tongbin, Lin Peng, Zhang Xiaoming, Dong Xiling, Cao Fei, Wang Le, Guo Xinxing. Optimization of preparation method of atorvastatin calcium sustained-release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 535-539. |
| [4] | Liang Haoran, Zhou Xin, Yang Yanfei, Niu Wenjie, Song Wenjie, Ren Zhiyuan, Wang Xueding, Liu Yang, Duan Wangping. Pathogenesis of femoral head necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in young adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 456-460. |
| [5] | Hu Yihua, Yang Chunhua, Lu Yuanyuan, Sun Deyi. Effect of electroacupuncture combined with triptolide on transforming growth factor beta expression in synovium and synovial fluid in a mouse model of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2252-2258. |
| [6] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [7] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [8] | Tang Shuo, Hou Decai. Correlation between traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types of femoral head necrosis and hip joint morphology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5867-5871. |
| [9] | Lin Ruohui, Chen Sainan, Ye Yunjin, Chen Juan, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang. Protective mechanism of Gushukang granule in a rat osteoporosis model based on TMT proteomic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5141-5147. |
| [10] | Wang Ding, Lin Tianye, Chen Weijian, Chen Jianfeng, Ou Huizhi, Li Hongzhu, Yang Peng, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Feng Zongquan. Medication rules and mechanism of femoral head necrosis: an analysis based on data mining and network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5148-5154. |
| [11] | Gao Tianhao, Qian Huifang, Yang Shangliang, Xin Chaofei, Lu Shitao, Xu Jianzhong. Calcium sulfate antibiotic carrier in the treatment of periprosthetic infection after arthroplasty and its effect on serum calcium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(30): 4823-4827. |
| [12] | Tang Shuo, Hou Decai. Constructing an animal model of femoral head necrosis: how to get closer to clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4691-4696. |
| [13] | Hong Xuezhi, Liu Lei, Yao Yunqian, Jiang Yuxin, Xu Jia, Mo Hanyou. Meta-analysis of complications and functional recovery of the hip after total hip arthroplasty in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(27): 4415-4420. |
| [14] | Wei Wei, Lou Pengqiang, Hou Decai. Animal models of femoral head necrosis: classification and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(26): 4211-4216. |
| [15] | Lin Haiqi, Chen Liang, Tang Lu, Weng Xiquan, Lin Wentao. Significance of urinary proteomics assessing pathological changes in the body [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3259-3266. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||