Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (11): 1752-1757.doi: 10.12307/2022.365
Previous Articles Next Articles
Osteosarcopenia: muscle-bone interactions
Li Xiaowei1, Deng Chengyuan2, Zhou Guijuan3, Chen Xiaocui3, Liao Ying3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, the Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China; 2Hunan Traditional Chinese Medical College, Zhuzhou 412008, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2021-01-18Revised:2021-01-20Accepted:2021-03-27Online:2022-04-18Published:2021-12-13 -
Contact:Liao Ying, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Li Xiaowei, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:School-level Major Special Project of University of South China, No. USCKF201902K02 (to LY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Xiaowei, Deng Chengyuan, Zhou Guijuan, Chen Xiaocui, Liao Ying. Osteosarcopenia: muscle-bone interactions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1752-1757.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
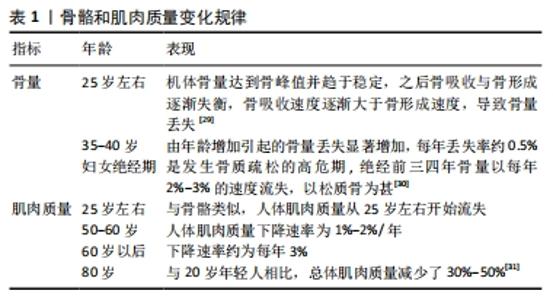
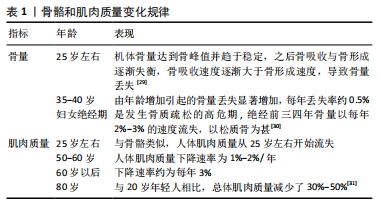
2.1 流行病学 由于人口老龄化的加快,随之而来的是肌少-骨质疏松症患病率的上升。中国>65岁的老年人中,男性肌少-骨质疏松症患病率为10.4%,女性为15.1%。而在伊朗的老年人口中,男性肌少-骨质疏松症患病率高达33.8%,女性为33.9%[9]。肌少-骨质疏松症患病率的上升带来了一系列的严重后果,基于日本标准(骨骼肌指数女性为5.46 kg/m2,男性为6.87 kg/m2)的肌少-骨质疏松症患者中,女性髋部骨折的患病率达到达44.7% 而男性为 81.1%[10],患者表现出骨骼肌肉系统功能的下降,如明显的握力降低、步速下降,以及骨代谢标志物显著增加[11]。对于既往有髋部骨折史的妇女,骨质疏松症和肌少症会加重患者的椎骨骨折的严重程度,低骨量和低肌肉量的妇女是椎骨骨折的高危人群[12]。 2.2 骨骼和肌肉的相互作用 骨骼和肌肉都起源于中胚层和外胚层间充质干细胞,在体内或体外因素下分化而来,相邻的解剖关系为力学信号及化学信号提供了基础条件。骨骼和肌肉之间的相互影响主要通过力学刺激与其分泌的生物活性因子实现的[13]。除此之外,内分泌、疾病、遗传、运动量等因素也共同影响着骨骼与肌肉表型。 2.2.1 肌肉对骨骼的作用 肌肉对骨骼的作用机制主要包括力学作用与化学作用。力学作用主要是通过肌肉收缩对骨骼产生应力刺激,促进骨骼生长发育,骨密度和骨强度增加。有研究显示注射肉毒杆菌毒素后动物出现了暂时的行走步态紊乱,但肌肉萎缩和骨量丢失却持续存在,说明了肌肉质量有助于维持正常骨量[14]。LAM等[15]发现动态电刺激引起的肌肉收缩能够部分抑制由于缺乏每日负重活动而引起的骨丢失和小梁结构退化,表明肌肉收缩能够部分减少骨丢失。肌肉对于骨骼的化学作用是指肌肉产生的化学物质如细胞因子、炎性因子、内分泌激素等通过旁分泌或者内分泌机制作用于成骨(前体)细胞、破骨细胞或骨细胞,产生促进成骨或者抑制破骨的作用。骨骼肌分泌体含有影响骨的各种分子,包括骨诱导因子、胰岛素样生长因子1、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素15、肌生长抑制素等,其中骨诱导因子主要通过促进骨形成来增加骨量[16-17]。肌肉生长抑制素是由骨骼肌分泌的一种细胞因子,抑制其表达会引起肌肉肥厚、骨量增加,当其水平升高时可导致骨密度下降,但是目前仍不清楚肌肉生长抑制激素是直接影响骨骼还是通过肌肉间接影响[18]。由此可见,肌肉的生物力学刺激对于骨骼的效应主要是促进成骨,而肌肉产生的生物活性因子对于骨骼的效应可以表现为多种形式,既可以像骨诱导因子那样促进成骨,也可能像肌肉生长抑制素那样导致骨密度下降。 2.2.2 骨骼对于肌肉的调节作用 骨骼对于肌肉的调节作用也是通过力学作用与化学作用实现的。骨细胞和成骨细胞可以分泌骨钙素、硬骨素、Indian Hedgehog(Ihh)等因子对肌肉作用。Ihh可以通过维持p21蛋白水平来促进鸡胚胎成肌细胞存活,而Ihh信号蛋白敲除的鸡胚胎中出现后肢肌肉明显缺失及胚胎中肌肉质量的丢失[19]。骨骼对肌肉也有力学作用上的影响。Connexin43(Cx43)是一种富含于成骨细胞(OBs)和骨细胞(OCYs)的缝隙连接蛋白,在机械传导中起着重要作用。SHEN等[20]在特异性间隙连接蛋白Cx43敲除的小鼠中观察到肱骨皮质厚度和密度的降低,髓腔横截面积的增大,肌肉质量以及力量的下降,这些肌肉缺陷伴随着骨钙素基因的mRNA丰度降低以及骨钙素含量的减少,表明了Cx43参与肌肉生长和功能调控,作者还发现体内注射羧化不全骨钙素(Glu-OC)可以部分挽救小鼠肌肉质量和握力的下降,作者据此认为成骨细胞/骨细胞中的Cx43可能通过羧化不全骨钙素的内分泌作用间接调节骨骼肌的生长和功能。 总之,骨骼和肌肉由于共同的起源以及邻近的解剖位置,力学信号和化学信号的交流密切,在人体生长发育的过程中相互促进发育、维持稳态,但是肌少-骨质疏松症发生发展的过程中,它们之间的机械与化学信号的交流可能成为肌少-骨质疏松症发病机制,造成骨骼肌肉系统质量丢失以及功能减退,骨质疏松症和肌少症还有共同的危险因素,这些危险因素背后原因隐藏着肌少-骨质疏松症的发病机制。 2.3 肌少-骨质疏松症的发病机制 肌少-骨质疏松症被用来描述肌少症和骨质疏松症共同存在的情况,这两种疾病都有着随年龄增长的运动系统功能减退和质量丢失,分别侧重于描述骨骼和肌肉,有学者声称“它们是一种疾病在不同生理系统中的表现[21]”,它们有着共同的发病机制,主要包括遗传、内分泌、某些疾病、个体运动量的减少等[22]。 因为肌肉和骨骼具有相同的起源,间充质干细胞可以分化而来,遗传因素可以同时影响这两种组织,根据KARASIK等[23]的研究,遗传影响对肌肉损失和骨质减少的贡献是60%-70%。遗传因素很大程度决定了不同部位的骨量差异以及形态,某些特定基因如甲基转移酶样21 C (METTL21C)被认为可导致肌肉减少和骨质疏松[24]。 某些内分泌因子如骨骼的维生素D、胰岛素样生长因子1和性激素等已经被证实会影响骨骼肌肉健康。维生素D受体在成骨细胞和成肌细胞中均有表达,一些维生素D缺乏的患者患有明显的骨质减少和肌肉消耗。胰岛素样生长因子1是全身特定组织分泌的,参与全身循环的是由肝脏分泌,作用于骨骼和肌肉的胰岛素样生长因子1主要来自组织间的自分泌和旁分泌[17]。性激素对骨骼肌肉系统的影响很常见的,绝经后妇女雌激素水平降低将明显增加肌少症和骨质疏松症的患病概率,临床大样本研究显示绝经后的妇女,首先出现骨量减少,随着病情发展发生肌肉质量的下降[22]。 陈锦成等[22]将疾病增加肌少-骨质疏松症的原因进行了归类:2型糖尿病可直接导致患者Ⅱ型肌纤维受损,随着病情发展导致肌肉质量的减少,1型糖尿病则主要引起骨量丢失;某些疾病如类风湿性关节炎会导致促炎细胞因子如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6升高的病理环境,在这种炎性反应状态下肌源性增生和分化受到抑制,肌肉降解加快;疾病导致药物使用如糖皮质激素会抑制蛋白质合成以及影响成骨细胞的增生与分化,增加患病概率;疾病状态下的个体运动量减少会影响骨钙素的分泌,而骨钙素的作用是刺激β细胞增生和胰岛素分泌,进而增加肌肉强度[25]。当身体缺乏机械刺激时,会导致肌肉无力以及重要器官周围的脂肪组织堆积永久化,这些组织表型有利于糖代谢障碍、慢性炎症的进展,加大骨质疏松症风险[26]。当人体因长期卧床、制动、脊髓损伤及肌肉减少等致使运动量减少时,骨骼受到的应力刺激也随之下降,破骨细胞重吸收的活性增强,成骨细胞介导的骨形成受到抑制,最终导致骨质疏松症的发生[27]。运动可以下调某些慢性炎症因子如白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α及C-反应蛋白,并且增加卫星细胞的募集和修复,在缺乏运动的老人群中表现出更低肌肉力量[28]。 2.4 肌少-骨质疏松症的预防 与大多数疾病类似,肌少-骨质疏松症的预防比治疗更重要,人体的骨骼和肌肉质量在年轻时期就达到峰值,之后开始随年龄增加逐渐下降,见表1。由于骨骼肌肉的峰值出现较早,之后开始下降,因此肌少-骨质疏松症的预防也应该从年轻时做起,目前手段主要包括患者教育、健康档案、倡导健康生活习惯,值得注意的是,肌少-骨质疏松症的预防对医务人员提出了新的要求,加强对医务人员的培训也是一个重点。"
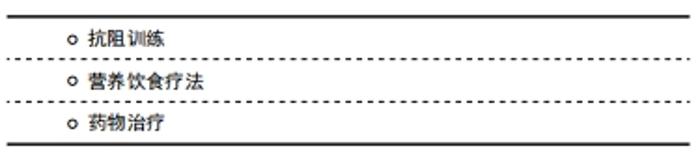
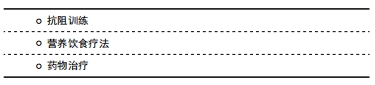
2.4.1 患者教育 根据肌少-骨质疏松症的高危因素、预防及干预措施,帮助个体建立预防或延缓肌少症的意识,促使其改变不健康的生活方式,以预防或延缓老年肌少-骨质疏松症的进展[32],其主要形式包括举办健康讲座、发放健康教育资料、推广健骨操等[33],也有部分临床工作者采用了微信等新兴网络平台对患者进行健康宣教并取得了满意结果[34]。 2.4.2 健康档案 根据具体患者的危险因素进行个性化、综合性管理的服务,根据患者具体情况制定指导方案非常重要,如合理的饮食方案,补充维生素D等营养素,选择适宜强度的运动方式,健康的作息等。个性化的健康管理能提高患者的依从性,提升治疗的效果[35]。然而中国慢病信息化管理还存在许多缺陷:①居民电子健康档案并未完成全国性系统建设,慢病管理缺少信息化基础;②现存居民档案未形成统一化管理,跨系统提取档案信息十分繁琐;③中国人口基数大,人口呈现流动季节性、地区性变化,给档案建立带来困难[36]。 2.4.3 肌少-骨质疏松症的发生发展 肌少-骨质疏松症的发生发展与生活习惯密切相关,在各行业均能发现生活习惯对于骨骼肌肉健康的影响。在电网职工的调查中发现增加牛奶饮用量和保持良好规律的运动锻炼习惯是可能的保护因素,研究还发现文化程度与骨质疏松症有关[37]。首都大学教师的调查中也发现运动和喝牛奶是骨质疏松症的保护因素,女性还有月经作为保护因素,而吸烟、饮酒和和碳酸饮料均为危险因素,且男性不良生活习惯的比例更大[38]。现代社会的工作特点也在影响人们的骨骼健康,研究发现久坐型和久站型工作环境更加容易导致骨质疏松,而活动型工作环境可以通过增加应力刺激、促进血液循环来预防骨质疏松[39]。不良生活习惯同样威胁着人们的肌肉系统,吸烟、营养不良是最为常见的危险因素[40]。研究者发现在休息或者某些运动状态下,吸烟者的肌肉组织能量供应会减少,肌肉组织的代谢产物清除速率下降。这种代谢变化会随着年龄增长出现,吸烟会加速这种变化,导致肌肉力量下降,质量丢失,以上的代谢变化会伴随衰老而出现,但吸烟会加重这样的变化[41]。令人遗憾的是,作为预防肌少-骨质疏松症的主力军,部分医务人员自身也未形成良好的生活习惯,在中青年医务人员中,相当比例的人员存在抽烟、饮酒、浓茶、咖啡等不良生活习惯[42]。 2.4.4 其他 除了患者的宣教与管理,骨质疏松的预防工作还面临着其他问题,现阶段中国医务人员的文化水平参差不齐,部分医务人员缺乏学习前沿知识主观能动性,知识结构陈旧,医务人员作为民众健康管理的先锋,自身知识匮乏势必会影响工作的开展。一项针对宜春市人民医院400名医务人员的随机抽样调查发现,仅50.75%的医务人员清楚观众所熟知的诊断标准,虽然有89.52%的医务人员参加体检,但是仅仅42.61%的体检项目中包含骨质疏松症筛查[43]。上海地区的抽样调查也发现了类似问题,医务人员自身的对骨质疏松症预防的知晓率不高,没有养成健康的生活习惯,其中以20-29岁和≥70岁的医务人员为主,作者呼吁医务人员完善继续教育系统,提高其管理水平及预防意识[42]。 2.5 肌少-骨质疏松症的治疗 肌少-骨质疏松症复杂的、多因素致病的特点要求多方面的预防和治疗策略[44],主要的防治措施包括:抗阻训练、营养饮食疗法、药物疗法等。其中营养饮食疗法是基础,运动疗法和应用最为广泛,药物防治肌少-骨质疏松症有望成为新的突破点。"

2.5.1 抗阻训练 抗阻训练是通过使用各种训练方式,如自由重量、举重器械、健身球、弹力带和不同的运动速度,来改善健康状况和提高运动成绩的一种训练方式[45]。它的优点在于能够改善心血管及肌肉功能,因而特别适用于老年人及虚弱人群[46]。高负荷和轻负荷抗阻训练都可以增加肌肉力量,相较之下高负荷组的力量增益更多,并且在一定程度上增加肌肉的质量[47]。LICHTENBERG等[48]的研究发现,在28周的干预期后,老年男性高强度抗阻训练组的骨骼肌质量指数和握力与不活跃的对照组相比有显著的组间差异,表明高强度抗阻训练是一种可行且高效和安全的抗肌肉减少症训练方式,对于老年人也同样适用。 但是在具体实施过程中,要根据患者的忍耐度及功能状态选择不同的强度以及类型,对疼痛患者要特别关注。在训练过程中每个主要肌肉群应至少进行两组一种运动,目标强度为8-12次最大重复(RM),对于初学者或者久坐的患者,应该从低强度开始,循序渐进。世卫组织对全球65岁及以上年龄组老年患者的建议是,每周应进行至少2 d肌肉强化活动,并且需要涉及脊柱、髋部等主大肌肉群[49]。但是不同部位对抗阻训练刺激骨量增加程度是不一样的,股骨转子和股骨转子间骨密度会因所进行的阻力锻炼而升高,股骨颈值没有明显变化,最大化的骨骼获益训练方案为较高幅度的机械负荷(最大幅度的80%-85%)[50]。 2.5.2 营养饮食疗法 营养饮食疗法是通过调节食物营养元素比例或者热量来预防和治疗肌少-骨质疏松症的一种方法。大多数老年人存在热量和蛋白质摄入不足,在疾病和外伤等情况下极易造成营养元素缺失。因此建议老年人在日常生活中要保持平衡膳食和充足营养。营养饮食疗法主要包括低脂饮食、补充维生素D、优质蛋白饮食等。 低脂饮食对于治疗肌少-骨质疏松症的作用目前并未得到重视,因为骨质疏松症长期以来被认为与肌肉或脂肪组织无关,然而近年的研究表明当脂肪过多或脂肪渗入骨骼时可能导致更高的骨折率。除了更高的骨折风险,总脂肪和腹部脂肪组织的增加会导致促炎性细胞因子的增加和激素紊乱,进一步造成肌肉和骨骼逐渐丧失和脂肪增加的恶性循环,据此ILICH等[51]建议通过调整饮食中的蛋白质/碳水化合物比例,以减少肥胖,保持肌肉和骨量,这体现了低脂饮食的对于防治肌少-骨质疏松症的重要性。 维生素D缺乏是老年人钙吸收不良的主要原因,进而导致了骨量的丢失,补充维生素D的研究表明,治疗组血浆钙和磷酸盐水平较对照组显著增加[52]。同时维生素D能够显著提高denosumab治疗骨质疏松症的疗效,在一项为期3年的回顾研究中发现,与单独接受denosumab治疗的患者相比,联合补充维生素D和钙片的患者髋关节和腰椎骨密度以及骨矿物质显著提高[53]。维生素D也被认为是肌萎缩相关的重要因素。动物实验发现在限制活动的小鼠中,低维生素D饮食加速了腓肠肌质量丢失和握力的下降。针对中国沈阳地区6 812名老年人的调查也发现,当血清25羟基维生素D3处于低水平时,握力显著降低,但是经常锻炼可以一定程度上减少握力的下降,作者据此建议老年人增加体力活动,适量补充维生素D,避免缺乏体力活动和维生素D缺乏引起的肌少症[54]。2011年,美国医学研究所(IOM)建议60岁以上的男性和女性每天应摄入800 IU (20 μg各种来源的维生素D,以保持骨骼健康防止摔伤[55]。也有作者认为每天10 μg就能将血清维生素D浓度维持在75-100 nmol/L 以满足人体需求[56]。 优质蛋白饮食对于骨骼肌肉系统健康的作用已经得到广泛研究并取得了认可。TIELAND等[57]发现当虚弱的老年人群进行长时间的运动训练时,膳食蛋白的补充是增加肌肉质量的必要条件,并且增加的蛋白质摄入量没有导致其他健康问题。据此作者强烈建议虚弱的老年人在进行抗阻运动训练的同时摄入更多的蛋白质以减少与年龄相关的肌肉质量丢失的程度,从而防止肌肉功能的减退以及质量的丢失。相关荟萃分析表明,与年轻人相比,老年人群对蛋白质的需求更大,高蛋白摄入与股骨颈和全髋关节骨密度之间呈正趋势,因此蛋白质可能在预防骨质流失和减缓骨质疏松症方面发挥有益的作用,且高蛋白摄入显著减少髋部骨折风险[58]。然而,目前针对老年人建议的蛋白质摄入量可能不足以维持肌肉质量和力量,进而影响了老年人的健康与独立生活能力[59]。根据《肌肉衰减综合征营养与运动干预中国专家共识》老年人蛋白质的推荐摄入量应维持在1.0-1.5 g/(kg?d),蛋白质来源应该以优质动物蛋白如乳清蛋白为主,因其富含较高比例的亮氨酸,可以促进骨骼肌蛋白合成[60]。 2.5.3 药物治疗 目前并未在临床中得到广泛应用,但是相关研究中发现某些类型的药物可以使肌少-骨质疏松症患者明显获益,显示出药物治疗骨骼肌肉减少症的潜力,主要种类包括:睾酮、雄激素/合成类激素、生长激素。 众所周知,睾酮与肌肉质量和力量的增加有关,但是在30岁以后,体内睾酮的数量逐渐递减,由此对肌肉造成了负面影响。一项对老年人类调查发现,男性血清睾酮水平与肌肉力量和骨微结构密切相关,高睾酮水平的男性肌肉质量更大,握力更强,骨密度更高,而在老年女性中,脱氢表雄酮的作用更加重要,高睾酮水平组除了更高的股骨颈密度以外,还表现出更强的参与运动的意愿 [61]。睾酮可以增加肌肉的蛋白质合成,健康成年男性皮下注射睾酮以后,骨骼肌蛋白质的分数合成率升高为原来的2倍但是分解率没有变化。并且在禁食状态下,睾酮注射增加了腿部动静脉必需和非必需的氮平衡,而没有增加氨基酸转运,作者据此推测睾酮注射导致骨骼肌中净蛋白质合成和细胞内氨基酸再利用的增加,并不会增加局部组织的氨基酸转运,这对于无法进食蛋白或者营养不良导致的肌少症患者来说具有重要意义[62]。睾酮也可以显著增加骨的强度以及骨密度,在为期1年的治中,睾酮水平较低的老年男性接受睾酮治疗后,他们的脊柱和股骨颈骨强度显著增加,脊柱比髋部更明显,小梁骨比富含皮质的外周骨增加更加明显[63] 。 雄激素的丢失会延长破骨细胞寿命并且缩短成骨细胞寿命进而导致骨吸收大于骨形成,增加骨重塑的速度。在任何年龄段,雄激素治疗都能通过雄激素受体保持松质骨的质量和完整性[64]。诺龙是一种注射用合成类固醇激素,在一项为期22周的研究中,诺龙显著减少了高山绵羊在16周冈下肌腱修复术后引起的肌肉萎缩,此外,作者还发现,如果在肌腱释放后立即应用类固醇,无论是否行冈下肌腱修复术,诺龙都很大程度上能减少肌腱被释放后引起的脂肪浸润[65]。MK-0773是一种选择性雄激素受体调节剂,旨在改善肌肉功能,同时最大限度地减少对其他组织的影响。6个月的治疗使老年女性的体质量和肌肉力量较对照组明显改善[66],相应的治疗组转氨酶出现了增高,在停药后恢复,治疗组女性并未出现雄性化表现。 生长激素可以增加老年男性肌肉质量和力量,但不能恢复年轻时的肌原纤维蛋白合成率。老年男性的肌肉中肌原纤维蛋白的合成速度比年轻人慢,相关研究认为胰岛素样生长因子1系统活性的降低可能是蛋白质合成减慢的一个决定因素 [67]。当生长激素与睾酮联合使用时,可以展现出比单独使用生长激素或者睾酮更强的增加肌肉质量的作用,并且伴随着脂肪含量的下降[68]。生长激素还能提高生长激素缺乏症患者远期骨密度,它的作用主要分为3个阶段:第1年骨密度开始下降,随后骨密度持续增加,60个月后形成稳定的平台[69]。"

| [1] COLLINS FL, RIOS-ARCE ND, SCHEPPER JD, et al. The Potential of Probiotics as a Therapy for Osteoporosis. Microbiol Spectr. 2017;5(4): 10.1128/microbiolspec.BAD-0015-2016. [2] 薛鹏, 李玉坤. 2017年版《原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南》解读[J].河北医科大学学报,2018,39(1):1-6. [3] KANIS JA, GLÜER CC. An update on the diagnosis and assessment of osteoporosis with densitometry. Committee of Scientific Advisors, International Osteoporosis Foundation. Osteoporos Int. 2000;11(3): 192-202. [4] WALSTON JD. Sarcopenia in older adults. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012; 24(6):623-627. [5] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.肌少症共识[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(3):215-227. [6] BINKLEY N, BUEHRING B. Beyond FRAX®: It’s Time to Consider “Sarco-Osteopenia”. J Clin Densitom. 2009;12(4):413-416. [7] CEVEI M, ONOFREI RR, CIOARA F, et al. Correlations between the Quality of Life Domains and Clinical Variables in Sarcopenic Osteoporotic Postmenopausal Women. J Clin Med. 2020;9(2):441. [8] NIELSEN BR, ANDERSEN HE, HADDOCK B, et al. Prevalence of muscle dysfunction concomitant with osteoporosis in a home-dwelling Danish population aged 65–93years - The Copenhagen Sarcopenia Study.Exp Gerontol. 2020;138:110974. [9] WANG YJ, WANG Y, ZHAN JK, et al. Sarco-Osteoporosis: Prevalence and Association with Frailty in Chinese Community-Dwelling Older Adults.Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:482940. [10] HIDA T, ISHIGURO N, SHIMOKATA H, et al. International, High prevalence of sarcopenia and reduced leg muscle mass in Japanese patients immediately after a hip fracture. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13(2):413-420. [11] DREY M, SIEBER CC, BERTSCH T, et al. Osteosarcopenia is more than sarcopenia and osteopenia alone. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2016;28(5):895-899. [12] DI MONACO M, CASTIGLIONI C, BARDESONO F, et al. Sarcopenia, osteoporosis and the burden of prevalent vertebral fractures: a cross-sectional study of 350 women with hip fracture. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2020;56(2):184-190. [13] 林华, 谢忠建, 朱梅, 等. 肌肉和骨骼的相互调节[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2016,9(3):236-239. [14] MANSKE SL, BOYD SK, ZERNICKE RF. Vertical ground reaction forces diminish in mice after botulinum toxin injection.J Biomech. 2011;44(4): 637-643. [15] LAM H, QIN YX. The effects of frequency-dependent dynamic muscle stimulation on inhibition of trabecular bone loss in a disuse model.Bone. 2008;43(6):1093-1100. [16] TAGLIAFERRI C, WITTRANT Y, DAVICCO MJ, et al. Muscle and bone, two interconnected tissues. Ageing Res Rev. 2015;21:55-70. [17] KAWAO N, KAJI H. Interactions between muscle tissues and bone metabolism. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(5):687-695. [18] BUEHRING B, BINKLEY N. Myostatin--the holy grail for muscle, bone, and fat?. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2013;11(4):407-414. [19] BREN-MATTISON Y, HAUSBURG M, OLWIN BB. Growth of limb muscle is dependent on skeletal-derived Indian hedgehog. Dev Biol. 2011;356(2):486-495. [20] SHEN H, GRIMSTON S, CIVITELLI R, et al. Thomopoulos, Deletion of Connexin43 in Osteoblasts/Osteocytes Leads to Impaired Muscle Formation in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(4):596-605. [21] BINKLEY N, KRUEGER D, BUEHRING B. What’s in a name revisited: should osteoporosis and sarcopenia be considered components of “dysmobility syndrome?”. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(12):2955-2959. [22] 陈锦成, 朱国涛, 刘洪文,等. “肌少-骨质疏松症”的共同发病机制[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2020,13(1):95-102. [23] KARASIK D, CUPPLES LA, HANNAN MT, et al. Genome screen for a combined bone phenotype using principal component analysis: the Framingham study. Bone. 2004;34(3):547-556. [24] HUANG J, HSU YH, MO C, et al. METTL21C is a potential pleiotropic gene for osteoporosis and sarcopenia acting through the modulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(7):1531-1540. [25] MERA P, LAUE K, FERRON M, et al. Osteocalcin Signaling in Myofibers Is Necessary and Sufficient for Optimum Adaptation to Exercise. Cell Metab. 2017;25(1):218. [26] PAGNOTTI GM, STYNER M, UZER G, et al. Combating osteoporosis and obesity with exercise: leveraging cell mechanosensitivity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(6):339-355. [27] 刘长江. 废用性骨质疏松症的防治研究进展[J].科技资讯,2020, 18(3):224-226. [28] PHU S, BOERSMA D, DUQUE G. Exercise and Sarcopenia. J Clin Densitom. 2015;18(4):488- 492. [29] 陈梦阳,谢菊英.骨质疏松症发病机制的研究进展[J].湘南学院学报(医学版),2018,20(1):63-66. [30] 张琚, 曾果.运动对骨量影响的研究进展[J].环境卫生学杂志, 2006,33(4):238-243. [31] MORLEY JE. Frailty and sarcopenia in elderly. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2016;128(Suppl 7):439-445. [32] 钟静,王秀华.老年人肌少症非药物干预的研究进展[J].中国护理管理, 2019,19(8):144-150. [33] 王泽洲,万和平,张天晔, 等. 海市部分社区居民骨质疏松预防知识、自我效能、行为状况及健康宣教效果分析[J].上海预防医学, 2017,29(12):922-925. [34] 甘萍, 迟中海, 李培杰, 等. 新形式健康教育对老年骨质疏松病人生活质量影响[J].齐鲁医学杂志,2017,32(1):78-81. [35] 杨红旗, 赵欣, 陈燕, 等. 骨质疏松症的健康管理[J].中国临床保健杂志, 2018,21(5):718-720. [36] 朱赛, 苏昕, 辛妮, 等. 信息化技术在慢病管理中的研究进展[J].中国医学装备,2019,16(5):143-146. [37] 王德杰, 郑傲, 潘杰.电网男职工骨质疏松症现状调查及危险因素分析[J].中国现代药物应用,2019,13(12):28-30. [38] 竹盈, 陈浩, 刘凤娟.生活方式与大学教师骨密度水平的相关性分析[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2019,18(11):1230-1233. [39] 刘金彦, 刘娜, 任宛丽.女性医护人员骨质疏松患病率调查及影响因素分析[J].实用预防医学,2019,26(2):95-97. [40] WANG H, HAI S, LIU Y, et al. Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Associated Factors in Community-dwelling Elderly Populations in Chengdu China. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019;50(2):224-228. [41] ALEXANDRE TDA S, DUARTE YA, SANTOS JL, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of sarcopenia among elderly in Brazil: Findings from the SABE study. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014;18(3):284-290. [42] 张琼, 陈慎.不同年龄段医务人员对骨质疏松症认知程度的比较[J].中国全科医学,2017,20(7):257-260. [43] 李百云, 熊东林, 熊毅丰.不同年龄段医务人员对骨质疏松症认知程度的比较[C].江西省中西医结合骨质疏松与骨矿盐疾病学术交流会资料汇编,2018. [44] HASSAN EB, DUQUE G. Osteosarcopenia: A new geriatric syndrome.Aust Fam Physician. 2017;46(11):849-853. [45] HONG AR, KIM SW. Effects of Resistance Exercise on Bone Health.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2018;33(4):435-444. [46] LIU Y, CHU JMT, YAN T, et al. Short-term resistance exercise inhibits neuroinflammation and attenuates neuropathological changes in 3xTg Alzheimer’s disease mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):4. [47] CSAPO R, ALEGRE LM. Effects of resistance training with moderate vs heavy loads on muscle mass and strength in the elderly: A meta‐analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2016;26(9):995-1006. [48] LICHTENBERG T, VON STENGEL S, SIEBER C, et al. The Favorable Effects of a High-Intensity Resistance Training on Sarcopenia in Older Community-Dwelling Men with Osteosarcopenia: The Randomized Controlled FrOST Study. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:2173-2186. [49] World Health Organization. Global recommendations on phys-ical activity for health. Geneva: World Health Organiza-tion. 2010:9-10. [50] KERR D, MORTON A, DICK I, et al.Exercise effects on bone mass in postmenopausal women are site-specific and load-dependent. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;11(2):218-225. [51] ILICH JZ, KELLY OJ, INGLIS JE, et al.Ormsbee, Interrelationship among muscle, fat, and bone: Connecting the dots on cellular, hormonal, and whole body levels.Ageing Res Rev. 2014;15:51-60. [52] FRANCIS RM, PEACOCK M, STORER JH, et al.Calcium malabsorption in the elderly: the effect of treatment with oral 25-hydroxyvitamin D3.Eur J Clin Invest. 1983;13(5):391-396. [53] SUZUKI T, NAKAMURA Y, KATO H. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation with 3-year denosumab treatment is beneficial to enhance bone mineral density in postmenopausal patients with osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;15:15-22. [54] YANG A, LV Q, CHEN F, et al.The effect of vitamin D on sarcopenia depends on the level of physical activity in older adults.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(3):678-689. [55] MEDICINE IO. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D, National Academies Press Washington, DC National Academies Press. 2011. [56] VAES AMM, TIELAND M, DE REGT MF, et al. Dose–response effects of supplementation with calcifediol on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status and its metabolites: A randomized controlled trial in older adults. Clin Nutr. 2018;37(3):808-814. [57] TIELAND M, DIRKS ML, VAN DER ZWALUW N, et al. Protein Supplementation Increases Muscle Mass Gain During Prolonged Resistance-Type Exercise Training in Frail Elderly People: A Randomized, Double-Blind. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012;13(8):713-719. [58] GROENENDIJK I, DEN BOEFT L, VAN LOON LJC, et al. High Versus low Dietary Protein Intake and Bone Health in Older Adults: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019;17:1101-1112. [59] LONNIE M, HOOKER E, BRUNSTROM JM, et al.Protein for Life: Review of Optimal Protein Intake, Sustainable Dietary Sources and the Effect on Appetite in Ageing Adults.Nutrients. 2018;10(3):360. [60] 肌肉衰减综合征营养与运动干预中国专家共识(节录)[J].营养学报, 2015(4):320-324. [61] KONG SH, KIM JH, LEE JH, et al. Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate and Free Testosterone but not Estradiol are Related to Muscle Strength and Bone Microarchitecture in Older Adults. Calcif Tissue Int. 2019; 105(3):285-293. [62] FERRANDO AA, TIPTON KD, DOYLE D, et al. Testosterone injection stimulates net protein synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1998;275(5):E864-871. [63] SNYDER PJ, KOPPERDAHL DL, STEPHENS-SHIELDS AJ, et al. Effect of Testosterone Treatment on Volumetric Bone Density and Strength in Older Men With Low Testosterone: A Controlled Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(4):471-479. [64] LINDBERG MK, VANDENPUT L, MOVÈRARE SKRTIC S, et al. Androgens and the skeleton. Minerva Endocrinol. 2005;30(1):15-25. [65] GERBER C, MEYER DC, FLÜCK M, et al. Anabolic Steroids Reduce Muscle Degeneration Associated With Rotator Cuff Tendon Release in Sheep.Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(10):2393-2400. [66] PAPANICOLAOU DA, ATHER SN, ZHU H, et al. A phase IIA randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial to study the efficacy and safety of the selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), MK-0773 in female participants with sarcopenia. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013;17(6):533-543. [67] WELLE S, THORNTON C, STATT M, et al. Growth hormone increases muscle mass and strength but does not rejuvenate myofibrillar protein synthesis in healthy subjects over 60 years old. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81(9):3239-3243. [68] BLACKMAN MR, SORKIN JD, MÜNZER T, et al. Growth hormone and sex steroid administration in healthy aged women and men a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2002;288(18):2282-2292. [69] WILHELM B, KANN PH. Long-term effects of 7-year growth hormone substitution on bone metabolism, bone density, and bone quality in growth hormone-deficient adults. Med Klin (Munich). 2004;99(10):569-577. [70] BINKLEY N, KRUEGER D, BUEHRING B. What’s in a name revisited: should osteoporosis and sarcopenia be considered components of “dysmobility syndrome?”. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(12):2955-2959. [71] 杨艳芳, 徐红. 肌少症,骨质疏松的关系及研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(98):150-151+155. [72] CHEN LK, LIU LK, WOO J, et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus Report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014; 15(2):95-101. [73] LANE NE. Epidemiology, etiology, and diagnosis of osteoporosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194(2 Suppl):S3-11. [74] 赵瑾, 常晶.老年肌少-骨质疏松症相关研究进展[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2020,19(9):713-716. |
| [1] | Lu Pan, Zhang Chunlin, Wang Yongkui, Yan Xu, Dong Chao, Yue Yisen, Li Long, Zhu Andi. Volume changes of cervical herniated discs after open-door laminoplasty and conservative treatment as assessed by three-dimensional volume method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1395-1401. |
| [2] | Lu Qinxue, Xu Ning, Yang Yinglan, Han Qianqian, Duanmu Xianyu, Guo Yuwei, Han Qing. Femoroacetabular impingement: strength trainings for nerve-muscle, peripheral muscle and core muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 786-791. |
| [3] | Zheng Zhenquan, Rong Jiesheng. Sarcopenia: age-related muscle mass loss and functional declines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 792-797. |
| [4] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin, Liu Jinyuan, Wang Xiaohu, Xu Xiaopei, Liu Zemin. Greater trochanter pain syndrome: anatomy, pathology, differential diagnosis and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 296-301. |
| [5] | Yang Xiaoxiao, Xu Yuanjing, Li Wentao, Wang Wenhao, Ma Zhenjiang, Wang Jinwu. Treatment of Achilles tendinitis with an ultrasonic device for emulsification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2259-2264. |
| [6] | Li Jianyi, Liu Zhiyuan, Deng Chengliang. Function and hot spot of adipose-derived stem cell exosomes in tissue regeneration and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2093-2098. |
| [7] | Liao Jianzhao, Xia Tian. The role of extracellular matrix in the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis and its clinical research value [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1937-1943. |
| [8] | Xu Jie, Zhou Wenqi, Luo Xiaobing. Visual analysis of patellofemoral pain syndrome research hotspots and content [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1877-1887. |
| [9] | Yang Xiaoxiao, Xu Yuanjing, Li Wentao, Wang Wenhao, Ma Zhenjiang, Wang Jinwu. Experimental study on treatment of Achilles tendinitis with ultrasound-guided phacoemulsification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [10] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [11] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [12] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [13] | Tang Shuo, Hou Decai. Correlation between traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types of femoral head necrosis and hip joint morphology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5867-5871. |
| [14] | Xiong Chen, He Guiping, Zhang Kun, He Xiao, Yang Jiarui, He Changjun, Wang Xiaolong, Wang Chen, Shi Zhengwei, Zhu Yangjun, Heng Lisong. Conservative treatment, open reduction, percutaneous minimally invasive plate internal fixation and intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5878-5887. |
| [15] | Dong Yi, Deng Jiupeng, Fan Xinhao, Xi Guangwei. Effect of high-concentration H2O2 immersion and ultrasonic treatment with different durations on interfacial bonding strength of fiber post and resin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(34): 5453-5458. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||