Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (12): 1937-1943.doi: 10.12307/2022.520
Previous Articles Next Articles
The role of extracellular matrix in the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis and its clinical research value
Liao Jianzhao, Xia Tian
- Graduate School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2021-05-31Revised:2021-06-25Accepted:2021-09-26Online:2022-04-28Published:2021-12-15 -
Contact:Xia Tian, MD candidate, Associate professor, Graduate School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liao Jianzhao, Master candidate, Graduate School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the First-class Discipline Construction and Opening Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019XK026 (to XT [project participant]); Innovation Program of Guangxi Graduate Education, No. YCBXJ2021019 (to XT) and YCSW2021219 (to LJZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liao Jianzhao, Xia Tian. The role of extracellular matrix in the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis and its clinical research value[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1937-1943.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
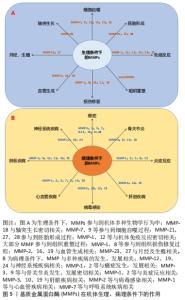
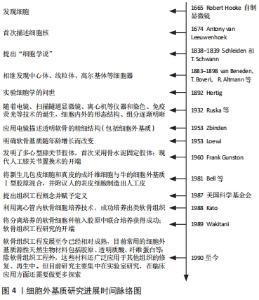
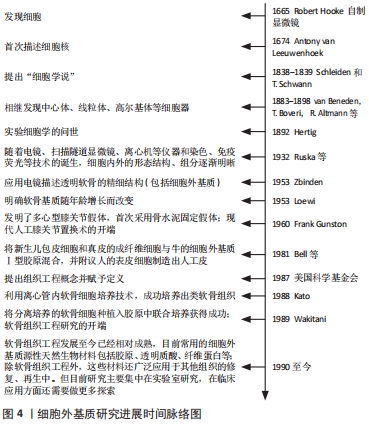
2.2 细胞外基质在机体中的作用 细胞外基质是由动态变化且相互连接的大分子组成的复杂三维网络结构,可以通过调节细胞间的信号转导、影响细胞表型,以形成适合细胞生存的特定结构[21]。细胞外基质的组分还作为细胞表面受体(如整合素等)的配体[22],经由多种类型的细胞表面受体接受并传递细胞外基质中的信号,并在基质和细胞之间产生动态的相互作用,进而调节一系列诸如细胞黏附、凋亡、增殖、迁移和分化等生物学行为,因此细胞外基质还被认为是细胞表型的主要调节因子[23]。在机体生长、发育和组织重塑的过程中,细胞外基质在降解和沉积之间形成动态平衡,此过程主要由基质降解酶介导,如基质金属蛋白酶等,以及细胞外基质内的基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂,在基质金属蛋白酶/基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂等共同作用下,细胞外基质的降解和合成形成动态平衡,以调节细胞外基质的结构和特性,维持生理条件下的细胞外基质代谢平衡[24]。近期研究表明,细胞外基质在机体生长、发育、衰老及多种疾病的发生、发展过程中发挥着重要作用,如影响细胞黏附和迁移、干细胞增殖和分化、维持生长因子水平等[25-26],见图5。"
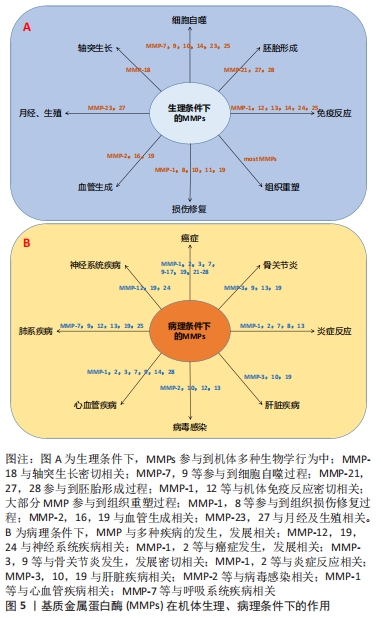
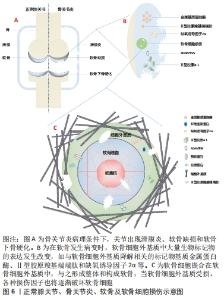
在肿瘤发生过程中,细胞外基质发生了明显的改变,如纤维间质硬度增加、细胞外基质成分过度沉积、蛋白水解酶释放增加等,从而导致细胞外基质结构的异常重塑和理化性质的改变[27-28]。细胞外基质硬度的改变传递出机械信号,因而与机械信号转导相关的Yes相关蛋白/转录共激活因子PDZ结合基序(YAP/TAZ)通路被激活,激活后的此通路将推动癌细胞增殖、侵入性迁移和转移[29-30]。此外细胞外基质在遗传性疾病及个体衰老的过程中也发挥着重要作用。 研究表明,细胞外基质的动态变化和特定遗传性疾病之间存在一定联系[31],如Stickler综合征和先天性脊柱骨骺发育不良是由于与细胞外基质胶原相关的突变,影响软骨和骨骼系统而造成。与细胞外基质相关的遗传病还包括皮肤弹性过度综合征、成骨不全和皮肤松弛症等[32]。一项对比年轻健康人和老年健康人纤维细胞的研究中发现,年轻健康组成纤维细胞分泌更高水平的细胞外基质成分,包括蛋白多糖、软骨连接蛋白等[33];结果还揭示了随着年龄的增长,细胞外基质结构的完整性将大幅下降,其中表现最为明显的则是皮肤上出现皱纹的过程,这与年龄相关的细胞外基质的物理特性变化,如胶原密度、纤维面积和厚度、以及硬度等密切相关[34-35]。 细胞外基质的变化贯穿了机体生命的始终,在机体生理变化和多种疾病的病理进程中均可作一定阐释。对于疾病的预防、诊断及后续的治疗均可从细胞外基质入手作更深入的研究,以期深化对细胞外基质的认识并加以利用,从不同角度阐释疾病的发生和发展,乃至为疾病的诊治拓宽视野、提供理论依据。 2.3 细胞外基质在骨关节炎发生、发展中的作用及其辅助诊断价值 骨关节炎的主要病理特征是软骨损伤,由于软骨中没有提供营养物质的血管,其营养获取只能经由滑膜渗透吸收,因此病理条件下软骨修复能力极差;软骨损伤主要包括软骨细胞外基质的异常代谢和软骨细胞的异常代谢、纤维化和凋亡[36]。此外,细胞外基质中还存在大量血清寡聚基质蛋白、血管性血友病因子、生长因子、Ⅱ型胶原羧基端端肽和基质金属蛋白酶等与软骨细胞代谢、骨关节炎形成密切相关的生物标记物[10,37]。 2.3.1 细胞外基质在骨关节炎发生、发展过程中的作用 软骨细胞外基质的破坏主要由蛋白多糖和纤维蛋白等物质的降解引起,并且伴随着Ⅱ型胶原等的减少及基质金属蛋白酶和Ⅰ型胶原等物质的增加[38]。正常条件下,成熟软骨细胞呈现静止状态且无有丝分裂活性,具有维持软骨细胞内代谢平衡及软骨细胞外基质组分稳定的作用。除合成代谢外,软骨的炎症反应也与软骨细胞外基质密切相关。在骨关节炎病理条件下,受应激、炎症递质等的影响,软骨细胞在NADPH氧化酶作用下产生过量的活性氧,而过量的活性氧,通过直接降解软骨细胞外基质组分、抑制软骨细胞外基质合成,发挥促软骨分解的作用,激活基质金属蛋白酶并诱导软骨细胞凋亡[39-40]。一项关于Matrilins在骨关节炎治疗中的作用的研究发现,Matrilins作为衔接蛋白,需要整合到软骨细胞外基质作为衔接蛋白而发挥促进软骨细胞外基质合成代谢功能,以维持软骨细胞外基质的稳定,发挥促软骨细胞增殖的作用;另外,Matrilins主要存在于软骨中,调节细胞外基质组织成分之间的相互作用,形成细胞间的网络结构;在Matrilins敲除小鼠模型中,软骨细胞外基质出现异常降解,且出现明显的炎症反应[41]。炎症过程中产生的促炎因子直接作用于软骨细胞,导致合成代谢-分解代谢平衡被破坏,进一步加剧软骨细胞外基质的破坏。 软骨细胞还受到软骨细胞外基质硬度等机械特性的影响。SANCHEZ-ADAMS等[42]研究表明,软骨细胞可以间接感受机械信号刺激,机械信号首先作用于软骨细胞外基质,再引起细胞外基质组分或机械特性的改变,软骨细胞外基质硬度变化产生的机械信号被Yes相关蛋白/转录共激活因子PDZ结合基序(YAP/TAZ)所感受,作为媒介将细胞外的机械信号传导到软骨细胞核内,调节增殖和分化等细胞行为。此外,上调Yes相关蛋白/转录共激活因子PDZ结合基序(YAP/TAZ)通路表达还可抑制软骨细胞凋亡、肥大,以及抑制核转录因子kB通路表达,减轻骨关节炎炎症反应,恢复软骨细胞外基质稳态[43]。由此也可以解释老年人骨关节炎高发的原因:随着机体的衰老,晚期糖基化终末产物在软骨细胞外基质聚集,晚期糖基化终末产物的蓄积将促进软骨细胞凋亡、破坏软骨细胞外基质,进而改变其机械特性,最终诱发或加重骨关节炎。 软骨细胞外基质作为关节软骨的重要组成部分,不仅是软骨细胞的生存环境,对软骨细胞起支撑和营养作用;同时还作为软骨细胞与外界进行信号交换的场所,其稳态对维持软骨细胞正常功能、及时应对外界环境变化具有至关重要的作用。 2.3.2 细胞外基质是骨关节炎生物标记物的来源 软骨细胞外基质还是骨关节炎生物标记物的丰富来源,如Ⅱ型胶原降解的标记物Ⅱ型胶原羧基端端肽和Ⅱ型胶原α1等;标志Ⅱ型胶原合成的ⅡA型前胶原氨基端肽、Ⅱ型原胶原N端前肽和Ⅱ型前胶原羧基端前肽等;还包括Sox9、缺氧诱导因子2α和基质金属蛋白酶等生物标记物。上述生物标记物与骨关节炎的发生、发展密切相关。如Sox9作为重要的转录因子,促进软骨合成标记物Ⅱ型胶原、Ⅸ型胶原和蛋白多糖等基因的转录,并且抑制基质金属蛋白酶的表达,从而维持关节软骨细胞表型的稳定[44-45]。而缺氧诱导因子2α作为骨关节炎中软骨分解代谢的“开关”,可以直接诱导与细胞外基质分解代谢相关的基因的表达,如上调基质金属蛋白酶在软骨细胞中的表达进而加速软骨退变[46],见图6。"
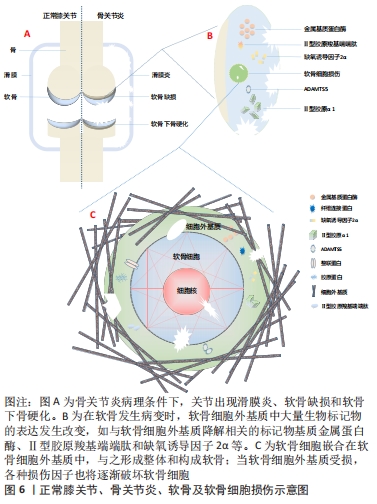
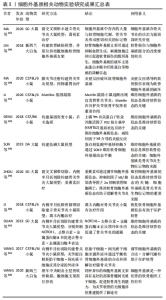
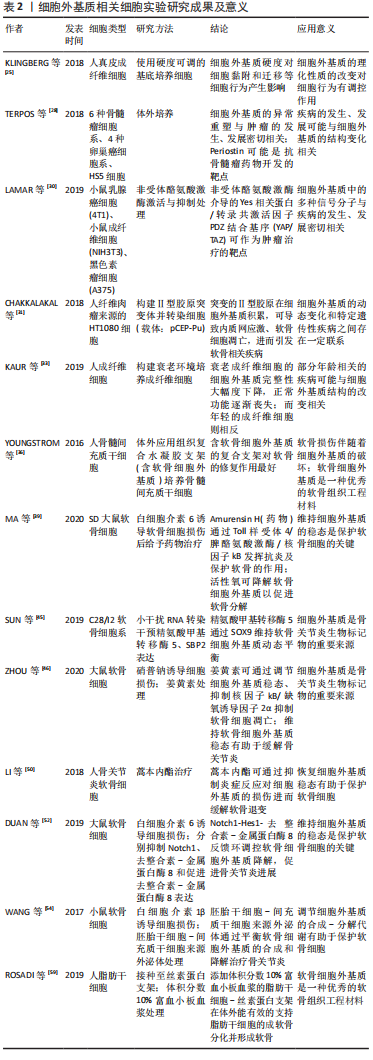
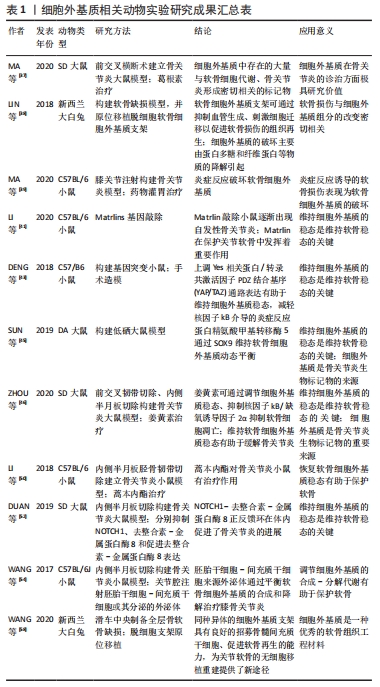
此外,一项对比大骨节病和骨关节炎软骨细胞细胞外基质降解差异的研究发现,骨关节炎关节软骨的蛋白多糖丢失较大骨节病关节软骨更严重,而大骨节病Ⅱ型胶原丢失更为明显[47],这表明软骨细胞外基质组分变化的差异还可作为鉴别诊断的依据。 可溶性软骨细胞外基质衍生的标记物可用于临床检测和影像学检查,并在骨关节炎临床试验中作为评估特定治疗方式的客观工具。关节组织的代谢变化可能发生在骨关节炎的早期,在明显的症状和结构改变出现前可以被认为是骨关节炎的早期诊断指标。目前除胶原相关标记物外,还有多种位于软骨细胞外基质的可溶性生物标记物,如基质金属蛋白酶等,也可以作为“诊断和药物开发工具”[48]。 因此,对细胞外基质更深入的研究有助于系统地阐释骨关节炎的发生、发展机制,更全面地认识骨关节炎;同时可用于寻求量化指标作为骨关节炎诊断及鉴别诊断依据,实现更精确的诊断;也为探讨骨关节炎的治疗方法提供新角度,早日实现骨关节炎的临床治愈。 2.4 细胞外基质在治疗骨关节炎方面的前景 骨关节炎的常用治疗方法包括口服消炎镇痛药、局部注射软骨保护剂、关节镜清理和关节置换等,近期研究还发现调节肠道菌群也是骨关节炎潜在的治疗方法[49]。但究其根本,软骨组织的修复是治疗骨关节炎的关键。目前针对软骨修复的治疗技术主要有细胞疗法和手术置换疗法,细胞疗法包括自体软骨细胞移植、基质诱导软骨细胞移植、间充质干细胞补充修复等;而关节置换疗法指更换关节内的受损组织,如同种异体软骨移植、镶嵌式成形术等。这些方法都取得了一定的临床疗效,但对透明软骨的功能修复存在术后长期的不稳定性,而如何恢复软骨细胞外基质的结构和稳定则是软骨功能修复的关键。 2.4.1 相关通路的研究 目前围绕抑制骨关节炎炎症反应和恢复软骨细胞外基质代谢平衡作出了许多研究。关于应用藁本内酯治疗骨关节炎的研究发现,藁本内酯的治疗作用主要是通过抑制肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6的表达以缓解炎症反应,通过下调基质金属蛋白酶和软骨蛋白聚糖抗体表达抑制细胞外基质组分的分解;藁本内酯还可以抑制软骨细胞核因子kB信号的转导,从而下调白细胞介素1β诱导的信号转导和转录激活因子3、细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B等通路的表达,实现抗炎和抑制软骨细胞外基质降解的功能[50-51]。因此磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B等通路可能是日后研究骨关节炎的新方向。此外,Notch通路抑制剂也是治疗骨关节炎的潜在药物。抑制Notch信号转导可降低去整合素-金属蛋白酶8和基质金属蛋白酶9的表达,促进Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白多糖的表达、促进软骨细胞增殖并抑制软骨细胞凋亡。进一步研究表明,去整合素-金属蛋白酶8过表达可激活Notch通路,而Notch的下游Hes1可与去整合素-金属蛋白酶8启动子结合,促进其基因转录[52]。由此,Notch-Hes1-去整合素-金属蛋白酶8形成正反馈环,加速软骨细胞外基质的破坏。并且DUAN等[52]还发现,Hes1基因敲除模型中,肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白多糖等的表达显著下调,去整合素-金属蛋白酶8的表达及与其相关的表皮生长因子-细胞外调节蛋白激酶/核转录因子κB信号转导也受到抑制,而表皮生长因子-细胞外调节蛋白激酶/核转录因子κB通路还参与到骨关节炎的炎症反应和软骨病变的细胞行为中。 2.4.2 细胞外基质组织工程支架的应用 目前基于细胞外基质的组织工程策略在多种组织再生的研究上已取得一定成绩,如心脏瓣膜、肌腱、肌肉和软骨等[36,53]。一项关于多能干细胞-骨髓间充质干细胞联合应用治疗骨关节炎的研究表明,由多能干细胞-骨髓间充质干细胞分泌、用于治疗骨关节炎的外泌体可以通过平衡软骨细胞外基质的合成和降解对骨关节炎起到良好的治疗作用[54]。为了更好地发挥这种优势,研究者们还引入了生物材料诱导特定的细胞行为,其中软骨细胞外基质被认为是优秀的天然生物材料,可刺激细胞迁移并促进软骨再生[55-56]。细胞外基质生物支架不仅保留了结构的完整性,还保留了原组织的天然组分,在体内特定的微环境下,可与接种的种子细胞或自体移植处细胞动态互作,提供必要的力学支持和细胞生长发育所需要的因子,利于细胞的黏附、增殖和分化;呈低免疫原性,增加了移植的成活率;具有一定的生物相容性和生物可降解性,且降解后的物质不影响正常的细胞行为。不同物种间同一组织来源的细胞外基质相对保守,也为该技术的应用及推广奠定基础。 目前软骨细胞外基质支架的提取主要利用脱细胞技术,通过脱细胞技术尽量除去细胞膜、细胞器和胞内蛋白等细胞组分,保留软骨细胞外基质生物力学特性及其生物学功能;并且软骨细胞外基质支架无组织特异性和免疫原性的特点有利于异种移 植[57]。软骨细胞外基质作为支架材料还能增强刺激因子诱导干细胞向软骨细胞分化[58],促进软骨细胞分泌细胞外基质,继而修复软骨缺损;较单纯的胶原支架组,软骨细胞外基质组新生软骨内基质含量更高、分布更均匀且特定蛋白表达更高[59]。此外,软骨细胞外基质支架还可以与其他材料联合使用,以弥补单独使用天然软骨细胞外基质支架孔隙率低、机械性能较弱、脱细胞过程某些成分丢失和不易成型等缺点;如SAEEDI GARAKANI等[60]制备的软骨细胞外基质-壳聚糖-琼脂糖复合支架克服了单纯使用软骨细胞外基质力学性能较差等缺点,具有良好的机械强度、高溶胀率、流变性和可控的生物降解率,更利于细胞的附着、生长。软骨细胞外基质支架还可以结合纳米微粒技术,制备纳米微粒细胞外基质支架实现局部软骨缺损的修复,且目前已有临床研究应用微粒细胞外基质支架全层移植修复局部软骨缺损[61]。 因此,基于细胞外基质的软骨组织工程策略在骨关节炎的治疗上具有广泛的应用前景,既可以在局部用药方面进行开发,如应用基于细胞外基质的药物递送体系修复局部软骨损伤;也可以结合材料学等相关学科扩展其临床应用,如结合其他天然生物材料、人工高分子材料改善细胞外基质支架性能,以实现更好的软骨修复作用。细胞外基质相关基础研究进度见表1,2。"
| [1] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715. [2] CONAGHAN PG, COOK AD, HAMILTON JA, et al. Therapeutic options for targeting inflammatory osteoarthritis pain. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(6):355-363. [3] KOLASINSKI SL, NEOGI T, HOCHBERG MC, et al. 2019 American college of rheumatology/arthritis foundation guideline for the management of osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(2):149-162. [4] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759. [5] SHARMA L. Osteoarthritis of the Knee. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(1):51-59. [6] ZHANG Z, HUANG C, JIANG Q, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis in China (2019 edition). Ann Transl Med. 2020; 8(19):1213. [7] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: a review. JAMA. 2020;325(6):568-578. [8] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072. [9] ZHENG L, ZHANG Z, SHENG P, et al. The role of metabolism in chondrocyte dysfunction and the progression of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;66:101249. [10] PENG Z, SSUN H, BUNPETCH V, et al. The regulation of cartilage extracellular matrix homeostasis in joint cartilage degeneration and regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120555. [11] SZUSTAK M, GENDASZEWSKA-DARMACH E. Extracellular nucleotides selectively induce migration of chondrocytes and expression of type II collagen. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):5227. [12] HUBER AK, PATEL N, PAGANI CA, et al. Immobilization after injury alters extracellular matrix and stem cell fate. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(10):5444-5460. [13] FANG T, ZHOU X, JIN M, et al. Molecular mechanisms of mechanical load-induced osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 2021;45(5):1125-1136. [14] RELLMANN Y, EIDHOF E, DREIER R. Review: ER stress-induced cell death in osteoarthritic cartilage. Cell Signal. 2021;78:109880. [15] 翟中和,王喜忠,丁明孝.细胞生物学.第4版[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2011:5-7,30-42. [16] LOEWI G. Changes in the ground substance of ageing cartilage. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953;65(2):381-388. [17] GUNSTON FH. Polycentric knee arthroplasty: prosthetic simulation of normal knee movement. 1971. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;446:11-12. [18] GREEN WT JR. Articular cartilage repair. Behavior of rabbit chondrocytes during tissue culture and subsequent allografting. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977;124:237-250. [19] BELL E, EHRLICH HP, SHER S, et al. Development and use of a living skin equivalent. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1981;67(3):386-392. [20] KATO Y, IWAMOTO M, KOIKE T, et al. Terminal differentiation and calcification in rabbit chondrocyte cultures grown in centrifuge tubes: regulation by transforming growth factor beta and serum factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85(24):9552-9556. [21] OXFORD JT, REECK JC, HARDY MJ. Extracellular matrix in development and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(1):205. [22] HAMIDI H, LVASKA J. Every step of the way: integrins in cancer progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(9):533-548. [23] PICKUP MW, MOUW JK, WEAVER VM. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014;15(12):1243-1253. [24] ZILE MR, O’MEARA E, CLAGGETT B, et al. Effects of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Biomarkers of Extracellular Matrix Regulation in Patients With HFrEF. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019; 73(7):795-806. [25] KLINGBERG F, CHAU G, WALRAVEN M, et al. The fibronectin ED-A domain enhances recruitment of latent TGF-β-binding protein-1 to the fibroblast matrix. J Cell Sci. 2018;131(5):jcs201293. [26] WALRAVEN M, HINZ B. Therapeutic approaches to control tissue repair and fibrosis: extracellular matrix as a game changer. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:205-224. [27] WINKLER J, ABISOYE-OGUNNIYAN A, METCALF KJ, et al. Concepts of extracellular matrix remodelling in tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Commun. 2020; 11(1):5120. [28] TERPOS E, CHRISTOULAS D, KASTRITIS E, et al. High levels of periostin correlate with increased fracture rate, diffuse MRI pattern, abnormal bone remodeling and advanced disease stage in patients with newly diagnosed symptomatic multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2016;6(10):e482. [29] THOMPSON BJ. YAP/TAZ: Drivers of tumor growth, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Bioessays. 2020;42(5):e1900162. [30] LAMAR JM, XIAO Y, NORTON E, et al. SRC tyrosine kinase activates the YAP/TAZ axis and thereby drives tumor growth and metastasis. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(7):2302-2317. [31] CHAKKALAKAL SA, HEILIG J, BAUMANN U, et al. Impact of arginine to cysteine mutations in collagen ii on protein secretion and cell survival. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(2):541. [32] NYSTROM A, BERNASCONI R, BORNERT O. Therapies for genetic extracellular matrix diseases of the skin. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:330-347. [33] KAUR A, ECKER BL, DOUGLASS SM, et al. Remodeling of the collagen matrix in aging skin promotes melanoma metastasis and affects immune cell motility. Cancer Discov. 2019;9(1):64-81. [34] HAYDONT V, BERNARD BA, FORTUNER NO. Age-related evolutions of the dermis: clinical signs, fibroblast and extracellular matrix dynamics. Mech Ageing Dev. 2019; 177:150-156. [35] FANE M, WEERARATNA AT. How the ageing microenvironment influences tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20(2):89-106. [36] YOUNGSTROM DW, CAKSTINA I, JAKOBSONS E. Cartilage-derived extracellular matrix extract promotes chondrocytic phenotype in three-dimensional tissue culture. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44(3):1040-1047. [37] MA TW, WEN YJ, SONG XP, et al. Puerarin inhibits the development of osteoarthritis through antiinflammatory and antimatrix-degrading pathways in osteoarthritis-induced rat model. Phytother Res. 2020. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6988. [38] LIN X, CHEN J, QIU P, et al. Biphasic hierarchical extracellular matrix scaffold for osteochondral defect regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):433-444. [39] MA P, YUE L, YANG H, et al. Chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of amurensin H by regulating TLR4/Syk/NF-κB signals. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(2): 1958-1968. [40] YAO M, ZHANG J, LI Z, et al. Marein protects human nucleus pulposus cells against high glucose-induced injury and extracellular matrix degradation at least partly by inhibition of ROS/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106126. [41] LI P, FLEISCHHAUER L, NICOLAE C, et al. Mice lacking the matrilin family of extracellular matrix proteins develop mild skeletal abnormalities and are susceptible to age-associated osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):666. [42] SANCHEZ-ADAMS J, LEDDY HA, MCNULTY AL, et al. The mechanobiology of articular cartilage: bearing the burden of osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2014;16(10):451. [43] DENG Y, LU J, LI W, et al. Reciprocal inhibition of YAP/TAZ and NF-κB regulates osteoarthritic cartilage degradation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4564. [44] SONG H, PARK KH. Regulation and function of SOX9 during cartilage development and regeneration. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;67(Pt 1):12-23. [45] SUN M, HUSSAIN S, HU Y, et al. Maintenance of SOX9 stability and ECM homeostasis by selenium-sensitive PRMT5 in cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(6):932-944. [46] ZHOU Y, MING J, DENG M, et al. Chemically modified curcumin (CMC2.24) alleviates osteoarthritis progression by restoring cartilage homeostasis and inhibiting chondrocyte apoptosis via the NF-κB/HIF-2α axis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020;98(10): 1479-1491. [47] 武世勋,吴翠艳,郭雄.大骨节病和骨性关节炎软骨细胞外基质的降解差异[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2021,42(2):306-310, 316. [48] HENROTIN Y, SANCHEZ C, BAY-JENSEN AC, et al. Osteoarthritis biomarkers derived from cartilage extracellular matrix: current status and future perspectives. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59(3):145-148. [49] BOER CG, RADJABZADEH D, MEDINA-GOMEZ C, et al. Intestinal microbiome composition and its relation to joint pain and inflammation. Nat Commun. 2019; 10(1):4881. [50] LI X, WU D, HU Z, et al. The protective effect of ligustilide in osteoarthritis: an in vitro and in vivo study. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(6):2583-2595. [51] ZHOU YAN, MING JIANGHUA, et al. Ligustilide attenuates nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in rat chondrocytes and cartilage degradation via inhibiting JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23:3357-3368. [52] DUAN B, LIU Y, HU H, et al. Notch1-ADAM8 positive feed-back loop regulates the degradation of chondrogenic extracellular matrix and osteoarthritis progression. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):134. [53] XING H, LEE H, LUO L, et al. Extracellular matrix-derived biomaterials in engineering cell function. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;42:107421. [54] WANG Y, YU D, LIU Z, et al. Exosomes from embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):189. [55] NOURI BARKESTANI M, NASERIAN S, UZAN G, et al. Post-decellularization techniques ameliorate cartilage decellularization process for tissue engineering applications. J Tissue Eng. 2021;12:2041731420983562. [56] MAYORCA-GUILIANI AE, WILLACY O, MADSEN CD, et al. Decellularization and antibody staining of mouse tissues to map native extracellular matrix structures in 3D. Nat Protoc. 2019;14(12):3395-3425. [57] XIA C, MEI S, GU C, et al. Decellularized cartilage as a prospective scaffold for cartilage repair. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101:588-595. [58] WANG Z, HAN L, SUN T, et al. Extracellular matrix derived from allogenic decellularized bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheets for the reconstruction of osteochondral defects in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2020;118:54-68. [59] ROSADI I, KARINA K, ROSLIANA I, et al. In vitro study of cartilage tissue engineering using human adipose-derived stem cells induced by platelet-rich plasma and cultured on silk fibroin scaffold. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):369. [60] SAEEDI GARAKANI S, KHANMOHAMMADI M, AYOUFI Z, et al. Fabrication of chitosan/agarose scaffolds containing extracellular matrix for tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;143:533-545. [61] MONIBI FA, COOK JL. Tissue-derived extracellular matrix bioscaffolds: emerging applications in cartilage and meniscus repair. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23(4):386-398. |
| [1] | Tan Xinfang, Guo Yanxing, Qin Xiaofei, Zhang Binqing, Zhao Dongliang, Pan Kunkun, Li Yuzhuo, Chen Haoyu. Effect of uniaxial fatigue exercise on patellofemoral cartilage injury in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Zhang Haobo, Zhao Yunan, Yang Xuejun. Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [5] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [6] | Lu Pan, Zhang Chunlin, Wang Yongkui, Yan Xu, Dong Chao, Yue Yisen, Li Long, Zhu Andi. Volume changes of cervical herniated discs after open-door laminoplasty and conservative treatment as assessed by three-dimensional volume method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1395-1401. |
| [7] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [8] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [9] | Tang Wenjing, Wu Siyuan, Yang Chen, Tao Xi. Inflammatory responses in post-stroke depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1278-1285. |
| [10] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [13] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [14] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [15] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||