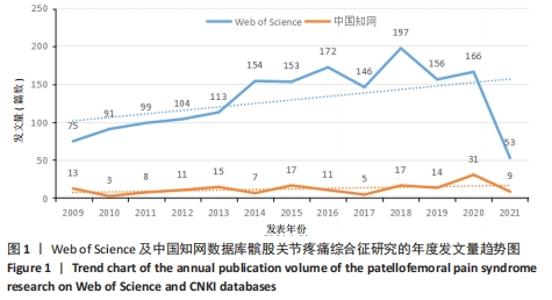
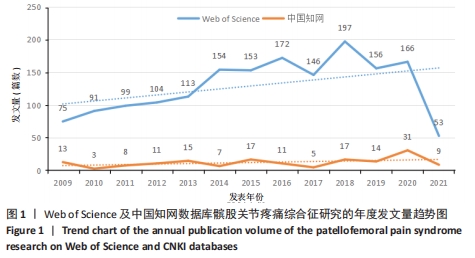
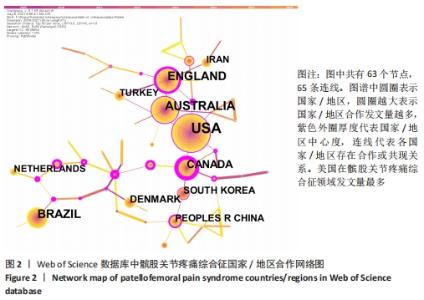
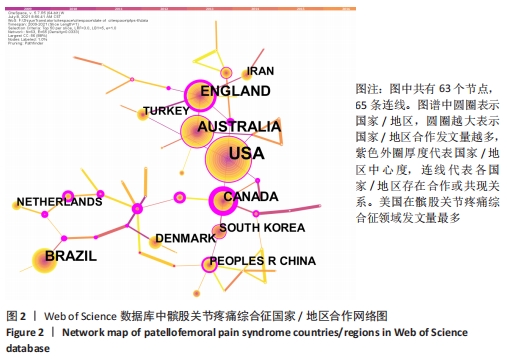
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (12): 1877-1887.doi: 10.12307/2022.511
Previous Articles Next Articles
Visual analysis of patellofemoral pain syndrome research hotspots and content
Xu Jie1, Zhou Wenqi2, Luo Xiaobing2
- 1Institute of Sports Medicine and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Sports Medicine, Sichuan Orthopedic Hospital, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-07-12Revised:2021-07-15Accepted:2021-08-12Online:2022-04-28Published:2021-12-14 -
Contact:Luo Xiaobing, Master, Master’s supervisor, Chief TCM physician, Department of Sports Medicine, Sichuan Orthopedic Hospital, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Xu Jie, Master candidate, Institute of Sports Medicine and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Plan, No. 2019YFF0301703 (to LXB); Sichuan Provincial Health Commission Cadre Protection Project, No. 2021-602 (to LXB); Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Special Project, No. YYZX2018007 (to ZWQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Jie, Zhou Wenqi, Luo Xiaobing. Visual analysis of patellofemoral pain syndrome research hotspots and content[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1877-1887.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

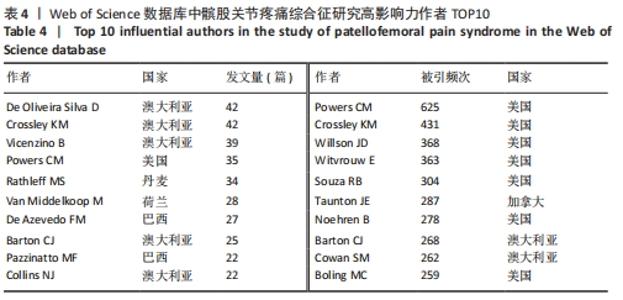
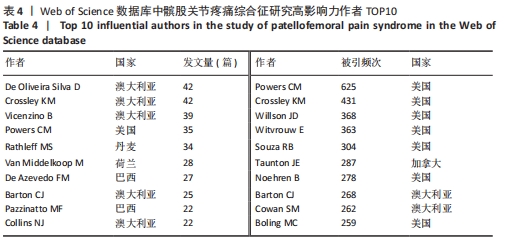
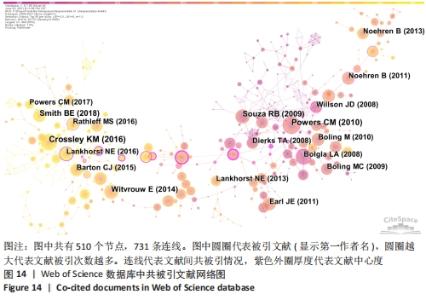
2.3 高影响力作者及合作关系分析 针对外文文献,可视化图谱共纳入928位作者,其中12位作者发文量≥ 20篇, 发文量最突出的是澳大利亚墨尔本拉筹伯大学教授De Oliveira Silva D(42篇)和澳大利亚墨尔本大学教授Crossley KM(42篇);发文量第3位的是澳大利亚昆士兰大学教授Vicenzino B(39篇);而Crossley KM教授和WITVROUW E教授的文献中心度是最高的。被引频次排名首位的作者是美国南加州大学教授Powers CM(625次),其次是美国北卡罗来纳大学教授 Crossley KM(431次)和美国特拉华大学教授Willson JD(368次)。各作者团队间彼此存在一定的合作,而在高产作者间更加明显,外文文献中缺乏中心度高的作者,高影响力作者中无中国学者,见图4,表4。"

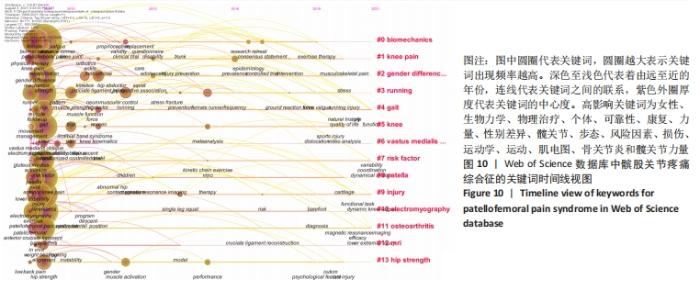
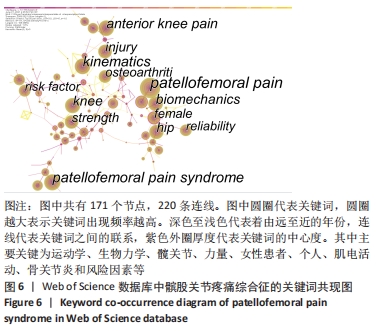
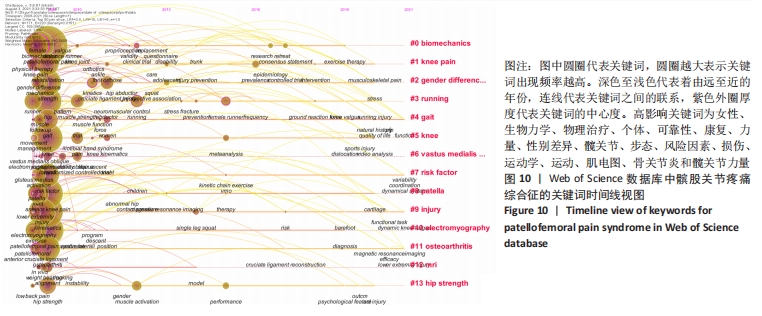
2.4.2 基于关键词聚类的研究前沿趋势分析 将Web of Science数据库所筛选出的文献,以Timeline view显示聚类关键词的时间动态变化。聚类模块值(Modularity,Q值)=0.801 2,表明聚类结构显著;聚类平均轮廓值(Silhouette:S值)=0.940 5,表明聚类可信[30]。①从2009年,“女性、生物力学、个体、可靠性、康复、力量、性别差异、髋关节、步态、风险因素、物理治疗、损伤、运动学、运动、肌电图、骨关节炎、髋关节力量”等关键词得到广泛关注;②2010-2013年,“足部矫形器、临床试验、髋关节外展、跑步、神经肌肉控制、女性、髂胫束综合征、随机对照试验、股内侧肌、肌肉激活”等关键词开始受到关注;③2013-2016年,“青少年、患病率、联合、女性跑者、Meta分析、单腿下蹲、表现、预防、应力性骨折、动力链运动”等关键词得到关注;④2016-2019年,“共识声明、研究回顾、地面反作用力、膝外翻、心理特征”等关键词受到关注;⑤2019-2021年,“运动疗法、功能、肌肉骨骼疼痛、动态系统、动态膝关节外翻、生活质量、跑步损伤、自然历史、功能任务、磁共振成像、下肢损伤”等成为新的词汇。预测国外将继续围绕髌股疼痛综合征与运动疗法、动态膝关节外翻、动态系统、生活质量、跑步损伤、磁共振成像和功能任务的研究主题继续深入研究。具体关键词随时间的变化趋势,见图10。"

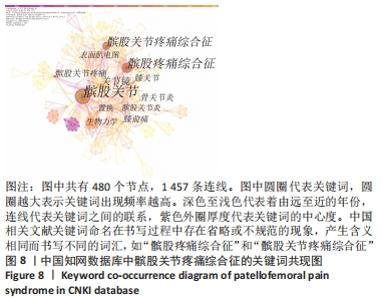
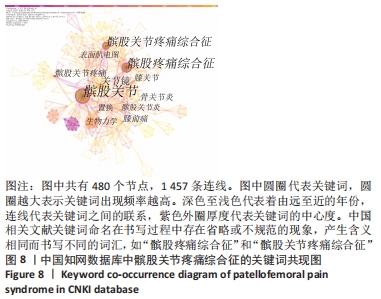
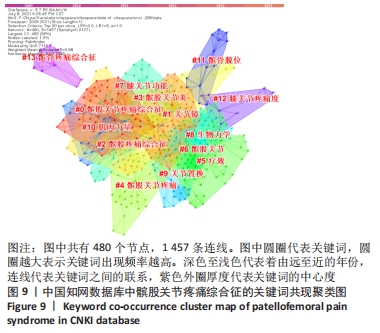
对中国知网数据库筛选出来的文献进行时间线视图分析,得到聚类模块值(Q=0.886),表明聚类结构显著;聚类平均轮廓值(S=0.966),表明聚类结果可信。①2009年,“关节镜、外侧高压综合征、三色散、软骨损伤、生物力学、骨性关节炎、P物质”等关键词得到广泛关注;②2010-2013年,“股内斜肌、股外斜肌、表面肌电图、外侧支持带松解、Meta分析、新型悬吊运动疗法、髋关节”等关键词开始受到关注;③2013-2016年,“关节成形术、髌股关节炎、肌电生物反馈、针药并用、运动疗法、康复治疗、中药热奄敷治疗”等关键词得到关注;④2016-2019年,“膝关节功能、股四头肌、力量训练、髌股关节应力”等关键词受到关注;⑤2019-2021年,“临床实践指南、解剖结构、髋周肌力训练、臀中肌、步态或跑步再训练、生物力学建模、电针仪疏密波”等成为新的词汇。预测中国将继续围绕髌股疼痛综合征与临床实践指南、解剖结构、髋周肌力训练、臀中肌、步态或跑步再训练、生物力学建模和电针仪疏密波的研究主题继续深入研究。具体关键词随时间的变化趋势,见图11。"

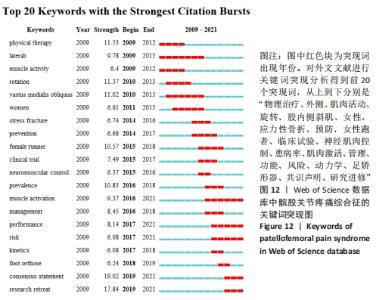
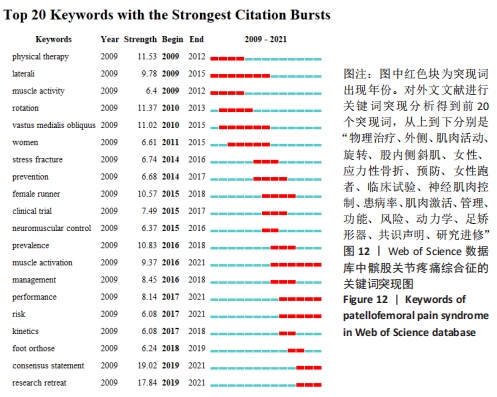
2.4.3 基于突现词的研究热点及前沿趋势分析 对Web of Science数据库所筛选出的被引文献频次最高的20个突现词中,突现词代表某段时间内经常被引用的关键字,从而指示热点和趋势。有12个突变词的突变周期均集中在 2015-2021年。突变强度最大的是“consensus statement”共识声明(19.02);其次是“research retreat”研究进修(17.84);排在第3位的是“physical therapy”物理治疗(11.53)。而近 5 年来突变强度较大的关键词包括:“consensus statement”共识声明(2019-2021年)、“research retreat”研究进修(2019-2021年)、“prevalence”患病率(2016-2018年)、“muscle activation”肌肉激活(2016-2021年)、“management”管理(2016-2018年),见图12。"
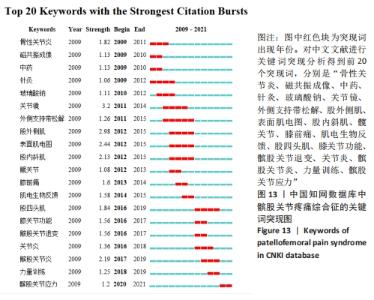
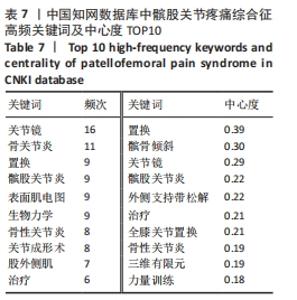
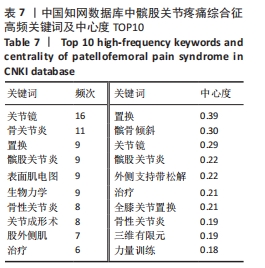
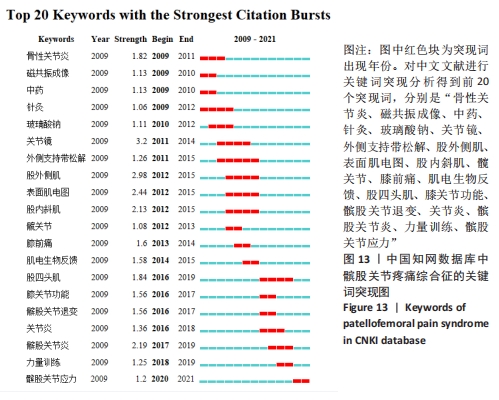
结合关键词的时间动态演变和Burst突现分析,可以对髌股关节疼痛综合征领域的研究发展及未来研究趋势形成一个大体的把握其中突现词“muscle activation”肌肉激活、“performance”功能、“risk”风险、“consensus statement”共识声明和“research retreat”研究进修都持续至今,很可能会一直保持研究热度。对中国知网数据库所筛选出的被引文献频次最高的20 个突现词中,有 13 个突变词的突变周期均集中在 2009-2015 年。突变强度最大的是关节镜(3.2);其次是股外侧肌(2.98);排在第3位的是表面肌电图(2.44)。而近5年来突变强度较大的关键词包括:髌股关节炎(2017-2019年)、股四头肌(2016-2019年)、膝关节功能(2016-2017年)、髌股关节退变(2016-2017年)、关节炎(2016-2018年),其中突现词髌股关节应力从2020年持续至今,未来可能会继续围绕髌股关节疼痛综合征和髌股关节应力研究,见图13。"
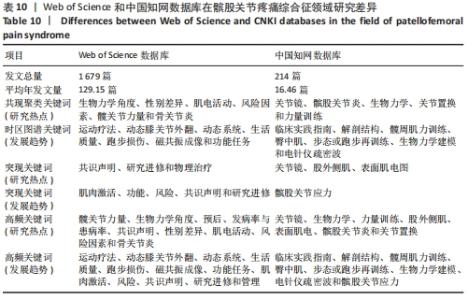
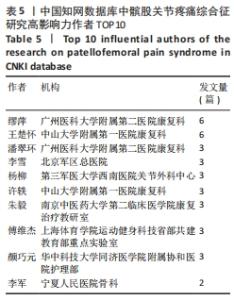
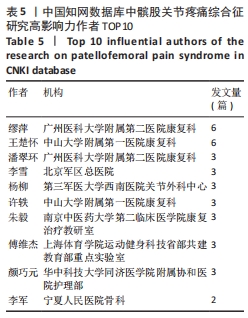
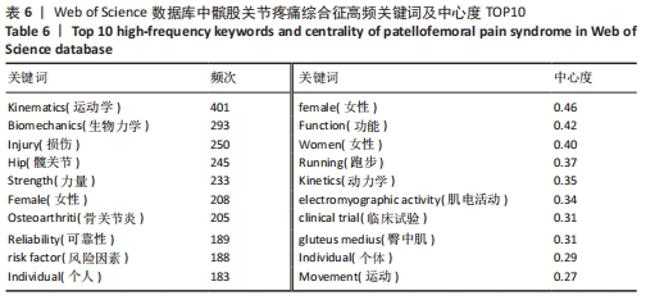
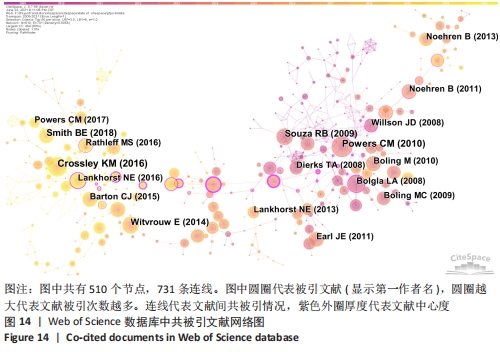
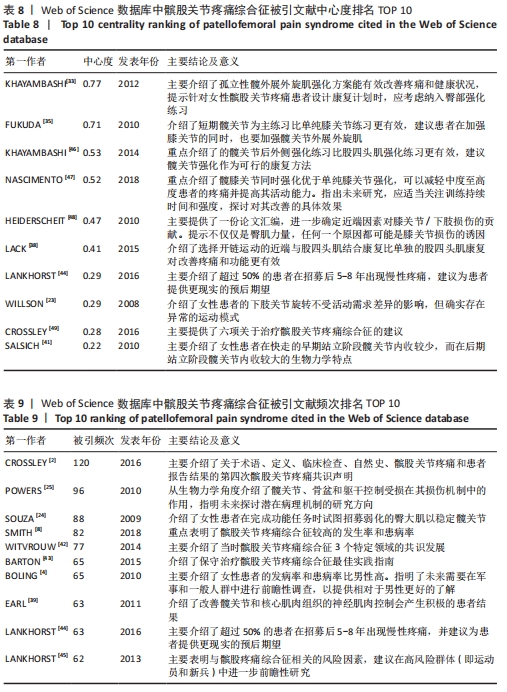
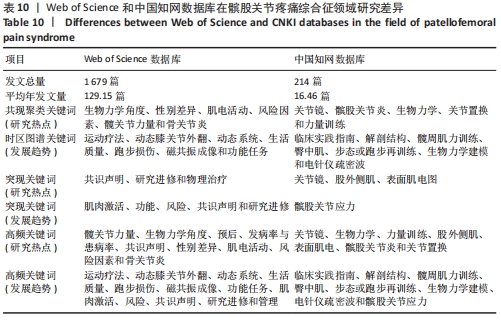
被引情况是反映研究热点的重要指标之一,通过对被引频次及中心性较高的文献进行阅读、分析,可以了解到关注度较高的一些研究成果,以揭示研究中令人关注的领域[31]。对被引用和中心度较高的前10条文献进行阅读分析,结果表明髋关节、生物力学、预后、发病率与患病率、共识声明等在该领域的某个阶段受到了研究者们广泛关注。在20篇高影响力文献中,有关于髋关节强化训练改善患者疼痛和功能的相关研究达8篇,占据着中心度排名的前6名,被引频次第3名和第8名,现有研究认为髋关节肌肉组织的薄弱会导致在动态负重活动时股骨内收和内侧旋转增加,这会增加外侧髌股关节压应力,导致髌骨平面过载长期以往造成髌股关节疼痛[32]。 以KHAYAMBASHI等[33]为首的高影响力学者为代表,研究发现为期8周的孤立性髋外展外旋肌强化训练相对于空白对照组能有效改善女性患者的疼痛、健康状况和髋关节力量,且运动组的改善在6个月的随访中得以维持。MASCAL等[34]首次证明,以髋关节和躯干力量为重点的锻炼计划在减少疼痛、改善髋关节运动和恢复功能方面是有效的。FUKUDA等[35]研究发现基于4周短期髋膝关节强化训练对减轻久坐女性患者下楼梯时疼痛更有效果,这与完全基于女性运动员研究的大多数报告形成了对比[36]。由于常见的臀部肌肉无力、年轻和久坐女性的发病率更 高[37]。类似的研究如LACK等[38]发现选择开链运动方式强化近端肢体对改善患者疼痛功能非常显著。建议后续研究应考虑运动类型、负荷和剂量来确定最有效的方案,且必须详细说明具体的运动描述。SOUZA等[24]通过表面肌电图发现女性患者在执行功能任务时髋关节内旋增加,同时伴随着髋部肌肉力量的下降和臀大肌肌电图信号强度的增加,表明臀大肌的激活增加以试图募集虚弱的肌肉,从而达到稳定髋关节。EARL等[39]研究发现强化核心肌群对改善患者症状同样有效。通过生物力学角度研究的相关文献有3篇,占据着中心度排名前10位的2篇,髌股关节疼痛综合征的病因和进展经常与过度的髌股关节应力有关。作为身体中最大的籽骨,髌骨用来增加股四头肌的力臂,提高了膝关节伸展力矩的能力。因此,髌股关节软骨在跑步和蹲下时分别承受7-20倍体质量的关节反作用力[32]。反复暴露在如此高的应力下会损伤髌后软骨,导致更大的力传递到受神经支配的软骨下骨[40]。这些最初的关节损伤加速了进一步软骨结构损伤的发展。 事实上,髌股骨关节病变的位置在最大负荷相关的髌股关节面区域最常见。因此,通过生物力学分析髌股关节在运动中所受压力分布尤其重要。以WILLSON等[23]为首的学者为代表,研究发现患者在单腿下蹲、跑步和重复单腿跳跃的不同难度活动中确实表现出膝关节外旋增加、膝关节内旋减少、髋内收增加及髋内旋减少。SALSICH等[41]研究发现女性患者在快走的早期站立阶段髋关节内收较少,而在后期站立阶段髋关节内收较大;较严重患者表现出膝关节外翻的额外特征,即早期站立时髋关节内收较大,自由速度行走后期站立时膝关节外翻较大,快速行走后期站立时髋关节内收较大,膝关节外翻较大。POWERS等[25]通过回顾性研究提出了髋关节损伤在多个平面对胫股和髌股力学产生不利影响的观点,因此针对近端损伤的干预措施能对患有各种膝关节疾病的患者有益。并将近端强化训练分为骨盆和躯干稳定性以及动态髋关节控制,且女性比男性更容易受到邻近的影响;有关该领域共识声明或指南共4篇,具有促进临床医生和研究人员对该领域达成系统性规范共识,以便更好和更一致的为评估和管理提供指导。同时,可以确定当前知识中的差距,并为未来的研究方向提供基础。其中以CROSSLEY等[2]被引频次最高为代表,发表了第四届髌股关节疼痛综合征共识声明,其中第一部分主要声明了关于该领域的术语、定义、临床检查、自然史、髌股关节疼痛和患者报告结果;第二部分主要为患者提供了6项治疗建议:运动疗法(特别是结合髋关节和膝关节锻炼),联合干预和足部矫形器,不推荐髌骨肌内效贴和增加腰椎活动度和电生理药物治疗。WITVROUW等[42]发表第3届髌股关节疼痛综合征共识声明,其重点介绍了3个特定领域共识的发展,自然病史和影响髌股关节疼痛的局部(膝关节区域)因素、影响髌股关节疼痛的躯干和远端因素、髌股关节疼痛的康复创新。BARTON等[43]主要提出了最佳保守治疗实践指南,即个性化定制的多模式干预方案,包括臀肌和股四头肌强化、髌骨肌内效贴以及强调教育和活动调整;涉及该疾病的发生率和患病率共2篇,分别排最高被引频次的第4和第7名,SMITH等[8]研究发现大约每10名新兵中就有一人,每14名青少年中就有一人在遭受疼痛。在过去的1年里,1/5的普通人经历过髌股关节疼痛。BOLING等[4]研究发现在美国海军学院女性发病率是男性的2.23倍,并且建议未来可以在军事和普通人群中进行前瞻性调查,以提供相对于男性更全面的了解;有关该疾病治疗预后有1篇文献,但同时占据着中心度第7名和被引文献第8名,可见预后情况是该领域关注对象。Lankhorst 等[44]于2016年研究发现超过50%的患者在初次治疗后5-8年出现慢性疼痛,但是没有影像学显示发展为膝骨关节炎,且提示持续更长时间的疼痛和更差的功能评分预示着不良的预后。建议提高对健康从业者和普通公众的教育使患者对预后有更现实的期望;关于该病损伤因素的研究有1篇,Lankhorst等[45]在于2013年基于47篇文献进行荟萃分析,纳入了523个变量,其中8个被合并,汇总显示较大的Q角、股沟角和髌骨倾斜角、髋关节外展力量较小、膝关节伸展峰值扭矩较低、髋关节外旋力量较小与髌股关节疼痛相关,而与足弓高度指数和适应角无关。并且后续研究建议在高风险群体(即运动员和新兵)中进一步前瞻性研究。 基于以上研究,总结归纳国内外研究热点及趋势,见表10。"
| [1] GAITONDE DY, ERICKSEN A, ROBBINS RC. Patellofemoral pain syndrome. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99(2):88-94. [2] CROSSLEY KM, STEFANIK JJ, SELFE J, et al. 2016 Patellofemoral pain consensus statement from the 4th International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat, Manchester. Part 1: Terminology, definitions, clinical examination, natural history, patellofemoral osteoarthritis and patient-reported outcome measures. Brit J Sport Med. 2016. [3] COPPACK RJ, ETHERINGTON J, WILLS AK. The effects of exercise for the prevention of overuse anterior knee pain: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sport Med. 2011;39(5):940-948. [4] BOLING M, PADUA D, MARSHALL S, et al. Gender differences in the incidence and prevalence of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Scand J Med Sci Spor. 2010;20(5):725-730. [5] DEY P, CALLAGHAN M, COOK N, et al. A questionnaire to identify patellofemoral pain in the community: an exploration of measurement properties. Bmc Musculoskel Dis. 2016;17(1):1-11. [6] CLARSEN B, KROSSHAUG T, BAHR R. Overuse injuries in professional road cyclists.Am J Sport Med. 2010;38(12):2494-2501. [7] KANNUS P, AHO H, JÄRVINEN M, et al. Computerized recording of visits to an outpatient sports clinic. Am J Sport Med. 1987;15(1):79-85. [8] SMITH BE, SELFE J, THACKER D, et al. Incidence and prevalence of patellofemoral pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0190892. [9] EIJKENBOOM JFA, WAARSING JH, OEI E HG, et al. Is patellofemoral pain a precursor to osteoarthritis? Patellofemoral osteoarthritis and patellofemoral pain patients share aberrant patellar shape compared with healthy controls. Bone Joint Res. 2018;7(9):541-547. [10] THOMAS MJ, WOOD L, SELFE J, et al. Anterior knee pain in younger adults as a precursor to subsequent patellofemoral osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Bmc Musculoskel Dis. 2010;11(1):1-8. [11] WILLY RW, HOGLUND LT, BARTON CJ, et al. Patellofemoral pain: clinical practice guidelines linked to the international classification of functioning, disability and health from the academy of orthopaedic physical therapy of the American physical therapy association. J Orthop Sport Phys. 2019;49(9):CPG1-CPG95. [12] DUNCAN R, PEAT G, THOMAS E, et al. Incidence, progression and sequence of development of radiographic knee osteoarthritis in a symptomatic population.Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70(11):1944-1948. [13] CHEN C, SONG M. Visualizing a field of research: a methodology of systematic scientometric reviews. PLoS One. 2019;14(10):e0223994. [14] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. [15] RADIN EL. A rational approach to the treatment of patellofemoral pain. Clin Orthop Relat R. 1979; (144):107-109. [16] SOUZA DR, GROSS MT. Comparison of vastus medialis obliquus: vastus lateralis muscle integrated electromyographic ratios between healthy subjects and patients with patellofemoral pain. Physical therapy. 1991;71(4):310-316. [17] POWERS CM, LANDEL R, PERRY J. Timing and intensity of vastus muscle activity during functional activities in subjects with and without patellofemoral pain. Physical therapy. 1996;76(9): 946-955. [18] GILLEARD W, MCCONNELL J, PARSONS D. The effect of patellar taping on the onset of vastus medialis obliquus and vastus lateralis muscle activity in persons with patellofemoral pain. Physical therapy. 1998;78(1):25-32. [19] WITVROUW E, LYSENS R, BELLEMANS J, et al. Intrinsic risk factors for the development of anterior knee pain in an athletic population: a two-year prospective study.Am J Sport Med. 2000; 28(4):480-489. [20] TAUNTON JE, RYAN MB, CLEMENT DB, et al. A retrospective case-control analysis of 2002 running injuries. Brit J Sport Med. 2002;36(2):95-101. [21] POWERS CM. The influence of altered lower-extremity kinematics on patellofemoral joint dysfunction: a theoretical perspective. J Orthop Sport Phys. 2003;33(11):639-646. [22] CROSSLEY KM, BENNELL KL, COWAN SM, et al. Analysis of outcome measures for persons with patellofemoral pain: which are reliable and valid? Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(5):815-822. [23] WILLSON JD, DAVIS IS. Lower extremity mechanics of females with and without patellofemoral pain across activities with progressively greater task demands. Clin Biomech. 2008;23(2):203-211. [24] SOUZA RB, POWERS CM. Differences in hip kinematics, muscle strength, and muscle activation between subjects with and without patellofemoral pain. J Orthop Sport Phys. 2009;39(1):12-19. [25] POWERS CM. The influence of abnormal hip mechanics on knee injury: a biomechanical perspective. J Orthop Sport Phys. 2010;40(2):42-51. [26] 张强,朱婵,近5年骨质疏松英文文献的计量学及可视化分析:Web of Science来源数据[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(17):2752-2758 . [27] LIANG C, LUO A, ZHONG Z. Knowledge mapping of medication literacy study: a visualized analysis using CiteSpace. Sage Open Med. 2018;6: 2050312118800199. [28] CHEN C, HU Z, LIU S, et al. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(5):593-608. [29] 杨晗,李涓,徐桂兴,等.国际近 15 年太极拳研究的文献计量及可视化分析[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(3):327-332. [30] 江明芳,谢志萍.基于Citespace的国内立体化教材研究的可视化知识图谱分析[J].高教论坛, 2020,(4):118-124. [31] 陈悦,宋超,周京生,等.文献计量学视角下的论文被引频次影响因素研究——兼评使用与被引之间关系[J].情报杂志,2019,38(4):96-104. [32] LEE T Q, MORRIS G, CSINTALAN RP. The influence of tibial and femoral rotation on patellofemoral contact area and pressure. J Orthop Sport Phys. 2003,33(11):686-693. [33] KHAYAMBASHI K, MOHAMMADKHANI Z, GHAZNAVI K, et al. The effects of isolated hip abductor and external rotator muscle strengthening on pain, health status, and hip strength in females with patellofemoral pain: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Sport Phys. 2012;42(1):22-29. [34] MASCAL CL, LANDEL R, POWERS C. Management of patellofemoral pain targeting hip, pelvis, and trunk muscle function: 2 case reports. J Orthop Sport Phys. 2003;33(11):647-660. [35] FUKUDA TY, ROSSETTO FM, MAGALHÃES E, et al. Short-term effects of hip abductors and lateral rotators strengthening in females with patellofemoral pain syndrome:a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Orthop Sport Phys. 2010;40(11):736-742. [36] ZACARON KAM, DIAS JMD, ABREU NS, et al. Physical activity levels, pain and swelling and their relationships with knee muscle dysfunction in elderly people with osteoarthritis. Braz J Phys Ther. 2006;10(3):279-284. [37] MAGALHÃES E, FUKUDA TY, SACRAMENTO SN, et al. A comparison of hip strength between sedentary females with and without patellofemoral pain syndrome. J Orthop Sport Phys. 2010;40(10):641-647. [38] LACK S, BARTON C, SOHAN O, et al. Proximal muscle rehabilitation is effective for patellofemoral pain:a systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Sport Med. 2015,49(21):1365-1376. [39] EARL JE, HOCH AZ. A proximal strengthening program improves pain, function, and biomechanics in women with patellofemoral pain syndrome. Am J Sport Med. 2011;39(1):154-163. [40] ATESHIAN GA, HUNG CT. Patellofemoral joint biomechanics and tissue engineering. Clin Orthop Relat R. 2005(436):81. [41] SALSICH GB, LONG-ROSSI F. Do females with patellofemoral pain have abnormal hip and knee kinematics during gait? Physiother Theor Pr. 2010; 26(3):150-159. [42] WITROUW E, CALLAGHAN MJ, STEFANIK JJ. Patellofemoral pain: consensus statement from the 3rd international patellofemoral pain rresearch retreat held in vancouver, September 2013. Br J Sports Med. 2014,48(6):411-414. [43] BARTON CJ, LACK S, HEMMINGS S, et al. The ‘Best Practice Guide to Conservative Management of Patellofemoral Pain’: incorporating level 1 evidence with expert clinical reasoning. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(14):923-934. [44] LANKHORST NE, VAN MIDDELKOOP M, CROSSLEY KM, et al. Factors that predict a poor outcome 5–8 years after the diagnosis of patellofemoral pain:a multicentre observational analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(14):881-886. [45] LANKHORST NE, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA SMA, VAN MIDDELKOOP M. Factors associated with patellofemoral pain syndrome: a systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(4):193-206. [46] KHAYAMBASHI K, FALLAH A, MOVAHEDI A, et al. Posterolateral hip muscle strengthening versus quadriceps strengthening for patellofemoral pain:a comparative control trial. Arch Phys Med Rehab. 2014;95(5):900-907. [47] NASCIMENTO LR, TEIXEIRA-SALMELA LF, SOUZA RB, et al. Hip and knee strengthening is more effective than knee strengthening alone for reducing pain and improving activity in individuals with patellofemoral pain:a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Orthop Sport Phys. 2018;48(1): 19-31. [48] HEIDERSCHEIT B C. Lower extremity injuries: is it just about hip strength? J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010;40(2):39-41. [49] CROSSLEY KM, VAN MIDDELKOOP M, CALLAGHAN MJ, et al. 2016 Patellofemoral pain consensus statement from the 4th International Patellofemoral Pain Research Retreat, Manchester. Part 2: recommended physical interventions (exercise, taping, bracing, foot orthoses and combined interventions). Br J Sports Med. 2016; 50(14):844-852. [50] 缪萍,王楚怀,潘翠环,等.闭链与开链运动对髌股疼痛综合征股四头肌作用的表面肌电图研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(12):1238-1242. [51] 郑光新,蒋长亮,黄迅悟,等.表面肌电图在评定髌股疼痛综合征患者髌骨动态稳定中的应用[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2014,36(9):676-679. [52] 缪萍,王楚怀,许轶,等.髌股疼痛综合征股外侧肌及股内斜肌的表面肌电特征[J].广东医学, 2012,33(24):3755-3757. [53] 李贝,杨康胜,詹铁军,等.髌骨外侧支持带松解结合内侧皱缩术治疗髌股关节外侧挤压综合征[J].实用骨科杂志,2020,26(3):267-270. [54] 施新革,侯文根,董玉珍,等.关节镜下射频气化在治疗髌股关节疼痛综合征中的应用[J].中华腔镜外科杂志(电子版),2011,4(4):307-309. [55] 王韬.全膝关节置换后关节线变化对髌股关节生物力学的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(13):1845-1851. [56] 高华利,肖涟波,张乾,等.髌股关节置换术治疗单纯髌股关节炎的疗效研究[J].中国骨伤, 2020,33(1):11-14. [57] 肖琦,孙武东,孙文文,等.强化髋关节周围肌肉力量训练对髌股关节疼痛综合征的疗效观察[J].中国社区医师,2020,36(2):12-13, 15. [58] 徐亮,马明,赵祥虎,等.核心肌群稳定性训练对髌股关节疼痛综合征的疗效观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2018,33(11):1314-1317. [59] 白震民,吕倩楠,赵爽,等.下肢补偿助力离心力量训练干预髌股疼痛综合征的研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2016,22(11):995-997,1009. [60] 胡浩宇.神经肌肉训练技术对髌股疼痛综合症(PFPS)患者的疗效及其影响研究[D].上海:上海体育学院, 2019. [61] 韩宜臻,葛媛莎,王辰,等.髌股关节疼痛综合征中医外治疗法研究进展[J].按摩与康复医学. 2019,10(18):53-55. [62] 王廷,晏圣松,许剑,等.宽筋活血汤联合针刺治疗髌股关节疼痛综合征35例[J].现代中医药. 2018,38(3):33-37. [63] 陈璐,薛明新,宋石龙,等.小针刀联合推拿治疗髌股关节疼痛综合征临床研究[J].针灸临床杂志,2020,36(8):36-40. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [3] | Li Zhiyi, He Pengcheng, Bian Tianyue, Xiao Yuxia, Gao Lu, Liu Huasheng. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ferroptosis mechanism research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1202-1209. |
| [4] | Zhao Jing, Liu Xiaobo, Zhang Yue, Zhang Jiaming, Zhong Dongling, Li Juan, Jin Rongjiang. Visualization analysis of neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy based on CiteSpace: therapeutic effects, hot spots, and developmental trends [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1234-1241. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [7] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [8] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [9] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [10] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [11] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [12] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [13] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [14] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [15] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||