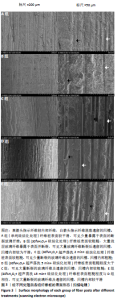
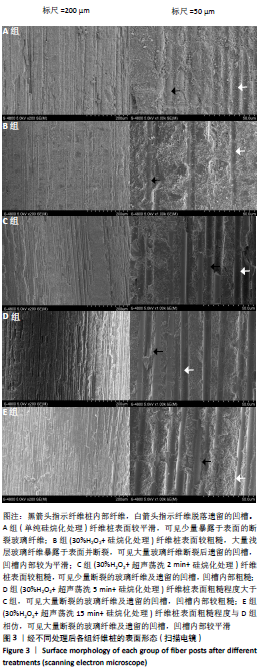
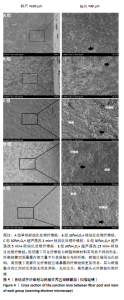
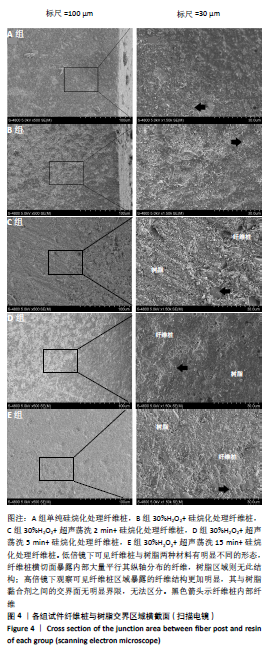
[1] CASTRO RF, MELO JDSS, DIAS LCL, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of filling material removal and re-filling after different retreatment procedures. Braz Oral Res. 2018;32:e94.
[2] PLOTINO G, ÖZYÜREK T, GRANDE NM, et al. Influence of size and taper of basic root canal preparation on root canal cleanliness:a scanning electron microscopy study. Int Endod J. 2019;52(3):343-351.
[3] VARELA P, SOUZA E, DE DEUS G, et al. Effectiveness of complementary irrigation routines in debriding pulp tissue from root canals instrumented with a single reciprocating file. Int Endod J. 2019;52(4): 475-483.
[4] TAYEB AH, AMINI E, GHASEMI S, et al. Cellulose Nanomaterials-Binding Properties and Applications:A Review. Molecules. 2018;23(10):2684.
[5] MALFERRARI S, MONACO C, SCOTTI R. Clinical evaluation of teeth restored with quartz fiber-reinforced epoxy resin posts. Int J Prosthodont. 2003;16(1):39-44.
[6] MONTICELLI F, GRANDINI S, GORACCI C, et al. Clinical behavior of translucent-fiber posts: a 2-year prospective study. Int J Prosthodont. 2003;16(6):593-596.
[7] AKSORNMUANG J, FOXTON RM, NAKAJIMA M, et al. Microtensile bond strength of a dual-cure resin core material to glass and quartz fibre posts. J Dent. 2004;32(6):443-450.
[8] D’ARCANGELO C, D’AMARIO M, PROSPERI GD, et al. Effect of surface treatments on tensile bond strength and on morphology of quartz-fiber posts. J Endod. 2007;33(3):264-267.
[9] MOSHARRAF R, RANJBARIAN P. Effects of post surface conditioning before silanization on bond strength between fiber post and resin cement. J Adv Prosthodont. 2013;5(2):126-132.
[10] HU X, LIU M, JI Y, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties and biosafety evaluation of surface-modified fiberglass-reinforced resin-based composite piles. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(6):70.
[11] GIACHETTI L, SCAMINACI RUSSO D, BALDINI M, et al. Push-out strength of translucent fibre posts cemented using a dual-curing technique or a light-curing self-adhering material. Int Endod J. 2012;45(3):249-256.
[12] GORACCI C, RAFFAELLI O, MONTICELLI F, et al. The adhesion between prefabricated FRC posts and composite resin cores: microtensile bond strength with and without post-silanization. Dent Mater. 2005; 21(5):437-444.
[13] MONTICELLI F, TOLEDANO M, TAY FR, et al. Post-surface conditioning improves interfacial adhesion in post/core restorations. Dent Mater. 2006;22(7):602-609.
[14] SOARES CJ, SANTANA FR, PEREIRA JC, et al. Influence of airborne-particle abrasion on mechanical properties and bond strength of carbon/epoxy and glass/bis-GMA fiber-reinforced resin posts. J Prosthet Dent. 2008;99(6):444-454.
[15] SCHMAGE P, CAKIR FY, NERGIZ I, et al. Effect of surface conditioning on the retentive bond strengths of fiberreinforced composite posts. J Prosthet Dent. 2009;102(6):368-377.
[16] BRAGA NM, SOUZA-GABRIEL AE, MESSIAS DC, et al. Flexural properties,morphology and bond strength of fiber-reinforced posts:influence of post pretreatment. Braz Dent J. 2012;23(6):679-685.
[17] MONTICELLI F, TOLEDANO M, TAY FR, et al. A simple etching technique for improving the retention of fiber posts to resin composites. J Endod. 2006;32(1):44-47.
[18] AKSORNMUANG J, CHUENARROM C, CHITTITHAWORN N. Effects of various etching protocols on the flexural properties and surface topography of fiber-reinforced composite dental posts. Dent MaterJ. 2017;36(5):614-621.
[19] NAVES LZ, SANTANA FR, CASTRO CG, et al. Surface treatment of glass fiber and carbon fiber posts: SEM characterization. Microsc Res Tech. 2011;74(12):1088-1092.
[20] MONTICELLT F, OSORIO R, SADEK FT, et al. Surface treatments for improving bond strength to prefabricated fiber posts: a literature review. Oper Dent. 2008;33(3):346-355.
[21] DE SOUSA MENEZES M, QUEIROZ EC, SOARES PV, et al. Fiber post etching with hydrogen peroxide: effect of concentration and application time. J Endod. 2011;37(3):398-402.
[22] CADORE-RODRIGES AC, GUILARDI LF, WANDSCHER VF, et al. Surface treatments of a glass-fiber reinforced composite: Effect on the adhesion to a composite resin. J Prosthodont Res. 2020;64(3):301-306.
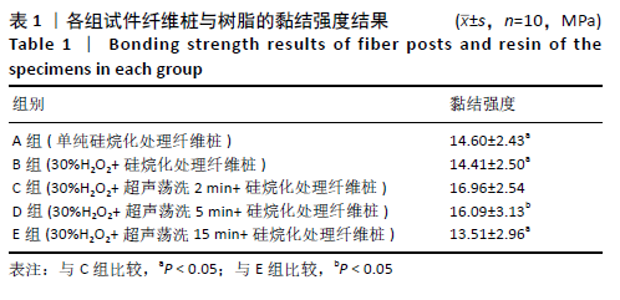
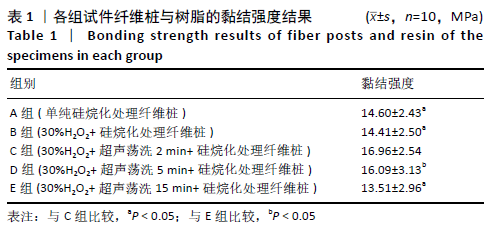
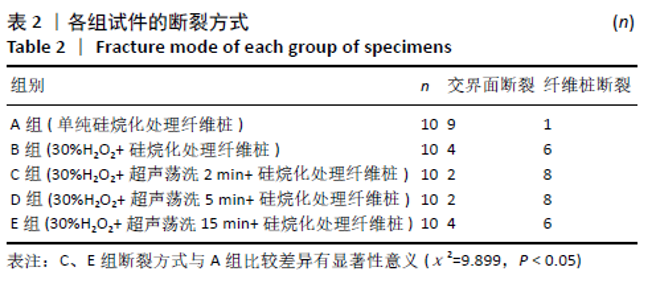
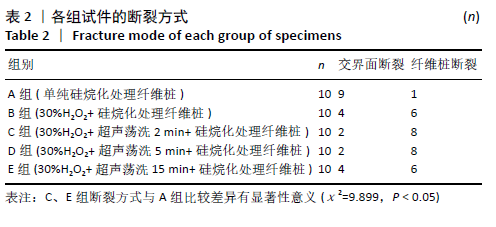
[23] 周晗,惠敏,苗德田,等.表面处理试剂及处理时间对玻璃纤维桩与树脂黏结强度的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(18):70-75.
[24] 杨晓晓,韩建民,李宁毅,等.不同冲洗剂对纤维桩黏结强度的影响[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2019,20(1):9-13.
[25] 李崴嵬,佟静,李娜,等.不同根管封闭剂及桩道牙本质的清洗方法对纤维桩黏结强度的影响[J].河北医药,2019,41(13):1985-1988.
[26] VAN MV, WERY M, WERNER M, et al. The Rpb9 subunit of RNA polymerase II binds transcription factor TFIIE and interferes with the SAGA and elongator histone acetyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277(12):10220-10225.
[27] MOSHARRAF R, BAGHAEI YN. Comparative evaluation of effects of different surface treatment methods on bond strength between fiber post and composite core. J Adv Prosthodont. 2012;4(2):103-108.
[28] KIM HD, LEE JH, AHN KM, et al. Effect of silane activation on shear bond strength of fiber-reinforced composite post to resin cement. J Adv Prosthodont. 2013;5(2):104-109.
[29] 张勇,钟波,谭建国,等.过氧化氢处理提高玻璃纤维桩与树脂水门汀的黏结强度[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2011,43(1):85-88.
[30] 李隽,胥春,郝轶,等.牵张应变作用下人牙周膜细胞形态及钙离子浓度变化的实验研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2009,25(10):582-585.
[31] 单晓莹,王仁飞.超声根管清洗增强纤维桩在根管内固位力的效果观察[J].浙江医学,2019,41(11):1176-1178.
[32] 肖燕,沈凯奇,郭嘉,等.纤维桩修复不同形态上颌尖牙根管的动力学与疲劳分析[J].口腔医学研究,2017,33(8):860-864.
[33] 周敏,郭庆泰,安钢,等.3种黏固剂及牙体预备时机对铸造桩核固位力的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2009,18(6):643-646. |