Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (36): 5878-5887.doi: 10.12307/2021.358
Previous Articles Next Articles
Conservative treatment, open reduction, percutaneous minimally invasive plate internal fixation and intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures: a network meta-analysis
Xiong Chen1, 2, He Guiping3, Zhang Kun2, He Xiao2, Yang Jiarui2, He Changjun2, Wang Xiaolong2, Wang Chen2, Shi Zhengwei2, Zhu Yangjun2, Heng Lisong2
- 1Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedic and Trauma, Honghui Hospital, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China; 3Pingliang Rehabilitation Center Hospital, Pingliang 744000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2021-03-23Revised:2021-03-25Accepted:2021-04-17Online:2021-12-28Published:2021-09-18 -
Contact:Heng Lisong, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedic and Trauma, Honghui Hospital, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Xiong Chen, Master candidate, Physician, Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China; Department of Orthopedic and Trauma, Honghui Hospital, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Research & Development Project in Shaanxi Province, No. 2017SF-197 (to HLS); the Xi’an Science and Technology Project, No. 20YXYJ004(8) (to HLS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiong Chen, He Guiping, Zhang Kun, He Xiao, Yang Jiarui, He Changjun, Wang Xiaolong, Wang Chen, Shi Zhengwei, Zhu Yangjun, Heng Lisong. Conservative treatment, open reduction, percutaneous minimally invasive plate internal fixation and intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures: a network meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5878-5887.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
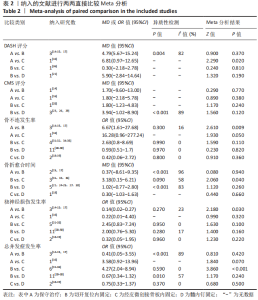
2.3 直接比较Meta分析结果 DASH评分方面:存在4种类型直接比较,保守治疗优于经皮微创接骨板内固定差异有显著意义(P < 0.05)。其中保守治疗与切开复位内固定相比(P=0.004,I2=82%)存在明显异质性,通过逐个剔除单个研究进行敏感性分析,结果未发生明显改变,表明结果稳健性较强。 CMS评分方面:存在4种类型直接比较,差异均无显著意义(P > 0.05)。其中切开复位内固定与髓内钉固定相比(P=0.000 1,I2=89%)存在明显异质性,通过逐个剔除单个研究进行敏感性分析,结果未发生明显改变,表明结果稳健性较强。 骨不连发生率方面:存在5种类型直接比较,切开复位内固定优于保守治疗(P < 0.05),其他3组间比较差异均无显著意义(P > 0.05),所有组间两两比较未发现明显异质性。 骨折愈合时间方面:存在4种类型直接比较,经皮微创接骨板内固定优于切开复位内固定(P < 0.05),其中保守治疗与切开复位内固定(P < 0.001,I2=96%)、切开复位内固定与经皮微创接骨板内固定(P=0.09,I2=58%)、切开复位内固定与髓内钉固定(P < 0.001,I2=83%)均存在明显异质性,对切开复位内固定与经皮微创接骨板内固定和切开复位内固定与髓内钉固定比较进行敏感性分析,结果未发生明显改变,表明结果稳健性较强。 医源性桡神经损伤发生率方面:存在5种类型直接比较,保守治疗优于切开复位内固定(P < 0.05)。所有组间两两比较未发现明显异质性。 总并发症发生率方面:存在5种类型直接比较,经皮微创接骨板内固定优于切开复位内固定(P < 0.05)。其中保守治疗与切开复位内固定(P=0.000 1,I2=89%)和切开复位内固定与髓内钉固定(P=0.01,I2=57%)存在明显异质性,通过逐个剔除单个研究进行敏感性分析,结果未发生明显改变,表明结果稳健性较强,见表2。"
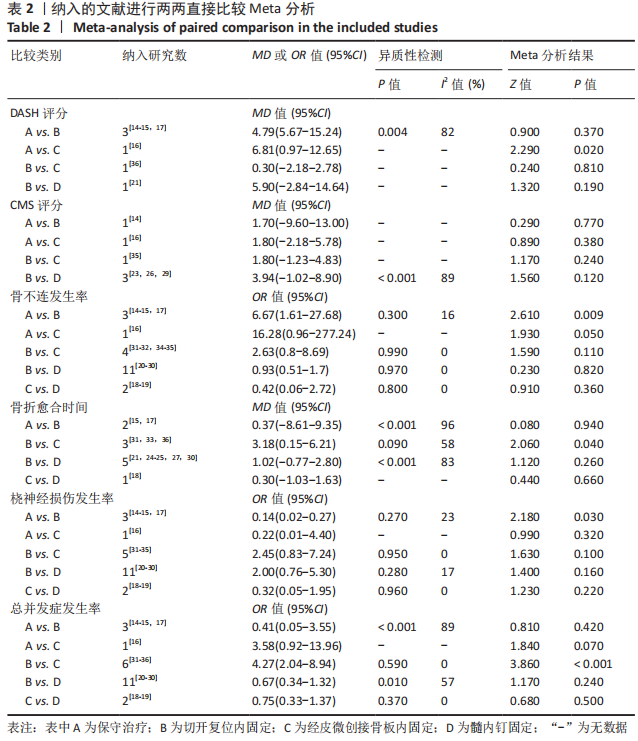
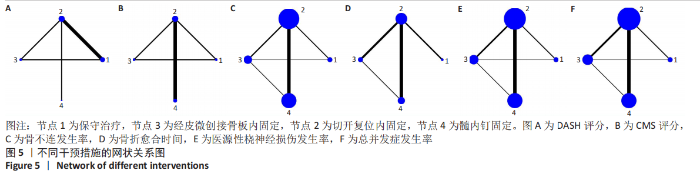
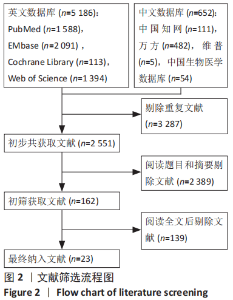
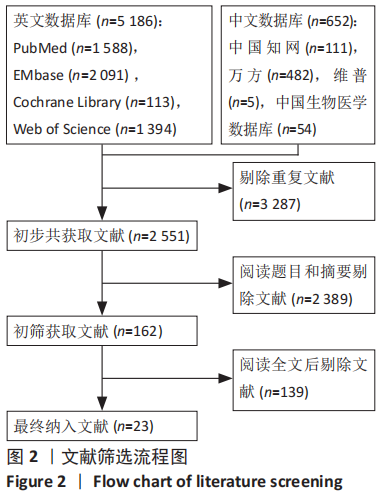
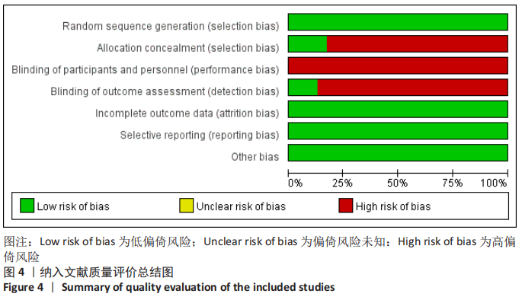
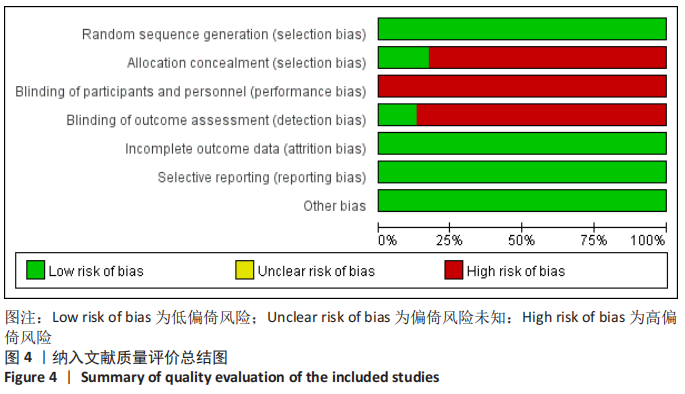
2.4 网状Meta分析结果 2.4.1 网络证据图 文章共涉及4种干预措施。在DASH评分方面共纳入6篇文献[14-17,21,36],形成个1闭合环,为保守-切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定;在CMS评分方面共纳入6篇文 献[14,16,23,26,29,35],形成1个闭合环,为保守-切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定;在骨不连发生率方面共纳入21篇文献[14-32,34-35],形成2个闭合环,分别为保守-切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定、切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定-髓内钉固定;在骨折愈合时间方面共纳入11篇文 献[15,17-18,21,24-25,27,30-31,33,36],形成个1闭合环,为切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定-髓内钉固定;在医源性桡神经损伤发生率方面共纳入22篇文献[14-35],形成2个闭合环,分别为保守-切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定、切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定-髓内钉固定;在总并发症方面共纳入23篇文献[14-36],形成2个闭合环,分别为保守-切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定,切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定-髓内钉固定。两节点之间连线越粗表示两两直接比较研究越多,节点越大表示纳入样本量越多,见图5。"

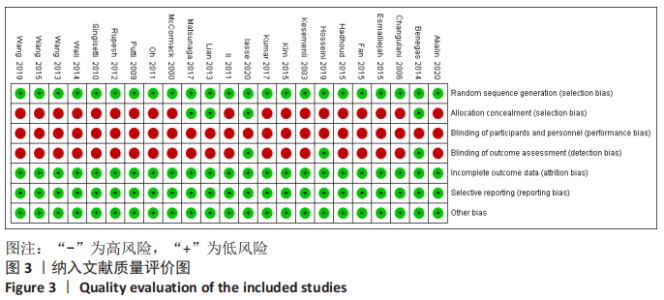
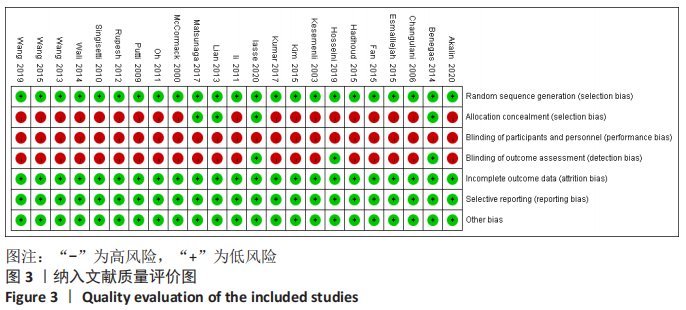
2.4.2 一致性检测 对各个结局指标纳入文献所得闭合环进行一致性测 ①DASH评分方面,对保守-切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定闭合环进行一致性检测,结果显示ROR值距离1较远,95%CI值下限接近1;②CMS评分方面,对保守-切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定闭合环进行一致性检测,结果显示ROR值接近1,95%CI值下限接近1;③骨不连发生率方面,分别对保守-切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定和切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定-髓内钉固定闭合环进行一致性检测,结果显示闭合环ROR值接近1,95%CI值下限接近1;④骨折愈合时间方面,对切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定-髓内钉固定闭合环进行一致性检测,结果显示ROR值距离1较远,95%CI值下限距离1较远;⑤医源性桡神经损伤发生率方面,分别对保守-切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定和切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定-髓内钉固定闭合环进行一致性检测,结果显示闭合环ROR值接近1,95%CI值下限接近1;⑥总并发症方面,分别对保守-切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定和切开复位内固定-经皮微创接骨板内固定-髓内钉固定闭合环进行一致性检测,结果显示2个闭合环ROR值接近1,95%CI值下限接近1。总体提示,文章的直接比较结果与间接比较结果较为一致,文章一致性较好,见图6。"


2.4.3 纳入研究各结果指标网状Meta分析结果 ①DASH评分方面,各个干预措施之间比较无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②CMS评分方面,各个干预措施之间比较无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③骨不连发生率方面,保守治疗与切开复位内固定、经皮微创接骨板内固定和髓内钉固定相比,治疗肱骨干骨折后的骨不连发生率较高(P < 0.05),其他各个干预措施之间比较无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④骨折愈合时间方面,各个干预措施之间比较无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑤医源性桡神经损伤发生率方面,保守治疗与切开复位内固定和髓内钉固定相比,治疗肱骨干骨折后的医源性桡神经损伤发生率较低(P < 0.05),经皮微创接骨板内固定和切开复位内固定相比,医源性桡神经损伤发生率较低(P < 0.05);⑥总并发症方面,各个干预措施之间比较无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图7。"
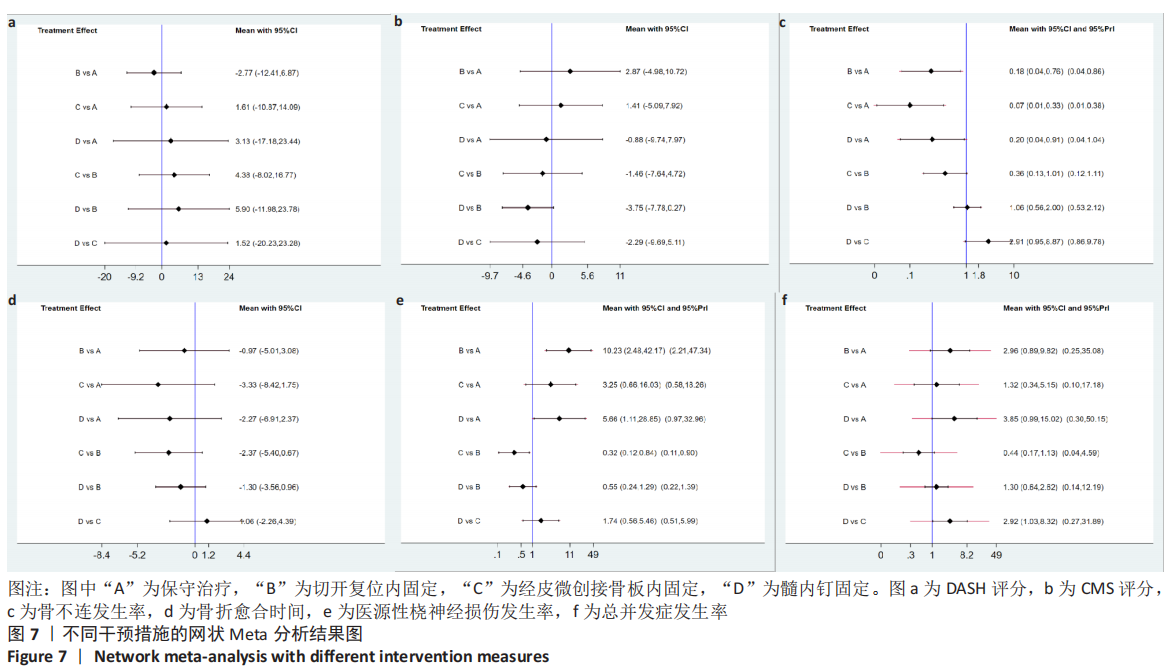

2.4.4 纳入研究各结果指标的网状Meta排序结果 ①DASH评分比较:切开复位内固定(74.2) >保守(49.3) >经皮微创接骨板内固定(39.3) >髓内钉固定(37.3),表明4种干预措施中,切开复位内固定治疗肱骨干骨折的DASH评分最优;②CMS评分比较:切开复位内固定(80.2) >经皮微创接骨板内固定(57.5) >保守(38.2) >髓内钉固定(24.1),表明4种干预措施中,切开复位内固定治疗肱骨干骨折的CMS评分最优;③骨不连比较结果:经皮微创接骨板内固定(98.0) >切开复位内固定(52.9) >髓内钉固定(48.0) >保守(1.1),表明4种干预措施中,经皮微创接骨板内固定治疗肱骨干骨折的骨不连发生率最低;④骨折愈合时间比较:经皮微创接骨板内固定(85.7) >髓内钉固定(65.9) >切开复位内固定(29.0) >保守(19.4),表明4种干预措施中,经皮微创接骨板内固定治疗肱骨干骨折的骨折愈合时间最快;⑤医源性桡神经损伤发生率比较结果:保守(96.7) >经皮微创接骨板内固定(63.0)>髓内钉固定(37.1) >切开复位内固定(3.3),表明4种干预措施中,保守治疗肱骨干骨折的医源性桡神经损伤发生率最低。⑥各个干预措施的总并发症比较结果:保守(86.6) >经皮微创接骨板内固定(75.6) >切开复位内固定(28.1) >髓内钉固定(9.6),表明4种干预措施中,保守治疗肱骨干骨折的总并发症发生率最低,见图8。"

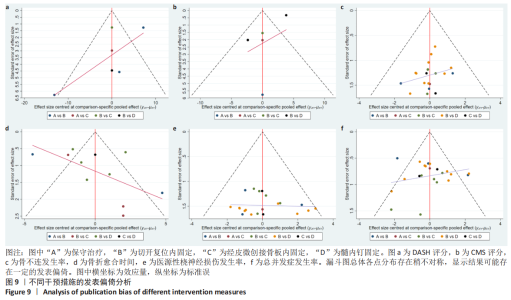
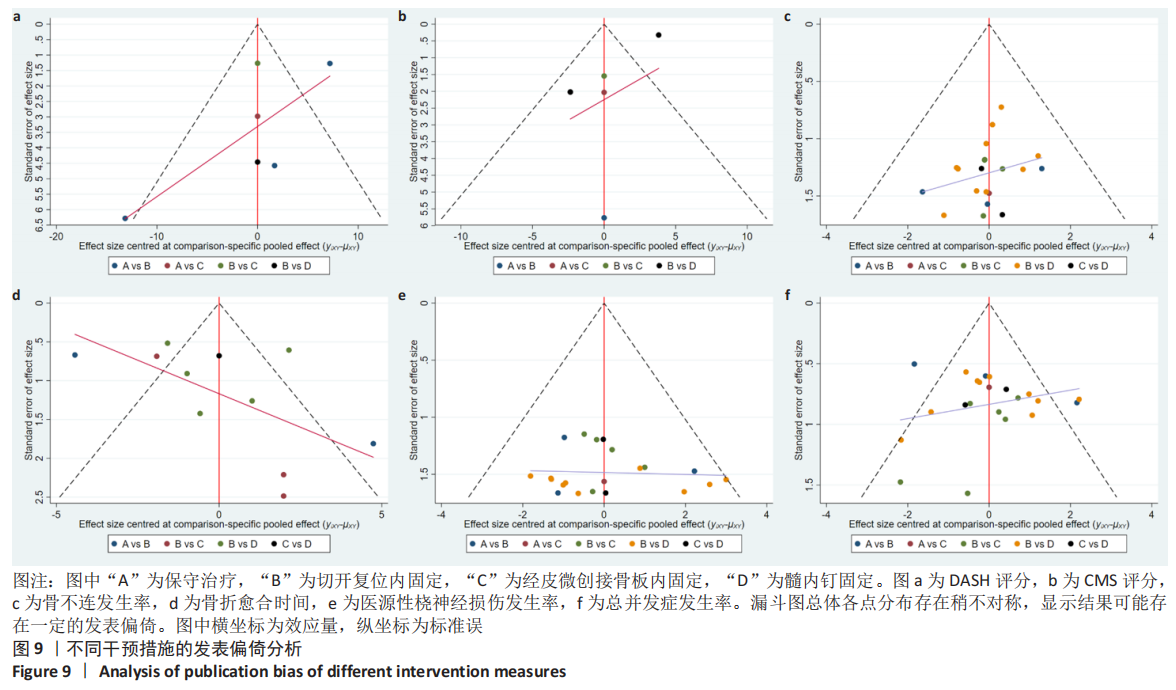
2.4.5 发表偏倚分析结果 对各个结局指标所纳入的研究绘制比较-校正漏斗图,此漏斗图中不同颜色点代表不同的两两间直接比较,相同颜色点代表相同两两间比较研究。若漏斗图未发现明显不对称,表明发表偏倚或小样本效应较小。①DASH评分方面,漏斗图分布较对称,但保守治疗与切开复位内固定比较的研究分布较远,提示保守治疗与切开复位内固定比较的研究可能存在发表偏倚或小样本效应,而其他研究存在发表偏倚或小样本效应较小;②CMS评分方面,漏斗图分布较对称,但髓内钉固定与切开复位内固定比较的研究分布较远,提示髓内钉固定与切开复位内固定比较的研究可能存在发表偏倚或小样本效应,而其他研究存在发表偏倚或小样本效应较小;③骨不连发生率方面,漏斗图分布较对称,提示研究存在发表偏倚或小样本效应较小;④骨折愈合时间方面,漏斗图分布可能存在不对称,且保守治疗与切开复位内固定比较的研究分布较远,提示保守治疗与切开复位内固定比较的研究可能存在发表偏倚或小样本效应,而其他研究存在发表偏倚或小样本效应较小;⑤医源性桡神经损伤发生率方面,漏斗图分布较对称,提示研究存在发表偏倚或小样本效应较小;⑥总并发症方面,漏斗图分布较对称,但保守治疗与切开复位内固定比较的研究分布较远,提示保守治疗与切开复位内固定比较的研究可能存在发表偏倚或小样本效应,而其他研究存在发表偏倚或小样本效应较小,见图9。"
| [1] COURT-BROWN CM, CAESAR B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury. 2006;37(8):691-697. [2] EKHOLM R, ADAMI J, TIDERMARK J, et al. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus. An epidemiological study of 401 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(11):1469-1473. [3] OLIVER WM, SEARLE HKC, NG ZH, et al. Fractures of the proximal- and middle-thirds of the humeral shaft should be considered as fragility fractures. Bone Joint J. 2020;102(11):1475-1483. [4] UPDEGROVE GF, MOURAD W, ABBOUD JA. Humeral shaft fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(4):87-97. [5] WALKER M, PALUMBO B, BADMAN B, et al. Humeral shaft fractures: a review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(5):833-844. [6] BEERES FJ, DIWERSI N, HOUWERT MR, et al. ORIF versus MIPO for humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized clinical trials and observational studies. Injury. 2020;1383(20):30939-30936. [7] 王磊,李子龙,袁斌斌,等.锁定钢板与顺行髓内钉治疗成人肱骨干骨折临床效果的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(24):3924-3930. [8] 曹春风,马坤龙,栾和旭,等.钢板内固定与髓内钉治疗肱骨干骨折的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(12): 1080-1087. [9] 王伟,陈永佳,沈磊,等.微创钢板内固定与传统手术治疗成人肱骨干骨折的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(35):5715-5723. [10] 薛镜,黄富国,项舟,等.顺行锁定髓内钉和动力加压钢板治疗肱骨干骨折的系统评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017, 25(22):2055-2060. [11] 邱皓,卢旻鹏,栾富钧,等.三种不同手术方式治疗肱骨干骨折的网络Meta分析[J].重庆医科大学学报,2017,42(2):163-168. [12] SCHOCH BS, PADEGIMAS EM, MALTENFORT M, et al. Humeral shaft fractures: national trends in management. J Orthop Traumatol. 2017;18(3):259-263. [13] 赵益峰,王满宜.肱骨干骨折的治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(10): 973-975. [14] RÄMÖ L, SUMREIN BO, LEPOLA V, et al. Effect of surgery vs functional bracing on functional outcome among patients with closed displaced humeral shaft fractures: the FISH randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1792-1801. [15] KUMAR S, SHANMUGAM N, KUMAR S, et al. Comparison between operative and non operative treatment of fracture shaft of humerus: an outcome analysis. Int J Res Orthop. 2017;3:445-450. [16] MATSUNAGA FT, TAMAOKI MJ, MATSUMOTO MH, et al. Minimally invasive osteosynthesis with a bridge plate versus a functional brace for humeral shaft fractures: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(7):583-592. [17] HOSSEINI KHAMENEH SM, ABBASIAN M, ABRISHAMKARZADEH H, et al. Humeral shaft fracture: a randomized controlled trial of nonoperative versus operative management (plate fixation). Orthop Res Rev. 2019;11:141-147. [18] LIAN K, WANG L, LIN D, et al. Minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis for mid-distal third humeral shaft fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(8):1025-1032. [19] BENEGAS E, FERREIRA NETO AA, GRACITELLI ME, et al. Shoulder function after surgical treatment of displaced fractures of the humeral shaft: a randomized trial comparing antegrade intramedullary nailing with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(6):767-774. [20] MCCORMACK RG, BRIEN D, BUCKLEY RE, et al. Fixation of fractures of the shaft of the humerus by dynamic compression plate or intramedullary nail. A prospective, randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000; 82(3):336-339. [21] AKALIN Y, ŞAHIN İG, ÇEVIK N, et al. Locking compression plate fixation versus intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures: which one is better? A single-centre prospective randomized study. Int Orthop. 2020;44(10):2113-2121. [22] KUMAR R, SINGH P, CHAUDHARY LJ, et al. Humeral shaft fracture management, a prospective study; nailing or plating. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2012;3(1):37-42. [23] LI Y, WANG C, WANG M, et al. Postoperative malrotation of humeral shaft fracture after plating compared with intramedullary nailing. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(6): 947-954. [24] CHANGULANI M, JAIN UK, KESWANI T. Comparison of the use of the humerus intramedullary nail and dynamic compression plate for the management of diaphyseal fractures of the humerus. A randomised controlled study. Int Orthop. 2007;31(3):391-395. [25] KESEMENLI CC, SUBAŞI M, ARSLAN H, et al. Comparison between the results of intramedullary nailing and compression plate fixation in the treatment of humerus fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2003;37(2):120-125. [26] FAN Y, LI YW, ZHANG HB, et al. Management of humeral shaft fractures with intramedullary interlocking nail versus locking compression plate. Orthopedics. 2015;38(9):825-829. [27] WALI MG, BABA AN, LATOO IA, et al. Internal fixation of shaft humerus fractures by dynamic compression plate or interlocking intramedullary nail: a prospective, randomised study. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2014;9(3):133-140. [28] PUTTI AB, UPPIN RB, PUTTI BB. Locked intramedullary nailing versus dynamic compression plating for humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2009; 17(2):139-141. [29] WANG C, DAI G, WANG S, et al. The function and muscle strength recovery of shoulder after humeral diaphysis fracture following plating and intramedullary nailing. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(8):1089-1094. [30] SINGISETTI K, AMBEDKAR M. Nailing versus plating in humerus shaft fractures: a prospective comparative study. Int Orthop. 2010;34(4):571-576. [31] HADHOUD MM, DARWISH AE, MESRIGA M MK. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis versus open reduction and plate fixation of humeral shaft fractures. Menoufia Med J. 2015;28(1):154. [32] OH CW, BYUN YS, OH JK, et al. Plating of humeral shaft fractures: comparison of standard conventional plating versus minimally invasive plating. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(1):54-60. [33] KIM JW, OH CW, BYUN YS, et al. A prospective randomized study of operative treatment for noncomminuted humeral shaft fractures: conventional open plating versus minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(4):189-194. [34] ESMAILIEJAH AA, ABBASIAN MR, SAFDARI F, et al. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis versus open reduction and internal fixation. Trauma Mon. 2015; 20(3):262-271. [35] WANG C, LI J, LI Y, et al. Is minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fracture advantageous compared with the conventional open technique? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(11):1741-1748. [36] WANG Z, SONG S, GUO Q, et al. Therapeutic effect of anterior approach MIPO combined with LCP in the treatment of humeral shaft fracture. Acta Medica Mediterranea. 2019;35(5):2765-2768. [37] SARMIENTO A, ZAGORSKI JB, ZYCH GA, et al. Functional bracing for the treatment of fractures of the humeral diaphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(4):478-486. [38] ALI E, GRIFFITHS D, OBI N, et al. Nonoperative treatment of humeral shaft fractures revisited. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(2):210-214. [39] 赵峰峰.普通加压钢板与锁定钢板内固定修复老年复杂性肱骨干中下段骨折的生物力学比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(26):3909-3915. [40] 王陶然,袁志,裴国献,等.可膨胀髓内钉与锁定加压钢板治疗肱骨干骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017, 19(7):566-571. [41] PAPASOULIS E, DROSOS GI, VERVERIDIS AN, et al. Functional bracing of humeral shaft fractures. A review of clinical studies. Injury. 2010;41(7):21-27. [42] HOHMANN E, GLATT V, TETSWORTH K. Minimally invasive plating versus either open reduction and plate fixation or intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25(10): 1634-1642. [43] SARGEANT HW, FARROW L, BARKER S, et al. Operative versus non-operative treatment of humeral shaft fractures: a systematic review. Shoulder Elbow. 2020;12(4): 229-242. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [5] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [6] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [7] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [8] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [9] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [10] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [11] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [12] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [13] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [14] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [15] | Liang Yan, Zhao Yongfei, Xu Shuai, Zhu Zhenqi, Wang Kaifeng, Liu Haiying, Mao Keya. Imaging evaluation of short-segment fixation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis assisted by highly selective nerve root block [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1423-1427. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||