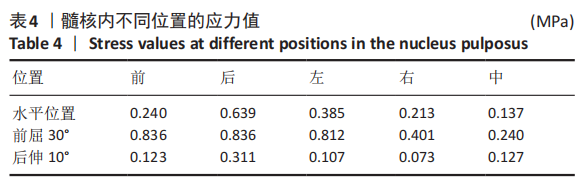
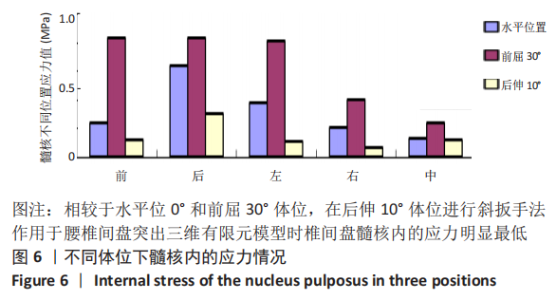
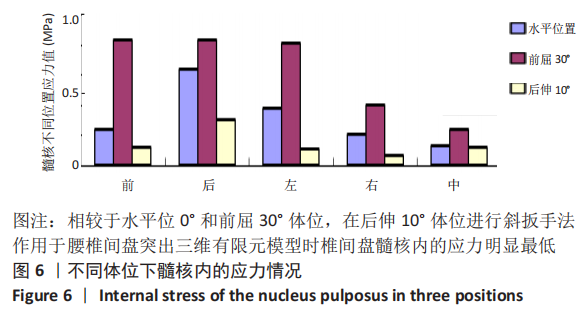
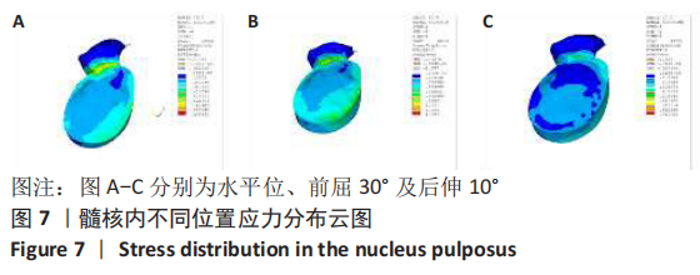
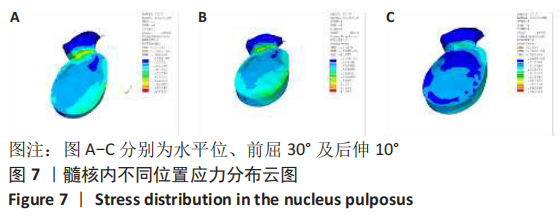
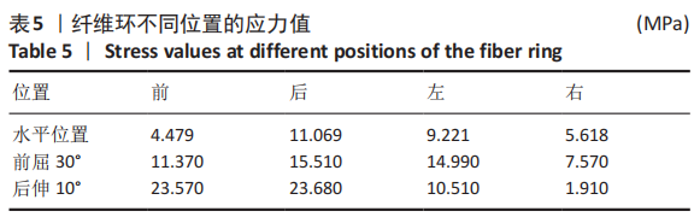
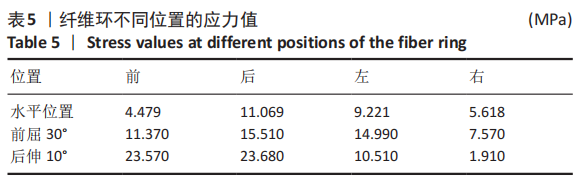
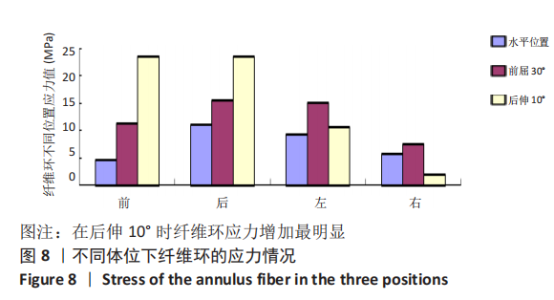
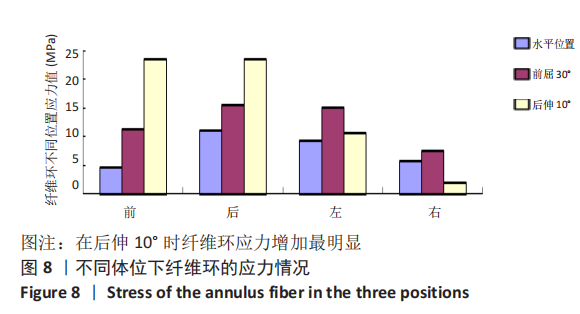
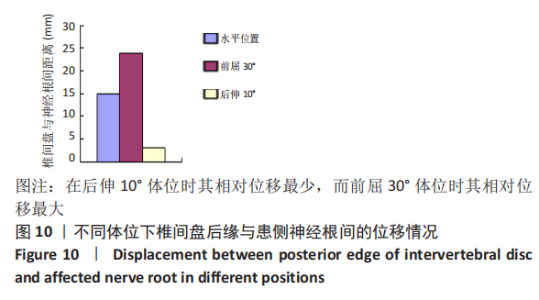
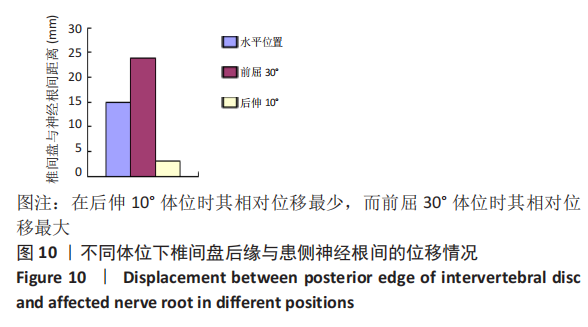
[1] SHENOY K, STEKAS N, DONNALLY CJ 3RD, et al. Retrolisthesis and lumbar disc herniation: a postoperative assessment of outcomes at 8-year follow-up. Spine J. 2019;19(6):995-1000.
[2] SHI R, WANG F, HONG X, et al. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy versus microendoscopic discectomy for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation: a meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2019; 43(4):923-937.
[3] 张勇, 李鹏, 杨洋. 中医推拿联合牵引治疗腰椎间盘突出症疗效及其对患者肌电图、血清IL-1β、TNF-α和血浆TXB2的影响[J]. 重庆医学,2019,48(19):3283-3286.
[4] 高春雨, 叶宜颖, 王宝剑,等. 针刀浅筋膜松解术联合神经根阻滞治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2020, 26(3):369-371.
[5] 王尚全, 尹逊路, 陈明,等. 腰椎斜扳手法联合悬吊运动训练治疗慢性非特异性腰痛的临床研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2018,33(7): 3186-3188.
[6] LOMELÍ-RIVAS A, LARRINÚA-BETANCOURT JE. Biomechanics of the lumbar spine: a clinical approach. Acta Ortopédica Mexicana. 2019; 33(3):185-191.
[7] NEWELL N, LITTLE J, CHRISTOU A, et al. Biomechanics of the human intervertebral disc: A review of testing techniques and results. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;69:420-434.
[8] WANG XD, FENG MS, HU YC. Establishment and Finite Element Analysis of a Three-dimensional Dynamic Model of Upper Cervical Spine Instability: F inite E lement of U pper C ervical I nstability. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3):500-509.
[9] XIE YZ, WANG X, JIAN Q, et al. Three dimensional finite element analysis used to study the influence of the stress and strain of the operative and adjacent segments through different foraminnoplasty technique in the PELD: Study protocol clinical trial (SPIRIT Compliant). Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(15):e19670.
[10] 田强, 钟侨霖, 赵家友,等. 提拉旋转斜扳法操作时腰椎椎间盘应力及应变的有限元研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2019,37(1):87-90.
[11] 田聪. 斜扳,旋转复位法对常用LDH后路手术后腰椎应力影响的有限元分析[D].南宁:广西中医药大学,2017.
[12] 舒新农, 牟文芝, 陈金凤,等. 斜扳手法与坐位直腰旋转手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的生物力学作用比较[J]. 针灸推拿医学(英文版), 2017,15(5):317-321.
[13] ZHONG ZC, WEI SH, WANG JP, et al. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine with a new cage using a topology optimization method. Med Eng Phys. 2006;28(1):90-98.
[14] SHARMA M, LANGRANA NA, RODRIGUEZ J. Modeling of facet articulation as a nonlinear moving contact problem: Sensitivity study on lumbar facet response. J Biomech Eng. 1998;120(1):118-125.
[15] GOEL VK, MONROE BT, GILBERTSON LG, et al. Interlaminar shear stresses and laminae separation in a disc: Finite element analysis of the L3-L4 motion segment subjected to axial compressive loads. Spine. 1995;20(6):689-698.
[16] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine. 1989;14(11):1256-1260.
[17] XIAO Z, WANG L, GONG H, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of three surgical scenarios of posterior lumbar interbody fusion by finite element analysis. BioMed Eng Online. 2012;11(1):31.
[18] 徐海涛,李松,刘澜,等.腰椎斜扳手法时椎间盘的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13):2335-2338.
[19] GBD 2016 DISEASE AND INJURY INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 - ScienceDirect. Lancet. 2017;390(10100): 1211-1259.
[20] WANG Y, DAI G, JIANG L, et al. The incidence of regression after the non-surgical treatment of symptomatic lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):530.
[21] 赵一宇,辛振刚,周元成,等.腰椎间盘突出症非手术疗法综述[J].当代医学,2018,24(36):184-187.
[22] 李建华,朱清广,房敏,等. 脊柱微调手法联合导引功法治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床观察[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2020,35(2):505-507.
[23] 宋宝,李华东,李梅梅. 瞬时强电针结合腰椎侧扳法治疗腰椎间盘突出症下肢麻木31例[J]. 中国针灸,2018,38(2):193-194.
[24] 沈国权.脊柱推拿的理论与实践——脊柱微调手法体系.北京: 人民卫生出版社,2016:723
[25] 张人文,莫灼锚,李冬,等. 二步加载分步求解在手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症有限元分析中的应用[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019, 27(1):1-5.
[26] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317.
[27] ZHU R, NIU WX, WANG ZP, et al. The Effect of Muscle Direction on the Predictions of Finite Element Model of Human Lumbar Spine. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:1-6.
[28] TIAN Q, FAN Z, ZHAO J, et al. Biomechanical Mechanism of Lumbar Spine with Chinese Spinal Manipulation: A Finite Element Study// 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). IEEE, 2019.
[29] 李战武, 王理康. 三维整肌、正脊手法治疗武警官兵急性腰扭伤的疗效[J]. 中华灾害救援医学,2014,2(8):433-435.
[30] 杨学锋,张晓刚,李具宝,等.模拟拔伸按压手法腰椎运动节段三维有限元模型分析[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2013,21(7):4-6. |