Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (28): 4575-4580.doi: 10.12307/2022.316
Previous Articles Next Articles
Electrospun fiber-based nerve tissue engineering scaffold: material, function and structure design strategy
Xue Xuexin, Liu Zhepeng
- Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Equipment, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
-
Received:2021-02-22Accepted:2021-04-15Online:2022-10-08Published:2022-03-24 -
Contact:Liu Zhepeng, PhD, Senior engineer, Master’s supervisor, Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Equipment, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China -
About author:Xue Xuexin, Master candidate, Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Equipment, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xue Xuexin, Liu Zhepeng. Electrospun fiber-based nerve tissue engineering scaffold: material, function and structure design strategy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4575-4580.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
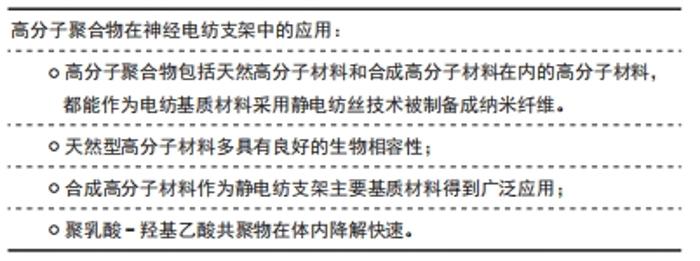
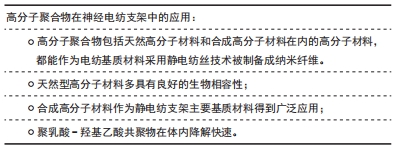
天然型高分子材料多具有良好的生物相容性,甚至提供特定的生化信号,为模拟细胞生长环境提供有利的生物属性,以此提高细胞的附着、增殖和迁移能力。不过天然型高分子材料的机械性能多不能满足机械性能要求,而需要采取特殊处理(如交联处理[4]、与合成高分子材料复合使用等方式[6])。壳聚糖是一种无毒性、无刺激性、非常安全的天然型高分子材料,为改善其机械强度不足的问题,LAU等[4]采用京尼平天然生物交联剂处理壳聚糖纳米纤维,得到的纳米纤维具备更高的刚度、更好的抗溶胀性和溶菌酶降解性,在神经细胞培养实验中,相比于未处理的壳聚糖纳米纤维,处理后的壳聚糖纺丝支架培养的神经突生长速率大幅提高。 合成高分子材料作为静电纺支架主要基质材料得到广泛应用[6-7]。合成高分子材料支架表现出较强的机械性能,其生物降解率也可通过混纺、表面改性等方式改变,且生产可控,作为支架基质材料优势显著。 聚己内酯是FDA批准的由ε-己内酯经开环聚合得到的低熔点聚合物,其生产成本低廉,并且由于机械强度好、结晶性高、生物吸附性和生物相容性等突出性能已被广泛应用于药物输送和组织工程[8]。SADERI等[9]发现聚己内酯/壳聚糖纳米纤维支架能够有效促进许旺细胞的附着和增殖能力,单纯的聚己内酯材料需要长达24个月才能体内降解,降解速度缓慢,而壳聚糖成分能够提高材料的降解速率和生物相容性。 聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物在体内降解快速(50∶50在体内一二个月就能降解),在美国通过FDA认证,被作为药用辅料收录进美国药典[10],其具有良好的薄膜成型能力、热稳定性、生物相容性和生物降解性,是一种优良的电纺基质材料。为改善聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物高疏水性导致细胞附着不良的问题,WANG等[5]将聚-L-赖氨酸涂层包覆在由聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物/多壁碳纳米管组成的取向纳米纤维支架表面上形成亲水表面,有效改善神经细胞附着状况。聚己内酯、聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物同其他合成聚合物如聚乳酸、聚乙烯醇等都具备增强复合型支架的机械性能[11],允许材料表面修饰的特点并具备一定的生物相容性。 2.2 复合型纤维材料在神经电纺支架中的应用 在目前组织工程支架的开发研究中,复合型材料支架的研究颇多。结合天然高分子材料或天然生物活性成分与合成高分子材料制备成的复合型支架,这种支架有更好的生物相容性,生化信号强烈,可吸收,机械强度较天然材料更好。木质素是一种由木材制成的生物聚合物,生产成本低廉,具有出色的抗氧化性能。WANG等[6]通过无溶剂开环聚合合成了木质素-聚己内酯共聚物,将木质素-聚己内酯共聚物与聚己内酯掺入并工程化为纳米纤维支架,以增强聚己内酯纳米纤维的机械性能,并赋予其良好的抗氧化性能[4 h内自由基抑制率高达(98.3±1.9)%]。研究发现,木质素共聚物的纳米纤维还增强了许旺细胞的髓磷脂碱性蛋白表达,并刺激DRG神经元的神经突向外生长[11]。SAUDI 等[11]开展了负载木质素的对齐电纺聚乙烯醇-聚癸二酸甘油酯纤维对神经细胞分化的研究,实验表明增加木质素百分比有增强细胞增殖的效果,合适百分比的木质素对细胞分化的积极作用较明显。可见复合型电纺支架的基质材料一般生物相容性较好,辅助生长的生物活性成分例如多糖类、蛋白多肽类、生长因子类也会具有增强纤维支架生物相容性的作用。因此,此类复合支架一般具备优秀的生物学特性。"
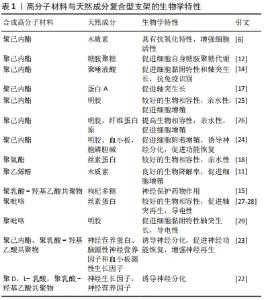
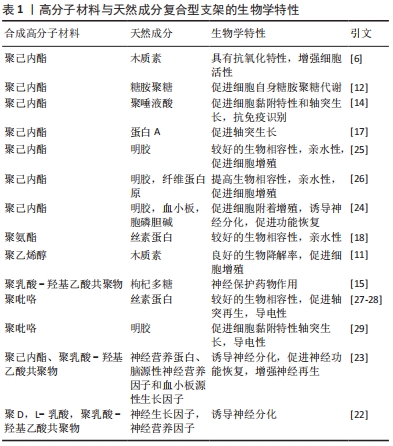
2.2.1 多糖类成分在神经电纺支架中的应用 模仿细胞外基质是支架研究的重点,而生物相容性是支架设计的基本要素。组织工程支架一般通过材料的表面改性或附加生物活性成分增强其生物相容性。存在于细胞表面和细胞外基质中的可溶性因子、生物分子等信号分子,几乎可以调节细胞功能的各个方面,因此附加生物活性成分(例如多糖类成分)能够有效增强电纺支架生物相容性,并使其具备一定综合性能(诱导分化等功能)。 糖胺聚糖是硫酸化多糖,已被证明可根据硫酸化的位置和程度来调节神经组织中的轴突生长[12],并且硫酸化与蛋白共价结合以蛋白聚糖的形式作为细胞外基质的主要成分存在。蛋白聚糖的许多生物学功能例如促进细胞的相互作用、分化和增殖,在生理和病理条件下都主要取决于糖胺聚糖链的特定结构特征。IDINIT等[12]开发了糖胺聚糖功能化聚己内酯纤维支架,表明糖胺聚糖功能化支架从促进细胞的自身天然糖胺聚糖代谢角度调节许旺细胞的黏附、增殖和分化。但是动物来源的糖胺聚糖很难分离和纯化,为降低支架的生产成本,MENEZES等[13]用生产成本低的硫酸纤维素作为糖胺聚糖模拟物进行研究,发现在神经元发育过程中硫酸纤维素仿天然细胞外基质,并能够促进神经元细胞外基质中的天然糖胺聚糖、硫酸软骨素A和硫酸软骨素C的代谢,起到影响神经生长因子结合和允许神经突长出的作用。多糖类混合支架如聚己内酯/聚唾液酸的纤维支架[14]、枸杞多糖封装的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物纳米纤维支架等都能增强支架生物相容性[15],具有引导轴突生长、刺激细胞外基质活性成分代谢等作用。 2.2.2 蛋白多肽类成分在神经电纺支架中的应用 蛋白通过与其受体识别,于强大的结合力下在方向上可以实现特异性结合。而适当的蛋白取向,通过特定的蛋白-受体相互作用引发所需的生物学反应,在引导神经细胞中发挥了至关重要的作用[16]。蛋白A是在金黄色葡萄球菌中发现的高度稳定表面受体,被广泛用于从血清中纯化免疫球蛋白G。LIN等[17]使用生物黏合剂将蛋白A固定在电纺纤维上,使用荧光标记评估这些结合蛋白的分布、可用性和构型,大鼠原代神经细胞实验结果表明,蛋白A与免疫球蛋白G的结合确实促进了神经元的轴突生长。另外,细胞的反应很大程度上取决于信号蛋白的功能,神经调节蛋白1Ⅲ型与蛋白A的结合会适度增加髓鞘的包埋长度。SHRESTHA等[18]从导电和富含蛋白质的角度设计聚氨酯/丝素蛋白/多壁碳纳米管的混合支架,具有较高的机械强度和良好的导电性,生物活性强,适合体外神经细胞再生。 多肽类物质作为一种生物活性分子多用来增强支架的黏附增殖效果。WANG等[19]设计合成了神经元刺激物谷氨酸的多肽,用于在神经组织工程应用中制造仿生3D支架,研究结果显示随着谷氨酸量的增加,支架的生物相容性和神经突生长的长度得到改善。由对齐的纤维制成的3D支架,可以引导神经突沿纤维各向异性生长。ZHANG等[20]在聚己内酯纳米纤维上掺入RGD肽形成了一层层的自组装肽涂层,这些自组装涂层的纳米纤维对pDNA / PEIpro复合物表现出良好的亲和力,因此可以促进此类复合物的有效负载和持续释放;更有价值的是,该研究利用肽涂层介导CRISPR- dCas9系统进行局部递送,簇状规则间隔的短回文重复序列(Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat,CRISPR)系统是生物学应用中进行精确基因组编辑的工具,CRISPR- dCas9可以用来激活或干扰特定的基因表达,并且该支架可以整合其他生物活性肽,为探究细胞-底物相互作用提供了研究平台。因此,在蛋白质与其受体识别的牵引、纤维取向诱导之下,微观层面调控神经分化的方向和状态具有可行性。神经细胞的轴突生长与分化有望做到人为可控的效果。 2.2.3 生长因子在神经电纺支架中的应用 已提出的在手术部位局部递送的神经营养因子,包括神经生长因子和胶质细胞系衍生的神经营养因子,可以增强周围神经的生长分化,这些神经营养因子在不同有效浓度下独立或协同地在神经元成活、神经分化和轴突再生中起重要作用[21]。 LIU等[22]用双电源静电纺丝技术制备了双组分静电纺丝,将神经生长因子和神经营养因子通过乳液静电纺丝分别包裹在聚D,L-乳酸和聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物纳米纤维中,使支架具备两种类型生长因子的持续释放能力。WHITEHEAD等[7]采用了可持续释放生长因子微球与定向纳米纤维结合的设计。 为了让生长因子的释放可控,HONG等[23]设计了3层纳米纤维的支架,每一层堆叠固定,且电纺用到的聚合物基材不同,第一层为对齐的聚己内酯纳米纤维层,辅助细胞向坐骨神经方向的附着和分化;第二、三层的聚乳酸羟基乙酸共聚物层充当生长因子储存器,以释放生长因子神经营养蛋白、脑源性神经营养因子和血小板源性生长因子。每个聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物层的生物降解率不同,可以控制释放具有不同模式的多种生长因子。 血小板富血浆含有多种高浓度的蛋白质和生长因子,如血小板衍生生长因子、血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子等,是理想的活性添加成分[24]。因此含有神经生长因子的生物成分,一般具有增强细胞活性、促进神经细胞轴突生长辅助分化的作用。高分子材料与天然成分的复合型支架的生物学特性,见表1。"
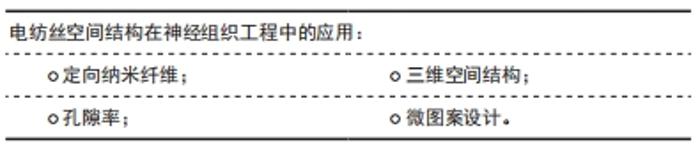
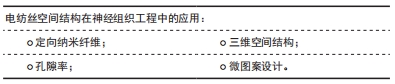
2.3.1 定向纳米纤维 定向形貌索引已被证明在神经元导向中起关键作用,具有定向结构的支架对于周围神经组织再生具有重要研究意义。定向排布的纤维结构更是开发仿生三维空间结构纳米纤维架构的基础。在神经组织工程培养中,纤维支架定向排列,细胞更容易依循纤维排列方向进行生长,具有形貌索引的效果。LIN等[30]用小鼠诱导的多能干细胞衍生神经干细胞,评估支架的细胞相容性和神经突引导作用,结果表明与随机取向的左旋聚乳酸纳米纤维相比,定向的左旋聚乳酸纳米纤维能够更好地引导神经突从神经衍射干细胞向外生长,促进神经突沿定向的纳米纤维生长。此外,还有RAMBURRUN等[31]设计的3-羟基丁酸酯和3-羟基戊酸酯共聚物/油酸镁定向纳米纤维,HUANG等[32]的具有均匀纵向导向提示和多孔鞘的复合支架,SONG等[33]的对齐的层粘连蛋白核心-聚二恶烷酮/胶原壳纤维基。定向纳米纤维支架是从神经生长分化的地形引导和生化信号提示的角度设计的,此设计思路被广泛引用于包括神经细胞支架在内的组织工程支架[18,23,25-28,33]。 2.3.2 孔隙率 静电纺丝技术能够制备具有纳米结构和高孔隙率的纤维支架。WU等[34]比较冻干和静电纺丝制备的壳聚糖支架对于周围神经再生的效果,由于孔隙率高,以电纺方式制成的支架具有增加接触面积的好处,并且静电纺丝的纳米纤维壳聚糖支架比冻干壳聚糖支架更适合实验细胞生长。 CNOPS等[35]在脊髓损伤大鼠模型中设计了具有不同纤维密度的支架并量化轴突生长,实验结果显示,更高的纤维孔隙率能够支持更好的轴突生长。 当纤维束之间的间隙较小(<1 μm)时,轴突生长更有效;此外,当纤维束之间的空间较大(> 1 μm)时,轴突更喜欢在狭窄的间隙(<1 μm)中单独生长。 但为了长期支持神经再生,支架应允许血管生长,以供氧和清除废物。最小的毛细管直径为5-10 μm[36],因此高纤维密度可能会限制血管向支架内生长。研究中观察到支架中具有较高纤维密度的血管数量较少,因此何种密度的纤维最合适目前还有待更多实验研究。 2.3.3 三维空间结构 天然细胞外基质是三维结构的,细胞天然处于立体的生长环境。与二维支架相比,三维定向的纳米纤维支架为细胞行为提供了另一个维度空间。在三维空间中的细胞形态生成、迁移和细胞相互作用,对调节神经细胞的生长和神经组织再生非常重要。模拟天然神经组织结构,开发出仿生三维取向支架在外周神经组织再生领域确实大有可为。YAO等[37]制备了具有定向形貌和软硬度的三维层次排列纤维蛋白水凝胶,植入到大鼠背侧半横断脊髓损伤模型中以桥接病变部位,结果显示出比随机纤维蛋白组快且多的性能恢复,在术后4周就能重建丰富的血管和大量轴突再生长。SHRESTHA等[18]采用干湿静电纺丝法制备了由聚己内酯、丝素蛋白和碳纳米管组成的具有分层排列结构的定向纳米纤维纱(纳米纤维束组装而成),之后将纤维纱封装在水凝胶壳中来制造3D核-壳支架,这些3D对齐的复合支架具有直接引导3D细胞排列和神经细胞沿纳米纤维纱线方向延伸的能力,并且模仿神经外膜层的水凝胶壳能够保护3D环境中的神经细胞组织。 2.3.4 微图案设计 微图案技术(光刻或软光刻)可以在生物材料表面上产生有序的结构,例如纳米级到微米级的凹槽、凹坑、柱子和孔,这项技术可以模拟刻画细胞生长和组织再生的微环境。微图案技术主要使用微建模方法制作微沟槽,是一种在纤维支架表面增加形貌特征的方案。作为最重要的微图案化技术之一,软光刻技术以其无毒、易于操作和快速原型而著称,并且因为它可以制造精确地形特征而在组织工程学中引起越来越多的关注。ZHANG等[38]开发了表面具有脊/槽结构的微图案化聚己内酯支架,微图案化聚己内酯支架表现出疏水性和较好机械性能的多孔微纳米复合结构。YAN等[39] 采用均匀旋转不锈钢圆柱形棒(凹槽和凸起结构)电纺接收杆制造的电喷纳米纤维网(形似瓦楞纸)具有对齐的山谷和山脊结构微图案,研究电刺激和微图案导电电纺纳米纤维网与神经生长因子结合对大鼠神经干细胞分化的协同效应,该研究通过多巴胺和苯胺四聚体的含量来调整纳米纤维网的亲水性,并且苯胺四聚体的存在使其具有良好的电活性和电导率,有效促进大鼠神经干细胞向神经元的分化并抑制星形胶质细胞的形成,支架上生长的神经细胞的细胞活力得到增强。 2.4 新型支架优化技术在神经电纺支架中的应用 "

2.4.1 增加电导率在神经电纺支架中的应用 周围神经由感觉神经和运动神经元组成,是电信号敏感的组织之一,其电导率从数mV/mm到数百mV/mm,取决于不同的神经成分[40]。前文有很多近年来的支架开发研究,部分研究也考虑了增强电导率这个方案。由于电学对于神经系统的修复和再生过程至关重要,改善生物材料的导电性也成为了近年来研究的热点之一[37-48]。 金属纳米粒子就是一种常规方案。AYDEMIR SEZER等[41]开发和研究了聚己内酯支架包含零价铁纳米粒子的可生物降解和可电导。还有的方法如掺入氧化石墨烯[42-44]、使用导电聚合物[15,19,45]、调整电导涂层浓度[45]、金纳米层溅射镀膜[46]、掺杂含铁的卟啉血红素等[47],研究结果表明都能具备良好的电导率,且均对神经细胞分化生长显示出显著的促进作用。 聚吡咯由于其优良的电气性能及良好的细胞和组织兼容性,是应用较广泛的电导聚合物材料[48-49],然而其溶解性和降解性差,要求使用聚吡咯与其他生物材料相结合,以开发合适的复合材料。WANG等[19]通过3D生物打印和静电纺丝制备了聚吡咯/丝素蛋白导电复合导管支架,电刺激接种在这些支架上的许旺细胞,结果细胞显示出更强的存活率、增殖和迁移,神经营养因子的表达也上调了。此外研究发现,电刺激构建的聚吡咯/丝素蛋白传导神经引导导管在体内促进轴突再生和髓鞘再生与MAPKs信号转导途径被电刺激激活有关。DU等[50]通过结合电纺丝和重结晶制备了壳/核聚(3,4-乙撑二氧噻吩)壳聚糖纳米纤维,具有极高电导率(高达0.194 5 S/cm)和超灵敏的压电性能(输出电压为22.5 mV),电刺激结果也表明其电活性效果优异。 此外,尽管尚不清楚其详细的机制,但最近的一些研究表明,局部施加电刺激可以在体内增强神经突的延伸并促进神经再生,这为神经组织工程提供了一种有效的方法[48]。电刺激被证明是一种有用的刺激轴突生长的手段。 2.4.2 改善局部缺氧在神经支架中的应用 周围神经损伤后,血液循环受损导致损伤部位缺血。在神经支架中接种的细胞,在缺血导致局部缺氧的状况下会出现短暂的生物活性衰减现象[51]。全氟三丁胺是全氟碳化物之一,具有很高的氧气溶解性[52]。MA等[53]将全氟三丁胺封装在电纺支架中,随着支架材料的降解,氧气缓慢释放,这为缺氧条件下的许旺细胞提高了培养环境的氧含量水平,提高存活率。此类方法可为许旺细胞提供长期氧气供应,并抵消缺氧在神经损伤的早期阶段对许旺细胞的有害影响[51-53];在血管网络建立之前为神经细胞生长提供有利的微环境,提高细胞存活率和神经再生能力。改善局部缺氧是细胞移植和周围神经损伤治疗的一个新方向。 2.4.3 核酸疗法在神经电纺支架中的应用 核酸疗法是一种通过核酸增强神经元的内在生长能力和克服抑制神经突生长的抑制环境来改善神经再生的方法[54]。核酸疗法通常有基因治疗和基因沉默两种。基因疗法通过将编码神经营养生长因子或纠正酶的基因引入受损的神经元来实现神经再生[54]。基因沉默通过核酸干扰(例如RNA干扰)来实现毒性蛋白表达水平的降低和神经损伤部位生长抑制信号的最小化,然而核酸疗法缺少一种递送系统。电纺细胞支架作为细胞载体是一种非常适合植入的细胞递送系统。MILBRETA等[55]将核酸miR-219 / miR-338模拟物与载体TransIT-TKO及Neurotrophin-3作为复合物掺入包含聚己内酯-共-乙基亚乙基磷酸酯的混合支架中,该系统在体内外能够持续地以非病毒形式传递microRNA(miR),显著增强髓鞘再生能力。核酸miR-219/miR-338在体外可促进原代大鼠胶质细胞分化和髓鞘形成。ZHANG等[56]通过这种静电纺纤维细胞培养支架进行系统的体外miR筛选,以实现最佳miR组合,促进神经元生长;此外,该研究还建立一种在体外和体内关系良好的新型miR-筛查基板,为进一步了解这些miR 的功能及其对神经元的影响提供途径。"

| [1] AMANI H, KAZEROONI H, HASSANPOOR H, et al. Tailoring synthetic polymeric biomaterials towards nerve tissue engineering: a review. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):3524-3539. [2] HOUSCHYAR KS, MOMENI A, PYLES MN, et al. The Role of Current Techniques and Concepts in Peripheral Nerve Repair. Plast Surg Int. 2016;2016:4175293. [3] AMANI H, MOSTAFAVI E, ARZAGHI H, et al. Three-Dimensional Graphene Foams: Synthesis, Properties, Biocompatibility, Biodegradability, and Applications in Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(1):193-214. [4] LAU YT, KWOK LF, TAM KW, et al. Genipin-treated chitosan nanofibers as a novel scaffold for nerve guidance channel design. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;162:126-134. [5] WANG J, TIAN L, CHEN N, et al. The cellular response of nerve cells on poly-l-lysine coated PLGA-MWCNTs aligned nanofibers under electrical stimulation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;91:715-726. [6] WANG J, TIAN L, LUO B, et al. Engineering PCL/lignin nanofibers as an antioxidant scaffold for the growth of neuron and Schwann cell. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;169:356-365. [7] WHITEHEAD TJ, AVILA COC, SUNDARARAGHAVAN HG. Combining growth factor releasing microspheres within aligned nanofibers enhances neurite outgrowth. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(1):17-25. [8] PALAMÀ IE, ARCADIO V, D’AMONE S, et al. Therapeutic PCL scaffold for reparation of resected osteosarcoma defect. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1): 12672. [9] SADERI N, RAJABI M, AKBARI B, et al. Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticle-doped electrospun PCL/chitosan nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018; 29(9):134. [10] DOS SANTOS FP, PERUCH T, KATAMI SJV, et al. Poly (lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) Scaffold Induces Short-term Nerve Regeneration and Functional Recovery Following Sciatic Nerve Transection in Rats. Neuroscience. 2019;396:94-107. [11] SAUDI A, AMINI S, AMIRPOUR N, et al. Promoting neural cell proliferation and differentiation by incorporating lignin into electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(glycerol sebacate) fibers. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:110005. [12] IDINI M, WIERINGA P, ROCCHICCIOLI S, et al. Glycosaminoglycan functionalization of electrospun scaffolds enhances Schwann cell activity. Acta Biomater. 2019;96:188-202. [13] MENEZES R, HASHEMI S, VINCENT R, et al. Investigation of glycosaminoglycan mimetic scaffolds for neurite growth. Acta Biomater. 2019;90:169-178. [14] ZHANG S, WANG XJ, LI WS, et al. Polycaprolactone/polysialic acid hybrid, multifunctional nanofiber scaffolds for treatment of spinal cord injury. Acta Biomater. 2018;77:15-27. [15] WANG J, TIAN L, HE L, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide encapsulated Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid Nanofibers: cost effective herbal medicine for potential application in peripheral nerve tissue engineering. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):8669. [16] PATZKE C, ACUNA C, GIAM LR, et al. Conditional deletion of L1CAM in human neurons impairs both axonal and dendritic arborization and action potential generation. J Exp Med. 2016;213(4): 499-515. [17] LIN J, CHOOI WH, ONG W, et al. Oriented and sustained protein expression on biomimicking electrospun fibers for evaluating functionality of cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111407. [18] SHRESTHA S, SHRESTHA BK, LEE J, et al. A conducting neural interface of polyurethane/silk-functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes with enhanced mechanical strength for neuroregeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;102:511-523. [19] WANG ZH, CHANG YY, WU JG, et al. Novel 3D Neuron Regeneration Scaffolds Based on Synthetic Polypeptide Containing Neuron Cue. Macromol Biosci. 2018;18(3). doi: 10.1002/mabi.201700251. [20] ZHANG K, CHOOI WH, LIU S, et al. Localized delivery of CRISPR/dCas9 via layer-by-layer self-assembling peptide coating on nanofibers for neural tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2020;256:120225. [21] CAO X, SHOICHET MS. Investigating the synergistic effect of combined neurotrophic factor concentration gradients to guide axonal growth. Neuroscience. 2003;122(2):381-389. [22] LIU C, WANG C, ZHAO Q, et al. Incorporation and release of dual growth factors for nerve tissue engineering using nanofibrous bicomponent scaffolds. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(4):044107. [23] HONG MH, HONG HJ, PANG H, et al. Controlled Release of Growth Factors from Multilayered Fibrous Scaffold for Functional Recoveries in Crushed Sciatic Nerve. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(2):576-586. [24] SAMADIAN H, EHTERAMI A, SARRAFZADEH A, et al. Sophisticated polycaprolactone/gelatin nanofibrous nerve guided conduit containing platelet-rich plasma and citicoline for peripheral nerve regeneration: In vitro and in vivo study. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;150:380-388. [25] BORAH R, INGAVLE GC, SANDEMAN SR, et al. Electrically conductive MEH-PPV:PCL electrospun nanofibres for electrical stimulation of rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(9):2342-2359. [26] SAADATKISH N, NOURI KHORASANI S, MORSHED M, et al. A ternary nanofibrous scaffold potential for central nerve system tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(9):2394-2401. [27] WANG L, WU Y, HU T, et al. Aligned conductive core-shell biomimetic scaffolds based on nanofiber yarns/hydrogel for enhanced 3D neurite outgrowth alignment and elongation. Acta Biomater. 2019;96:175-187. [28] ZHAO Y, LIANG Y, DING S, et al. Application of conductive PPy/SF composite scaffold and electrical stimulation for neural tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2020;255:120164. [29] NAGHAVI ALHOSSEINI S, MOZTARZADEH F, KARKHANEH A, et al. Improved cellular response on functionalized polypyrrole interfaces. J Cell Physiol. 2019;10.1002/ jcp.28173. [30] LIN C, LIU C, ZHANG L, et al. Interaction of iPSC-derived neural stem cells on poly(L-lactic acid) nanofibrous scaffolds for possible use in neural tissue engineering. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(2):697-708. [31] RAMBURRUN P, KUMAR P, CHOONARA YE, et al. Design and characterisation of PHBV-magnesium oleate directional nanofibers for neurosupport. Biomed Mater. 2019;14(6):065015. [32] HUANG L, ZHU L, SHI X, et al. A compound scaffold with uniform longitudinally oriented guidance cues and a porous sheath promotes peripheral nerve regeneration in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2018;68:223-236. [33] SONG SJ, SHIN YC, KIM SE, et al. Aligned laminin core-polydioxanone/collagen shell fiber matrices effective for neuritogenesis. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1):570. [34] WU YX, MA H, WANG JL, et al. Production of chitosan scaffolds by lyophilization or electrospinning: which is better for peripheral nerve regeneration? Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(6):1093-1098. [35] CNOPS V, CHIN JS, MILBRETA U, et al. Biofunctional scaffolds with high packing density of aligned electrospun fibers support neural regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(12):2473-2483. [36] CAO Y, WU T, YUAN Z, et al. Three-dimensional imaging of microvasculature in the rat spinal cord following injury. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12643. [37] YAO S, YU S, CAO Z, et al. Hierarchically aligned fibrin nanofiber hydrogel accelerated axonal regrowth and locomotor function recovery in rat spinal cord injury. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:2883-2895. [38] ZHANG L, CHEN S, LIANG R, et al. Fabrication of alignment polycaprolactone scaffolds by combining use of electrospinning and micromolding for regulating Schwann cells behavior. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(12):3123-3134. [39] YAN H, WANG Y, LI L, et al. A micropatterned conductive electrospun nanofiber mesh combined with electrical stimulation for synergistically enhancing differentiation of rat neural stem cells. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(13):2673-2688. [40] FRANK JA, ANTONINI MJ, ANIKEEVA P. Next-generation interfaces for studying neural function. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37(9):1013-1023. [41] AYDEMIR SEZER U, OZTURK YAVUZ K, ORS G, et al. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles containing nanofiber scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020;14(12):1815-1826. [42] GUO Z, LIANG J, POOT AA, et al. Fabrication of poly (trimethylene carbonate)/reduced graphene oxide-graft-poly (trimethylene carbonate) composite scaffolds for nerve regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2019;14(2):024104. [43] FANG X, GUO H, ZHANG W, et al. Reduced graphene oxide-GelMA-PCL hybrid nanofibers for peripheral nerve regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(46):10593-10601. [44] MAGAZ A, LI X, GOUGH JE, et al. Graphene oxide and electroactive reduced graphene oxide-based composite fibrous scaffolds for engineering excitable nerve tissue. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;119:111632. [45] MAGAZ A, SPENCER BF, HARDY JG, et al. Modulation of Neuronal Cell Affinity on PEDOT-PSS Nonwoven Silk Scaffolds for Neural Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(12):6906-6916. [46] WANG Y, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z, et al. An injectable high-conductive bimaterial scaffold for neural stimulation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;195:111210. [47] HSU CC, SERIO A, AMDURSKY N, et al. Fabrication of Hemin-Doped Serum Albumin-Based Fibrous Scaffolds for Neural Tissue Engineering Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(6):5305-5317. [48] THRIVIKRAMAN G, BODA SK, BASU B. Unraveling the mechanistic effects of electric field stimulation towards directing stem cell fate and function: A tissue engineering perspective. Biomaterials. 2018;150:60-86. [49] ZHAO YH, NIU CM, SHI JQ, et al. Novel conductive polypyrrole/silk fibroin scaffold for neural tissue repair. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(8):1455-1464. [50] DU L, LI T, JIN F, et al. Design of high conductive and piezoelectric poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/chitosan nanofibers for enhancing cellular electrical stimulation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;559:65-75. [51] ZHU S, GE J, WANG Y, et al. A synthetic oxygen carrier-olfactory ensheathing cell composition system for the promotion of sciatic nerve regeneration. Biomaterials. 2014;35(5):1450-1461. [52] MA T, ZHU L, YANG Y, et al. Enhanced in vivo survival of Schwann cells by a synthetic oxygen carrier promotes sciatic nerve regeneration and functional recovery. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1):e177-e189. [53] MA T, YANG Y, QUAN X, et al. Oxygen carrier in core-shell fibers synthesized by coaxial electrospinning enhances Schwann cell survival and nerve regeneration. Theranostics. 2020;10(20):8957-8973. [54] ZHANG N, CHIN JS, CHEW SY. Localised non-viral delivery of nucleic acids for nerve regeneration in injured nervous systems. Exp Neurol. 2019;319: 112820. [55] MILBRETA U, LIN J, PINESE C, et al. Scaffold-Mediated Sustained, Non-viral Delivery of miR-219/miR-338 Promotes CNS Remyelination. Mol Ther. 2019;27(2):411-423. [56] ZHANG N, MILBRETA U, CHIN JS, et al. Biomimicking Fiber Scaffold as an Effective In Vitro and In Vivo MicroRNA Screening Platform for Directing Tissue Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6(9):1800808. [57] DEMIR US, SHAHBAZI R, CALAMAK S, et al. Gold nano-decorated aligned polyurethane nanofibers for enhancement of neurite outgrowth and elongation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(6):1604-1613. |
| [1] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [5] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [6] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [7] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [8] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [9] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [10] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [11] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [12] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [13] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [14] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [15] | Xu Lei, Han Xiaoqiang, Zhang Jintao, Sun Haibiao. Hyaluronic acid around articular chondrocytes: production, transformation and function characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 768-773. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||