设计:随机分组对比病例分析。
时间及地点:于2007年1月至2011年1月在福建省立医院及福建省立医院病案室完成。
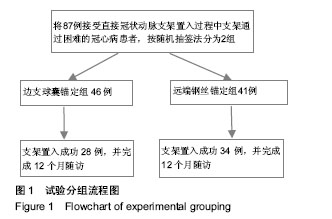
对象:选择2007年1月至2011年1月在福建省立医院接受直接冠状动脉支架置入过程中支架通过困难的冠心病患者87例,按随机抽签法分2组治疗,分别在支架通过困难时采用边支球囊锚定(n=46)或远端钢丝锚定(n=41)进行支架置入治疗。
入选标准:经冠状动脉造影明确有行冠状动脉内支架置入的适应证;冠状动脉造影证实冠状动脉病变属长病变、扭曲病变或钙化病变等冠状动脉复杂病变者;靶病变血管直径大于2.5 mm以上者;行冠状动脉内支架置入时,在正确合理地使用指引导管技术、导引钢丝技术、复杂病变局部充分预扩张及运用双钢丝等技术基础上,支架通过仍困难时采用边支球囊锚定或远端钢丝锚定方法进行支架置入治疗者。
排除标准:靶病变血管直径小于2.5 mm者;靶病变为简单病变者;存在冠状动脉介入治疗的一般禁忌证,如存在出血倾向或凝血功能障碍,或有抗血小板和/或抗凝治疗禁忌,或至少半年内不能持续进行双联抗血小板治疗等冠心病介入治疗禁忌证。
药物洗脱支架:包括CYPHER SELETE支架、Xience V支架、FIREBIRD支架一共3种类型的支架,3种支架经过测试无细胞毒性,血液及组织相容性好。
强生西罗莫司药物洗脱冠状动脉支架系统[商品名:CYPHER SELECT,强生(上海)医疗器材有限公司]。该支架是由316L不锈钢支架和递送系统组成,支架表面涂覆有雷帕霉素(西罗莫司)与聚合物的混合涂层,支架的药物含量为140 μg/cm2,最大支架(4 mm×33 mm)上的最大药量为419 μg。输送系统为快速交换型球囊扩张导管,导管涂有亲水性涂层。
雅培依维莫司药物洗脱冠脉支架系统[商品名:Xience V,雅培医疗器械贸易(上海)有限公司]:该产品由XIENCE V支架平台、载体、药物及支架输送系统4个方面结合组成。Xience V支架采用由钴铬合金制成的VISION支架作为平台,Xience V支架以氟聚合物为载体,使用西罗莫司的衍生物依维莫司为洗脱药物,依维莫司的浓度为100 μg/cm2。输送系统为快速交换型球囊扩张导管,导管涂有亲水性涂层。
微创雷帕霉素洗脱支架系统[商品名:FIREBIRD,微创医疗器械(上海)有限公司]:该产品由药物洗脱支架和球囊扩张导管组成。支架材料为316 L不锈钢,支架表面的膜由雷帕霉素和高分子生物材料(乙烯-醋酸乙烯共聚物)组成。输送系统为快速交换型球囊扩张导管,导管涂有亲水性涂层。
方法:
常规治疗:冠状动脉造影证实冠状动脉狭窄性病变属长病变、扭曲病变或钙化病变等冠状动脉复杂病变,在采用了常规治疗方法如强支撑导管、深插指引导管、增加支撑力强导丝(双导丝技术)、再次高压预扩张病变处等,支架均未能通过病变血管处,未取得成功。在此基础上采用边支球囊锚定或远端钢丝锚定方法进行支架置入治疗。支架成功置入后,所有患者均给予最优化冠心病二级预防药物治疗。
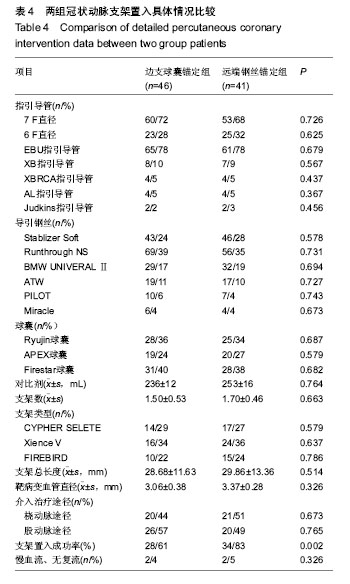
冠状动脉造影及药物洗脱支架置入:患者平卧于导管床上,取右桡动脉穿刺成功后(必要时行股动脉穿刺),鞘管内注入硝酸甘油200 μg,以防血管痉挛;注入肝素3 000 U,介入治疗前追加至肝素100 U/kg,以减少血栓形成和发生桡动脉闭塞的可能性;沿导引钢丝送入6 F(1 F=0.133 mm)动脉造影导管进行左、右冠状动脉造影,明确病变部位及狭窄程度。根据血管病变特征选择支撑性强的指引导管与钢丝。在强支撑指引导管、病变部位充分球囊扩张及双钢丝等技术基础上出现支架通过困难时采用边支球囊锚定和远端钢丝锚定方法进行支架置入治疗。
边支球囊锚定方法[2]:即先将第一根导丝钢丝送达靶病变狭窄处,在病变近端选择一支合适的分支血管并送另一根导引钢丝至分支血管的远端,沿导引钢丝送入与分支血管直径相同的球囊并以6-8大气压持续扩张(提高球囊或支架的推送力)达到锚定的目的,此时迅速从第一根导引钢丝推送支架至病变血管处的一种锚定方法。
远端钢丝锚定方法[4]:选用6 F指引导管,必要时选用7 F指引导管,两根钢丝均通过病变至远端正常冠状动脉,选取远端冠状动脉相同直径的球囊沿钢丝送至病灶远端并持续扩张,然后迅速沿另一根钢丝置入支架至病灶远端,抽空第一个球囊回撤至病变近端,再调节置入支架的位置满意后扩张释放支架。
支架置入成功标准:支架置入病变处经充分扩张后,术后管腔残余狭窄≤ 20%,心肌梗死溶栓试验(TIMI)Ⅲ级血流,无血管夹层、撕裂、急性再闭塞,无主要心血管事件(死亡、心肌梗死、急诊冠状动脉旁路移植)发生。
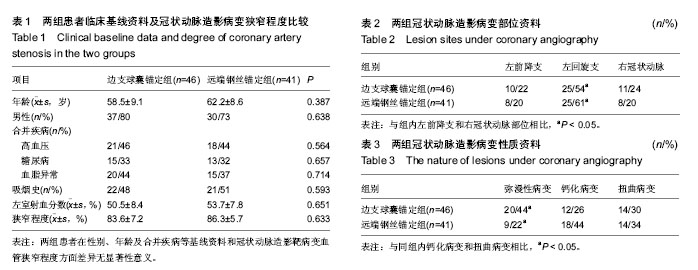
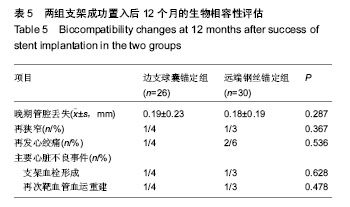
主要观察指标:统计所有患者的临床资料,支架置入前冠状动脉造影结果;支架置入时使用指引导管、指引钢丝、球囊、支架的具体情况;支架置入后12个月时的生物相容性问题,包括主要不良心脏事件、再发心绞痛、再狭窄和晚期管腔丢失结果。主要不良心脏事件定义为心血管死亡、明确的或很有可能的支架血栓形成、非致死性心肌梗死或靶血管血运重建。再狭窄包括支架内再狭窄和节段内再狭窄。
统计学分析:以SPSS 17.0统计学软件进行统计学分析,计量资料表示为x±s,计量资料的组间比较采用t 检验;定性资料的组间比较采用χ2检验,以P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。