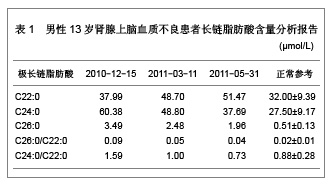
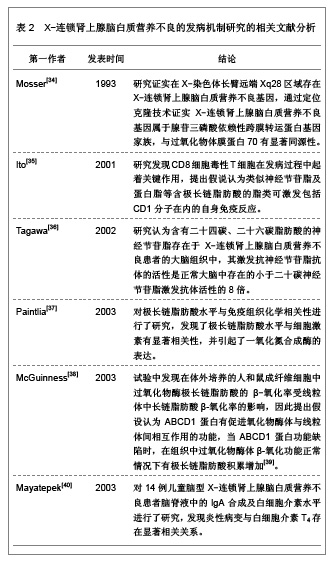
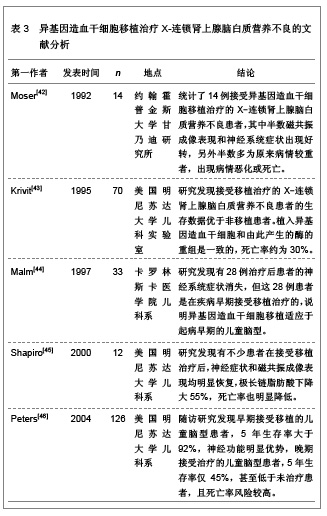
| [1] 韩新,李斌,旷艳红,等.X-连锁型肾上腺脑白质营养不良1例家系报告[J].中国医学创新,2009,6(28):129-130.[2] Mahmood A,Raymond GV,Dubey P,et al.Survival analysis of haematopoietic cell transplantation for childhood cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: a comparison study.Lancet Neurol.2007;6(8):687-692.[3] Bezman L,Moser AB,Raymond GV,et al. Adrenoleukodystrophy: incidence, new mutation rate, and results of extended family screening.Ann Neurol. 2001;49(4): 512-517.[4] 陈珺,张健,王得新.检测阿狄森氏病患者血浆极长链脂肪酸的重要意义[J].中华内科杂志,2007,46(9):733-735.[5] Linnebank M,Kemp S,Wanders RJ,et al.Methionine metabolism and phenotypic variability in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Neurology.2006;66(3):442-443.[6] 王志红.X-连锁肾上腺-脑白质营养不良发病机制的研究[D].福建:福建医科大学,2011:1-113.[7] 谢海花,柯龙凤,王志红,等.一个有三例女性X-连锁肾上腺-脑白质营养不良杂合子患者家系基因突变分析[J].中华医学遗传学杂志,2010,27(2):144-148.[8] Linnebank M,Semmler A,Kleijer WJ,et al.The cystathionine beta-synthase variant c.844_845ins68 protects against CNS demyelination in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Hum Mutat. 2006;27(10):1063-1064.[9] Moser HW,Raymond GV,Dubey P.Adrenoleukodystrophy: new approaches to a neurodegenerative disease.JAMA.2005; 294(24):3131-3134.[10] Moser HW, Mahmood A, Raymond GV.X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Nat Clin Pract Neurol.2007;3(3): 140-151.[11] Kishi T,Tanaka Y,Ueda K.Evidence for hypomethylation in two children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and leukoencephalopathy.Cancer.2000;89(4):925-931.[12] Afman LA,Van Der Put NM,Thomas CM,et al.Reduced vitamin B12 binding by transcobalamin II increases the risk of neural tube defects.QJM.2001;94(3):159-166.[13] von Castel-Dunwoody KM,Kauwell GP,Shelnutt KP, et al. Transcobalamin 776C->G polymorphism negatively affects vitamin B-12 metabolism.Am J Clin Nutr.2005;81(6): 1436-1441.[14] Bi XH,Zhao HL,Zhang ZX,et al.Association analysis of CbetaS 844ins68 and MTHFD1 G1958A polymorphisms with Alzheimer's disease in Chinese.J Neural Transm.2010; 117(4): 499-503.[15] Semmler A,Bao X,Cao G,et al.Genetic variants of methionine metabolism and X-ALD phenotype generation: results of a new study sample.J Neurol.2009;256(8):1277-1280.[16] Janosíková B,Pavlíková M,Kocmanová D,et al.Genetic variants of homocysteine metabolizing enzymes and the risk of coronary artery disease.Mol Genet Metab.2003;79(3): 167-175.[17] Chu ML,Sala DA,Weiner HL.Intrathecal baclofen in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Pediatr Neurol.2001;24(2):156-158.[18] 柯龙凤.X-连锁肾上腺脑白质营养不良的分子生物学研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2011:1-31.[19] Shapiro E,Krivit W,Lockman L,et al.Long-term effect of bone-marrow transplantation for childhood-onset cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Lancet.2000; 356(9231): 713-718.[20] 平莉莉,包新华,王爱花,等.X连锁肾上腺脑白质营养不良89例临床特征及基因型/表型关系[J].中华儿科杂志,2007,45(3): 203-207.[21] 胡兰.X-连锁肾上腺脑白质营养不良发病机理及药物治疗的研究[D].北京:中国协和医科大学,2002:1-96.[22] 陆松,程楠,胡纪源,等.肾上腺脑白质营养不良脊髓-周围神经病型1例[J].安徽医学,2003,24(1):67-68.[23] Takemoto Y,Suzuki Y,Tamakoshi A,et al.Epidemiology of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy in Japan.J Hum Genet. 2002;47(11):590-593.[24] 施晓容.肾上腺脑白质营养不良临床及分子生物学研究[D].福建:福建医科大学,2002:1-40.[25] 许家和,桑磊,牟善兰.肾上腺脑白质营养不良2例[J].安徽医学, 2000,8(1):46-47.[26] 王学禹,王海虹,孟庆辉.X连锁肾上腺脑白质营养不良1例[J].实用儿科临床杂志,1999,14(2):123.[27] 贾蓓.X-连锁智力障碍基因诊断体系的建立及应用[D].湖南:中南大学,2006:1-60.[28] 潘虹,熊晖,张月华,等.X-连锁的肾上腺脑白质营养不良患者ABCD1基因突变分析[J].中华医学遗传学杂志,2004,21(1):1-4.[29] 宋建波,刘起旺.肾上腺脑白质营养不良研究进展[J].国外医学(临床放射学分册),2005,28(6):377-380.[30] 应艳琴,罗小平,魏虹.X-连锁肾上腺脑白质营养不良ABCD1基因突变分析[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2007,22(8):569-572.[31] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2012-08-10. https://www.cnki.net[32] SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2012-08-10.http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl[33] Engelen M,Ofman R,Dijkgraaf MG,et al.Lovastatin in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.N Engl J Med.2010;362(3):276-277.[34] Mosser J,Douar AM,Sarde CO,et al.Putative X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene shares unexpected homology with ABC transporters.Nature.1993;361(6414):726-730.[35] Ito M,Blumberg BM,Mock DJ,et al.Potential environmental and host participants in the early white matter lesion of adreno-leukodystrophy: morphologic evidence for CD8 cytotoxic T cells, cytolysis of oligodendrocytes, and CD1-mediated lipid antigen presentation.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.2001;60(10):1004-1019.[36] Tagawa Y,Laroy W,Nimrichter L,et al.Anti-ganglioside antibodies bind with enhanced affinity to gangliosides containing very long chain fatty acids.Neurochem Res.2002; 27(7-8):847-855.[37] Paintlia AS,Gilg AG,Khan M,et al.Correlation of very long chain fatty acid accumulation and inflammatory disease progression in childhood X-ALD: implications for potential therapies.Neurobiol Dis.2003;14(3):425-439.[38] McGuinness MC,Lu JF,Zhang HP,et al.Role of ALDP (ABCD1) and mitochondria in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Mol Cell Biol.2003;23(2):744-753.[39] 谢海花.X-连锁肾上腺-脑白质营养不良患者ALD基因突变分析及ALDP突变体的原核表达[D].福建:福建医科大学,2009:1-96.[40] Mayatepek E,Baumann M,Meissner T,et al.Role of leukotrienes as indicators of the inflammatory demyelinating reaction in x-linked cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy.J Neurol. 2003;250(10):1259-1260.[41] 王旭,邹丽萍,方方,等.肾上腺脑白质营养不良临床及实验室随访研究[J].实用诊断与治疗杂志,2007,21(9):641-643.[42] Moser HW,Moser AB,Smith KD,et al.Adrenoleukodystrophy: phenotypic variability and implications for therapy.J Inherit Metab Dis.1992;15(4):645-664.[43] Krivit W,Lockman LA,Watkins PA,et al.The future for treatment by bone marrow transplantation for adrenoleukodystrophy, metachromatic leukodystrophy, globoid cell leukodystrophy and Hurler syndrome.J Inherit Metab Dis.1995;18(4):398-412.[44] Malm G,Ringdén O,Anvret M,et al.Treatment of adrenoleukodystrophy with bone marrow transplantation.Acta Paediatr.1997;86(5):484-492.[45] Shapiro E,Krivit W,Lockman L,et al.Long-term effect of bone-marrow transplantation for childhood-onset cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Lancet. 2000; 356(9231): 713-718.[46] Peters C,Charnas LR,Tan Y,et al.Cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: the international hematopoietic cell transplantation experience from 1982 to 1999.Blood.2004; 104(3):881-888.[47] 张灵艳,陈燕萍.肾上腺脑白质营养不良的临床及影像研究进展[J].医学影像学杂志,2007,17(9):995-997.[48] 黄烨,艾冬云,徐丽,等.肾上腺脑白质营养不良患者行异体外周血造血干细胞移植的护理[J].护理研究,2012,26(23):2163-2164.[49] 陈静,段李东,田昆仑.肾上腺脑白质营养不良的磁共振成像诊断[J].中国美容医学,2011,20(Z1):287.[50] 卓勤俭,孟彩云,王瑞明.肾上腺脑白质营养不良/肾上腺脊髓神经病1例[J].中国实用医刊,2010,37(11):81-82.[51] Moser HW.Therapy of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. NeuroRx. 2006;3(2):246-253.[52] Pujol A,Ferrer I,Camps C,et al.Functional overlap between ABCD1 (ALD) and ABCD2 (ALDR) transporters: a therapeutic target for X-adrenoleukodystrophy.Hum Mol Genet.2004; 13(23): 2997-3006.[53] Eichler FS,Ren JQ,Cossoy M,et al.Is microglial apoptosis an early pathogenic change in cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy?Ann Neurol.2008;63(6):729-742.[54] Kim JY,Shen S,Dietz K,et al.HDAC1 nuclear export induced by pathological conditions is essential for the onset of axonal damage.Nat Neurosci.2010;13(2):180-189.[55] Kazantsev AG,Thompson LM.Therapeutic application of histone deacetylase inhibitors for central nervous system disorders.Nat Rev Drug Discov.2008;7(10):854-868.[56] Fourcade S,López-Erauskin J,Galino J,et al.Early oxidative damage underlying neurodegeneration in X-adrenoleukodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet.2008; 17(12): 1762-1773.[57] Peters C,Charnas LR,Tan Y,et al.Cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy:The international hematopoietic cell transplantation experience from 1982 to 1999.Blood. 2004; 104(3):881–888.[58] Loes DJ,Hite S,Moser H,et al.Adrenoleukodystrophy: a scoring method for brain MR observations.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.1994;15(9):1761-1766.[59] Mahmood A,Dubey P,Moser HW,et al.X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: therapeutic approaches to distinct phenotypes.Pediatr Transplant.2005;9Suppl7:55-62. [60] Bacigalupo A.Management of acute graft versus host disease.Br J Haematol.2007;137(2):87-98[61] Blanc KL,Frassoni F,Ball L,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant,severe,acute graft-versus-host disease:a phase Ⅱ study.Lancet.2008;371(9624): 1579-1586.[62] Messina C,Faraci M,Fazio V de,et al. Prevevtion and treatment of acute GVHD.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008; 41Suppl2:S65-S70. |