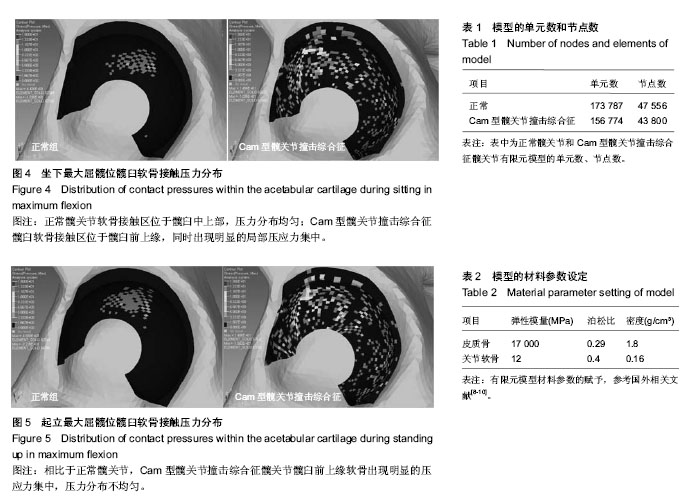
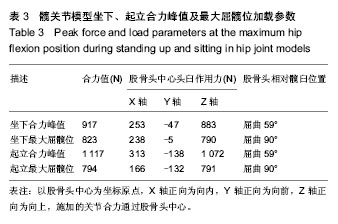
| [1] Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, et al. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(417):112-120.
[2] Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, et al. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(7): 1012-1018.
[3] Harris-Hayes M, Royer NK. Relationship of acetabular dysplasia and femoroacetabular impingement to hip osteoarthritis: a focused review. PMR. 2011;3(11):1055-1067.
[4] Notzli HP, Wyss TF, Stoecklin CH, et al. The contour of the femoral head-neck junction as a predictor for the risk of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(4): 556-560.
[5] Pustoc HA, Cheze L. Normal and osteoarthritic hip joint mechanical behaviour: a comparison study. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2009;47(4):375-383.
[6] Anderson AE, Ellis BJ, Maas SA, et al. Effects of idealized joint geometry on finite element predictions of cartilage contact stresses in the hip. J Biomech. 2010;43(7): 1351-1357.
[7] Anderson AE, Ellis BJ, Maas SA, et al. Validation of finite element predictions of cartilage contact pressure in the human hip joint. J Biomech Eng. 2008;130(5):51008.
[8] Dalstra M, Huiskes R, van Erning L. Development and validation of a three-dimensional finite element model of the pelvic bone. J Biomech Eng. 1995;117(3):272-278.
[9] Jorge JP, Simoes FM, Pires EB, et al. Finite element simulations of a hip joint with femoroacetabular impingement. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2012.
[10] Shepherd DE, Seedhom BB. A technique for measuring the compressive modulus of articular cartilage under physiological loading rates with preliminary results. Proc Inst Mech Eng H.1997;211(2):155-165.
[11] Caligaris M, Ateshian GA. Effects of sustained interstitial fluid pressurization under migrating contact area, and boundary lubrication by synovial fluid, on cartilage friction. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16(10):1220-1227.
[12] Bergmann G, Deuretzbacher G, Heller M, et al. Hip contact forces and gait patterns from routine activities. J Biomech. 2001;34(7):859-871.
[13] Adams D, Swanson SA. Direct measurement of local pressures in the cadaveric human hip joint during simulated level walking. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985;44(10):658-666.
[14] Brown TD, Shaw DT. In vitro contact stress distributions in the natural human hip. J Biomech. 1983;16(6):373-384.
[15] Rushfeldt PD, Mann RW, Harris WH. Improved techniques for measuring in vitro the geometry and pressure distribution in the human acetabulum. II Instrumented endoprosthesis measurement of articular surface pressure distribution. J Biomech. 1981;14(5):315-323.
[16] Carlson CE, Mann RW, Harris WH. A radio telemetry device for monitoring cartilage surface pressures in the human hip. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1974;21(4):257-264.
[17] Hodge WA, Fijan RS, Carlson KL, et al. Contact pressures in the human hip joint measured in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83(9):2879-2883.
[18] Afoke NY, Byers PD, Hutton WC. Contact pressures in the human hip joint. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987;69(4):536-541.
[19] Sparks DR, Beason DP, Etheridge BS, et al. Contact pressures in the flexed hip joint during lateral trochanteric loading. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(2):359-366.
[20] von Eisenhart R, Adam C, Steinlechner M, et al. Quantitative determination of joint incongruity and pressure distribution during simulated gait and cartilage thickness in the human hip joint. J Orthop Res. 1999;17(4):532-539.
[21] Wagner S, Hofstetter W, Chiquet M, et al. Early osteoarthritic changes of human femoral head cartilage subsequent to femoro-acetabular impingement. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2003;11(7):508-518.
[22] Bittersohl B, Hosalkar HS, Kim YJ, et al. Delayed gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (dGEMRIC) of hip joint cartilage in femoroacetabular impingement (FAI): Are pre- and postcontrast imaging both necessary? Magn Reson Med. 2009;62(6):1362-1367.
[23] Bittersohl B, Steppacher S, Haamberg T, et al. Cartilage damage in femoroacetabular impingement (FAI): preliminary results on comparison of standard diagnostic vs delayed gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of cartilage (dGEMRIC). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(10): 1297-1306.
[24] Jessel RH, Zilkens C, Tiderius C, et al. Assessment of osteoarthritis in hips with femoroacetabular impingement using delayed gadolinium enhanced MRI of cartilage. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30(5):1110-1115.
[25] Sah RL, Kim YJ, Doong JY, et al. Biosynthetic response of cartilage explants to dynamic compression. J Orthop Res. 1989;7(5):619-636.
[26] Harris MD, Reese SP, Peters CL, et al. Three-dimensional quantification of femoral head shape in controls and patients with cam-type femoroacetabular impingement. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(6):1162-1171.
[27] Chegini S, Beck M, Ferguson SJ. The effects of impingement and dysplasia on stress distributions in the hip joint during sitting and walking: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(2):195-201.
[28] Buschmann MD, Kim YJ, Wong M, et al. Stimulation of aggrecan synthesis in cartilage explants by cyclic loading is localized to regions of high interstitial fluid flow. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999;366(1):1-7.
[29] Kim YJ, Sah RL, Grodzinsky AJ, et al. Mechanical regulation of cartilage biosynthetic behavior: physical stimuli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;311(1):1-12.
[30] Parkkinen JJ, Lammi MJ, Helminen HJ, et al. Local stimulation of proteoglycan synthesis in articular cartilage explants by dynamic compression in vitro. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(5):610-620.
[31] Kurz B, Jin M, Patwari P, et al. Biosynthetic response and mechanical properties of articular cartilage after injurious compression. J Orthop Res. 2001;19(6):1140-1146.
[32] Piscoya JL, Fermor B, Kraus VB, et al. The influence of mechanical compression on the induction of osteoarthritis- related biomarkers in articular cartilage explants. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(12):1092-1099.
[33] Torzilli PA, Grigiene R, Huang C, et al. Characterization of cartilage metabolic response to static and dynamic stress using a mechanical explant test system. J Biomech. 1997; 30(1):1-9.
[34] O'Hara BP, Urban JP, Maroudas A. Influence of cyclic loading on the nutrition of articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990; 49(7):536-539.
[35] Beaule PE, Zaragoza E, Motamedi K, et al. Three-dimensional computed tomography of the hip in the assessment of femoroacetabular impingement. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(6):1286-1292.
[36] Konrath GA, Hamel AJ, Olson SA, et al. The role of the acetabular labrum and the transverse acetabular ligament in load transmission in the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80(12):1781-1788.
[37] Ateshian GA, Ellis BJ, Weiss JA. Equivalence between short-time biphasic and incompressible elastic material responses. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(3):405-412. |