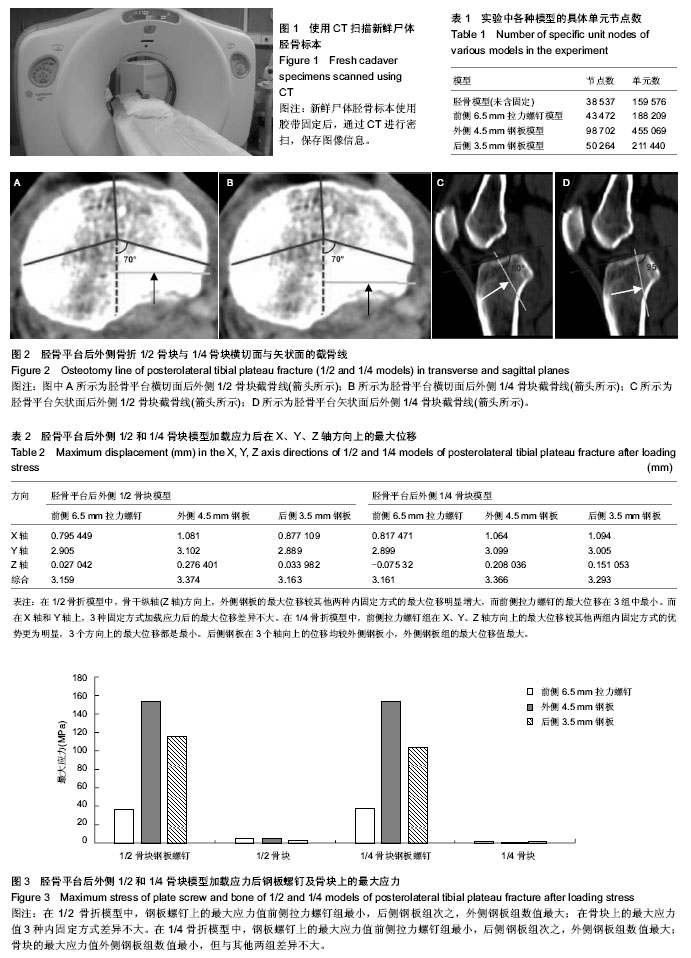
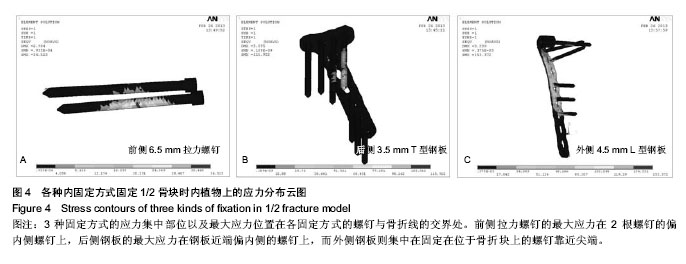
| [1] Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D. The tibial plateau fracture:the Toronto experience 1968-1975. Clin Orthop. 1979;138:94-104.
[2] Papagelopoulos PJ, Partsinevelos AA, Themistocleous GS, et al. Complications after tibia plateau fracture surgery.Injury. 2006;37(6):475-484.
[3] Stauffer KD, Tuttle TA, Elkins AD, et al. Complications associated with 696 tibial plateau leveling osteotomies (2001-2003). J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2006;42(1):44-50.
[4] Cross WW 3rd, Levy BA, Morgan JA, et al. Periarticular raft constructs and fracture stability in split-depression tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2013;44(6):796-801.
[5] Heikkilä JT, Kukkonen J, Aho AJ, et al. Bioactive glass granules: a suitable bone substitute material in the operative treatment of depressed lateral tibialplateau fractures: a prospective, randomized 1 year follow-up study. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(4):1073-1080.
[6] Hsieh CH, Huang HT, Liu PC,et al.Anterior approach for posteromedial tibial plateau fractures. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2010;26(3):130-135.
[7] Helfet DL, Haas NP, Schatzker J,et al.AO philosophy and principles of fracture management-its evolution and evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(6):1156-1160.
[8] Khan RM,Khan SH,Ahmad AJ,et al.Tibial plateau fractures.A new classification scheme. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;375: 231-242.
[9] Gicquel T, Najihi N, Vendeuvre T,et al. Tibial plateau fractures: reproducibility of three classifications (Schatzker, AO, Duparc) and a revised Duparc classification. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(7):805-816.
[10] Luo CF, Sun H, Zhang B. Three-column fixation for complex tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(11):683-692.
[11] Carlson DA. Posterior bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19:73-78.
[12] Ren WF,Zhang NN,Zhu YY,et al. Medial plus anterolateral approaches for the treatment of tibial plateau fractures involving three columns. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(9): 768-771.
[13] Berber R,Lewis CP, Copas D,et al.Postero-medial approach for complex tibial plateau injuries with a postero-medial or postero-lateral shear fragment.Injury. 2013. pii: S0020-1383 (13)00563-9.
[14] Chiu CH, Cheng CY, Tsai MC, et al. Arthroscopy-assisted reduction of posteromedial tibial plateau fractures with buttress plate and cannulated screw construct.Arthroscopy. 2013;29(8):1346-1354.
[15] Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett HC, et al. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage. 2006; 31(3):1116-1128.
[16] Sonoda N, Chosa E, Totoribe K,et al. Biomechanical analysis for stress fractures of the anterior middle third of the tibia in athletes:nonlinear analysis using a three-dimensional finite element method. J Orthop Sci. 2003;8:505-513.
[17] Lacroix D, Prendergast PJ. Three-dimensional Simulation of Fracture Repair in the Human Tibia. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2002;5(5):369-376.
[18] 罗从风,胡承方,高洪,等. 基于CT的胫骨平台骨折的三柱分型[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2009,11(3):201-206.
[19] Patange Subba Rao SP, Lewis J, Haddad Z,et al. Three-column classification and Schatzker classification: a three- and two-dimensional computed tomography characterisation and analysis of tibial plateau fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013. [Epub ahead of print]
[20] Wismans J, Veldpaus F, Janssen J, et al. A three-dimensional mathematical model of the knee-joint. J Biomech. 1980;13(8): 677-685.
[21] Howard NE, Phaff M, Aird J,et al. Does human immunodeficiency virus status affect early wound healing in open surgically stabilised tibial fractures?: A prospective study. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(12):1703-1737.
[22] Uchiyama S, Itsubo T, Nakamura K,et al. Effect of early administration of alendronate after surgery for distal radial fragility fracture on radiological fracture healing time.Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11):1544-1550.
[23] Matsunaga FT, Tamaoki MJ, Matsumoto MH, et al. Treatment of the humeral shaft fractures--minimally invasive osteosynthesis with bridge plate versus conservative treatment with functional brace: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2013;14:246.
[24] Urita A, Iwasaki N, Kondo M, et al. Effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on bone healing at osteotomy sites after forearm bone shortening. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38(3): 498-503.
[25] Epari DR, Kassi JP, Schell H, et al. Timely fracture-healing requires optimization of axial fixation stability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(7):1575-1585.
[26] Lin CL, Chang YH, Pai CA. Evaluation of failure risks in ceramic restorations for endodontically treated premolar with MOD preparation. Dent Mater. 2011;27(5):431-438.
[27] Chevalier Y, Quek E, Borah B,et al. Biomechanical effects of teriparatide in women with osteoporosis treated previously with alendronate and risedronate: results from quantitative computed tomography-based finite element analysis of the vertebral body. Bone. 2010;46(1):41-48.
[28] Burstein A,Reilly D.Aging of bone tissue:mechanica properties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58:82-86.
[29] 孙荣鑫,张玉新,白靖平,等.Sanders II型跟骨骨折内固定治疗的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,8(20):1409-1412.
[30] Gilula L, Persenaire M.Subsequent fractures post-vertebral augmentation: analysis of a prospective randomized trial in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(1):221-227.
[31] Henderson CE, Lujan TJ, Kuhl LL, et al. 2010 Mid-America Orthopaedic Association Physician in Training Award: Healing Complications Are Common After Locked Plating for Distal Femur Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(6):1757- 1765.
[32] Herrera A, Ibarz E, Cegoñino J, et al. Applications of finite element simulation in orthopedic and trauma surgery. World J Orthop. 2012; 3(4): 25-41.
[33] Liu XS, Wang J, Zhou B,et al. Fast trabecular bone strength predictions of HR-pQCT and individual trabeculae segmentation-based plate and rod finite element model discriminate postmenopausal vertebral fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(7):1666-1678.
[34] Varga P, Schefzig P, Unger E, et al. Finite element based estimation of contact areas and pressures of the human scaphoid in various functional positions of the hand. J Biomech. 2013;46(5):984-990.
[35] Nishiyama KK, Macdonald HM, Hanley DA, et al. Women with previous fragility fractures can be classified based on bone microarchitecture and finite element analysis measured with HR-pQCT. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(5):1733-1740.
[36] Meng L, Zhang Y, Lu Y. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of mini-external fixation and Kirschner wire internal fixation in Bennettfracture treatment. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(1):21-29.
[37] Kantardzi? I, Vasiljevi? D, Blazi? L,et al. Influence of cavity design preparation on stress values in maxillary premolar: a finite element analysis. Croat Med J. 2012;53(6):568-576.
[38] Jia YW, Cheng LM, Yu GR, et al. A finite element analysis of the pelvic reconstruction using fibular transplantation fixed with four different rod-screw systems after type I resection. Chin Med J. 2008;121(4):321-326.
[39] Graeff C, Marin F, Petto H,et al.High resolution quantitative computed tomography-based assessment of trabecular microstructure and strength estimates by finite-element analysis of the spine, but not DXA, reflects vertebral fracture status in men with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Bone. 2013;52(2):568-577.
[40] Wang X, Sanyal A, Cawthon PM,et al. Prediction of new clinical vertebral fractures in elderly men using finite element analysis of CT scans. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(4):808-816. |