| [1] De la Torre JC. Vascular basis of Alzheimer's pathogenesis. Ann N Y Ac AD Sci. 2002; 977:196-215. [2] 吴峰,黄河浪. 阿尔茨海默病的危险因素研究进展[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志,2011,15(4):336-339.[3] Kramer MS,Cutler N,Feighner J,et al. Distinct mecha-nism for antidepressant activity by blockade of central sub-stance Preceptors. Science. 1998;281:1640-1645. [4] Arinami T,Li L,Mitsushio H,et al. An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin converting enzyme gene is associated with both brain substance P contents and affec-tive disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 1996;40: 1122-1127.[5] Ohrui T, Tomita N, Sato-Nakagawa T, et al. Effects of brain-penetrating ACE inhibitors on Alzheimer disease pro-gression. Neurology. 2004;63(7): 1324-1330. [6] Sayed-Tabatabaei FA, Oostra BA, Isaacs A, et al. ACEpolymorphisms. Circ Res. 2006; 98(9): 1123-1133. [7] Fleming I. Signaling by the angiotensin-converting enzyme. Cir Res. 2006;98(7): 887-896. [8] Hemming ML,Selkoe DJ.Amyloidβ-protein is degraded by cellu-lar angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and elevated by an ACE inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(45): 37644- 37650. [9] Ohrui T, Tomita N, Sato-Nakagawa T, et al. Effects of brain-penetrating ACE inhibitors on Alzheimer disease pro-gression. Neurology. 2004;63(7): 1324-1330. [10] Todd B, McGuinness AP. Prevention of dementia by ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers -potential but notproven S. Passmore Article first published online: 14 OCT 2010. [11] Wolozin B, Lee A, Whitmer R, et al. Use of angiotensin re-ceptor blockers is associated with a lower incidence and pro-gression of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2008;4(4): T118. [12] Li L, Zhang ZF, Holscher C. (Val8) glucagon-like peptide-1 prevents tau hyperphosphorylation,impairment of spatial learning and altra-structural cellular damage induced by streptozotocin in rat brains. Europ J Pharmacol. 2012;674 (2-3): 280-286. [13] 张金生,徐娜,王俊英,等.血清中血管紧张素转化酶测定的临床应用[J].国外医学:临床生物化学与检验学分册, 2005, 26(10): 730-732. [14] 贾建平.神经病学[M]. 6版. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2008: 214-219. [15] 贾建平,刘峥. PSEN2基因启动子多态性与阿尔茨海默病易患性的关联研究[J].中华神经科杂志,2007,40(1): 18-22. [16] Jack CR Jr, Barkhof F, Bemstein MA, et al. Steps to standardization and validation of hoppocampal volumetry as a biomarker in clinical trials and diagnostic criterion for Alzheimer`s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011; 7(4): 474-485. [17] 于荣焕,王荫华. 画钟试验和 MMSE 对阿尔茨海默病筛查的临床意义[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2004,10(3):139-140. [18] Eckman EA, Adams SK, Troendle FJ. Regulation of steadystate beta-amyloid levels in the brain by neprilysin and endohelin converting enzyme, but not angiotensin-converting en-zyme. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(41): 30471-30478. [19] 吴峰,黄河浪. 阿尔茨海默病的危险因素研究进展[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2011,15(4) :336-339.[20] Hort J, O’Brien JT, Gainotti G, et al. EFNS guidelines for the diagnosis and management of Alzheimer disease. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(10):1236-1248. [21] Fiona C, Laila A, John S, et al. Gender-specific association of the angiotensin converting enzyme gene with Alzheimer' s disease. Neurosci Lett. 2000;280:215-219. [22] Hu J,Igarashi A,Kamata M,et al.Angiotensin-converting enzym degres Alzheimer amyloid beta -peptide ( Abeta) ; retards A beta aggregation, deposition, fibril Formation; and inhibits cytotoxicity. Bilo Chem. 2001;276 (51): 47863-47868.[23] Amar K, MacGowan S, Wilcock G, et al. Are genetic factors impor-tant in the aetiology of leukoaraiosis? Results from a memory clinic population. Int J Geriatr Psyehiatry. 1998;13(9): 585-590. [24] Narain Y, Yip A, Murphy T, et al. The ACE gene and alzheimer's disease susceptibility. J Med Genet. 2000;37(9): 695-697.[25] Buss S,Muller-Thomsen T, Hoek C,et al.No association between DCP1 genotyPe and late-onset Alzheimer disease. Am J Med Genet. 2002;114(4):440-445. [26] Carbonell J, Allen R, Kalsi Q, et al. Variation in the DCPIgene,eneoding the angiotensin converting enzyme ACE,is not associated with inereased suseePtibility to Alzheimer, 5disease. Psyehiatr Genet. 2003;13(1):47-50. [27] 侯建萍,黄明方,罗助荣,等.高血压左心室肥厚患者ACE和Chymase基因多态性与心房颤动的相关性研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2009,34(2):143-146. [28] Kolscha H,Jessena F,Freymanna N,et al. ACE I/D polymor-phism is a risk factor of Alzheimer’s disease but not of vascular de-mentia. Neurosci Lett. 2005;377(1): 37-39.[29] 吴传深,周东丰,管振金,等.血管紧张素转换酶基因多态性与中国汉族迟发性阿尔茨海默病的关系[J].中华医学遗传学杂志, 2002, 19(5): 401-404. [30] Kehoe PG,Miners S,Love S.Angiotensins in Alzheimer's disease-friend or foe. Trends Ncurosci. 2009;32(12):619-628. [31] Spence JD. Preventing dementia by treating hypertension and preventing stroke. Hypertension. 2004;44(1): 20-21. [32] Gesang L, Liu G, Gen W, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism and its association with essential hypertension in Tibetan population. Hyerten Res. 2002;25 (3): 481. [33] Bawazier LA,Sja'bani M,Haryana SM,et al. Relationship of angioten-sin converting enzyme gene polymorphism and hypertension in yogyakar-taindonesia. Acta Med Indones. 2010; 42(4):192-198. [34] Higaki J, Baba S, Katsuya T, et al. Deletion allele ofangiotensin2 converting enzyme gene increases risk of essential hypertension in Japanese men: the Suita Study. Circulation. 2000;101:2060-2065. [35] 董会奕,李秋荣,王勤,等. 血管紧张素转换酶基因和 eNOS 基因多态性与原发性高血压的相关性研究[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2006,8(8):1059-1061. [36] Agerholm-Larsen B,Nordestgaard BG,Tybjaerg-Hansen A,et al.ACE gene polymorphism in cardiovascular in Whites. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;20(13): 484-492.[37] 杜明艳,丁文军. 血管紧张素转化酶基因 I/D 多态性与脑梗死后抑郁相关[J].基础医学与临床,2012;32(9):1040-1043. [38] 廖媛,官志忠. 阿尔茨海默病发病机制中炎性反应的研究进展[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2011,31(2) :351-354.[39] Rozzln L, Chilovl BV, Bertoletti E,et al.Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition modulate the rate of amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Int J Geriatr Psyehlatry. 2006;21(6): 550-555. [40] Catto A, Carter AM, Barret JH, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion Polymorphism and cerebrovascular disease. Stroke. 1996;27(3): 435-440. |


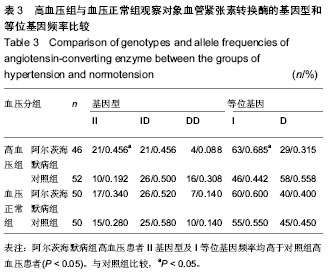
.jpg)