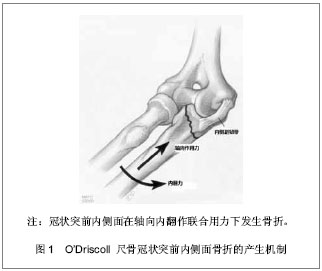
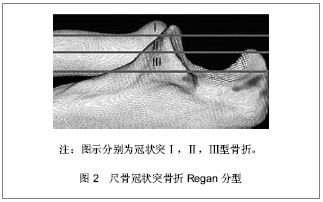
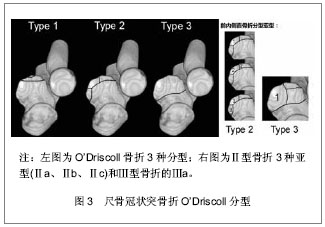
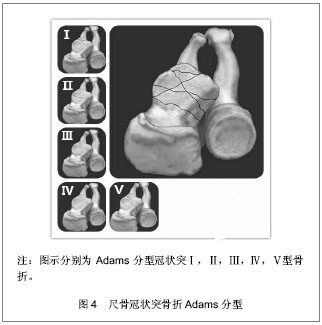
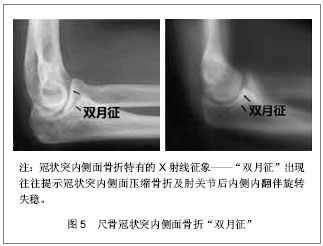
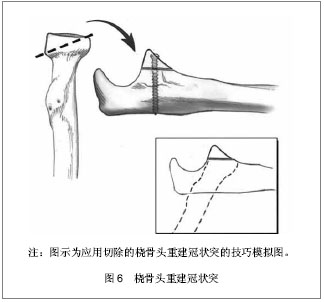
| [1] Weber MF, Barbosa DM, Belentani C, et al. Coronoid process of the ulna: paleopathologic and anatomic study with imaging correlation. Emphasis on the anteromedial “facet”. Skeletal Radiol.2009;38:61-67.
[2] Jason R. Hull, MD, John R, et al.Role of the coronoid process in varus osteoarticular stability of the elbow. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14:441-446.
[3] Lee SK, Kim HY, Kim KJ, et al.Coronoid plate fixation of type II and III coronoid process fractures: outcome and prognostic factors.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2012;22: 213-219.
[4] Wells J, Ablove RH. Coronoid fractures of the elbow. Clin Med Res. 2008; 6(1):40-44.
[5] Doornberg JN, de Jong IM, Lindenhovius AL, et al. The anteromedial facet of the coronoid process of the ulna.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16:667-670.
[6] O’Driscoll SW, Jupiter JB, Cohen MS et al. Difficult elbow fractures: pearls and pitfalls. Instr Course Lect. 2003; 52: 113-134.
[7] Regan W, Morrey B. Fractures of the coronoid process of the ulna. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1989;71:1348-1354.
[8] Adams JE, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Kallina CF 4th, et al. Fractures of the coronoid: morphology based upon computer tomography scanning. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2012;21: 782-788.
[9] Sanchez-Sotelo J, O'Driscoll SW, Morrey BF. Medial oblique compression fracture of the coronoid process of the ulna.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14: 60-64.
[10] Beingessner DM, Stacpoole RA, Dunning CE, et al. The effect of suture fixation of type I coronoid fractures on the kinematics and stability of the elbow with and without medial collateral ligament repair. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16: 213-217.
[11] Samii A, Zellweger R. Fractures of the Coronoid Process of the Ulna:Which Ones to Fix and Which Ones to Leave Alone: A Review. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg.2008;34:113-119.
[12] Beingessner DM, Dunning CE, Stacpoole RA ,et al. The effect of coronoid fractures on elbow kinematics and stability. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2007;22:183-190.
[13] Jeon IH, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Zhao K, et al. The contribution of the coronoid and radial head to the stability of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94-B:86-92.
[14] Closkey RF, Goode JR, Kirschenbaum D, et al. The role of the coronoid process in elbow stability: a biomechanical analysis of axial loading. J Bone Joint Surg.2000;82A: 1749-1753.
[15] Doornberg JN, Ring D. Coronoid fracture patterns. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31:45-52.
[16] O’Driscoll SW, Jupiter JB, King GJW, et al. The unstable elbow. J Bone Jt Surg Am.2000; 82:724-738.
[17] Chamseddine AH, Zein HK, Hamdan HR, et al. Unstable elbow dislocation with coronoid process fracture associated with distal radius fracture: a case report and review of the literature. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2010; 20:157-163.
[18] Manidakis N, Sperelakis I, Hackney R, et al. Fractures of the ulnar coronoid process. Injury Int J Care Injured. 2012;43: 989-998.
[19] Van Tongel A, Macdonald P, Van Riet R. Elbow arthroscopy in acute injuries. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012; 20(12):2542-2548.
[20] Garrigues GE, Wray WH 3rd, Lindenhovius AL, et al. Fixation of the coronoid process in elbow fracture-dislocations.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(20):1873-1881.
[21] Wang X, Chang SM, Yu GR. Anteromedial coronoid facet fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2013;23(3):251-255.
[22] Budoff JE. Coronoid fractures. J Hand Surg Am.2012; 37(11):2418-2423.
[23] Hausman MR, Klug RA, Qureshi S, et al.Arthroscopically Assisted Coronoid Fracture Fixation A Preliminary Report.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466:3147-3152.
[24] Doornberg JN, Ring DC. Fracture of the anteromedial facet of the coronoid process. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88A(10): 2216-2224.
[25] Reichel LM, Milam GS, Reitman CA. Anterior approach for operative fixation of coronoid fractures in complex elbow instability.Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg.2012;16(2):98-104.
[26] Han SH, Yoon HK, Rhee SY. Anterior approach for fixation of isolated type III coronoid process fracture. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2013 ;23(4):395-405.
[27] Pollock JW, Brownhill J, Ferreira L, et al. The effect of anteromedial facet fractures of the coronoid and lateral collateral ligament injury on elbow stability and kinematics. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009;91(6):1448-1458.
[28] Ring D, Doornberg JN. Fracture of the anteromedial facet of the coronoid process surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(Suppl 2 Pt. 2:):267-283.
[29] Ring D. Fractures of the coronoid process of the ulna. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31(10):1679-1689.
[30] Kloen P, Buijze GA. Treatment of proximal ulna and olecranon fractures by dorsal plating. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2009; 21(6):571-585.
[31] Moon JG, Zobitz ME, An KN, et al. Optimal screw orientation for fixation of coronoid fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23(4):277-280.
[32] McKee MD, Pugh DM, Wild LM, et al. Standard surgical protocol to treat elbow dislocations with radial head and coronoid fractures. Surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;Suppl 1(Pt 1):22-32.
[33] van Riet RP, Morrey BF, O’Driscoll SW. Use of osteochondral bone graft in coronoid fractures. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2005; 14(5):519-523.
[34] Kohls-Gatzoulis J, Tsiridis E, Schizas C. Reconstruction of the coronoid process with iliac crest bone graft. J Shoulder Elbow Surg .2004; 13:217-220.
[35] Chung CH, Wang SJ, Chang YC, et al. Reconstruction of the coronoid process with iliac crest bone graft in complex fracture-dislocation of elbow. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007; 127:33-37.
[36] Wu H, Liao Q, Zhu Y. Surgical reconstruction of comminuted coronoid fracture in terrible triad injury of the elbow. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2012; 22:667-671.
[37] van Riet RP, Morrey BF, O'Driscoll SW. Use of osteochondral bone graft in coronoid fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14:519-523.
[38] Alolabi B, Gray A, Ferreira LM, et al. Reconstruction of the coronoid using an extended prosthesis: an in vitro biomechanical study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2012; 21: 969-976.
[39] Fern SE, Owen JR, Ordyna NJ, et al. Complex varus elbow instability: a terrible triad model. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2009; 18(2):269-274.
[40] Turker M, Derincek A, Canar M. Coronoid fractures and elbow instability, general review and clinical presentation. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2010;20:353-358.
[41] Rodriguez Martin J, Pretell-Mazzini J, Andres-Esteban EM, et al. Outcomes after terrible triads of the elbow treated with the current surgical protocols. A review.Int Orthop. 2011;35(6): 851-860.
[42] Foruria AM, Augustin S, Morrey BF, et al. Heterotopic ossification after surgery for fractures and fracture-dislocations involving the proximal aspect of the radius or ulna. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(10):e661-667.
[43] Zeiders GJ, Patel MK.Management of unstable elbows following complex fracture dislocations the "terrible triad" injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90 Suppl 4:75-84.
[44] Egol KA, Immerman I, Paksima N, et al. Fracture-dislocation of the elbow functional outcome following treatment with a standardized protocol. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2007;65(4): 263-270.
[45] Ring D, Guss D, Jupiter JB. Reconstruction of the coronoid process using a fragment of discarded radial head. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(3):570-574. |