| [1]Bauchet L, Lonjon N, Perrin FE, et al. Strategies for spinal cord repair after injury: a review of the literature and information. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2009;52(4):330-351.
[2]肖志满,胡建中,吕红斌,等.川芎嗪对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后巨噬细胞移动抑制因子表达的影响[J].中南大学学报:医学版,2012, (10): 1031-1036.
[3]Crowe MJ, Bresnahan JC, Shuman SL, et al. Apoptosis and delayed degeneration after spinal cord injury in rats and monkeys. Nat Med. 1997; 3(1): 73-76.
[4]Cao Q, Zhang YP, Iannotti C, et al. Functional and electrophysiological changes after graded traumatic spinal cord injury in adult rat. Exp Neurol. 2005;191 Suppl 1: S3-S16.
[5]Fehlings MG, Tator CH. The relationships among the severity of spinal cord injury, residual neurological function, axon counts, and counts of retrogradely labeled neurons after experimental spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 1995;132(2): 220-228.
[6]Park E, Velumian AA, Fehlings MG. The role of excitotoxicity in secondary mechanisms of spinal cord injury: a review with an emphasis on the implications for white matter degeneration. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21(6): 754-774.
[7]Kadota R, Koda M, Kawabe J, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) protects oligpdendrocyte and promotes hindlimb functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. PLoS One. 2012;7(11): e50391.
[8]Bracken MB, Shepard MJ, Collins WF, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of methylprednisolone or naloxone in the treatment of acute spinal-cord injury. Results of the Second National Acute Spinal Cord Injury Study. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322(20): 1405-1411.
[9]Hall ED, Springer JE. Neuroprotection and acute spinal cord injury: a reappraisal. Neuro Rx. 2004;1(1): 80-100.
[10]Nicola NA, Metcalf D, Matsumoto M, et al. Purification of a factor inducing differentiation in murine myelomonocytic leukemia cells. Identification as granulocyte colony- stimulating factor. J Biol Chem. 1983;258(14):9017-9023.
[11]Roberts AW. G-CSF: a key regulator of neutrophil production, but that's not all. Growth Factors. 2005;23(1): 33-41.
[12]Gibson CL, Bath PM, Murphy SP. G-CSF reduces infarct volume and improves functional outcome after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005; 25(4):431-439.
[13]Six I, Gasan G, Mura E, et al. Beneficial effect of pharmacological mobilization of bone marrow in experimental cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;458(3): 327-328.
[14]Piao CS, Gonzalez-Toledo ME, Gu X, et al. The combination of stem cell factor and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor for chronic stroke treatment in aged animals. Exp Transl Stroke Med. 2012;4(1):25.
[15]Zhao LR, Piao CS, Murikinati SR, et al. The Role of Stem Cell Factor and Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor in Treatment of Stroke. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov. 2012.
[16]Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Lee CC, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor for acute ischemic stroke: a randomized controlled trial. CMAJ. 2006;174(7): 927-933.
[17]Kawabe J, Koda M, Hashimoto M, et al. Neuroprotective effects of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and relationship to promotion of angiogenesis after spinal cord injury in rats: laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;15(4): 414-421.
[18]Sanli AM, Serbes G, Caliskan M, et al. Effect of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor on spinal cord tissue after experimental contusion injury. J Clin Neurosci. 2010; 17(12):1548-1552.
[19]李一帆,陈东,张大威,等.急性大鼠脊髓损伤Allen's法模型的改良及电生理评价[J].中国实验诊断学, 2010,14(8):1169-1172.
[20]陈永刚,王栓科,耿彬,等.三磷酸腺苷联合BMSCs移植修复大鼠脊髓损伤的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2010, 24(10): 1233-1238.
[21]Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(1): 1-21.
[22]Yang JR, Liao CH, Pang CY, et al. Transplantation of porcine embryonic stem cells and their derived neuronal progenitors in a spinal cord injury rat model. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(2): 201-208.
[23]Metz GA, Merkler D, Dietz V, et al. Efficient testing of motor function in spinal cord injured rats. Brain Res. 2000;883(2): 165-177.
[24]Romeo C, Raveendran AT, Sobha NM, et al. Cholinergic receptor alterations in the brain stem of spinal cord injured rats. Neurochem Res. 2013;38(2): 389-397.
[25]Rivlin AS, Tator CH. Objective clinical assessment of motor function after experimental spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurosurg. 1977;47(4): 577-581.
[26]Song Y, Zeng Z, Jin C, et al. Protective effect of ginkgolide B against acute spinal cord injury in rats and its correlation with the Jak/STAT signaling pathway. Neurochem Res. 2013;38(3): 610-619.
[27]Wang J, Ma C, Rong W, et al. Bog bilberry anthocyanin extract improves motor functional recovery by multifaceted effects in spinal cord injury. Neurochem Res. 2012;37(12): 2814-2825.
[28]Osada T, Watanabe M, Hasuo A, et al. Efficacy of the coadministration of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and stem cell factor in the activation of intrinsic cells after spinal cord injury in mice. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010;13(4): 516-523.
[29]Guo Y, Zhang H, Yang J, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor improves alternative activation of microglia under microenvironment of spinal cord injury. Neuroscience. 2013.
[30]Pitzer C, Klussmann S, Krüger C, et al. The hematopoietic factor granulocyte-colony stimulating factor improves outcome in experimental spinal cord injury. J Neurochem. 2010;113(4): 930-942.
[31]Chen WF, Jean YH, Sung CS, et al. Intrathecally injected granulocyte colony-stimulating factor produced neuroprotective effects in spinal cord ischemia via the mitogen-activated protein kinase and Akt pathway. Neuroscience. 2008;153(1): 31-43.
[32]Nishio Y, Koda M, Kamada T, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor attenuates neuronal death and promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury in mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2007;66(8): 724-731.
[33]Chen WF, Sung CS, Jean YH, et al. Suppressive effects of intrathecal granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on excessive release of excitatory amino acids in the spinal cerebrospinal fluid of rats with cord ischemia: role of glutamate transporters. Neuroscience. 2010;165(4): 1217-1232.
[34]Pan HC, Cheng FC, Lai SZ, et al. Enhanced regeneration in spinal cord injury by concomitant treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and neuronal stem cells. J Clin Neurosci. 2008;15(6): 656-664.
[35]Urdzikova L, Jendelova P, Glogarova K, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow stem cells as well as mobilization by granulocyte-colony stimulating factor promotes recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. Journal of Neurotrauma. 2006;23(9): 1379-1391.
[36]Silvestris N, Del Re M, Azzariti A, et al. Optimized granulocyte colony-stimulating factor prophylaxis in adult cancer patients: from biological principles to clinical guidelines. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012;16 Suppl 2: S111-117.
[37]Takahashi H, Yamazaki M, Okawa A, et al. Neuroprotective therapy using granulocyte colony-stimulating factor for acute spinal cord injury: a phase I/IIa clinical trial. Eur Spine J. 2012; 21(12): 2580-2587.
[38]Durafourt BA, Moore CS, Zammit DA, et al. Comparison of polarization properties of human adult microglia and blood-derived macrophages. Glia. 2012;60(5): 717-727.
[39]Legacy J, Hanea S, Theoret J, et al. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor promotes regeneration of retinal ganglion cells in vitro through a mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci Res. 2013.
[40]Metz GA, Curt A, van de Meent H, et al. Validation of the weight-drop contusion model in rats: a comparative study of human spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2000;17(1): 1-17.
[41]Schneider A, Wysocki R, Pitzer C, et al. An extended window of opportunity for G-CSF treatment in cerebral ischemia. BMC Biol. 2006;4: 36. |
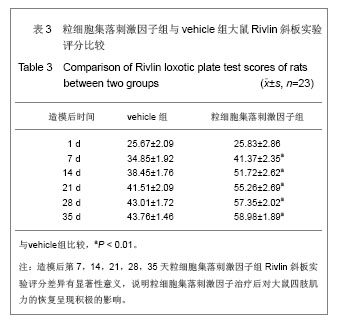
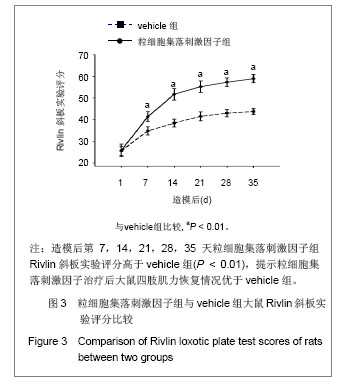
.jpg)