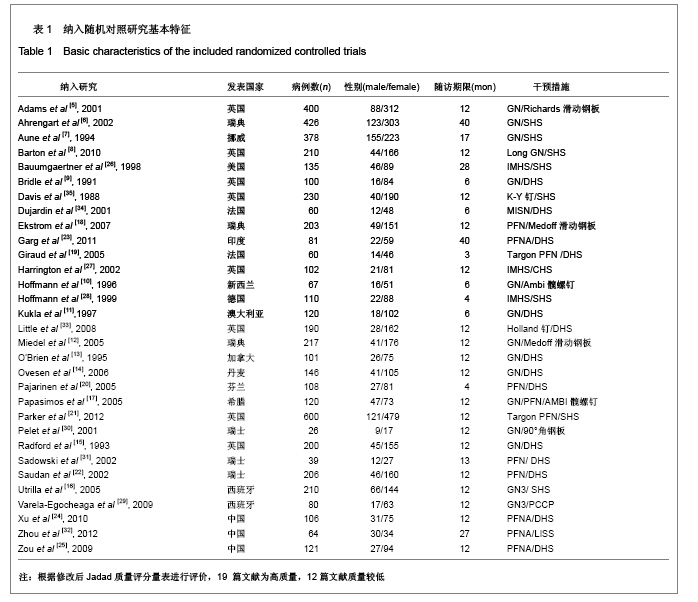
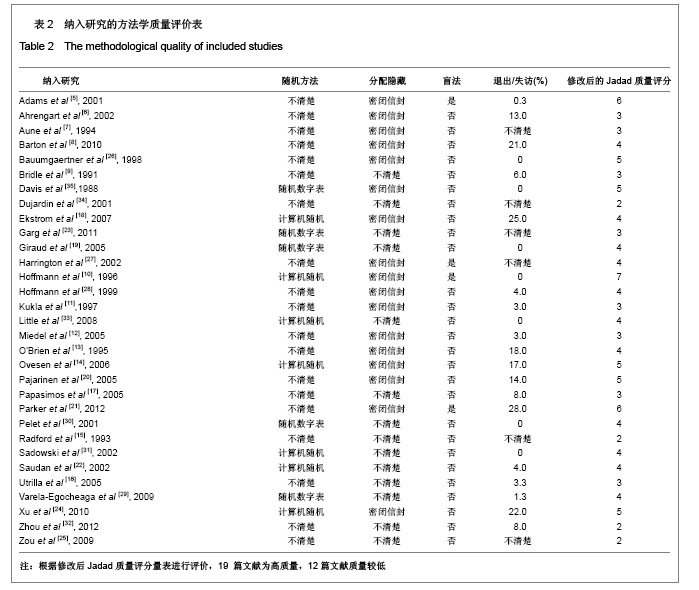
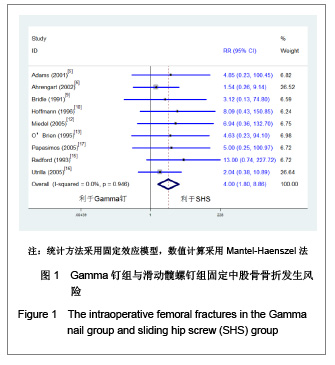
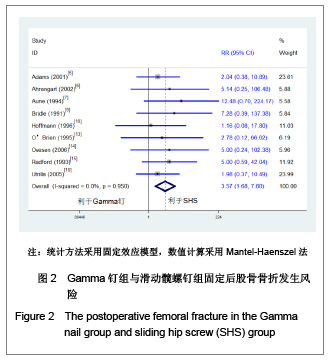
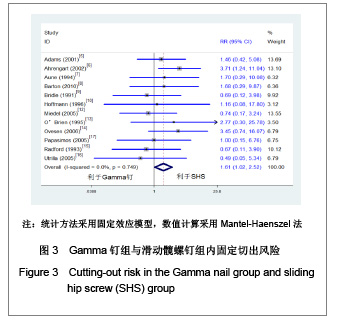
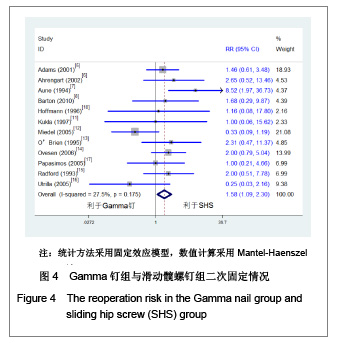
| [1] He QX, Xie GZ. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(13):2371-2375. 何启新,谢广中.人工股骨头置换与动力髋螺钉置入内固定修复老年股骨转子间骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13):2371-2375. [2] Canale ST, BeatyJH. Beijing: People's Military Medical Press. 2011. Canale ST, BeatyJH.坎贝尔骨科固定学[M]. 11版.北京:人民军医出版社,2011.[3] Lin PC, Chang SY. Functional recovery among elderly people one year after hip fracture surgery. J Nurs Res. 2004;12(1):72-82. [4] Collaboration TC. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions 4.2.2. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2004.[5] Adams CI, Robinson CM, Court-Brown CM, et al. Prospective randomized controlled trial of an intramedullary nail versus dynamic screw and plate for intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(6):394-400.[6] Ahrengart L, Törnkvist H, Fornander P, et al. A randomized study of the compression hip screw and gamma nail in 426 fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(401):209-222.[7] Aune AK, Ekeland A, Odegaard B, et al. Gamma nail vs compression screw for trochanteric femoral fractures 15 reoperations in a prospective, randomized study of 378 patients. Acfa Orthop Scand. 1994;65(2):127-130. [8] Barton TM, Gleeson R, Topliss C, et al. A comparison of the long gamma nail with the sliding hip screw for the treatment of AO/OTA 31-A2 fractures of the proximal part of the femur: a prospective randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92(4):792-798. [9] Bridle SH, Patel AD, Bircher M, et al. Fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. A randomised prospective comparison of the gamma nail and the dynamic hip screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(2):330-334. [10] Hoffman CW, Lynskey TG. Intertrochanteric fractures of the femur: a randomized prospective comparison of the gamma nail and the ambl hip screw. Aust N Z J Surg. 1996;66(3):151-155.[11] Kukla C, Heinz T, Berger G, et al. Gamma nail vs. dynamic hip screw in 120 patients over 60 years-A randomized trial. Acta Chir Austriaca. 1997;29(5):290-293. [12] Miedel R, Ponzer S, Törnkvist H, et al. The standard Gamma nail or the Medoff sliding plate for unstable trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87-B: 68-75. [13] O'Brien PJ, Meek RN, Blachut PA, et al. Fixation of intertrochanteric hip fractures: gamma nail versus dynamic hip screw. a randomized, prospective study. Can J Surg. 1995;(38):516-520. [14] Ovesen O, Andersen M, Poulsen T, et al. The trochanteric gamma nail versus the dynamic hip screw: a prospective randomised study. One-year follow-up of 146 intertrochanteric fractures. Hip Int. 2006;16(4):293-298.[15] Radford PJ, Needoff M, Webb JK. A prospective randomised comparison of the dynamic hip screw and the gamma locking nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993;75-B:789-793. [16] Utrilla AL, Sanz Reig J, Miralles MF, et al. Trochanteric gamma nail and compression hip screw for trochanteric fractures a randomized, prospective, comparative study in 210 elderly patients with a new design of the gamma nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(4):229-233. [17] Papasimos S, Koutsojannis CM, Panagopoulos A, et al. A randomised comparison of AMBI, TGN and PFN for treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(7):462-468. [18] Ekström W, Karlsson-Thur C, Larsson S, et al. Functional outcome in treatment of unstable trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures with the proximal femoral nail and the medoff sliding plate. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(1):18-25. [19] Giraud B, Dehoux E, Jovenin N, et al. Pertrochanteric fractures: a randomized prospective study comparying dynamic screw plate and intramedullary fixation. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2005;91(8):732-736. [20] Pajarinen J, Lindahl J, Michelsson O, et al. Pertrochanteric femoral fractures treated with a dynamic hip screw or a proximal femoral nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87-B:76-81.[21] Parker MJ, Bowers TR, Pryor GA. Sliding hip screw versus the Targon PF nail in the treatment of trochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94-B:391-397. [22] Saudan M, Lübbeke A, Sadowski C, et al. Pertrochanteric fractures: is there an advantage to an intramedullary nail? a randomized, prospective study of 206 patients comparing the dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16(6):386-393.[23] Garg B, Marimuthu K, Kumar V, et al. Outcome of short proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw for fixation of unstable trochanteric fractures. A randomised prospective comparative trial. Hip Int. 2011;21(05):531-536. [24] Xu YZ, Geng DC, Mao HQ, et al. A comparison of the proximal femoral nail antirotation device and dynamic hip screw in the treatment of unstable pertrochanteric fracture. J Int Med Res. 2010;38(4):1266-1275. [25] Zou J, Xu Y, Yang H. A comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw devices in trochanteric fractures. J Int Med Res. 2009;37(4):1057-1064. [26] Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM. Intramedullary versus extramedullary fixation for the treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; (348):87-94. [27] Harrington P, Nihal A, Singhania AK. Intramedullary hip screw versus sliding hip screw for unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures in the elderly. Injury. 2002;33(1):23-28. [28] Hoffmann R, Schmidmaier G, Schulz R, et al. Classic nail versus DHS. A prospective randomised study on operative fixation of trochanteric femur fractures. Unfallchirurg. 1999; 102(3):182-190.[29] Varela-Egocheaga JR, Iglesias-Colao R, Suárez-Suárez MA, et al. Minimally invasive osteosynthesis in stable trochanteric fractures: a comparative study between Gotfried percutaneous compression plate and Gamma 3 intramedullary nail. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(10): 1401-1407.[30] Pelet S, Arlettaz Y, Chevalley F. Per-and subtrochanteric femoral fractures management with blade plate versus gamma nail fixation: a prospective randomized study. Swiss Surg. 2001;7(3):126-133. [31] Sadowski C, Lübbeke A, Saudan M, et al. Treatment of reverse oblique and transverse intertrochanteric fractures with use of an intramedullary nail or a 95° screw-plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(3):372-381.[32] Zhou F, Zhang ZS, Yang H, et al. Less invasive stabilization system (LISS) versus proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) in treating proximal femoral fractures: a prospective randomized study. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(3):155-162. [33] Little NJ, Verma V, Fernando C, et al. A prospective trial comparing the Holland nail with the dynamic hip screw in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008:90(8):1073-1078. [34] Dujardin FH, Benez C, Polle G, et al. Prospective randomized comparison between a dynamic hip screw and a mini-invasive static nail in fractures of the trochanteric area: preliminary results. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(6):401-406. [35] Davis TR, Sher JL, Checketts RG, et al. lntertrochanteric fractures of the femur: a prospective study comparing the use of the Kiintscher-Y nail and a sliding hip screw. Injury. 1988; 19(6):421-426. |