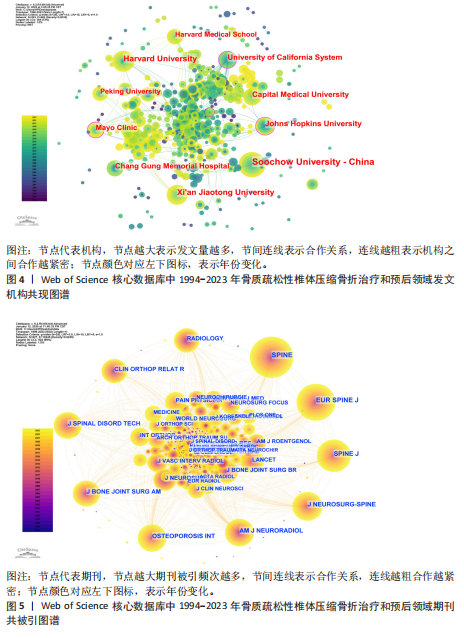
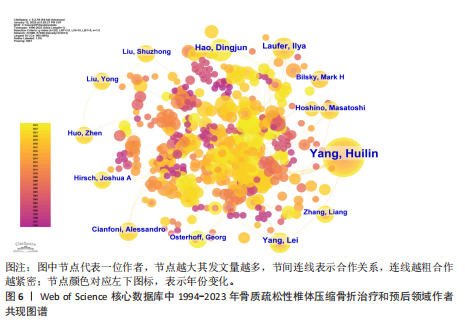
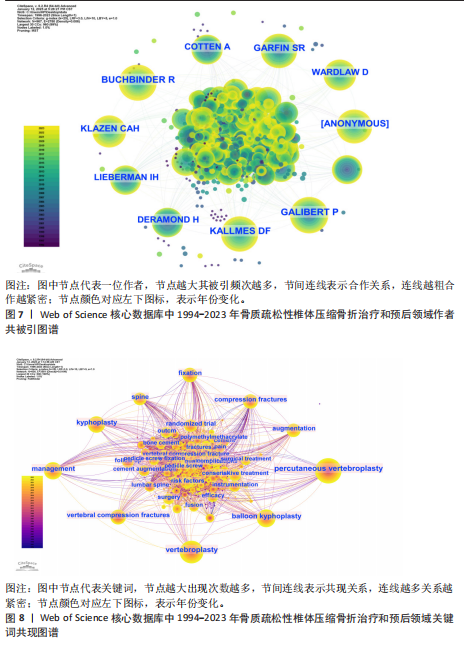
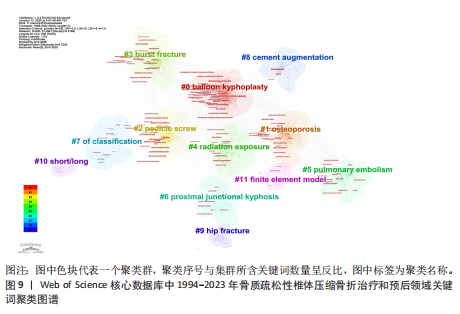
[1] GLASER DL, KAPLAN FS. Osteoporosis. Definition and clinical presentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(24 Suppl):12S-16S.
[2] STRÖM O, BORGSTRÖM F, KANIS JA, et al. Osteoporosis: burden, health care provision and opportunities in the EU: a report prepared in collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA). Arch Osteoporos. 2011;6:59-155.
[3] KARMAKAR A, ACHARYA S, BISWAS D, et al. Evaluation of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Management of Symptomatic Osteoporotic Compression Fracture. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(8):RC07-RC10.
[4] BEALL DP, OLAN WJ, KAKAD P, et al. Economic Analysis of Kiva VCF Treatment System Compared to Balloon Kyphoplasty Using Randomized Kiva Safety and Effectiveness Trial (KAST) Data. Pain Physician. 2015;18(3):E299-306.
[5] 中华医学会骨科学分会.骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南(2022年版)[J].中华骨科杂志, 2022,42(22):1473-1491.
[6] 邱贵兴,裴福兴,胡侦明,等.中国骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南(全文)(骨质疏松性骨折诊断及治疗原则)[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(6):117-120.
[7] GARFIN SR, BUCKELY RA, LEDLIE J, et al. Balloon kyphoplasty for symptomatic vertebral body compression fractures results in rapid, significant, and sustained improvements in back pain, function, and quality of life for elderly patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19):2213-2220.
[8] BURTON AW, MENDEL E. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Pain Physician. 2003;6(3):335-341.
[9] GALIBERT P, DERAMOND H, ROSAT P, et al. Note préliminaire sur le traitement des angiomes vertébraux par vertébroplastie percutanée. Neurochirurgie. 1987;33:166-168.
[10] ZHANG L, LIU Z, WANG J, et al. Unipedicular versus bipedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a prospective randomized study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:145.
[11] BALKARLI H, DEMIRTAS H, KILIC M, et al. Treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty under local anesthesia: clinical and radiological results. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(9):16287-16293. eCollection 2015.
[12] LONG Y, YI W, YANG D. Advances in Vertebral Augmentation Systems for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Res Manag. 2020;2020:3947368.
[13] LI J, XU L, LIU Y, et al. Open Surgical Treatments of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2023; 15(11):2743-2748.
[14] 姜宇,郭昭庆,陈仲强,等.陈旧性骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折继发胸腰椎后凸畸形的手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2023, 43(7):465-470.
[15] HSIEH JY, WU CD, WANG TM, et al. Reduction of the domino effect in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures through short-segment fixation with intravertebral expandable pillars compared to percutaneous kyphoplasty: a case control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:75.
[16] NORIEGA D, MAESTRETTI G, RENAUD C, et al. Clinical Performance and Safety of 108 SpineJack Implantations: 1-Year Results of a Prospective Multicentre Single-Arm Registry Study. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:173872.
[17] LAREDO JD, HAMZE B. Complications of percutaneous vertebroplasty and their prevention. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2005; 26(2):65-80.
[18] MATHIS JM. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: complication avoidance and technique optimization. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24(8):1697-1706.
[19] KIM YY, RHYU KW. Recompression of vertebral body after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(11):1907-1912.
[20] FREEDMAN BA, HELLER JG. Kummel Disease: A Not-So-Rare Complication of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009;22(1):75-78.
[21] LIAO H, TANG M, LI L, et al. A Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization of Medical Big Data Research. Sustainability. 2018;10:166.
[22] CHENG K, GUO Q, YANG W, et al. Mapping Knowledge Landscapes and Emerging Trends of the Links Between Bone Metabolism and Diabetes Mellitus: A Bibliometric Analysis From 2000 to 2021. Front Public Health. 2022;10:918483.
[23] VAN ECK NJ, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523-538.
[24] SYNNESTVEDT MB, CHEN C, HOLMES JH. CiteSpace II: visualization and knowledge discovery in bibliographic databases. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2005;2005:724.
[25] JENSEN ME, EVANS AJ, MATHIS JM, et al. Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997;18(10):1897-1904.
[26] KALLMES DF, COMSTOCK BA, HEAGERTY PJ, et al. A Randomized Trial of Vertebroplasty for Osteoporotic Spinal Fractures. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(6):569-579.
[27] KLAZEN CA, LOHLE PN, DE VRIES J, et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2010; 376(9746):1085-1092.
[28] 张毅,李唯,邵杰,等.骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折PVP/PKP术后二次骨折的危险因素分析及预测模型建立[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(9):785-792.
[29] SUTIPORNPALANGKUL W, ZAMBRANA L, GIANAKOS A, et al. Comparison of Sagittal Balance between Radiofrequency Targeted Vertebral Augmentation and Balloon Kyphoplasty in Treatment of Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Retrospective Study. J Med Assoc Thai. 2016;99(9):1025-1032.
[30] VOORMOLEN MHJ. Kyphoplasty. Neuroradiology. 2011;53 Suppl 1(S1):S203-205.
[31] CAO Z, WANG G, HUI W, et al. Percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures improves spino-pelvic alignment and global sagittal balance maximally in the thoracolumbar region. PLoS One. 2020;15(1):e0228341.
[32] YOKOYAMA K, KAWANISHI M, YAMADA M, et al. Postoperative change in sagittal balance after Kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(4):744-749.
[33] BOHNER M, SANTONI BLG, DÖBELIN N. beta-tricalcium phosphate for bone substitution: Synthesis and properties. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:23-41.
[34] 栾伟,陈家瀚,滕勇,等.新型可吸收骨水泥的制备及其应用于小牛椎体标本压缩性骨折椎体成形术的生物力学研究[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2022,27(10):721-728.
|