中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (17): 4377-4389.doi: 10.12307/2026.148
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
复方甜地丁对乳腺增生小鼠模型的干预作用及机制
武祎琳1,田红英1,孙佳乐1,焦佳佳1,赵梓涵1,邵金环1,赵凯悦1,周 敏1,李 倩1,2,李泽鑫1,岳昌武1
- 1延安大学基础医学院微生物药物创新与转化重点实验室,陕西省延安市 716000; 2延安大学附属医院检验科,陕西省延安市 716000
-
收稿日期:2025-04-04接受日期:2025-08-13出版日期:2026-06-18发布日期:2025-12-01 -
通讯作者:李倩,副主任检验技师,延安大学基础医学院微生物药物创新与转化重点实验室,陕西省延安市 716000;延安大学附属医院检验科,陕西省延安市 716000 并列通讯作者:李泽鑫,硕士,延安大学基础医学院微生物药物创新与转化重点实验室,陕西省延安市 716000 并列通讯作者:岳昌武,博士,教授,博士生导师,延安大学基础医学院微生物药物创新与转化重点实验室,陕西省延安市 716000 -
作者简介:第一作者:武祎琳,女,1999年生,山西省人,汉族,硕士。 并列第一作者:田红英,女,1976年生,陕西省人,汉族,硕士,副教授。 -
基金资助:延安市科技计划 (2024-SFGG-201);陕西省自然科学计划(2024JC-YBMS-755)
Intervention effect and mechanism of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae in a mouse model of breast hyperplasia
Wu Yilin1, Tian Hongying1, Sun Jiale1, Jiao Jiajia1, Zhao Zihan1, Shao Jinhuan1, Zhao Kaiyue1, Zhou Min1, Li Qian1, 2, Li Zexin1, Yue Changwu1
- 1Yan’an Key Laboratory of Microbial Drug Innovation and Transformation, School of Basic Medicine, Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2025-04-04Accepted:2025-08-13Online:2026-06-18Published:2025-12-01 -
Contact:Li Qian, Associate chief technician, Yan’an Key Laboratory of Microbial Drug Innovation and Transformation, School of Basic Medicine, Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China; Department of Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China Co-corresponding author: Li Zexin, MS, Yan’an Key Laboratory of Microbial Drug Innovation and Transformation, School of Basic Medicine, Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China Co-corresponding author: Yue Changwu, PhD, Professor, Doctor’s supervisor, Yan’an Key Laboratory of Microbial Drug Innovation and Transformation, School of Basic Medicine, Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Wu Yilin, MS, Yan’an Key Laboratory of Microbial Drug Innovation and Transformation, School of Basic Medicine, Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China Tian Hongying, MS, professor, Yan’an Key Laboratory of Microbial Drug Innovation and Transformation, School of Basic Medicine, Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China Wu Yilin and Tian Hongying contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:Yan’an Science and Technology Program, No. 2024-SFGG-201; Shaanxi Provincial Natural Science Program, No. 2024JC-YBMS-755
摘要:
文题释义:
甜地丁:是一种传统中药材,属于豆科植物,具有清热解毒、消肿散结的功效,在中医中常用于治疗乳腺疾病、炎症和感染等。
短链脂肪酸:是肠道菌群发酵膳食纤维产生的一类重要代谢产物,主要包括乙酸、丙酸和丁酸等。短链脂肪酸不仅是肠道细胞的重要能量来源,还具有抗炎、免疫调节和维持肠道屏障功能的作用。
背景:乳腺增生是一种常见的良性乳腺疾病,主要由内分泌失调引起,表现为乳腺组织的异常增生。近年来,中药复方和益生菌在调节内分泌及改善肠道微生态等方面显示出良好的潜力,为乳腺增生的治疗提供了新的思路。
目的:观察中药复方及益生菌复方发酵对小鼠乳腺增生的作用及机制,为乳腺增生的临床治疗与预防提供新的理论及实验依据。
方法:①运用网络药理学工具预测甜地丁(地锦草)的抗乳腺增生活性及其潜在作用靶点和信号通路。数据库包括:TCMSP、OMIM、GeneCards 数据库、UniProt 网站、Venny 2.1.0 网站、Metascape、HERB网站和STRING 数据库。网络药理学可以通过网络分析、计算机系统分析预测筛选得到中药活性成分对应的靶点、疾病靶点和作用通路等关键信息,因此逐渐广泛用于中药的研究。②实验通过给小鼠注射雌激素和孕激素诱导建立乳腺增生模型,设立正常对照组小鼠每天腹腔注射生理盐水,模型组、给药组小鼠每天腹腔注射0.5 mg/kg苯甲酸雌二醇注射液,持续注射25 d。第26天起,停止注射苯甲酸雌二醇,正常对照组小鼠每天继续肌肉注射生理盐水,模型组和给药组小鼠肌肉注射5 mg/kg 的黄体酮注射液,持续注射 5 d。造模结束后各组分别进行给药,正常组和模型组灌胃0.2 mL/d生理盐水;阳性对照组(消症丸组)按 0.9 mg/g灌胃消症丸水溶液;复方甜地丁低、中、高剂量组按照 0.75,1.5,3.0 mg/(g·d)灌胃复方甜地丁水溶液,中药菌发酵低、中、高剂量组按照 0.75,1.5,3.0 mg/(g·d)灌胃复方药水溶液,连续给药30 d。
结果与结论:①网络药理学研究结果表明,甜地丁复方 (地锦草)含有46种活性成分,与1 213个潜在靶点相关。与已知的588个乳腺增生靶点比对后,推测其中50个靶点可能与该复方对乳腺增生的直接作用有关。②药物干预后,甜地丁高剂量组与未治疗组相比无明显变化,其他干预组肝脏指数均有所降低(P < 0.05)。③在肾脏和子宫指数方面,甜地丁中剂量组与对照组相比显著降低(P < 0.05);在子宫指数方面,模型组与对照组相比显著升高(P < 0.01)。④经过1个月的药物治疗,消症丸组、甜地丁低、中、高剂量组和中药菌发酵低、中、高剂量组乳腺组织中的小叶和腺泡数量减少,导管开口缩小。随着药物剂量增加,乳腺组织弥漫性增生情况明显改善。⑤ELISA结果显示,与模型组相比,中药菌发酵中剂量组干预后雌激素E2水平较低(P < 0.05)。此外,甜地丁低剂量组的卵泡刺激素水平低于模型组(P < 0.05)。⑥对小鼠模型的干预导致所有组的短链脂肪酸和肠道菌群丰度发生变化。⑦上述结果证实,复方甜地丁及其益生菌发酵产物通过调节激素水平、改善肠道菌群结构和增加短链脂肪酸含量,显著改善了小鼠乳腺增生。
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-0508-3257 (Wu Yilin); https://orcid.org/0009-0000-0430-2792 (Li Qian); https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2679-5772 (Yue Changwu)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
武祎琳, 田红英, 孙佳乐, 焦佳佳, 赵梓涵, 邵金环, 赵凯悦, 周 敏, 李 倩, 李泽鑫, 岳昌武. 复方甜地丁对乳腺增生小鼠模型的干预作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(17): 4377-4389.
Wu Yilin, Tian Hongying, Sun Jiale, Jiao Jiajia, Zhao Zihan, Shao Jinhuan, Zhao Kaiyue, Zhou Min, Li Qian, Li Zexin, Yue Changwu. Intervention effect and mechanism of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae in a mouse model of breast hyperplasia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4377-4389.
A total of 65 mice were included in the experiment. Among them, 63 mice were included in the result analysis. Two mice died due to stress reactions and inability to adapt to the environment. Finally, 63 mice were left for the statistical result analysis.
The KEGG signaling pathway prediction for the compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae in treating breast hyperplasia
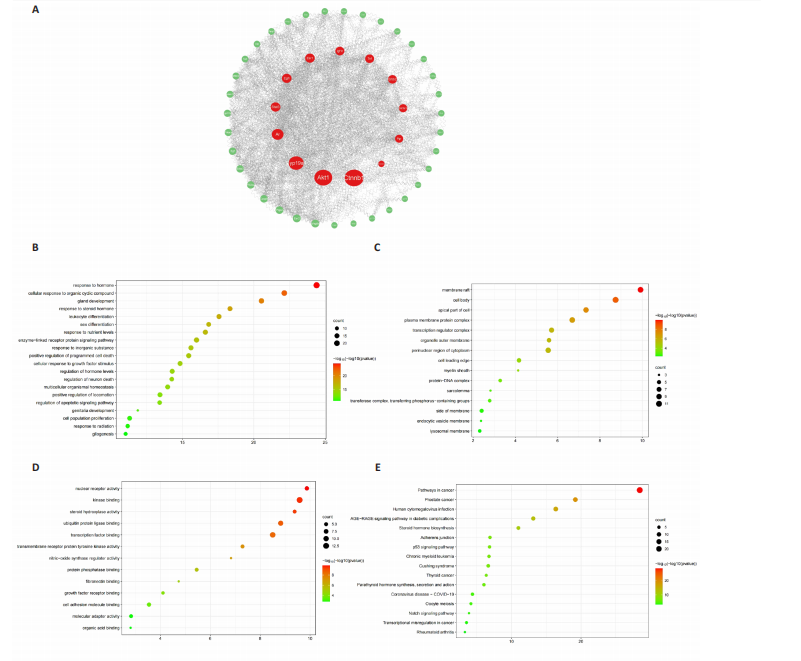
According to the screening criteria of active ingredients and action targets, a total of 46 active ingredients and 1 213 action targets of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae were collected. By finding the intersection genes between Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and breast hyperplasia, it was discovered that 50 genes were related to breast hyperplasia. Then, the top 30 target genes with the highest degree values among the intersection genes were imported into the Cytoscape 3.6.0 software to draw a PPI network diagram (Figure 1A). It was found that Phenyl phenylacetate, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, cyclohexanone, protocatechuate, and methyl 2-(4-(hydroxymethyl) phenyl) acetate were the five nodes with relatively large degree values. This indicates that these proteins play an important role in the PPI network and may be the key targets for Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae in treating breast hyperplasia. The biological processes, cellular components, and molecular functions of the intersection targets were analyzed using Metascape. The results showed that in terms of biological processes, it was mainly manifested as the cell’s response to hormones, response to organic cyclic compounds, gland development, and response to inorganic substances (Figure 1B). For cellular components, it was mainly manifested as membrane rafts, the apical part of the cell, plasma membrane protein complex, transcriptional regulatory complex, and the perinuclear region of the cytoplasm (Figure 1C). For molecular functions, it was mainly manifested as nuclear receptor activity, steroid hydroxylase activity, protein phosphatase binding, and cell adhesion molecule binding (Figure 1D). A KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was carried out on the intersection genes (Figure 1E). The Metascape online website was used to conduct a KEGG pathway analysis on the intersection genes between Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and breast hyperplasia disease (Figure 1F), and 15 important pathways related to the intervention of breast hyperplasia by Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae were predicted. The results showed that the targets were mainly enriched in cancer-related signaling pathways, prostate cancer signaling pathways, Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) receptor signaling pathways, advanced glycation end-products-receptor for advanced glycation end-products (AGE-RAGE) signaling pathways, and Ras signaling pathways. Most of these pathways are related to inflammation, suggesting that Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae may intervene in breast hyperplasia by inhibiting inflammatory signaling pathways. The active ingredients of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae may participate in biological processes such as hormone regulation, cell proliferation, and differentiation through these potential targets, affecting the physiological activities of cells. At the same time, based on the results of the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis, it is speculated that this compound may reduce the stimulation of the breast tissue by inflammatory reactions through inhibiting inflammatory signaling pathways, thereby intervening in the development of breast hyperplasia.
Establishment of a mouse model of breast hyperplasia
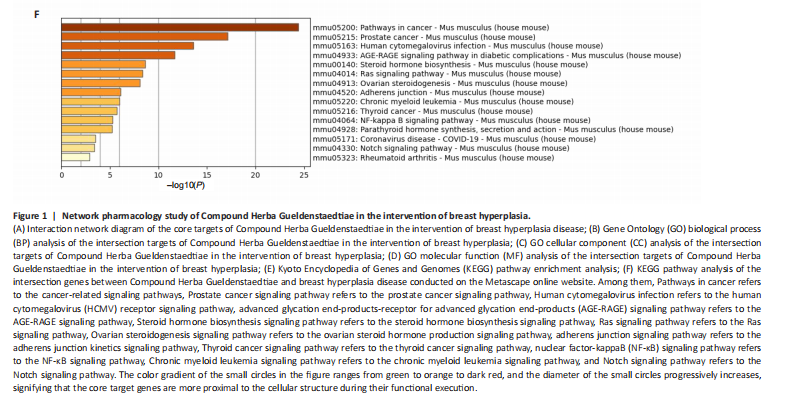
The model of breast hyperplasia was tested by changes in organ indexes
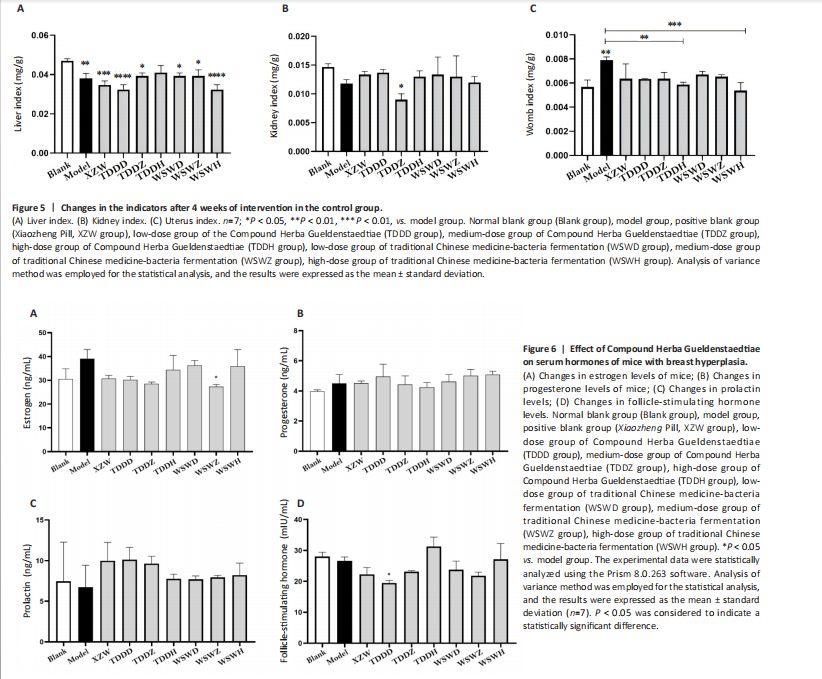
After estrogen modeling, the organs of the female mice exhibited changes. Specifically, the uterine index value increased when compared to the blank group. Conversely, the liver index of the mice in the model group decreased (Figure 2), suggesting that the model was successfully established.
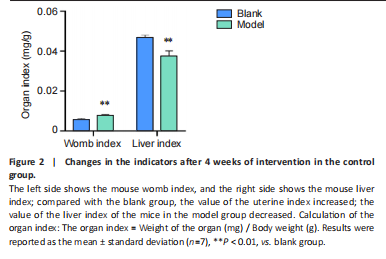
Use of hematoxylin-eosin staining to verify the breast hyperplasia model
After the intervention, mice with mammary gland hyperplasia were selected for pathological tissue sectioning, and the results were observed under a microscope (Figure 3). The number of mammary glands and lobules in the model group increased, ducts dilated, and breast tissue extensively proliferated. Confirmed the successful establishment of a mouse mammary gland hyperplasia model. The combined injection of estrogen and progesterone disrupts the hormonal balance in mice. Estrogen stimulates the growth of mammary ducts and acini, while progesterone promotes the development of mammary lobules. Excessive amounts of both hormones lead to abnormal hyperplasia of the mammary tissue. At the same time, the hormonal changes affect the physiological functions of the uterus and liver, which are reflected in the changes of the organ indices. This indicates a close relationship between hormonal imbalance, breast hyperplasia, and changes in organ functions.
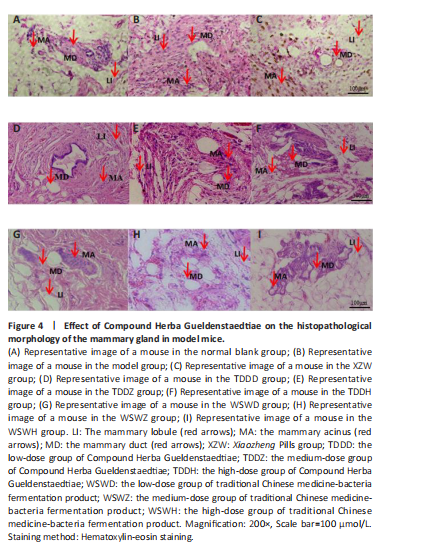
Effect of traditional Chinese medicine compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae on pathological morphology of mammary gland tissue in mice with breast hyperplasia
After 30 days of drug administration, the pathological morphology of mammary tissue in each group revealed distinct differences. The blank group exhibited normal mammary duct size, with scattered and sparse mammary lobules containing a small number of acini, and no evidence of diffuse hyperplasia (Figure 4A). In contrast, the model group displayed a significant increase in the number and volume of mammary lobules, diffuse hyperplasia, an increased number of acini, and abnormally enlarged mammary ducts compared with the blank group (Figure 4B). The XZW group exhibited a notable decrease in the count of mammary lobules and acini, a diminution in ductal orifice dimensions, and a substantial enhancement in the severity of hyperplasia (Figure 4C). Mice treated with compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae water at varying doses exhibited a decrease in the number of mammary lobules and acini, as well as a reduction in mammary duct orifice size. The improvement in diffuse hyperplasia of mammary tissue increased with the escalation of drug dose (Figure 4D–F). Similarly, mice treated with microbial fermentation compound drugs at low, medium, and high doses demonstrated a decreased number of mammary lobules and acini, reduced ductal orifice size, and an enhanced improvement in diffuse hyperplasia of mammary gland tissue with increasing drug dose (Figure 4G–I). These findings confirm that both methods of treatment with compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae can effectively ameliorate mammary gland hyperplasia in mice. The Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its microbial fermentation products may improve the pathological morphology of the mammary tissue by regulating the hormone levels and inhibiting the excessive proliferation of mammary epithelial cells. The effect of the high-dose group is more significant. It may be because a higher dose can more effectively regulate the relevant signaling pathways, inhibit the cell proliferation signals, and promote the normal differentiation of cells, thus alleviating breast hyperplasia.
Detection of organ index in mice
Figure 5 shows that compared to the blank group, the model group has a higher uterine index, followed by a higher liver index. After intervention, except for the TDDH group, the liver index of the blank group contracted when parallel (Figure 5A). Compared with the Blank group, the renal index of the TDDZ group decreased (P < 0.05), while there were no abnormalities in the other groups (Figure 5B). In contrast to the model group, the uterine index decreased in both the TDDH and WSWH groups (P < 0.01 in the TDDH group and P < 0.001 in the WSWH group). No abnormalities were found in the other intervention groups (Figure 5C), indicating that the TDDH and WSWH groups had uterine damage during the intervention period for breast hyperplasia. The results indicate that the two different treatment methods of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae have certain effects on the uterus and liver; However, there are differences in organ index, which hinders its comprehensive application as a therapeutic agent for mice. The establishment of the breast hyperplasia model leads to hormonal imbalance, affecting the normal functions of the uterus and liver and causing changes in their indices. After drug intervention, there are differences in the effects of each dosage group on different organs, which may be due to the different metabolism and action targets of the active ingredients of the drugs in the body. For example, certain ingredients may preferentially act on the liver, regulating the metabolic function of the liver, thereby reducing the liver index; while the effect on the uterus may be related to hormonal regulation. By regulating the levels of estrogen and progesterone, it affects the growth and development of the uterus.
Effect of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae on serum hormone levels in mice with breast hyperplasia
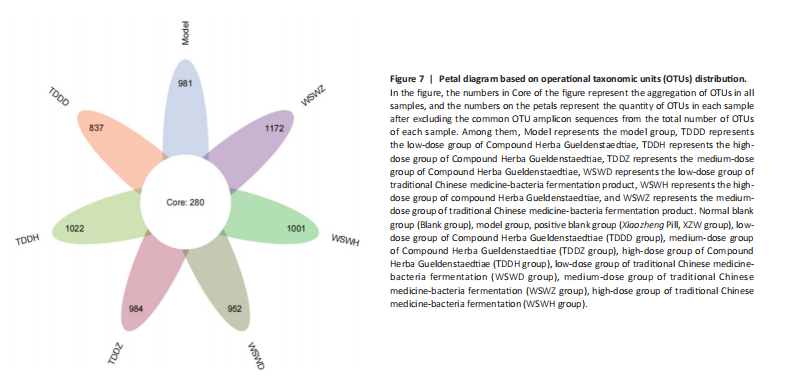
Hormone levels (estrogen, progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and prolactin) in the serum of mice with breast hyperplasia were measured using ELISA (Figure 6). There was no statistically difference in estrogen levels between the model and blank groups (P > 0.05). In contrast to the model group, there was no significant variation in estrogen levels among the positive blank (XZW group), TDDD, TDDZ, TDDH, WSWD and WSWH groups (P > 0.05). Notably, the estrogen level in the WSWZ group was significantly lower than that in the model group (P < 0.05) (Figure 6A). No evident difference in progesterone levels was examined between the model and blank groups (P > 0.05). Similarly, no diversity in progesterone levels were found among the positive blank (XZW group), TDDD, TDDH, WSWD, WSWZ and WSWH groups compared with the model group (P > 0.05) (Figure 6B). There was no obviously disparity in prolactin levels between the model and blank groups (P > 0.05). Similarly, patentably Indistinctness in prolactin levels were discerned among the positive blank (XZW group), TDDD, TDDH, WSWD, WSWZ and WSWH groups compared with the model group (P > 0.05) (Figure 6C). No evident variation in FSH levels was examined between the model and blank groups (P > 0.05). No evident disparity in estrogen levels were found among the positive blank (XZW group), TDDZ, TDDH, WSWD, WSWZ and WSWH groups compared with the model group (P > 0.05). Conversely, the estrogen level in the TDDD group was significantly lower than that in the model group (P < 0.05) (Figure 6D). These findings suggest that the TDDD group may decrease FSH levels in mice with breast hyperplasia, while the medium dose of compound sweetener may reduce estrogen levels in these mice. The balance of hormone levels is crucial for the normal development and functional maintenance of mammary gland tissues. The Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae may affect the secretion and metabolism of hormones by regulating the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. The low-dose water extract of Herba Gueldenstaedtiae reduces the level of FSH, likely through a feedback regulation mechanism that decreases the secretion of FSH by the pituitary gland. The medium-dose microbial fermentation group reduces the level of estrogen, possibly by influencing the synthesis or metabolic process of estrogen, thereby affecting the development of breast hyperplasia.
Effect of compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae on intestinal flora in mice with breast hyperplasia
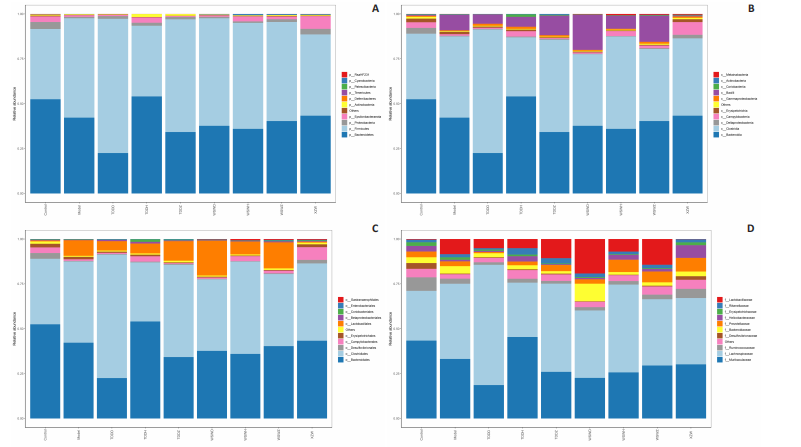
In order to test the species composition diversity within each sample group, based on the results of OTUs clustering analysis and research requirements, the common and unique OTUs among different samples (groups) were analyzed. When the number of samples (groups) is greater than 5, a petal diagram is drawn. It can intuitively show the number of OTUs contained in each group and obtain the number of OTU intersections shared by all groups. The results are as follows. The number of OTUs contained in each group is 981 in the model group, 837 in the TDDD group, 984 in the TDDZ group, 1 022 in the TDDH group, 952 in the WSWD group, 1 172 in the WSWZ group, and 1001 in the WSWH group. The number of OTU intersections is 280. The above results indicate that there are differences in abundance among the groups and they are also interrelated. After drug administration, the types of intestinal flora in mice increased, suggesting that Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae can regulate the diversity of the intestinal microbiota in the mouse model of mammary gland hyperplasia (Figure 7).
Analysis of intestinal flora structure of mice in each group after different drug intervention
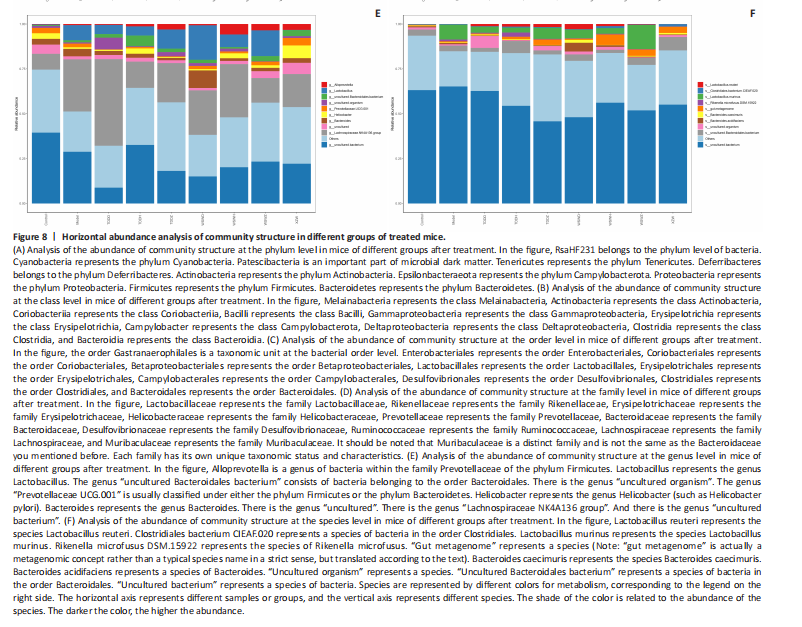
Based on the Species annotation results for each group of samples, the relative abundance of species at various taxonomic levels (Family, Phylum, Class, Order, Genus, and Species) was ascertained. Figure 8 reveals that, at the phylum level (Figure 8A), the intestinal community structure of mice in all groups was predominantly characterized by Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes. In comparison to the blank group, Bacteroidetes diminished while Firmicutes expanded in the model group. Contrasting with the model group, the abundance of Firmicutes escalated in all experimental groups except the TDDH group; notably, the proportions of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes in the TDDH group resembled those of the blank group. These findings indicate a decrease in Bacteroidetes and an increase in Firmicutes in mice with breast hyperplasia. Following high-dose administration of the Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae water decoction, Bacteroidetes levels were restored while Firmicutes decreased, thus ameliorating the dysbiosis induced by breast hyperplasia.
At the class level, the intestinal flora structure and distribution among all mouse groups showed that the dominant classes were Clostridia and Bacteroidetes (Figure 8B). Compare with the model group, the TDDH group showed an increase in Bacteroidetes and a decrease in Clostridia. Conversely, the other experimental groups displayed contrasting trends. The TDDH group’s Bacteroidetes and Clostridia proportions were nearly identical to those of the blank group. These outcomes suggest that high-dose treatment with the compound SGD can reverse the decline in Bacteroidetes and the rise in Clostridia associated with breast hyperplasia in mice.
At the order level, the composition and distribution of intestinal flora in each group of mice were predominantly characterized by Clostridia and Bacteroidetes (Figure 8C). The model group displayed a reduced abundance of Bacteroides and an increased abundance of Clostridia compared with the blank group. Aside from the TDDH group, the remaining experimental groups demonstrated similar trends; however, the Bacteroidetes and Clostridia levels in the TDDH group were comparable to those of the blank group.
At the family level, the distribution structure of intestinal flora in mice across each group indicated dominance by Lachnospiraceae and Muribaculaceae (Figure 8D). The model group had decreased populations of Muribaculaceae and Ruminococcaceae but elevated populations of Spiralaceae and Lactobacillaceae. Notably, Ruminococcaceae play a critical role in degrading resistant starch, with the XZW group exhibiting the most significant recovery in this aspect.
The intestinal flora structure distribution at the level of each group of mice (Figure 8E) primarily featured Lachnospiraceae as the predominant bacterial group. In comparison to the blank group, the model group displayed an improved population of Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group species and a decrease in uncultured Bacteroidales bacterial species. However, following drug intervention, the TDDH group’s microbiota recovered, with Lactobacillus levels surpassing those of the blank group.
At the species level, the distribution of intestinal flora in each group of mice (Figure 8F) revealed that uncultured bacterial species did not significantly differ in abundance between the model and blank groups. Nevertheless, after drug intervention, there was an increase in the abundance of uncultured Bacteroidales bacterial kinds. There is a close relationship between the intestinal flora and breast hyperplasia. Breast hyperplasia may disrupt the balance of the intestinal flora, leading to a decrease in beneficial bacteria and an increase in harmful bacteria. The Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its fermentation products can regulate the structure of the intestinal flora and increase the abundance and diversity of beneficial bacteria. For example, the high-dose Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae restores the level of Bacteroidetes and reduces the level of Firmicutes. This may be achieved by regulating the intestinal internal environment, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria, and promoting the reproduction of beneficial bacteria, thus improving the intestinal microecology. The changes in the intestinal flora may in turn affect the health of the mammary gland tissue through the gut-mammary axis. Beneficial bacteria and their metabolites may regulate the body’s immune function and hormone levels, indirectly inhibiting breast hyperplasia.
Effect of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae on intestinal short-chain fatty acids in mice with breast hyperplasia
The analysis of the effects of various drug interventions on intestinal SCFAs in each mouse group, as depicted in Figure 9, revealed several notable findings. Compared with the blank group, the model group demonstrated an evident decrease in acetic acid content, indicating a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). This suggests that mammary gland hyperplasia in mice impacts acetic acid levels. Conversely, the TDDZ group displayed a substantial increase in acetic acid content relative to the model group, also indicating a statistical distinction (P < 0.001). Furthermore, both TDDD and TDDH groups demonstrated markedly higher acetic acid levels compared with the model group (P < 0.0001), as illustrated in Figure 9A.
Propionic acid levels in the model group were notably lower than in the blank
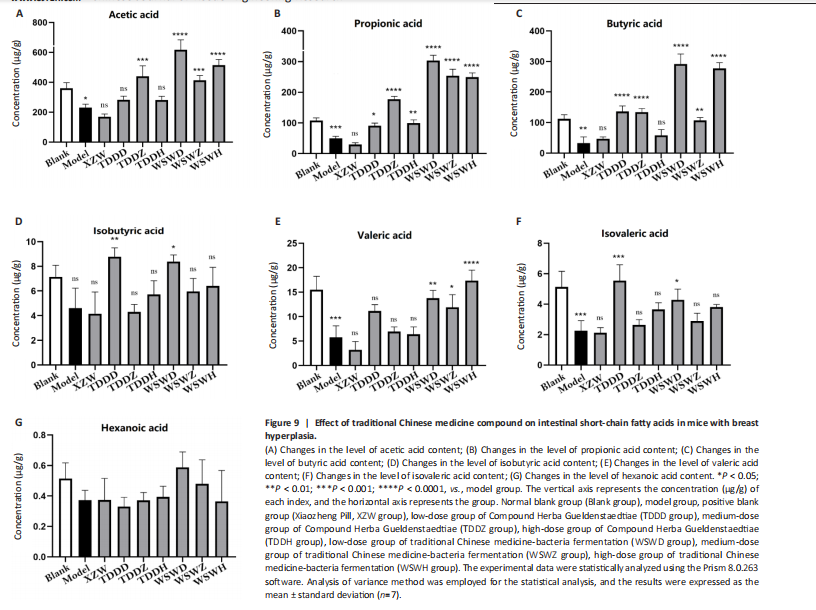
group, indicating a statistically significant difference (P < 0.001). However, when comparing the model group and the TDDD group, an increase in propionic acid content was observed, with a significant statistical difference
(P < 0.05), as shown in Figure 9B.
Regarding butyric acid, the TDDZ, TDDH, WSWD, and WSWH groups exhibited considerable variations in butyric acid content, which were statistically significant (P < 0.0001), as seen in Figure 9C. This suggests that the compound could enhance butyric acid levels in mice following water decoction and microbial probiotic fermentation.
The levels of isobutyric acid remained unchanged between the model group and the blank group, suggesting that the isobutyric acid levels in mice were not affected by the modeling process. When comparing the model group to the other groups, no significant changes were observed, indicating that the compound had no effect on isobutyric acid in mice, as depicted in Figure 9D.
Valeric acid levels in the model group were significantly reduced compared with the blank group (P < 0.001). However, there was no significant difference in valeric acid content (P > 0.05), suggesting that the compound’s water decoction treatment did not affect valeric acid levels in mice. Nevertheless, when compared with the model group, the WSWD, WSWZ, and WSWH groups showed increased valeric acid content, with statistical differences, as seen in Figure 9E. This indicates that microbial probiotic fermentation could elevate valeric acid levels in mice.
The blank group had evidently higher levels of isovaleric acid than the model group (P < 0.01). The XZW, TDDZ, TDDH, and WSWH groups did not exhibit significant changes in isovaleric acid content (P > 0.05). However, the TDDD and WSWD groups displayed improved isovaleric acid levels, as depicted in Figure 9F, suggesting that low doses of traditional Chinese medicine could significantly enhance isovaleric acid content.
Lastly, caproic acid levels remained unaffected across all intervention groups, as shown in Figure 9G. This demonstrates that there is no significant difference in caproic acid content in the bodies of mice with breast hyperplasia after being treated with this compound medication.
These findings indicate that different drugs exert varying effects on intestinal metabolites in mice, potentially related to alterations in the abundance of intestinal flora species. SCFAs are important metabolites of the intestinal flora and play a crucial role in maintaining intestinal health and regulating the body’s metabolism. Breast hyperplasia affects the metabolic function of the intestinal flora, leading to abnormal production of SCFAs. The Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its fermentation products regulate the intestinal flora, promote the growth and metabolism of beneficial bacteria, and increase the production of SCFAs. For example, acetic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid can bind to free fatty acid receptors to regulate intestinal immunity, inhibit inflammatory responses, and also affect fat metabolism and energy balance, thereby improving breast hyperplasia. Changes in the levels of valeric acid and isovaleric acid may also be related to the regulation of the intestinal flora. They may be involved in certain physiological processes of the body and have an impact on the development of breast hyperplasia.

| [1] SUN S, ZHANG K, WANG Y, et al. Pharmacodynamic structure of deer antler base protein and its mammary gland hyperplasia inhibition mechanism by mediating Raf-1/MEK/ERK signaling pathway activation. Food Funct. 2023;14(7):3319-3331. [2] PING Y, GAO Q, LI C, et al. Construction of microneedle of atractylodes macrocephala Rhizoma aqueous extract and effect on mammary gland hyperplasia based on intestinal flora. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14: 1158318. [3] YAN Z, YUN-YUN L, ZHOU T, et al. The relationship between using estrogen and/or progesterone and the risk of mammary gland hyperplasia in women: a meta-analysis. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2022;38(7):543-547. [4] LIU Y, WU D, WANG K, et al. Dose-dependent effects of royal jelly on estrogen- and progesterone-induced mammary gland hyperplasia in rats. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2022;66 (5):e2100355. [5] HU X, GUO J, ZHAO C, et al. The gut microbiota contributes to the development of Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mice. ISME J. 2020;14(7):1897-1910. [6] HU X, HE Z, ZHAO C, et al. Gut/rumen-mammary gland axis in mastitis: gut/rumen microbiota-mediated “gastroenterogenic mastitis”. J Adv Res. 2024;55: 159-171. [7] HEATH H, MOGOL AN, SANTALIZ CASIANO A, et al. Targeting systemic and gut microbial metabolism in ER (+) breast cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2024;35(4):321-330. [8] LIANG Y, ZENG W, HOU T, et al. Gut microbiome and reproductive endocrine diseases: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1164186. [9] XIONG Y, LU X, LI B, et al. Bacteroides fragilis transplantation reverses reproductive senescence by transporting extracellular vesicles through the gut-ovary axis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025;12(9):e2409740. [10] LI L, WANG R, ZHANG A, et al. Evidence on efficacy and safety of Chinese medicines combined western medicines treatment for breast cancer with endocrine therapy. Front Oncol. 2021;11:661925. [11] WANG X, ZHANG P, ZHANG X. Probiotics regulate gut microbiota: an effective method to improve immunity. Molecules. 2021;26(19):6076. [12] JIA Y, LIU X, JIA Q, et al. The anti-hyperplasia of mammary gland effect of protein extract HSS from Tegillarca granosa. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;85:1-6. [13] YOU Z, SUN J, XIE F, et al. Modulatory effect of fermented papaya extracts on mammary gland hyperplasia induced by estrogen and progestin in female rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:8235069. [14] PATIL V, RUTERBUSCH JJ, CHEN W, et al. Multiplicity of benign breast disease lesions and breast cancer risk in African American women. Front Oncol. 2024; 14:1410819. [15] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. [16] KLASSEN CL, HINES SL, GHOSH K. Common benign breast concerns for the primary care physician. Cleve Clin J Med. 2019;86(1):57-65. [17] FRAKER JL, CLUNE CG, SAHNI SK, et al. Prevalence, impact, and diagnostic challenges of benign breast disease: a narrative review. Int J Womens Health. 2023;15:765-778. [18] PARIDA S, SHARMA D. The microbiome-estrogen connection and breast cancer risk. Cells. 2019;8(12):1642. [19] LABORDA-ILLANES A, SANCHEZ-ALCOHOLADO L, DOMINGUEZ-RECIO ME, et al. Breast and gut microbiota action mechanisms in breast cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(9):2465. [20] LUO J, YANG J, PENG M, et al. Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine wuwei xiaodu drink for wound infection: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(48):e32135. [21] WEI S, QIAN L, NIU M, et al. The modulatory properties of Li-Ru-Kang treatment on hyperplasia of mammary glands using an integrated approach. front pharmacol. 2018;9:651. [22] WANG Y, WEI S, GAO T, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of a TCM formula Li-Ru-Kang in rats with hyperplasia of mammary gland and the underlying biological mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1318. [23] SUN L, GUO D, LIU Q, et al. Efficacy of Lubeikangru formulation in mice with hyperplasia of the mammary glands induced by estrogen and progesterone. J Tradit Chin Med. 2019;39(2):174-180. [24] SUN L, GUO DH, LIU F, et al. A mouse model of mammary hyperplasia induced by oral hormone administration. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2017; 14(4):247-252. [25] SANCHEZ AM, FLAMINI MI, ZULLINO S, et al. Regulatory actions of LH and follicle-stimulating hormone on breast cancer cells and mammary tumors in rats. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:239. [26] KOŁODZIEJSKA R, TAFELSKA-KACZMAREK A, PAWLUK M, et al. Ashwagandha-induced programmed cell death in the treatment of breast cancer. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024;46(7):7668-7685. [27] LIN W, GU C, CHEN Z, et al. Exploring the relationship between gut microbiota and breast cancer risk in European and East Asian populations using Mendelian randomization. BMC Cancer. 2024;24 (1):970. [28] SOTO-MARTIN EC, WARNKE I, FARQUHARSON FM, et al. Vitamin biosynthesis by human gut butyrate-producing bacteria and cross-feeding in synthetic microbial communities. mBio. 2020;11(4):e00886-20. [29] BARRETO HC, ABREU B, GORDO I. Fluctuating selection on bacterial iron regulation in the mammalian gut. Curr Biol. 2022;32(15):3261-3275.e4. [30] ZHANG L, ZHANG Z, XU L, et al. Maintaining the balance of intestinal flora through the diet: effective prevention of illness. Foods. 2021;10(10):2312. [31] WANG QR, SHAO J. Chinese medicinal formulae treat inflammatory bowel diseases through maintaining gut flora homeostasis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022;47(22):5997-6004. [32] NING Y, XU F, XIN R, et al. Palmatine regulates bile acid cycle metabolism and maintains intestinal flora balance to maintain stable intestinal barrier. Life Sci. 2020;262:118405. [33] ZHAO C, HU X, QIU M, et al. Sialic acid exacerbates gut dysbiosis-associated mastitis through the microbiota-gut-mammary axis by fueling gut microbiota disruption. Microbiome. 2023;11(1):78. [34] LI Y, LIU M, KONG B, et al. The role of selenium intervention in gut microbiota homeostasis and gene function in mice with breast cancer on a high-fat diet. Front Microbiol. 2024;15:1439652. [35] XUE M, JI X, LIANG H, et al. The effect of fucoidan on intestinal flora and intestinal barrier function in rats with breast cancer. Food Funct. 2018;9(2):1214-1223. [36] ZHANG D, JIAN YP, ZHANG YN, et al. Short-chain fatty acids in diseases. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):212. [37] FUSCO W, LORENZO MB, CINTONI M, et al. Short-chain fatty-acid-producing bacteria: key components of the human gut microbiota. Nutrients. 2023;15(9):2211. [38] KIM CH. Complex regulatory effects of gut microbial short-chain fatty acids on immune tolerance and autoimmunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023;20(4):341-350. [39] MURADÁS TC, FREITAS RD, GONÇALVES JI, et al. Potential antitumor effects of short-chain fatty acids in breast cancer models. Am J Cancer Res. 2024;14(5): 1999-2019. |
| [1] | 周思瑞, 徐玉坤, 赵可伟. 白芷细胞外囊泡对抗黑色素的思路和方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1747-1754. |
| [2] | 陈钰璘, 何莹莹, 胡 凯, 陈枝凡, 聂 莎, 蒙衍慧, 李闰珍, 张小朵, 李宇稀, 唐耀平. 瓜蒌类外泌体囊泡防治动脉粥样硬化的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781. |
| [3] | 彭志伟, 陈 雷, 佟 磊. 木犀草素促进糖尿病小鼠创面愈合的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [4] | 陈伊娴, 陈 晨, 卢立恒, 汤锦鹏, 于晓巍. 雷公藤甲素治疗骨关节炎的网络药理学分析与实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [5] | 王 杰, 黄 芮, 张 也, 首朝曦, 姚 杰, 刘辰希, 廖 健. 益生菌在种植体周炎中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 901-907. |
| [6] | 顾富城, 杨美鑫, 吴伟欣, 蔡玮俊, 钦洋溢, 孙铭一, 孙 健, 耿秋东, 李 楠, . 龟鹿二仙胶对膝骨关节炎大鼠肠道菌群的影响:机器学习与16S rDNA分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 1058-1072. |
| [7] | 杨 玲, 戴家惠, 周 涵, 杨 麟, 卞伯高, 刘 刚. 中等强度运动改善高尿酸血症小鼠肾脏损伤与炎症反应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(18): 4638-4648. |
| [8] | 柴金莲, 梁学振, 孙铁锋, 李树栋, 李 威, 李广政, 于华芸, 王 平. 鹿角胶调控肠道菌群-胆汁酸代谢通路改善激素性股骨头坏死模型大鼠的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(18): 4568-4581. |
| [9] | 吴 雪, 张林翱, 罗世芳, 刘非凡, 万 艳, 白元美, 曹菊林, 解宇环, 郭沛鑫. 丹灯通脑软胶囊抗缺血性脑卒中:指纹图谱与网络药理学分析药效及作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(17): 4517-4528. |
| [10] | 赵 宇, 薛 云, 黄家俊, 吴迪友, 杨 彬, 黄俊卿. 菟丝子总黄酮抑制激素性股骨头坏死的成骨细胞凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(17): 4289-4298. |
| [11] | 付 晓, 李纪高, 闫小楠, 宋 哲, 郭岳峻, 李韩冰, 周 全. 中药有效成分治疗类风湿关节炎:基于核因子κB信号通路的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(16): 4180-4192. |
| [12] | 邹玉雄, 刘晓蒙, 刘 英, 朱 玥, 李书明, 郭芳阳, 庾馨予, 聂鹤云, 刘 潜, 敖梅英. 脑瘫饮改善雌雄幼鼠脑瘫:基于“肠-脑-肌”轴的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(16): 4054-4066. |
| [13] | 周 武, 张静馨, 刘远程, 胡承龙, 王斯奇, 许建霞, 黄 海, 韦四喜. 紫堇灵治疗急性髓系白血病:潜在机制的网络药理学分析和实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(16): 4088-4104. |
| [14] | 黄 磊, 王向红, 张先绪, 李世成, 罗志强. 核因子E2相关因子2调控非感染性脊柱疾病的机制与治疗潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(15): 3971-3982. |
| [15] | 孙 龙, 吴海洋, 仝林建, 刘 睿, 杨伟光, 肖 剑, 刘立策, 孙志明. 瘦素调控骨代谢的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 3100-3108. |
Breast hyperplasia is mainly a benign disorder of breast structure caused by endocrine disorders, which is closely related to the changes in the levels of hormones such as estrogen and progesterone[1-3]. Notably, breast hyperplasia is recognized as an important risk factor for breast cancer. Therefore, early intervention for breast hyperplasia is crucial to prevent its progression to breast cancer, which may otherwise affect the physical and mental health of patients. This disease is particularly common among women aged 35–49 years[4].
Breast hyperplasia is not only caused by endocrine disorders. Research shows that when the gut microbiota is severely imbalanced, it can also affect the body’s endocrine system, especially the breast tissue of women[5,6]. Moreover, an increasing number of studies indicate that gut microbiota dysbiosis may also affect the body’s endocrine system, thus influencing the health of breast tissue[7,8]. For example, certain gut bacteria (such as enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis) can metabolize estrogen[9], and its activity may affect the risk of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Therefore, regulating the gut microbiota and its metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), may provide new ideas for the treatment of breast hyperplasia. Traditional Chinese medicine regulates the endocrine system through multiple pathways and improves the pathological state of breast tissue[10], while probiotics enhance the body’s immune function by regulating the balance of the gut microbiota[11]. However, the roles and mechanisms of compound formulas of traditional Chinese medicine and fermented products of probiotic compounds in the treatment of breast hyperplasia remain unclear.
This study aimed to investigate the intervention effects and mechanisms of the compound formula of Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and the fermented products of probiotic compounds on breast hyperplasia in mice. The potential targets and signaling pathways were predicted using network pharmacology tools. Combined with animal experiments, a comprehensive evaluation was carried out at multiple levels, including histopathology, hormone levels, gut microbiota, and SCFAs. The innovation of this study lies in the first-time application of the combination of a compound formula of traditional Chinese medicine and fermented products of probiotic compounds in the intervention study of breast hyperplasia. This not only provides new theoretical and experimental support for the clinical treatment of breast hyperplasia but also offers a new direction for the modern research and application of compound formulas of traditional Chinese medicine.
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
Design
This study is a randomized controlled animal experimental study.
Time and Setting
The experiment was completed in the Key Laboratory of Innovation and Transformation of Microbial Medicine at Yan’an University from January 2022 to March 2023.
Materials
Strains
The yeast and Acetobacterium used in this study were sourced from Angel Yeast Co. Ltd., Shenzhen, Chian, whereas Lactobacillus and black tea were obtained from the Department of Microbiology at Yan’an University. The Angelica, Honeysuckle and Dandelion used in this study were sourced from Anguo Guangsheng Commercial and Trading Co. Ltd., Baoding, China, Bupleurum used in this study were sourced from Danbell Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Liuan, China.
Animals
The study included 65 female Kunming mice, aged between 7–8 weeks and weighing 18–22 g, which were acquired from Jiangsu Huazuangxinuo Medical Technology Co. Ltd. (License number: SCXK (Su) 2020-0009). Prior to the experiment, the mice were housed for one week in the Animal Experiment Center of Yan’an University under standard conditions with access to regular diet and water, and were kept in an environment with a temperature range of 20–22 °C, humidity between 50%–60%, and a 12-hour light-dark cycle. All animal experiments were authorized by Animal Ethics Committee of Yan’an University (Approval No. 2020-009) and complied with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Experimental Animals.
Reagents
Estradiol benzoate injection was obtained from Ningbo Sansheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Progesterone injection was sourced from Zhejiang Xianju Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Xiaozheng Pill was provided by Lei-yun Shang Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and Honeysuckle flower were collected by our research team. Dandelion, Angelica, and Bupleurum were purchased from Anguo Guangsheng Trading Co., Ltd. The embedding box used in the study was acquired from Jiangsu Shiqin Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd. Lastly, the biochemical reagents involved in the experiment were procured from Beijing Solaibao Technology Co., Ltd.
Methods
Grouping of animals and Intervention measures for each group
In this study, the method of combining estrogen with progesterone was used to jointly induce a model of mammary gland hyperplasia in mice[12,13]. The cycle lasts for 1 month, and then traditional Chinese medicine intervention will be carried out. According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the daily dosage of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae for adults is 60 g/d, and the yield of the medicinal powder of the compound after treatment is 10%. The average human body weight is 70 kg. The body surface area between humans and animal is calculated, using the Meeh-Rubner formula, that is, A (body surface area, calculated in m²) = K×{[w (body weight, calculated in g)⅔]/1000} (K is a constant, 9.1 for mice), the dosage of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae for mice is 1.5 mg/(g·d). The dosage of the medicine obtained by the above method is the medium dosage. Thus, the high dosage of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae can be obtained as 3.0 mg/(g·d), and the low dosage is
0.75 mg/(g·d). The mice were randomly divided into nine groups, with seven mice in each group. They were the normal blank group (blank group), the model group, the positive blank group [Xiaozheng Pills (XZW) group, 0.9 mg/(g·d)], the low-dose group of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae [TDDD group, 0.75 mg/(g·d)], the medium-dose group of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae [TDDZ group, 1.5 mg/(g·d)], the high-dose group of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae [TDDH group, 3.0 mg/(g·d)], the low-dose group of traditional Chinese medicine-bacteria fermentation product [WSWD group, 0.75 mg/(g·d)], the medium-dose group of traditional Chinese medicine-bacteria fermentation product [WSWZ group, 1.5 mg/(g·d)], and the high-dose group of traditional Chinese medicine-bacteria fermentation product [WSWH group, 3.0 mg/(g·d)].
Mice in the normal blank group were intraperitoneally injected with normal saline daily. Mice in the model group and the drug-administration groups were intraperitoneally injected with estradiol benzoate injection at a concentration of 0.5 mg/kg daily for 25 consecutive days. Starting from the 26th day, the injection of estradiol benzoate injection was stopped. Mice in the normal blank group were intramuscularly injected with normal saline daily, while mice in the model group and the drug-administration groups were intramuscularly injected with progesterone injection at a concentration of 5 mg/kg for 5 consecutive days. After modeling, each group was administered drugs respectively. Mice in the normal group and the model group were intragastrically administered with 0.2 mL/d of normal saline. Mice in the positive blank group (Xiaozheng Pills group) were intragastrically administered with an aqueous solution of Xiaozheng Pills at a dose of 0.9 mg/g.
Mice in the low-dose, medium-dose, and high-dose groups of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae. were intragastrically administered with an aqueous solution of the compound medicine at doses of 0.75 mg/(g·d), 1.5 mg/(g·d), and 3.0 mg/(g·d) respectively. Mice in the low-dose, medium-dose, and high-dose groups of the traditional Chinese medicine-bacteria fermentation product were intragastrically administered with an aqueous solution of the compound medicine at doses of 0.75 mg/(g·d), 1.5 mg/(g·d), and 3.0 mg/(g·d) respectively. The administration was continued for 30 days.
Target prediction of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae in breast hyperplasia diseases
The active ingredients of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae were searched and screened using the TCMSP (https://old.tcmsp-e.com)and HERB (http://herb.ac.cn) databases. These candidate active ingredients were then imported into the TCMSP platform to search for all potential targets. The collected target names were standardized using the Uniprot (https://www.uniprot.org)database to establish a component-target dataset. Disease-related protein targets were collected from the Genecard (https://www.genecards.org) database using “breast hyperplasia” as the keyword. The potential anti-breast hyperplasia targets of the Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae were intersected with the selected targets of its active ingredients. These targets were then imported into VENNY2.1 (https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es) for visual analysis.
The protein-protein interaction (PPI) map of the intersecting genes waw built from the STRING (https://cn.string-db.org) database. Topology analysis of the PPI map was performed using Cytoscape 3.6.0 software, and the core targets within the intersection of traditional Chinese medicine and breast hyperplasia diseases were identified based on their betweenness centrality values.
The Metascape (https://metascape.org)database was utilized to perform gene ontology (GO) enrichment and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis on the intersection targets.
Preparation and fermentation of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae
The herbal concoction comprised of Angelica (Anguo Guangsheng Commercial and Trading Co. Ltd., Baoding, China), Bupleurum (Danbell Biotechnology Co. Ltd., Liuan, China), Honeysuckle (Anguo Guangsheng Commercial and Trading Co. Ltd., Baoding, China), Dandelion (Anguo Guangsheng Commercial and Trading Co. Ltd., Baoding, China), and Herba Gueldenstaedtiae in a ratio of 1:1:2:1:1. To prepare the decoction, ten times the volume of water relative to the herbs was added into a decoction machine. The mixture was then boiled until it reached a simmer for 60 minutes, after which it was filtered. An amount of water 8 times that used initially joined to the residue. The process, which involved boiling to a simmer for 40 minutes followed by filtration, was then repeated. The combined filtrates were then packed into a sterile container and underwent vacuum freeze-drying to produce 100 g of compound powder, resulting in a yield of 10%. Distilled water was employed throughout the application.
For further processing, the compound herbs were finely crushed to a 40-mesh size, wrapped in gauze, and suspended in a decoction machine. This setup was heated at 80 °C for one hour using distilled water and the process was repeated two to three times after cooling. The sterilized medicinal materials were transferred into a sterile culture bottle. To this, 2.4 mL of Lactobacillus plantarum (Department of Microbiology at Yan’an University, Yan’an, China) and camellia (Department of Microbiology at Yan’an University, Yan’an, China), 0.3 g of yeast (Angel Yeast Co. Ltd., Shenzhen, China) and Acetobacter species (Angel Yeast Co. Ltd., Shenzhen, China), and 120 mL of sterile water were added. The mixture was stirred under sterile conditions. Following sealing, fermentation was initiated at 37 °C for a duration of seven days. On the 8th day, the powder was filtered, freeze-dried, stored for future use, and prepared with distilled water.
Grouping and treatment of experimental animals
Sixty-three female Kunming mice were divided into groups, with the subsequent administration of drugs and other details provided in Table 1.
In addition to the blank group, mice in the model, XZW, TDDD, TDDZ, TDDH, WSWD, WSWZ, and WSWH groups were treated with hormones to establish breast hyperplasia models (0.5 mg/kg estradiol benzenate was injected intramuscularly for 25 days, which was then converted to 5 mg/kg progesterone on day 26. The blank group underwent a 5-day intramuscular injection, while the model group was given a single intramuscular injection of normal saline.
Detection of mouse organ index
Afterwards the final administration, all mice were fasted for 12 hours without access to water. On the subsequent morning, following the final weighing, the moustings of the mice were trimmed from both sides, and the eyeballs were extracted for blood sampling. The blood samples were carefully placed in separation tubes that contained a coagulant. These tubes were then allowed to stand for 30 minutes at room temperature to ensure complete coagulation of the blood. Subsequently, the tubes were centrifuged at a speed of 3 000 revolutions per minute for a duration of 5 minutes at a temperature of 4 °C.
After blood collection, the mice were swiftly euthanized, and the breast, uterus, kidney, liver, and spleen of the mice in each group were harvested on ice. The weight of the organs was measured and recorded using an electronic balance. The organ index was computed as follows: Organ index = weight of the organ (mg)/body weight (g).
Histopathological analysis of the breast
The mouse breast tissues collected were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde
for a duration of 12–18 hours. Following fixation, the tissues underwent dehydration and were embedded in paraffin. Subsequently, breast tissue samples measuring 5–7 micrometers were sectioned using a microtome. The sections were then stained with hematoxylin and eosin and examined microscopically in each instance.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Mice were fasted for 12 hours following the final dose. Subsequently, on the ensuing morning, the mice were weighed and whisked, after which blood samples were harvested from the ocular region into a tube containing a procoagulant. These samples were then allowed to rest for 30 minutes before being subjected to centrifugation at 4 °C.
Operation steps:
(1) First, set up the standard wells and sample wells. There are six different concentrations in the standard wells, and 50 μL of each concentration is added to the enzyme-labeled wells.
(2) Determine the number of sample wells according to the experimental requirements. Add 10 μL of the corresponding sample to each sample well first, and then add 40 μL of the sample diluent. The blank well is left untreated.
(3) Except for the untreated blank well, add 100 μL of the detection antibody labeled with horseradish peroxidase to each of the six standard wells and the sample wells to be tested. Cut the sealing film of the appropriate size according to the area of the enzyme-labeled plate to be covered, and stick it tightly on the enzyme-labeled wells. Finally, place it in a 37 °C incubator for 60 minutes.
(4) After the first incubation, remove the sealing film, forcefully shake out the liquid in the enzyme-labeled wells, and pat dry on filter paper. Add 300 μL of the washing solution to both the standard wells and sample wells, let it stand at room temperature for 1 minute, forcefully shake out the washing solution, and pat dry on filter paper. Repeat the plate-washing process 5 times in succession.
(5) After the plate-washing is completed, a color-development reaction is required. This step needs to be carried out in the dark. Add 50 μL of Substrate A and 50 μL of Substrate B to each well under dark conditions, cover with a sealing film, and incubate at 37 °C in the dark for 15 minutes.
(6) Add 50 μL of the stop solution to each well. Measure the absorbance value of each well at a wavelength of 450 nm within 15 minutes.
Result Judgment: Take the standard product concentration as the abscissa of the regression equation, and the absorbance value measured at a wavelength of 450 nm by the microplate reader as the ordinate to draw a linear regression curve of the standard product. Calculate the concentration values of each sample according to the curve equation.
Detection of short-chain fatty acids
This study was conducted by the Shanghai Zhongke New Life Biotechnology Co. Ltd. Initially, the samples were thawed on ice. Subsequently, 30 mg of each sample was placed in a 2 mL glass centrifuge tube, followed by the addition of 900 μL of 0.5% phosphoric acid. The mixture was resuspended and then shaken for a duration of 2 minutes. After centrifugation at a force of 14 000×g for a period of 10 minutes, 800 μL of supernatant was extracted and an equal volume of ethyl acetate was added for further extraction. This solution was then shaken for 22 minutes, followed by another centrifugation at 14 000×g for 10 minutes. The upper organic phase, amounting to 600 μL, was then combined with 4-methylvaleric acid (with a final concentration of 500 μmol/L) serving as an internal standard. This mixture was subsequently introduced into the injection bottle for Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry analysis. The injection volume was set at 1 μL with a split ratio of 10:1. Samples were separated using an Agilent DB-FFAP capillary column within a gas chromatography system. The temperature program commenced at an initial temperature of 90 °C, which was then increased to 160 °C at a rate of 10 °C per minute. It was further elevated to 240 °C at a rate of 40 °C per minute and maintained for a duration of 5 minutes. Helium served as the carrier gas with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. For mass spectrometric detection, analyzed by 5977B MSD mass spectrometer and detected by SCAN/SIM mode. Data pertaining to chromatographic peak areas and retention times were extracted using the MSD ChemStation software. Subsequently, a standard curve was constructed to calculate the content of SCFAs present in the samples.
Detection of intestinal flora
On the penultimate day of the drug intervention, the mice were induced to defecate via tail lifting. The feces were then collected and placed into a sterile Eppendorf tube using sterilized forceps. Immediately post compilation, the sample was stored in a –80 °C refrigerator. The intestinal microbial flora of the mice was determined using 16S rDNA amplicon sequencing. This experiment was outsourced to Shanghai Zhongko New Life Biotechnology Co. Ltd. The variation in the 16S rDNA V3-V4 hypervariable region’s nucleotide sequence in the fecal samples was analyzed, and the fecal gut microbiota of mice in each group was assessed using relevant bioinformatics software. The genomic DNA was extracted using the magnetic beads soil and fecal Genomic DNA extraction kit (DP712), and its concentration and purity were evaluated using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. For amplification, specific primers with Barcode were used, based on the selected sequencing region. The PCR was performed using Phusion® High-Fidelity PCR Master Mix with GC Buffer and high efficiency, high-fidelity enzyme from New England Biolabs to ensure amplification efficiency and accuracy. The samples were pooled at equal concentrations according to the PCR product concentrations. After thorough mixing, 1×TAE was used to purify the PCR products electrophoresis on 2% agarose gel, and the target band was recovered by excising the gel. The Qiagen GelExtraction Kit was employed for product purification. Subsequently, The TruSeq® DNA Polymerase Free Chain Reaction Sample Preparation Kit was utilized for library construction. Following validation of the constructed library via Qubit quantification and library detection, Illumina NovaSeq6000 sequencer PE250 reads were employed for on-machine sequencing. FLASH software was used to perform double-ended sequence stitching. Simultaneously, read quality and merge efficacy were filtered through quality blank, yielding clean data.
Sequence analysis was carried out using the UPARSE software package and the RDP classifier algorithm. Sequences with a similarity of ≥ 97% were clustered into the same operational taxonomic units (OTUs), followed by alignment of the OTU representative sequences with corresponding reference data for species annotation. Each Alpha diversity curve was used to assess the saturation of the overall experimental microbial community detected.
Main observation indicators
Histopathological morphology; Organ index; Hormone level indicators; Proportions of gut microbiota at different taxonomic levels; SCFA indicators.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of the experimental data was conducted using Prism 8.0.263 software (La Jolla, CA, USA), employing one-way analysis of variance for comparison. Results were reported as the mean ± standard deviation and one-way analysis of variance is used for intergroup comparisons. A P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The numerical values conform to the normal distribution.
Breast hyperplasia is a common breast disease mainly caused by endocrine disorders. Its main pathogenesis is the secretion of estrogen and progesterone, which leads to the excessive proliferation of breast epithelial cells and the hyperplasia of breast tissue[1]. Certain types of mammary gland hyperplasia, especially those with atypical hyperplasia lesions, significantly increase the risk of breast cancer[14,15]. In recent years, the incidence of mammary gland hyperplasia has been on the rise, particularly among women aged 35 to 49[16,17]. In recent years, with the continuous in-depth research on the relationship between the gut microbiota and breast diseases, more and more studies have shown that the imbalance of the gut microbiota may affect the endocrine system, thus influencing estrogen levels and, in turn, the health of breast tissue[18,19]. Therefore, studying the pathogenesis and intervention measures of mammary gland hyperplasia is of great clinical significance.
In this study, network pharmacology tools were used to predict the potential target sites and signaling pathways of Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its probiotic fermentation products on mammary gland hyperplasia. The results showed that Herba Gueldenstaedtiae contained 46 active ingredients, which were related to 1 213 potential target sites, among which 50 target sites might directly act on mammary gland hyperplasia, mainly involving biological processes such as hormonal response, cell proliferation, and inflammatory response. The KEGG pathway enrichment analysis showed that the compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae might intervene in mammary gland hyperplasia by inhibiting inflammatory signaling pathways (such as the Ras signaling pathway, AGE-RAGE signaling pathway, etc.). The compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae is composed of a variety of traditional Chinese medicines, including Angelica sinensis, Bupleurum chinense, Lonicera japonica, Taraxacum mongolicum, and Caulis Clematidis Armandii, etc. It has the effects of reducing inflammation and swelling in treating hepatitis, pyelonephritis, mammary gland hyperplasia, etc., and Angelica sinensis and Bupleurum chinense also have the curative effects of anti-inflammation and repair[20]. These ingredients may improve the pathological state of mammary gland hyperplasia by regulating the metabolism of estrogen and progesterone and inhibiting the excessive proliferation of breast epithelial cells. Through animal experiments, we further verified the intervention effect of Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its fermentation products on mammary gland hyperplasia. We established a mouse model of mammary gland hyperplasia by injecting estrogen and progesterone, and explored the improvement effect and mechanism of different concentrations of the traditional Chinese medicine compound and the probiotic composite fermentation products on mice with mammary gland hyperplasia. The results showed that the uterine index and liver index of the model group mice increased significantly. The pathological section results of the breast tissue showed an increase in the number of mammary gland lobules and alveoli and the dilation of the ducts. These manifestations were reversed after administration. Some studies have shown that in the rat model of mammary gland hyperplasia induced by estrogen and progesterone, obvious pathological changes occurred in the breast tissue, including an increase in the number of mammary gland lobules and alveoli, and the dilation of the alveolar lumen and ducts[4], indicating that hormone-induced mammary gland hyperplasia has similar histological characteristics in different animal models; and after giving some drug treatments, the increase in mammary gland lobules in mice and rats can be improved[21-23], which is consistent with our research results. These results indicate that the compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its fermentation products have a significant improvement effect on mammary gland hyperplasia.
The balance of hormone levels is crucial for maintaining the normal physiological state of breast tissue. Changes in hormone levels may lead to abnormal hyperplasia of breast tissue. Some studies have established a mouse model of mammary gland hyperplasia by gavage administration of estradiol valerate tablets and progesterone capsules to mice, and found that the levels of estradiol and progesterone in the serum of the model mice were abnormal, the breast tissue was hyperplastic, and the expressions of estrogen receptor α and progesterone receptor increased[24]. FSH can change the expressions of genes involved in adhesion, movement, and invasion in breast cancer cells by activating its receptor, indicating that FSH may have a direct effect on breast tissue and may promote the development of breast cancer[25]; changes in FSH levels may indirectly affect breast tissue by regulating the secretion of estrogen and progesterone. For example, an increase in FSH levels may lead to an increase in estrogen levels, thus promoting the hyperplasia of breast tissue[26]. We detected the changes in the hormone levels of estrogen, progesterone, FSH, and prolactin in the serum of mice after intervention with different drug concentrations through an ELISA experiment. We found that after administering the medium dose of Herba Gueldenstaedtiae, the estrogen level in the serum of mice decreased significantly, and the low dose of Herba Gueldenstaedtiae could reduce the FSH level in the serum of mice, but the medium, high, and low doses of the drug had no effect on progesterone and prolactin; this indicates that Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its fermentation products may affect mammary gland hyperplasia by regulating hormone levels, but the effects on progesterone and prolactin levels are not significant, which may be related to the pathogenesis and complexity of mammary gland hyperplasia and further research is needed.
In addition, the compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae may also indirectly affect the health of breast tissue by regulating the gut microbiota. In recent years, the relationship between the gut microbiota and mammary gland hyperplasia has attracted widespread attention. Some studies have pointed out that the imbalance of the gut microbiota may lead to endocrine disorders, which in turn affect breast tissue. For example, certain gut bacteria (such as estrobolome) can metabolize estrogen, and their activity may affect the risk of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer[27]. The gut microbiota is divided into major flora and minor flora. The major flora are beneficial flora, which play a leading role in maintaining human health, and the minor flora have certain pathogenicity and harm human health[28,29]. An increase in the number of beneficial flora can also inhibit the growth of harmful flora, prevent harmful bacteria from damaging the body’s health, and play a protective role[30]. The dynamic balance between the human body and microorganisms is called micro-ecological balance. If there are more harmful flora than beneficial flora, it will affect the micro-ecological balance in the body, cause ecological imbalance, threaten the normal physiological functions of the host, and may lead to the occurrence of diseases in the body[31,32].The gut will undergo specific physiological changes, transmit signals through the gut-mammary pathway, migrate from the gut to the mammary gland, allowing specific beneficial bacteria to enter the mammary gland to play a role, which can inhibit the growth of pathogens, enhance immune ability, maintain the integrity of the blood-milk barrier, and have a good therapeutic effect on mammary gland hyperplasia, mastitis, and breast cancer[5,33]. We analyzed the changes in the gut microbiota of mice after different drug interventions through 16S rDNA sequencing. The results showed that the Compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its fermentation products could significantly regulate the structure and diversity of the gut microbiota. At the phylum level, the structure of the gut microbiota of the model group mice changed, manifested as a decrease in Bacteroidetes and an increase in Firmicutes. It has been found in the breast cancer mouse model induced by a high-fat diet that Bacteroidetes decreased while Firmicutes increased, and this change is related to obesity-related metabolic disorders and endocrine disorders, which may further affect the health of breast tissue[34]. After intervening with a high dose of the compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae in mice, the level of Bacteroidetes recovered and Firmicutes decreased. In another study, researchers found that fucoidan could significantly increase the diversity of the gut microbiota and increase the ratio of Bacteroidetes to Firmicutes[35], indicating that Herba Gueldenstaedtiae can improve the imbalance of the gut microbiota caused by mammary gland hyperplasia.
SCFAs are an important part of the metabolites of the gut microbiota and have a variety of physiological functions such as regulating intestinal immunity, maintaining the intestinal barrier function, and affecting the host’s metabolism[36,37]. SCFAs can also regulate the intestinal barrier function and immune response by inhibiting histone deacetylase (HDAC) and activating G protein-coupled receptors (GPRs)[38]. We analyzed the changes in the SCFAs in the gut of mice after different drug interventions through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry technology. The results showed that the contents of acetic acid, propionic acid, and valeric acid in the model group mice decreased significantly. Acetic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid exert anti-inflammatory and energy metabolism-regulating effects by binding to free fatty acid receptors (FFAR2, FFAR3)[37]. This indicates that mammary gland hyperplasia may affect the production of SCFAs by influencing the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. However, after intervention with Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its fermentation products, the contents of acetic acid, propionic acid, and valeric acid in the gut of mice increased significantly, indicating that Herba Gueldenstaedtiae can increase the production of SCFAs by regulating the metabolic function of the gut microbiota, thus improving mammary gland hyperplasia. Studies have pointed out that SCFAs have shown significant anti-tumor effects in in vitro experiments. These SCFAs affect breast cancer cells through multiple mechanisms, including inhibiting cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis, and reducing cell migration[39]. These changes suggest that the changes in SCFAs caused by Herba Gueldenstaedtiae may be closely related to the occurrence and development of mammary gland hyperplasia, and this finding provides a new theoretical basis for the treatment of mammary gland hyperplasia by traditional Chinese medicine compounds through regulating the gut microbiota.
In conclusion, we have studied that Herba Gueldenstaedtiae significantly improved the occurrence and development of mammary gland hyperplasia in mice through the synergistic effect of multiple components and multiple target sites. Through network pharmacology tools, pathological methods, and ELISA detection, it was found that after administering the traditional Chinese medicine compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae, mammary gland hyperplasia was improved. Its mechanism of action may involve regulating the metabolism of estrogen and progesterone, inhibiting the inflammatory response, and regulating the gut microbiota and its metabolite SCFA levels. This provides a new theoretical basis and experimental foundation, and also provides a new idea for the study of the relationship between the gut microbiota and breast diseases. In addition, it is worthy of further in-depth study whether the traditional Chinese medicine compound Herba Gueldenstaedtiae in this study directly acts by regulating neurotransmitters in the hypothalamus or indirectly regulates related neurotransmitters through the microbiota-gut-brain axis.
Limitations
Although this study has achieved certain results, there are still some limitations. Firstly, this study was only conducted in animal models, lacking verification from clinical trials. Future research needs to further validate the intervention effect of Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its fermentation products on breast hyperplasia in clinical patients. Secondly, this study mainly focused on the changes in the gut microbiota and SCFAs, but did not explore the specific mechanisms in depth. Future research needs to further reveal the specific molecular mechanisms by Herba Gueldenstaedtiae and its fermentation products regulate the gut microbiota and SCFAs.
Conclusions
The traditional Chinese medicine formulation, Herba Gueldenstaedtiae water decoction combined with Yibiao fermentation, has been shown to ameliorate breast hyperplasia in mice. The underlying mechanism may involve modulation of FSH and estrogen levels in vivo, optimization of intestinal flora structure, and an increase in SCFA content. Notably, acetic acid, which is present at the highest concentration, along with propionic acid and butyric acid, can significantly reduce the gradation of interleukin-6, prostaglandins, arachidonic acid, and other inflammatory cytokines, thereby exerting a positive effect on breast hyperplasia intervention. Additionally, components such as Lonicerae and dandelion, found in the Herba Gueldenstaedtiae formulation, enhance the abundance and diversity of beneficial bacteria in the mouse intestine, bolstering the body’s immune response regulation and influencing disease progression. This research introduces a novel candidate drug and establishes a new direction for the development of natural therapeutics against breast hyperplasia disorders.
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
研究表明,甜地丁含有多种活性成分,如黄酮类、多糖类和生物碱类化合物,具有抗炎、抗氧化和免疫调节作用。文章通过甜地丁复方及其益生菌发酵产物,探究其对乳腺增生的干预作用,揭示了其通过调节肠道菌群和短链脂肪酸水平改善乳腺增生的潜在机制。研究表明,短链脂肪酸通过调节免疫细胞活性和抑制炎症因子释放,能够影响全身炎症反应和内分泌平衡。文章通过检测小鼠肠道短链脂肪酸水平,发现甜地丁复方及其益生菌发酵产物能够显著增加乙酸、丙酸和丁酸含量,进而改善乳腺增生的病理状态。#br# 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||