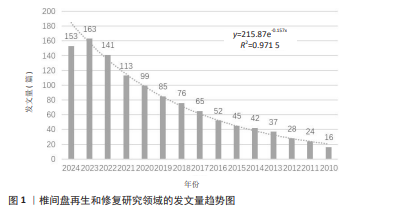
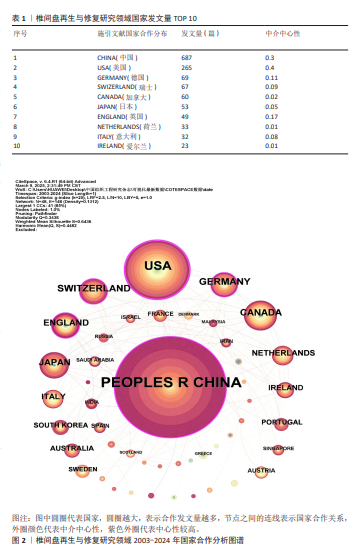
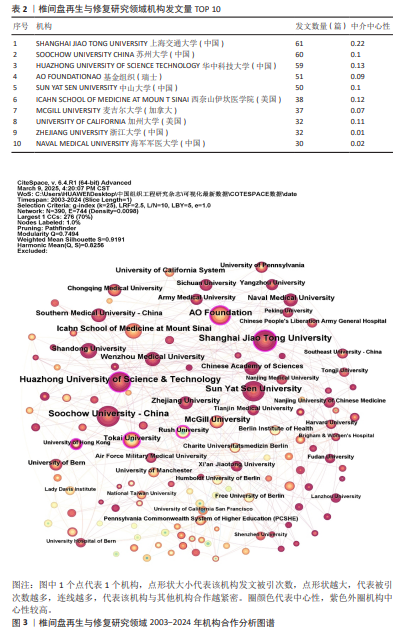
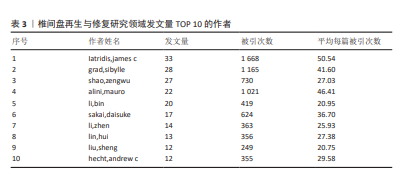
[1] BUSER Z, ORTEGA B, D’ORO A, et al. Spine Degenerative Conditions and Their Treatments: National Trends in the United States of America. Global Spine J. 2018; 8(1):57-67.
[2] CIEZA A, CAUSEY K, KAMENOV K, et al. Global estimates of the need for rehabilitation based on the Global Burden of Disease study 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2021;396(10267):2006-2017.
[3] 蔡熊熊,应镒剑,张迟,等.椎间盘退变水凝胶修复策略的研究进展[J].现代实用医学,2024,36(7):974-977.
[4] 柳绪超,秦雷,易伟宏.干细胞移植治疗椎间盘退变的研究现状[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(12):1138-1143.
[5] 刘亭亭,韩长旭,王国强.细胞移植修复椎间盘的新视角与新进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(1):154-158.
[6] 宋婵婵,冉兵,宗毅,等.椎间盘退变机制及修复生物工程支架研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2022,28(9):657-663.
[7] 潘玉军,时长江,曹胜,等.负载外泌体的可注射葡聚糖/明胶复合水凝胶修复大鼠椎间盘退变[J].中国组织工程研究, 2023,27(34):5477-5482.
[8] CAO S, MA Y, YANG H, et al. Long noncoding RNA HCG18 Promotes Extracellular Matrix Degradation of Nucleus Pulposus Cells in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Regulating the miR-4306/EPAS1 Axis. World Neurosurg. 2023;172:52-61.
[9] WANG L, WANG Y, JIAO J, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Carrying MicroRNAs for Modulating Autophagy and Cellular Degeneration in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2025;50(1):7-19.
[10] 赵盾,祁令臣,徐金凡,等.膝骨关节炎疼痛领域热点与前沿的可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(15):3280-3289.
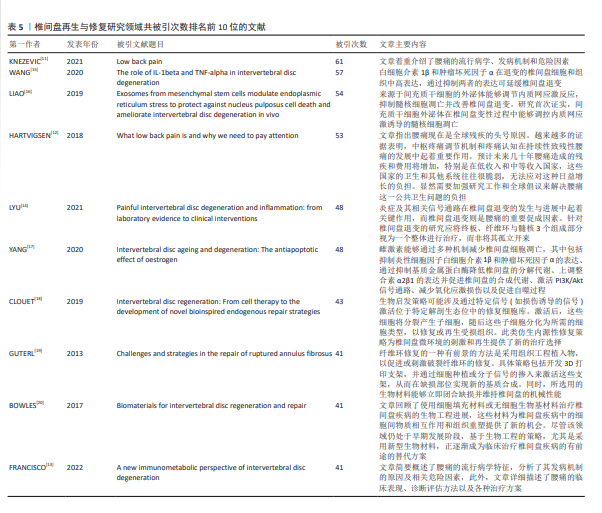
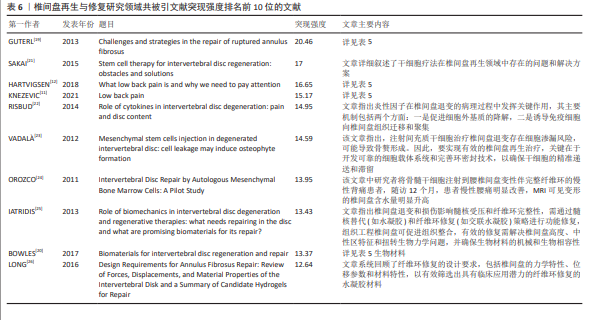
[11] KNEZEVIC NN, CANDIDO KD, VLAEYEN J, et al. Low back pain. Lancet. 2021;398(10294): 78-92.
[12] HARTVIGSEN J, HANCOCK MJ, KONGSTED A, et al. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet. 2018; 391(10137):2356-2367.
[13] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZALEZ-GAY MA, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(1):47-60.
[14] LYU FJ, CUI H, PAN H, et al. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):7.
[15] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1beta and TNF-alpha in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110660.
[16] LIAO Z, LUO R, LI G, et al. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells modulate endoplasmic reticulum stress to protect against nucleus pulposus cell death and ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Theranostics. 2019;9(14):4084-4100.
[17] YANG S, ZHANG F, MA J, et al.Intervertebral disc ageing and degeneration: The antiapoptotic effect of oestrogen. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100978.
[18] CLOUET J, FUSELLIER M, CAMUS A, et al.Intervertebral disc regeneration: From cell therapy to the development of novel bioinspired endogenous repair strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;146:306-324.
[19] GUTERL CC, SEE EY, BLANQUER SB, et al. Challenges and strategies in the repair of ruptured annulus fibrosus. Eur Cell Mater. 2013;25:1-21.
[20] BOWLES RD, SETTON LA. Biomaterials for intervertebral disc regeneration and repair. Biomaterials. 2017;129:54-67.
[21] SAKAI D, ANDERSSON GB. Stem cell therapy for intervertebral disc regeneration: obstacles and solutions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015; 11(4):243-256.
[22] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10(1):44-56.
[23] VADALÀ G, SOWA G, HUBERT M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells injection in degenerated intervertebral disc: cell leakage may induce osteophyte formation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(5):348-355.
[24] OROZCO L, SOLER R, MORERA C, et al. Intervertebral disc repair by autologous mesenchymal bone marrow cells: a pilot study. Transplantation. 2011;92(7):822-828.
[25] IATRIDIS JC, NICOLL SB, MICHALEK AJ, et al. Role of biomechanics in intervertebraldisc degeneration and regenerative therapies: what needs repairing in the disc and what are promising biomaterials for its repair? Spine J. 2013;13(3):243-262.
[26] LONG RG, TORRE OM, HOM WW, et al. Design Requirements for Annulus Fibrosus Repair: Review of Forces, Displacements, and Material Properties of the Intervertebral Disk and aSummary of Candidate Hydrogels for Repair. J Biomech Eng. 2016;138(2):21007.
[27] PANEBIANCO CJ, CONSTANT C, VERNENGO AJ, et al. Combining adhesive and nonadhesive injectable hydrogels for intervertebral disc repair in an ovine discectomy model. JOR Spine. 2023;6(4):1293.
[28] BASATVAT S, BACH FC, BARCELLONA MN, et al. Harmonization and standardization of nucleus pulposus cell extraction and culture methods. JOR Spine. 2023; 6(1):1238.
[29] DISTEFANO TJ, VASO K, PANEBIANCO CJ, et al. Hydrogel-Embedded Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Microspheres for the Delivery of hMSC-Derived Exosomes to Promote Bioactive Annulus Fibrosus Repair. Cartilage. 2022;13(3):788738969.
[30] PANEBIANCO CJ, RAO S, HOM WW, et al. Genipin-crosslinked fibrin seeded with oxidized alginate microbeads as a novel composite biomaterial strategy for intervertebral disc cell therapy. Biomaterials. 2022;287:121641.
[31] GULLBRAND SE, ASHINSKY BG, LAI A, et al. Development of a standardized histopathology scoring system for intervertebral disc degeneration and regeneration in rabbit models:An initiative of the ORS spine section. JOR Spine. 2021; 4(2):1147.
[32] DISTEFANO TJ, SHMUKLER JO, DANIAS G, et al. Development of a two-part biomaterial adhesive strategy for annulus fibrosus repair and ex vivo evaluation of implant herniation risk. Biomaterials. 2020; 258:120309.
[33] SARAVI B, LI Z, BASOLI V, et al.In Vitro Characterization of a Tissue Renin-Angiotensin System in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Cells. 2022;11(21):3418.
[34] GUO W, DOUMA L, HU MH, et al.Hyaluronic acid-based interpenetrating network hydrogel as a cell carrier for nucleus pulposus repair. Carbohydr Polym. 2022; 277:118828.
[35] CUNHA C, LEITE PC, FERREIRA JR, et al.Therapeutic Strategies for IVD Regeneration through Hyaluronan/SDF-1-Based Hydrogel and Intravenous Administration of MSCs. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(17):9609.
[36] RUSSO F, AMBROSIO L, PEROGLIO M, et al.A Hyaluronan and Platelet-Rich Plasma Hydrogel for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Delivery in the Intervertebral Disc: An Organ Culture Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(6):2963.
[37] ZHAO K, ZHANG Y, LIAO Z, et al.Melatonin mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the EGR1/DDX3X pathway. FASEB J. 2024;38(24):70143.
[38] LIAO Z, TONG B, ZHANG X, et al.Selective cargo sorting in stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles: impact on therapeutic efficacy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Clin Transl Med. 2023;13(12):1494.
[39] LIAO Z, KE W, LIU H, et al. Vasorin-containing small extracellular vesicles retard intervertebral disc degeneration utilizing an injectable thermoresponsive delivery system. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1): 420.
[40] PAN C, HOU W, DENG X, et al. The Pivotal Role of Nrf2 Signal Axis in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. J Inflamm Res. 2023; 16:5819-5833.
[41] LIANG H, LUO R, LI G, et al. Lysine methylation of PPP1CA by the methyltransferase SUV39H2 disrupts TFEB-dependent autophagy and promotes intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30(9):2135-2150.
[42] WU ZL, LIU Y, SONG W, et al. Role of mitophagy in intervertebral disc degeneration: A narrative review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2025;33(1):27-41.
[43] KANG L, LIU S, LI J, et al. The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant MitoQ protects against intervertebral disc degeneration by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and redox imbalance. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(3): 12779.
[44] DENG C, LU C, WANG K, et al. Celecoxib ameliorates diabetic sarcopenia by inhibiting inflammation, stress response, mitochondrial dysfunction, and subsequent activation of the protein degradation systems. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15: 1344276.
[45] 罗林钊,刘晏东,张彦军,等.炎症细胞因子及其相关通路在椎间盘退变中的作用机制[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2024, 46(10):1842-1848.
[46] SONG Y, LU S, GENG W, et al. Mitochondrial quality control in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(7): 1124-1133.
[47] ZHU S, WANG J, SUO M, et al. Can extracellular vesicles be considered as a potential frontier in the treatment of intervertebral disc disease? Ageing Res Rev. 2023;92:102094.
[48] PEREZ-CRUET M, BEERAVOLU N, MCKEE C, et al. Potential of Human Nucleus Pulposus-Like Cells Derived From Umbilical Cord to Treat Degenerative Disc Disease. Neurosurgery. 2019;84(1):272-283.
[49] EKRAM S, KHALID S, BASHIR I, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their chondroprogenitor derivatives reduced pain and inflammation signaling and promote regeneration in a rat intervertebral disc degeneration model. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(8):3191-3205.
[50] SU KK, YU DC, CAO XF, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Nuclear Pulposus Cells Degeneration Through the miR-145a-5p/USP31/HIF-1alpha Signaling Pathway. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024;20(8):2268-2282.
[51] PANG X, YANG H, PENG B.Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of chronic discogenic low back pain. Pain Physician. 2014;17(4):525-530.
[52] YUAN X, LI T, SHI L, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-26a-5p via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis through METTL14/NLRP3. Mol Med. 2021; 27(1):91.
[53] PENG S, LIU X, CHANG L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Rejuvenated Stem Cells Inactivate NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis of Nucleus Pulposus Cells via the Transfer of Antioxidants. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2024;21(7):1061-1077.
[54] JIA S, YANG T, GAO S, et al. Exosomes from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration via repairing mitochondrial dysfunction. J Orthop Translat. 2024;46:103-115.
[55] AMBROSIO L, SCHOL J, RUIZ-FERNANDEZ C, et al. ISSLS PRIZE in Basic Science 2024: superiority of nucleus pulposus cell- versus mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles in attenuating disc degeneration and alleviating pain. Eur Spine J. 2024;33(5):1713-1727.
[56] MARBAN E. The Secret Life of Exosomes: What Bees Can Teach Us About Next-Generation Therapeutics. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(2):193-200.
[57] 石坤,黄勇,黄雷震,等.水凝胶再生修复退变椎间盘的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(3):275-284.
[58] CORREA S, GROSSKOPF AK, LOPEZ HH, et al. Translational Applications of Hydrogels. Chem Rev. 2021;121(18):11385-11457.
[59] BIAN C, CHEN G,CHENG X, et al. Facile fabrication of nano-bioactive glass functionalized blended hydrogel with nucleus pulposus-derived MSCs to improve regeneration potential in treatment of disc degeneration by in vivo rat model. Nanomedicine. 2025;63:102790.
[60] WANG X, YU L, DUAN J, et al. Anti-Stress and Anti-ROS Effects of MnOx-Functionalized Thermosensitive Nanohydrogel Protect BMSCs for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(29): 2400343.
[61] XU J, LIU S, WANG S, et al. Decellularised nucleus pulposus as a potential biologic scaffold for disc tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;99: 1213-1225.
[62] BAILEY A, ARAGHI A, BLUMENTHAL S, et al. Prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled study of anular repair in lumbar discectomy: two-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(14):1161-1169.
[63] 王宇鹏, 银和平, 吴一民, 等.缝合和粘合两种方法修复山羊腰椎间盘纤维环缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(26): 4156-4161.
[64] YANG JJ, LIN YY, CHAO KH, et al. Gelatin-Poly (gamma-Glutamic Acid) Hydrogel as a Potential Adhesive for Repair of Intervertebral Disc Annulus Fibrosus: Evaluation of Cytocompatibility and Degradability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021; 46(4):243-249.
[65] LI J, YUAN X, LI F, et al. A novel full endoscopic annular repair technique combined with autologous conditioned plasma intradiscal injection: a new safe serial therapeutic model for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation. Ann Palliat Med. 2021;10(1):292-301.
[66] TANG G, LI Y, LIU Y, et al. Robustly Injectable Tetra-PEG Hydrogel Sealants for Annulus Fibrosus Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025; 14(3):2403163.
[67] JU Y, MA S, FU M, et al. Polyphenol-modified biomimetic bioadhesives for the therapy of annulus fibrosus defect and nucleus pulposus degeneration after discectomy. Acta Biomater. 2024;189:116-129.
[68] ZHANG X, ZHAI H, ZHU X, et al. Polyphenol-Mediated Adhesive and Anti-Inflammatory Double-Network Hydrogels for Repairing Postoperative Intervertebral Disc Defects. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(40): 53541-53554.
[69] LIU M, CUI Z, XU D, et al. Chitin nanocrystal-reinforced chitin/collagen composite hydrogels for annulus fibrosus repair after discectomy. Mater Today Bio. 2025;31: 101537. |