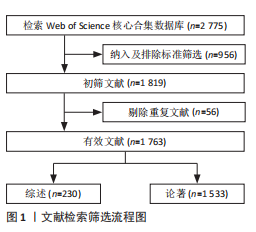
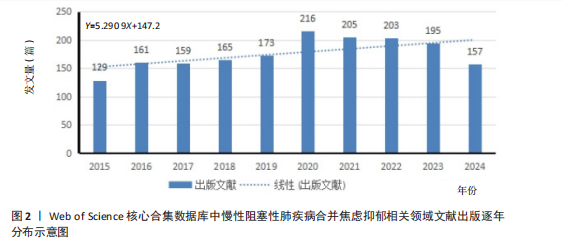
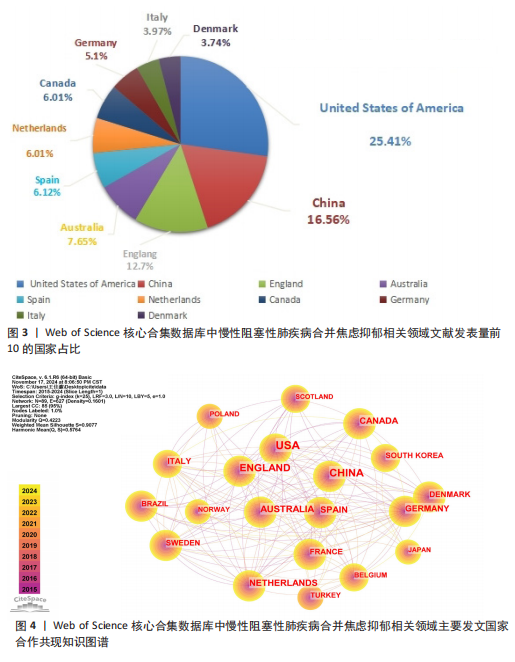
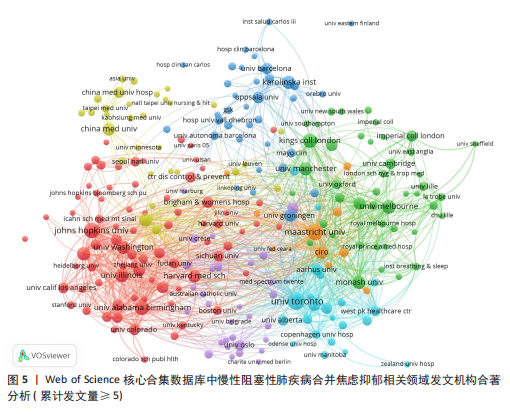
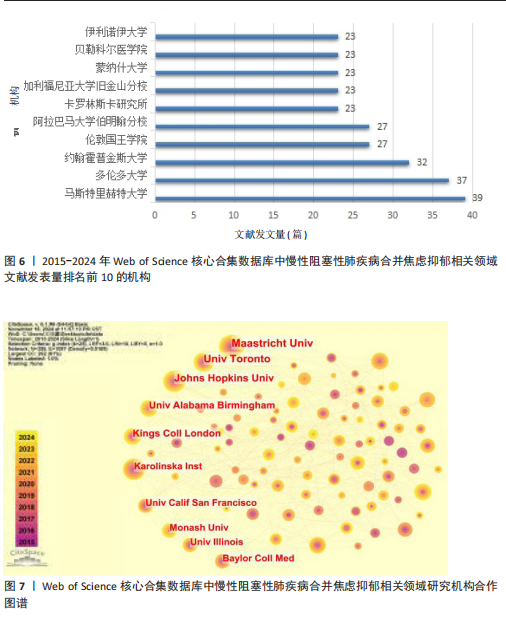
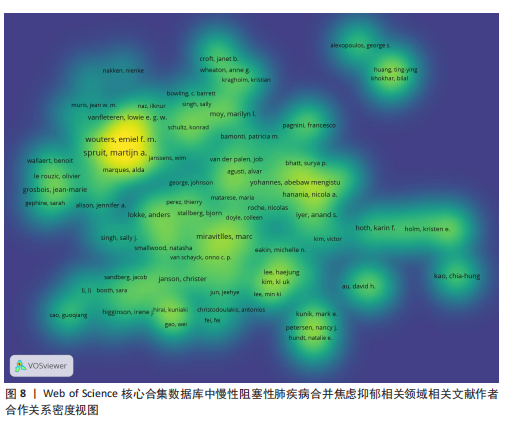
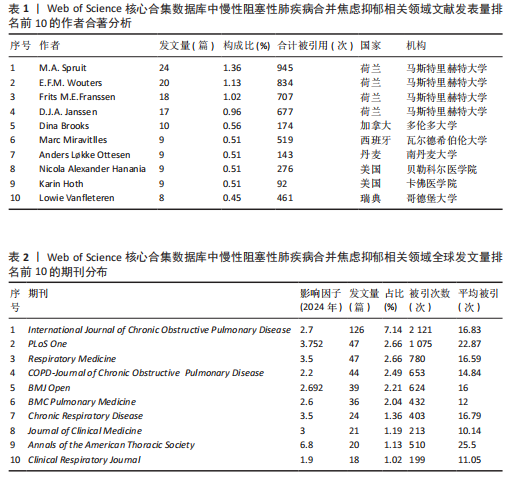
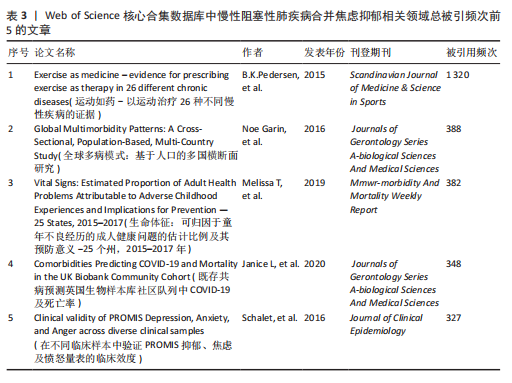
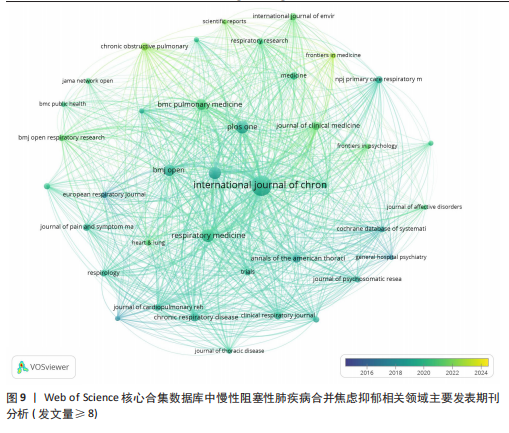
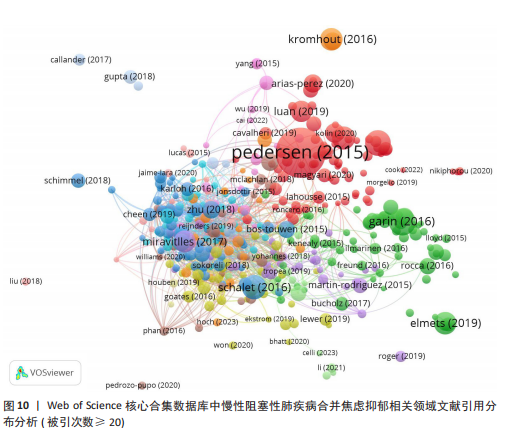
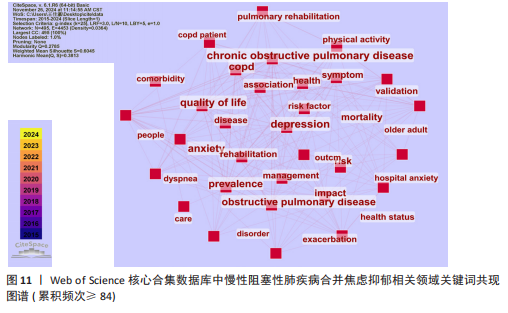
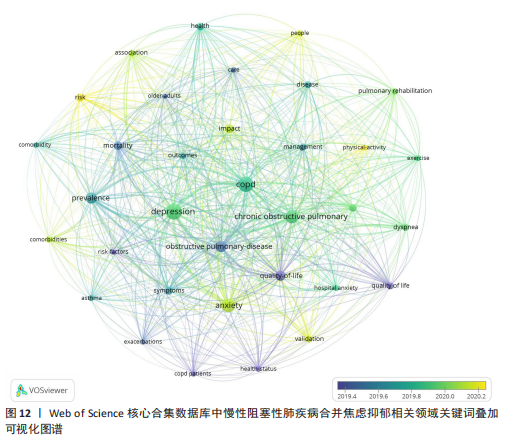
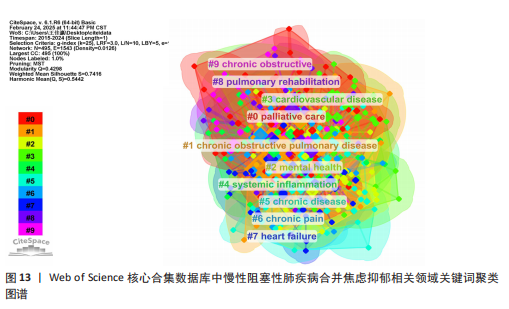
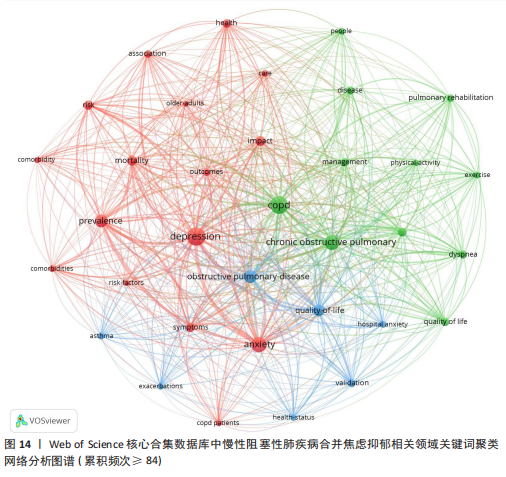
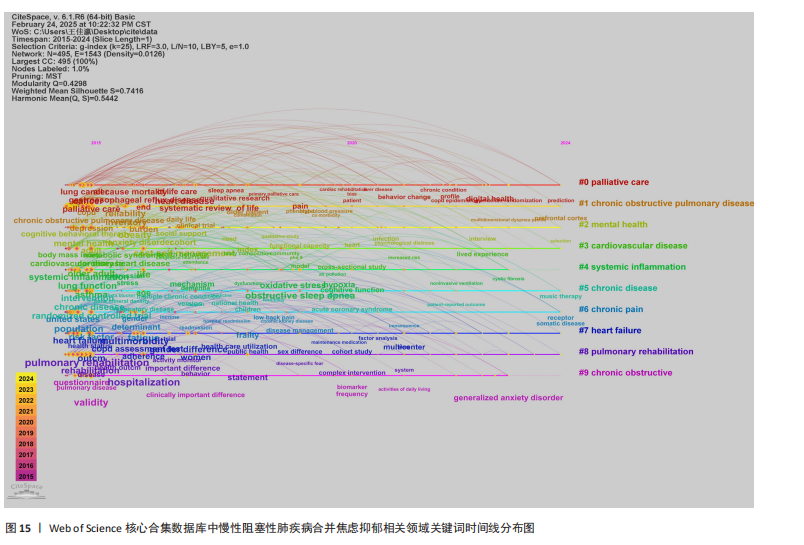
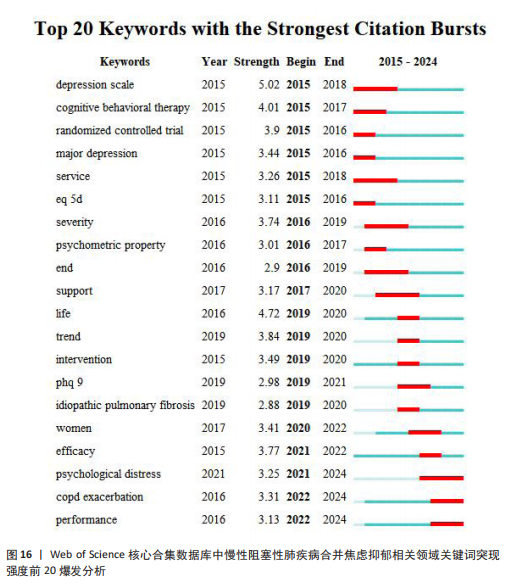
[1] CHRISTENSON SA, SMITH BM, BAFADHEL M, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2022;399(10342):2227-2242.
[2] LI HY, GAO TY, FANG W, et al. Global, regional and national burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease over a 30-year period: Estimates from the 1990 to 2019 Global Burden of Disease Study. Respirology. 2023;28(1):29-36.
[3] GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 2024;403(10440):2100-2132.
[4] AGUSTÍ A, CELLI BR, CRINER GJ, et al. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2023 Report: GOLD Executive Summary. Eur Respir J. 2023;61(4):2300239.
[5] SAMPAIO MS, VIEIRA WA, BERNARDINO ÍM, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease as a risk factor for suicide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir Med. 2019;151:11-18.
[6] BENZO R, HOULT J, MCEVOY C, et al. Promoting Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Wellness through Remote Monitoring and Health Coaching: A Clinical Trial. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2022; 19(11):1808-1817.
[7] HUANG J, BIAN Y, ZHAO Y, et al. The Impact of Depression and Anxiety on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Acute Exacerbations: A prospective cohort study. J Affect Disord. 2021;281:147-152.
[8] 裴文婧,李萍,汪若文,等.慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者焦虑抑郁现况及其影响因素[J].中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2024,23(7):457-464.
[9] NINKOV A, FRANK JR, MAGGIO LA. Bibliometrics: Methods for studying academic publishing. Perspect Med Educ. 2022;11(3):173-176.
[10] LONG Y, ZHAO S, TANG X, et al. Research status and prospect of purification technology of sulfur-containing odor gas. J Environ Sci (China). 2025;149:301-313.
[11] SUN SW, QI C, XIONG XZ. Challenges of COPD Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Pathogens. 2022;11(12): 1484.
[12] LAM GY, WEN C, RONKSLEY PE, et al. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Healthcare Use, Exacerbations, and Mortality: A Population Study. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2024;21(9):1281-1288.
[13] ALSALLAKH MA, SIVAKUMARAN S, KENNEDY S, et al. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on the incidence and mortality of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: national interrupted time series analyses for Scotland and Wales. BMC Med. 2021;19(1):124.
[14] POUCINEAU J, KHLAT M, LAPIDUS N, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on COPD Patient Mortality: A Nationwide Study in France. Int J Public Health. 2024; 69:1606617.
[15] STOUSTRUP AL, JANSSEN DJA, NAKKEN N, et al. Association of inadequate social support and clinical outcomes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - A cross-sectional study. Respir Med. 2024; 226:107625.
[16] VAN HERCK M, ANTONS J, VERCOULEN JH, et al. Pulmonary Rehabilitation Reduces Subjective Fatigue in COPD: A Responder Analysis. J Clin Med. 2019; 8(8):1264.
[17] SMID DE, FRANSSEN FM, HOUBEN-WILKE S, et al. Responsiveness and MCID Estimates for CAT, CCQ, and HADS in Patients With COPD Undergoing Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A Prospective Analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017;18(1):53-58.
[18] HOUBEN CHM, SPRUIT MA, LUYTEN H, et al. Cluster-randomised trial of a nurse-led advance care planning session in patients with COPD and their loved ones. Thorax. 2019;74(4):328-336.
[19] MESQUITA R, FRANSSEN FM, HOUBEN-WILKE S, et al. What is the impact of impaired left ventricular ejection fraction in COPD after adjusting for confounders? Int J Cardiol. 2016;225: 365-370.
[20] MARTÍNEZ-GESTOSO S, GARCÍA-SANZ MT, CARREIRA JM, et al. Impact of anxiety and depression on the prognosis of copd exacerbations. BMC Pulm Med. 2022; 22(1):169.
[21] WRZECIONO A, CZECH O, BUCHTA K, et al. Assessment of Stress, Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms in Patients with COPD during In-Hospital Pulmonary Rehabilitation: An Observational Cohort Study. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(3):197.
[22] 李兴洋,孙婉琪,尹孟洁,等.慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者睡眠质量和焦虑抑郁情况及其影响因素:一项多中心横断面研究[J].中国全科医学,2024,27(20):2437-2444.
[23] HUANG K, HUANG K, XU J, et al. Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in China: Results from the China Pulmonary Health [CPH] Study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:3387-3396.
[24] HAN YY, YAN Q, CHEN W, et al. Child maltreatment, anxiety and depression, and asthma among British adults in the UK Biobank. Eur Respir J. 2022;60(4): 2103160.
[25] LONG J, OUYANG Y, DUAN H, et al. Multiple Factor Analysis of Depression and/or Anxiety in Patients with Acute Exacerbation Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020;15:1449-1464.
[26] STROLLO HC, NOURAIE SM, HOTH KF, et al. Association of Systemic Inflammation with Depressive Symptoms in Individuals with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021;16:2515-2522.
[27] LONG J, XU P, CHEN J, et al. Inflammation and comorbidities of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: The cytokines put on a mask! Cytokine. 2023;172:156404.
[28] HILLAS G, PERLIKOS F, TSILIGIANNI I, et al. Managing comorbidities in COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:95-109.
[29] ATLANTIS E, FAHEY P, COCHRANE B, et al. Bidirectional associations between clinically relevant depression or anxiety and COPD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest. 2013;144(3):766-777.
[30] ZHANG F, ZHONG R, LI S, et al. Acute Hypoxia Induced an Imbalanced M1/M2 Activation of Microglia through NF-κB Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice and Wild-Type Littermates. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9:282.
[31] COLONNA M, BUTOVSKY O. Microglia Function in the Central Nervous System During Health and Neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Immunol. 2017;35:441-468.
[32] TANIGUCHI A, TSUGE M, MIYAHARA N, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidative Defense in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(10):1537.
[33] MASOUDI M, GOODARZI M, RAHMANI MA, et al. Vitamin C improved anxiety and depression like behavior induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in adolescent rats by influencing on oxidative stress balance, neurotransmitter systems, and inflammatory response. Nutr Neurosci. 2024:1-10. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2024.2389499.
[34] LI Z, CHEN K, SHAO Q, et al. Nanoparticulate MgH2 ameliorates anxiety/depression-like behaviors in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis by regulating microglial polarization and oxidative stress. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):16.
[35] PINTANA H, SAENGMEARNUPARP T, APAIJAI N, et al. Chronic Exposure with 5‐Alpha Reductase Inhibitor Ameliorates Anxiety and Depression‐like Behaviors By Reducing Systemic Oxidative Stress in D‐galactose‐Induced Aging Male Rats. Alzheimers Dement. 2023;19(S13):doi:10.1002/alz.074018
[36] BORROTO-ESCUELA DO, AMBROGINI P, CHRUŚCICKA B, et al. The Role of Central Serotonin Neurons and 5-HT Heteroreceptor Complexes in the Pathophysiology of Depression: A Historical Perspective and Future Prospects. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1927.
[37] MARGOLIS KG, CRYAN JF, MAYER EA. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: From Motility to Mood. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(5): 1486-1501.
[38] BHATT S, DEVADOSS T, MANJULA SN, et al. 5-HT3 receptor antagonism a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of depression and other disorders. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(9):1545-1559.
[39] ZAILANI H, SATYANARAYANAN SK, LIAO WC, et al. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Managing Comorbid Mood Disorders in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A Review. J Clin Med. 2023;12(7):2653.
[40] YE J, LI P, LIU P, et al. Serum Metabolomics Analysis Revealed Metabolic Pathways Related to AECOPD Complicated with Anxiety and Depression. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024;19:2135-2151.
[41] TANG T, LI Z, LU X, et al. Development and validation of a risk prediction model for anxiety or depression among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease between 2018 and 2020. Ann Med. 2022;54(1):2181-2190.
[42] CHOI JS, KWAK SH, SON NH, et al. Sex differences in risk factors for depressive symptoms in patients with COPD: The 2014 and 2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. BMC Pulm Med. 2021;21(1):180.
[43] CHEN X, GUO Y, ZHANG T, et al. Effects of cognitive behavioral therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2024;21(3):288-306.
[44] SOHANPAL R, PINNOCK H, STEED L, et al. Tailored, psychological intervention for anxiety or depression in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), TANDEM (Tailored intervention for ANxiety and DEpression Management in COPD): protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 202;21(1):18.
[45] TAYLOR SJC, SOHANPAL R, STEED L, et al. Tailored psychological intervention for anxiety or depression in COPD (TANDEM): a randomised controlled trial. Eur Respir J. 2023;62(5):2300432.
[46] SOHANPAL R, MAMMOLITI KM, BARRADELL A, et al. Patient perspectives on the Tailored intervention for Anxiety and Depression Management in COPD (TANDEM): a qualitative evaluation. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024;24(1):960.
[47] WAN X, HUANG H, LIANG D, et al. Effect of remote mindfulness-based interventions on symptoms of anxiety and depression in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2022;12(2): e055369.
[48] GIUSTI EM, PAPAZIAN B, MANNA C, et al. The Effects of an Acceptance and Commitment-Informed Interdisciplinary Rehabilitation Program for Chronic Airway Diseases on Health Status and Psychological Symptoms. Front Psychol. 2022;12:818659.
[49] 何金泉,卢梦琴,刘聪聪,等.桂枝龙骨牡蛎汤联合重复经颅磁刺激在慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并焦虑抑郁症中的应用[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2025,43(7):204-207.
[50] 方盛,张海峰,颜平康.俞募配穴中药贴敷治疗稳定期慢性阻塞性肺疾病伴焦虑抑郁的临床研究[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2024,51(5):159-163.
[51] WANG X, REN H, REN J, et al. Machine learning-enabled risk prediction of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with unbalanced data. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023;230:107340.
[52] XUE M, JIA S, CHEN L, et al. CT-based COPD identification using multiple instance learning with two-stage attention. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023;230: 107356.
[53] ZHU Z, ZHAO S, LI J, et al. Development and application of a deep learning-based comprehensive early diagnostic model for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res. 2024;25(1):167.
[54] KUMAR S, BHAGAT V, SAHU P, et al. A novel multimodal framework for early diagnosis and classification of COPD based on CT scan images and multivariate pulmonary respiratory diseases. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024;243:107911. |