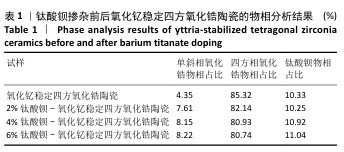
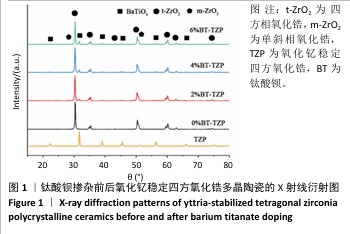
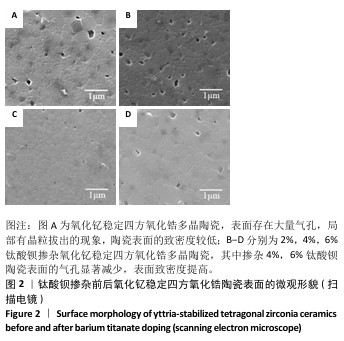
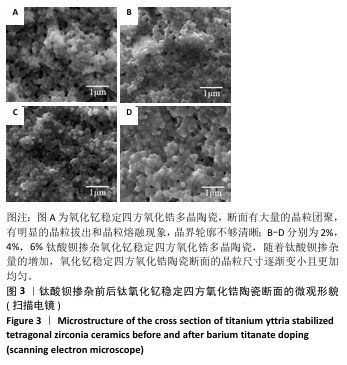
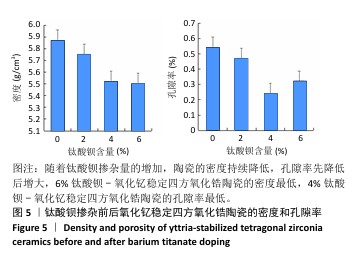
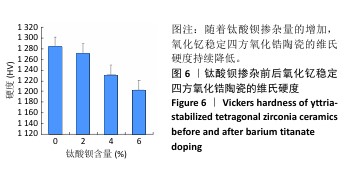
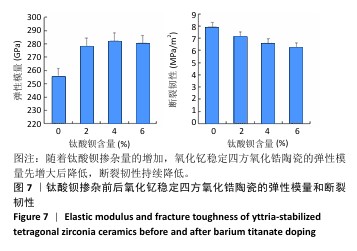
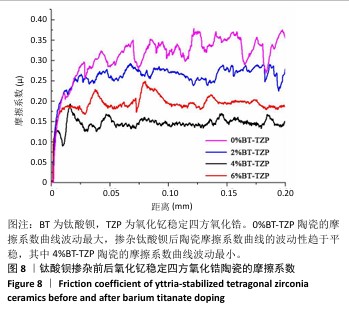
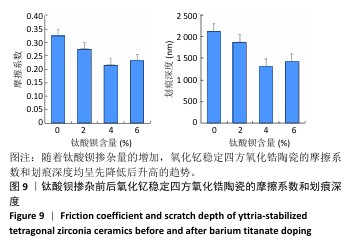
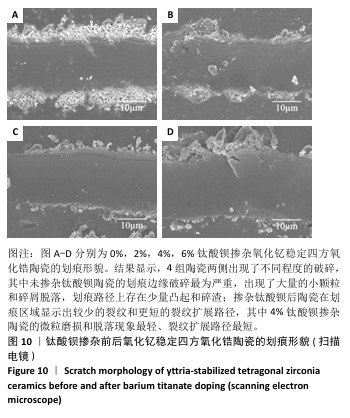
[1] 郭卉君,汤慧萍,邢旺,等.齿科修复用氧化锆陶瓷的增材制造现状及进展[J].中国有色金属学报,2024,34(4):1308-1328.
[2] ZHANG Y, LAWN BR. Novel Zirconia Materials in Dentistry. J Dent Res. 2018;97(2):140-147.
[3] GAUTAM C, JOYNER J, GAUTAM A, et al. Zirconia based dental ceramics: structure, mechanical properties, biocompatibility and applications. Dalton Trans. 2016;45(48):19194-19215.
[4] KAIZER MR, MORAES RR, CAVA SS, et al. The progressive wear and abrasiveness of novel graded glass/zirconia materials relative to their dental ceramic counterparts. Dent Mater. 2019;35(5):763-771.
[5] 宣璐,徐雨薇.服役环境对牙科氧化锆陶瓷可靠性和疲劳性能的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2021,37(6):749-752.
[6] 周云光,董彪,岳新伟,等.牙科氧化锆陶瓷微尺度磨削力研究[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版),2020,41(4):557-562.
[7] CHĘCIŃSKA K, CHĘCIŃSKI M, SIKORA M, et al. The Effect of Zirconium Dioxide (ZrO2) Nanoparticles Addition on the Mechanical Parameters of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Experimental Studies. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(5):1047.
[8] DU Q, CUI T, NIU G, et al. Improving Bond Strength of Translucent Zirconia Through Surface Treatment With SiO2-ZrO2 Coatings. Oper Dent. 2023;48(6):666-676.
[9] KUNRATH MF, GUPTA S, LORUSSO F, et al. Oral Tissue Interactions and Cellular Response to Zirconia Implant-Prosthetic Components: A Critical Review. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(11): 2825.
[10] 樊光娆,苏海军,张军,等.牙科用氧化锆陶瓷的稳定性、制备工艺及临床应用研究进展[J].硅酸盐学报,2018,46(9):1263-1272.
[11] 王继德,邓久鹏,沈宝莲,等.三种表面粗化方式与氧化锆陶瓷粘接性及抗折强度:谁更有优势?[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(26):4196-4201.
[12] 樊云光,夏晓光,周婧,等.颗粒级配对直写成型氧化锆陶瓷机械性能的影响研究[J].陶瓷学报,2023,44(1):148-153.
[13] 刘超,郑俊杰,刘向锋,等.超疏水氧化锆陶瓷表面的激光加工+硅油修饰+热处理复合工艺及机理研究 [J].中国激光,2023,50(16):
190-202.
[14] ADABO GL, LONGHINI D, BALDOCHI MR, et al. Reliability and lifetime of lithium disilicate, 3Y-TZP, and 5Y-TZP zirconia crowns with different occlusal thicknesses. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(7):3827-3838.
[15] BALTAZAR J, RODRIGUES PAIS ALVES MF, MARTINS MA, et al. Flexural strength of 3Y-TZP bioceramics obtained by direct write assembly as function of residual connected-porosity. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2022;126:105035.
[16] BEGAND S, SPINTZYK S, GEIS-GERSTORFER J, et al. Fracture toughness of 3Y-TZP ceramic measured by the Chevron-Notch Beam method: A round-robin study. Dent Mater. 2022;38(7):1128-1139.
[17] BENALCÁZAR JALKH EB, BERGAMO ETP, CAMPOS TMB, et al. Stability of fatigued and aged ZTA compared to 3Y-TZP and Al2O3 ceramic systems. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2022;135:105451.
[18] CHEN B, YAN Y, XIE H, et al. Effects of Tribochemical Silica Coating and Alumina-Particle Air Abrasion on 3Y-TZP and 5Y-TZP: Evaluation of Surface Hardness, Roughness, Bonding, and Phase Transformation. J Adhes Dent. 2020;22(4):373-382.
[19] DE AZEVEDO-SILVA LJ, FERRAIRO BM, MINIM PR, et al. Bovine hydroxyapatite/3Y-TZP bioceramic: Aligning 3Y-TZP content with sintering parameters. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2024;156:106569.
[20] DENRY I, ABDELAAL M, DAWSON DV, et al. Effect of crystalline phase assemblage on reliability of 3Y-TZP. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(2): 238-247.
[21] JERMAN E, LÜMKEMANN N, EICHBERGER M, et al. Impact of varying step-stress protocols on the fatigue behavior of 3Y-TZP, 4Y-TZP and 5Y-TZP ceramic. Dent Mater. 2021;37(7):1073-1082.
[22] SAHOO N, CARVALHO O, ÖZCAN M, et al. Ultrashort pulse laser patterning of zirconia (3Y-TZP) for enhanced adhesion to resin-matrix cements used in dentistry: An integrative review. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023;143:105943.
[23] SMIRNOV A, YANUSHEVICH O, KRIKHELI N, et al. 3Y-TZP/Ta Biocermet as a Dental Material: An Analysis of the In Vitro Adherence of Streptococcus Oralis Biofilm and an In Vivo Pilot Study in Dogs. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024;13(2):175.
[24] 李照寅,徐锦泱,冀敏,等.不同烧结工艺下3Y-TZP陶瓷的铣削性能研究[J].工具技术,2022,56(2):25-29.
[25] 王兴明,王焕平,刘思琪,等.氧化物着色剂对3Y-TZP陶瓷色度及力学性能的影响[J].机械工程材料,2018,42(4):48-52.
[26] 李欢,薛屺,牟军,等.低温烧结3Y-TZP陶瓷的研究[J].人工晶体学报,2018,47(6):1204-1209.
[27] BAJRAKTAROVA-VALJAKOVA E, KORUNOSKA-STEVKOVSKA V, KAPUSEVSKA B, et al. Contemporary Dental Ceramic Materials, A Review: Chemical Composition, Physical and Mechanical Properties, Indications for Use. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018;6(9): 1742-1755.
[28] CHO SW, NAM DH, KIM LH, et al. Preparation of BaTiO3/Cu2O and BaTiO3/Cu2O/Au Complexes: Their Photocatalytic and Antipathogenic Effect. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016;16(5):5133-5137.
[29] JHA AK, PRASAD K. Ferroelectric BaTiO3 nanoparticles: biosynthesis and characterization. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010;75(1):330-334.
[30] LEE H, KIM TH, PATZNER JJ, et al. Imprint Control of BaTiO3 Thin Films via Chemically Induced Surface Polarization Pinning. Nano Lett. 2016;16(4):2400-2406.
[31] LI C, HUANG L, LI T, et al. Ultrathin BaTiO₃-based ferroelectric tunnel junctions through interface engineering. Nano Lett. 2015;15(4): 2568-2573.
[32] LIN ZH, YANG Y, WU JM, et al. BaTiO3 Nanotubes-Based Flexible and Transparent Nanogenerators . J Phys Chem Lett. 2012;3(23):3599-3604.
[33] SANTIAGO SANTOS GO, FREITAS BERGAMASKI FO, MAGALHÃES LG, et al. Electrochemical Synthesis of La-Doped BaTiO₃ Nanopowders. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2020;20(2):1033-1038.
[34] TAN VT, VINH T, KHOI VM, et al. A New Approach for the Fabrication of Tetragonal BaTiO₃ Nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2021; 21(4):2692-2701.
[35] YANG J, ZHANG J, LIANG C, et al. Ultrathin BaTiO3 nanowires with high aspect ratio: a simple one-step hydrothermal synthesis and their strong microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(15): 7146-7151.
[36] ZHENG H, WANG J, LOFLAND SE, et al. Multiferroic BaTiO3-CoFe2O4 Nanostructures. Science. 2004;303(5658):661-663.
[37] 石纪军,邓一星,孙国梁,等.亚毫米级氧化锆陶瓷微珠的制备与表征[J].中国陶瓷,2021,57(1):24-29.
[38] TONG H, TANAKA CB, KAIZER MR, et al. Characterization of three commercial Y-TZP ceramics produced for their high-translucency, high-strength and high-surface area. Ceram Int. 2016;42(1 Pt B):1077-1085.
[39] 王富强,嵇阿琳,白侠,等.单边切口梁法测试针刺C/C复合材料断裂韧性[J].固体火箭技术,2013,36(4):564-568.
[40] KATADA H, INOKOSHI M, KAMIJO S, et al. Effects of multiple firings on the translucency, crystalline phase, and mechanical strength of highly translucent zirconia. Dent Mater J. 2024;43(2):294-302.
[41] 焦更生,卢国锋,李桂.氧化锆掺杂BaTiO3陶瓷显微结构和介电性能研究[J].材料导报,2014,28(8):28-31,45. |