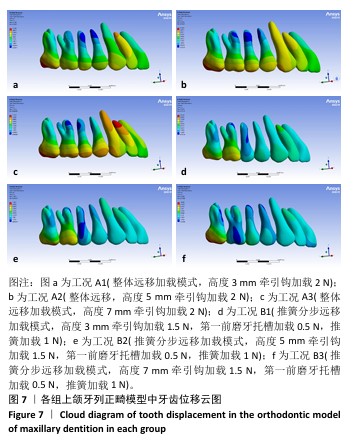
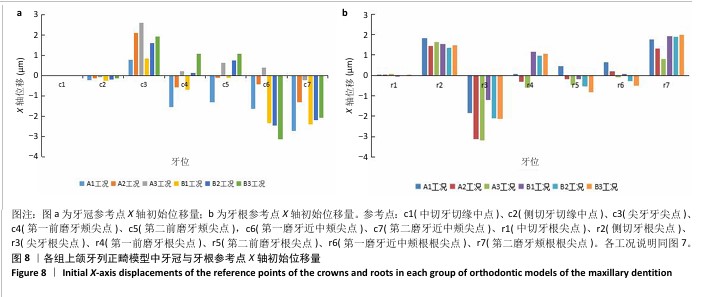
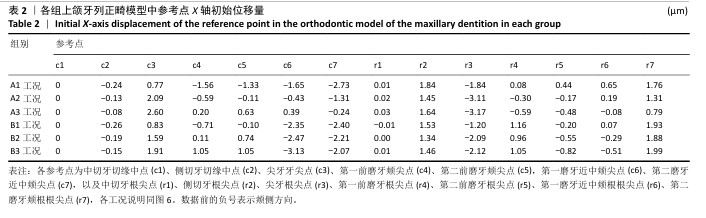
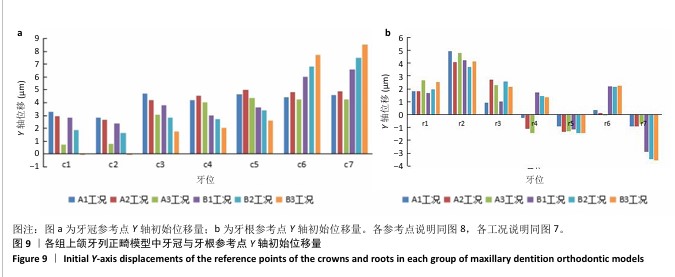
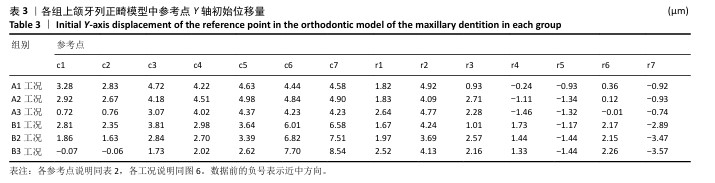
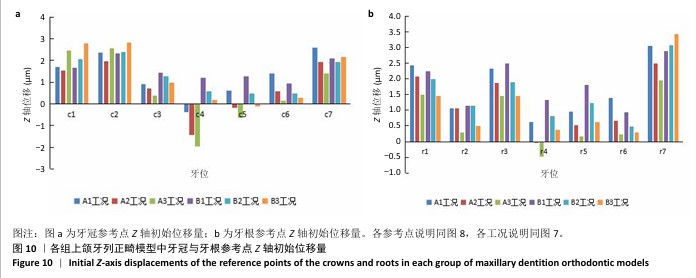
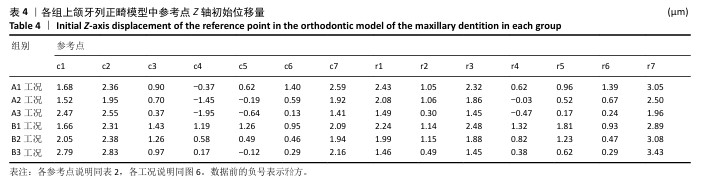
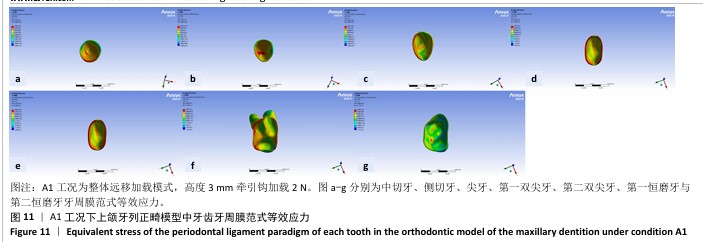
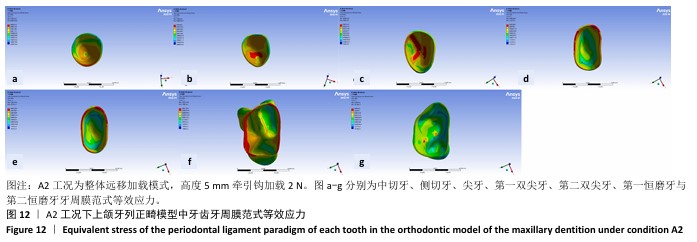
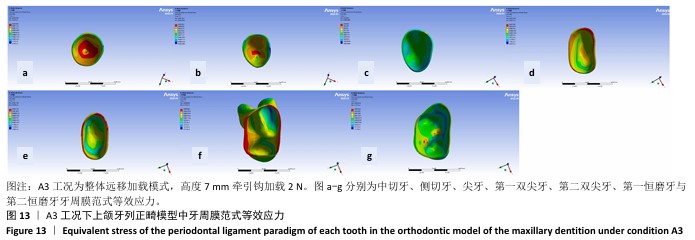
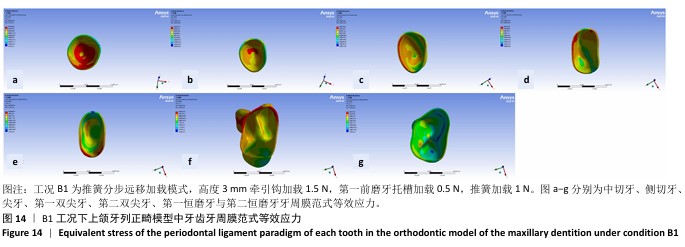
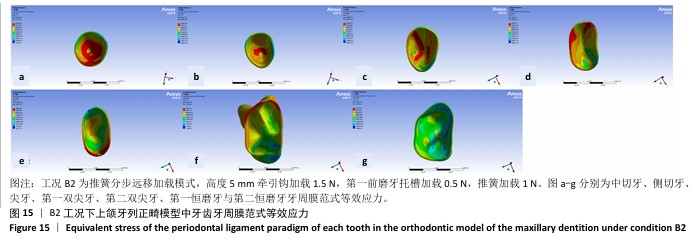
[1] 傅民魁,张丁,王邦康,等.中国25392名儿童与青少年错(牙合)畸形患病率的调查[J].口腔正畸学,2002,9(4):151-151.
[2] 杨偲偲,黄远亮,张蕾.应用CBCT评价隐形矫治技术远中移动上颌磨牙的临床疗效[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2016,25(2):86-90.
[3] MARURE PS, PATIL RU, REDDY S, et al. The effectiveness of pendulum, K-loop, and distal jet distalization techniques in growing children and its effects on anchor unit: A comparative study. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2016;34(4):331-340.
[4] RAGHIS TR, ALSULAIMAN TMA, MAHMOUD G, et al. Efficiency of maxillary total arch distalization using temporary anchorage devices (TADs) for treatment of Class II-malocclusions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Orthod. 2022;20(3):100666.
[5] PARK H, BAE S, KYUNG H, et al. Simultaneous incisor retraction and distal molar movement with microimplant anchorage. World J Orthod. 2004;5(2):164-171.
[6] OZKALAYCI N, YETMEZ M. A New Orthodontic Appliance with a Mini Screw for Upper Molar Distalization. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2016; 2016:5728382.
[7] JANSSENS Y, FOLEY PF, BEYLING F, et al. Quality of occlusal outcome in adult class II patients after maxillary total arch distalization with interradicular mini-screws. Head Face Med. 2024;20(1):27.
[8] AMMOURY MJ, MUSTAPHA S, DECHOW PC, et al. Two distalization methods compared in a novel patient-specific finite element analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2019;156(3):326-336.
[9] XIE LL, CHU DY, WU XF. Simple and effective method for treating severe adult skeletal class II malocclusion: A case report. World J Orthop. 2024;15(10):965-972.
[10] 黄宇文.有限元分析在口腔生物力学中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(13):2423-2426.
[11] KATTA M, PETRESCU SM, DRAGOMIR LP, et al. Using the Finite Element Method to Determine the Odonto-Periodontal Stress for a Patient with Angle Class II Division 1 Malocclusion. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023; 13(9):1567.
[12] KURUTHUKULAM RM, PATIL AS. The center of resistance of a tooth: a review of the literature. Biophys Rev. 2023;15(1):35-41.
[13] 刘刚,蔡留意,张月兰,等.个体化舌侧矫治微种植体远移下牙列有限元模型的构建与验证[J].安徽医科大学学报,2018,53(7): 1129-1134.
[14] 王文栋,王云龙,姚瑶,等.不同位置微种植支抗压入整个上牙列的三维有限元分析[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2023,30(2):86-91.
[15] LIU TC, CHANG CH, WONG TY, et al. Finite element analysis of miniscrew implants used for orthodontic anchorage. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2012;141(4)468-476.
[16] 赵志河,赵美英.上颌复合体及上颌牙弓阻力中心位置的研究[J].口腔正畸学杂志,1994(1):25-26.
[17] ROSA WGN, DE ALMEIDA-PEDRIN RR, OLTRAMARI PVP, et al. Total arch maxillary distalization using infrazygomatic crest miniscrews in the treatment of Class II malocclusion: a prospective study. Angle Orthod. 2023;93(1):41-48.
[18] RAGHIS TR, ALSULAIMAN TMA, MAHMOUD G, et al. Skeletal and dentoalveolar changes after total maxillary arch distalization using the casted palatal plate vs. buccal miniscrews: A randomized clinical trial. Int Orthod. 2023;21(4):100808.
[19] CERATTI C, SERAFIN M, DEL FABBRO M, et al. Effectiveness of miniscrew-supported maxillary molar distalization according to temporary anchorage device features and appliance design: systematic review and meta-analysis. Angle Orthod. 2024;94(1):107-121.
[20] TANG Y, LU W, ZHANG Y, et al. Variations in the alveolar bone morphology in maxillary molar area: a retrospective CBCT study. BMC Oral Health. 2023;24(1):872.
[21] WEN X, PEI F, JIN Y, et al. Exploring the mechanical and biological interplay in the periodontal ligament. Int J Oral Sci. 2025;17(1):23.
[22] SHAIKH A, JAMDAR AF, GALGALI SA, et al. Efficacy of infrazygomatic crest implants for full-arch distalization of maxilla and reduction of gummy smile in class II malocclusion. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2021; 22(10):1135-1143.
[23] 钟昱科.上颌后牙区微种植体稳定性的锥形束CT研究[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2021.
[24] 仲伟洁,叶俊杰,王华,等.不同垂直骨面型成年患者颧牙槽嵴有效骨量的CBCT研究[J].口腔医学,2021,41(12):1077-1080,1093.
[25] BILLIET T, DE PAUW G, DERMAUT L. Location of the centre of resistance of the upper dentition and the nasomaxillary complex. An experimental study. Eur J Orthod 2001;23:263-273.
[26] KAWAMURA J, PARK JH, KOJIMA Y, et al. Biomechanical analysis for total distalization of the maxillary dentition: A finite element study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2021;160(2):259-265.
[27] LEE SK, ABBAS NH, BAYOME M, et al. A comparison of treatment effects of total arch distalization using modified C-palatal plate vs buccal miniscrews. Angle Orthod. 2018;88(1):45-51.
[28] HAMANAKA R, YAMAGUCHI R, KUGA D, et al. An Efficient Distalization Technique Using Coil Springs and Mini Screws—A Finite Element Analysis. Appl Sci (Basel). 2022;12(20):10346.
[29] YONA S, MEDINA O, SHVALB N, et al. Computational modeling of maxillary canine orthodontic movement. Heliyon. 2024;10(14):e34175.
[30] OWAYDA A, AL-SABBAGH R, FARAH H, et al. The effectiveness of the total-maxillary-arch-distalization approach in treating class II division 1 malocclusion: A systematic review. Clin Oral Investig. 2024;28(6):333.
[31] LEE BW. Relationship between tooth-movement rate and estimated pressure applied. J Dent Res. 1965;44(5):1053.
[32] SCHWARZ AM. Tissue changes incidental to orthodontic tooth movement. International Journal of Orthodontia Oral Surgery and Radiography. 1932;18(4):331-352.
[33] TEPEDINO M, D’ANNIBALE F, GIORGIO I, et al. Predictive models for bone remodeling during orthodontic tooth movement: a scoping review on the “biological metamaterial” periodontal ligament interface. Continuum Mech Therm. 2025;37(1).doi:10.1007/s00161-024-01336-x
[34] ALHAZMI AS. Bone Remodeling Optimization in Orthodontics: Harnessing Periodontal Ligament Cell-derived Exosomes and Anti-inflammatory Compounds. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2025; 26(1):77-85. |