[1] 陶恩东,夏伟杰,王福林,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体通过PI3K/AKT信号通路逆转高糖诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨功能障碍[J].温州医科大学学报,2024,54(8):641-649.
[2] DU YX, ZHAO YT, SUN YX, et al. Acid sphingomyelinase mediates ferroptosis induced by high glucose via autophagic degradation of GPX4 in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis. Mol Med. 2023;29(1):125.
[3] JIN Z, LEE B. Boosting glycolysis to combat fragile bone in type 1 diabetes. Cell Chem Biol. 2023;30(9):1002-1003.
[4] CHEN Y, ZHAO W, HU A, et al. Type 2 diabetic mellitus related osteoporosis: focusing on ferroptosis. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):409.
[5] JIA X, ZHANG G, YU D. Application of extracellular vesicles in diabetic osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15: 1466775.
[6] OUYANG Z, KANG D, LI K, et al. DEPTOR exacerbates bone-fat imbalance in osteoporosis by transcriptionally modulating BMSC differentiation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;151:113164.
[7] QIN W, SHANG Q, SHEN G, et al. Restoring bone-fat equilibrium: Baicalin’s impact on P38 MAPK pathway for treating diabetic osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;175:116571.
[8] LI M, XIE Z, LI J, et al. GAS5 protects against osteoporosis by targeting UPF1/SMAD7 axis in osteoblast differentiation. Elife. 2020;9:e59079.
[9] 毛钰涵,王甲甲.非编码 RNA 在糖尿病性骨质疏松症中作用的研究进展[J].中国现代医药杂志,2024,26(6):90-94.
[10] 魏咸亭,陈宝康,董鑫,等.姜黄素调控HO-1改善高糖环境下骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].局解手术学杂志,2024,33(9):783-787.
[11] 张锦明,田滢舟,赵玲,等.淫羊藿苷促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化缓解小鼠骨质疏松的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(19): 2991-2996.
[12] 常俊杰,解强,刘亦冰,等.高糖对骨髓间充质干细胞作用机制的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(10): 1551-1555.
[13] CAI F, LIU Y, LIU K, et al. Diabetes mellitus impairs bone regeneration and biomechanics. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):169.
[14] KAWADA-HORITANI E, KITA S, OKITA T, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent type 1 diabetes induced by immune checkpoint blockade. Diabetologia. 2022;65(7):1185-1197.
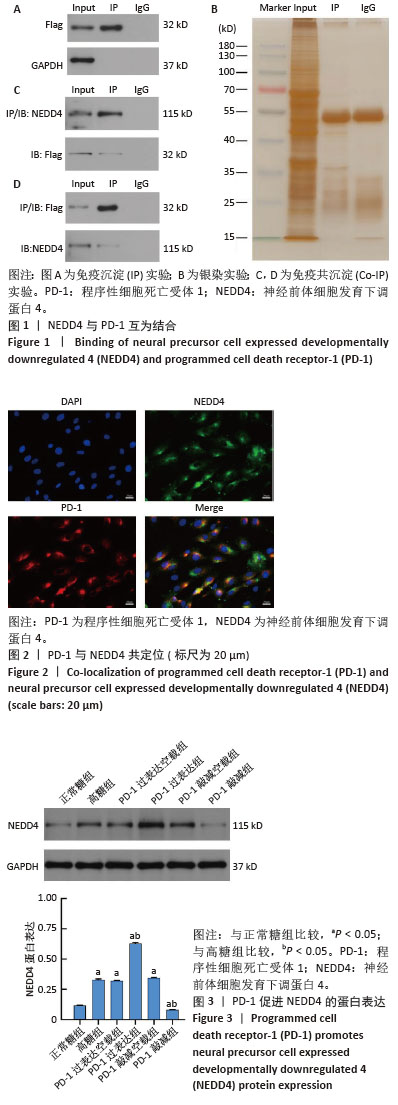
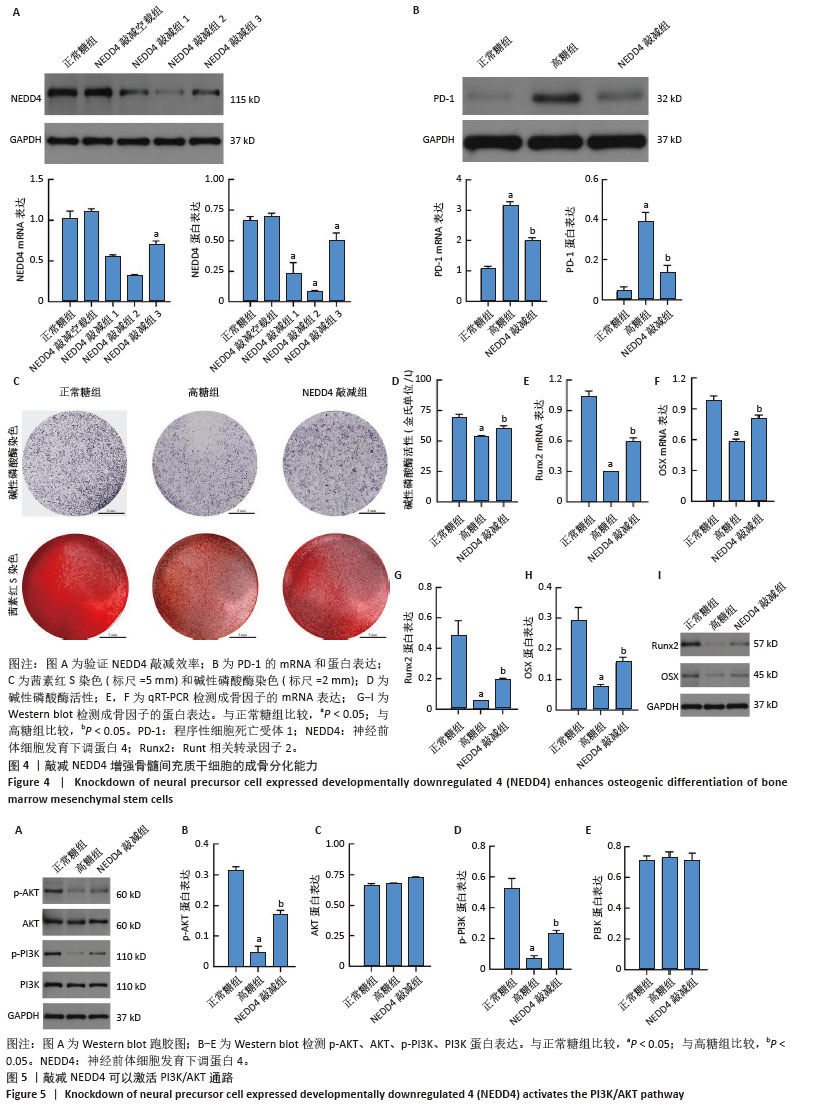
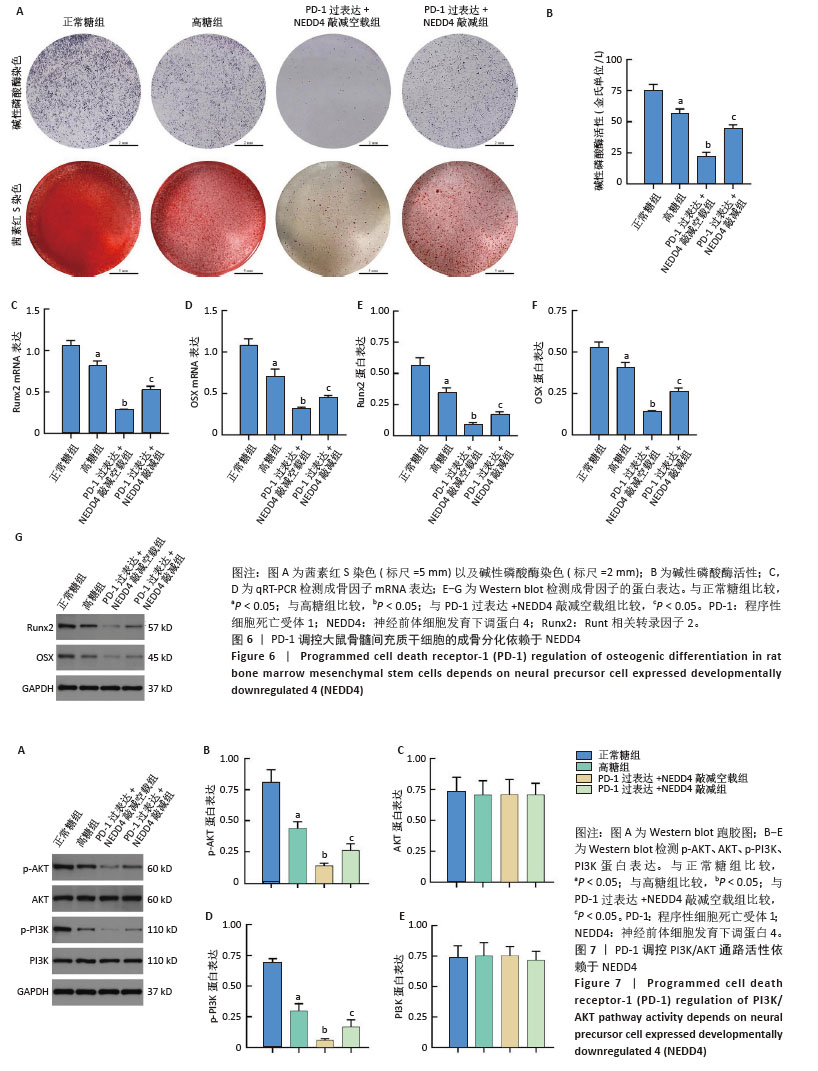
[15] 韩念荣,黄异飞,艾克热木·吾斯曼,等.高糖环境中程序性细胞死亡受体1抑制大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(19) 3961-3967.
[16] 张万里,白涛,韩念荣,等.程序性细胞死亡受体1影响高糖条件下成骨细胞分化的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(17): 3521-3528.
[17] LIU R, ZENG LW, LI HF, et al. PD-1 signaling negatively regulates the common cytokine receptor γ chain via MARCH5-mediated ubiquitination and degradation to suppress anti-tumor immunity. Cell Res. 2023;33(12):923-939.
[18] XU K, CHU Y, LIU Q, et al. NEDD4 E3 Ligases: Functions and Mechanisms in Bone and Tooth. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(17):9937.
[19] 范凯健,钮艾雯,吴辉辉.淫羊藿苷通过PI3K/AKT 信号通路促进 MC3T3-E1细胞的增殖分化[J].中南药学,2025,23 (2):417-422.
[20] 吴秋,李心乐,张平.力学刺激通过PI3K/Akt通路促进骨质疏松小鼠的脂解和骨生成[J].天津医科大学学报,2024,30(2):144-151.
[21] LI B, ZHANG S, YUN X, et al. NEDD4’s effect on osteoblastogenesis potential of bone mesenchymal stem cells in rats concerned with PI3K/Akt pathway. Differentiation. 2025;141:100830.
[22] XU W, HU P, WANG J, et al. Neural Precursor Cell-Expressed Developmentally Downregulated Protein 4 (NEDD4)-Mediated Ubiquitination of Glutathione Peroxidase 4 (GPX4): A Key Pathway in High-Glucose-Induced Ferroptosis in Corpus Cavernosum Smooth Muscle Cells. Biomolecules. 2024;14(12):1552.
[23] 林园园,马医林,雷烨.利拉鲁肽联合唑来膦酸、碳酸钙D3治疗糖尿病性骨质疏松症的效果及对OPG、Apelin-13的影响[J].临床医学研究与实践,2024,9(21):33-36.
[24] ZHANG X, KRISHNAMOORTHY S, TANG CT, et al. Association of Bone Mineral Density and Bone Turnover Markers with the Risk of Diabetes: Hong Kong Osteoporosis Study and Mendelian Randomization. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(12):1782-1790.
[25] FU F, LUO H, DU Y, et al. AR/PCC herb pair inhibits osteoblast pyroptosis to alleviate diabetes-related osteoporosis by activating Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2023;27(22):3601-3613.
[26] ZHANG E, MIRAMINI S, ZHANG L. The impact of osteoporosis and diabetes on fracture healing under different loading conditions. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024;244:107952.
[27] FAN D, LU J, YU N, et al. Curcumin Prevents Diabetic Osteoporosis through Promoting Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis Coupling via NF-κB Signaling. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:4974343.
[28] 阿布都拉·米热合买提,祖丽胡马·热合曼,李包娟,等.高糖高脂诱发骨髓间充质干细胞损伤及铁死亡通路信号异常[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2024,40(17):2508-2512.
[29] XU C, WANG Z, LIU YJ, et al. Harnessing GMNP-loaded BMSC-derived EVs to target miR-3064-5p via MEG3 overexpression: Implications for diabetic osteoporosis therapy in rats. Cell Signal. 2024;118:111055.
[30] LUO M, ZHAO Z, YI J. Osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell in hyperglycemia. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1150068.
[31] LIN K, ZHOU E, SHI T, et al. m6A eraser FTO impairs gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer through influencing NEDD4 mRNA stability by regulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023;42(1):217.
[32] TIAN X, CHEN Y, PENG Z, et al. NEDD4 E3 ubiquitin ligases: Promising biomarkers and therapeutic targets for cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;214:115641.
[33] ZENG R, XIONG Y, LIN Z, et al. E3 Ubiquitin Ligases: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Skeletal Pathology and Degeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:6948367.
[34] HUANG X, JIE S, LI W, et al. GATA4-activated lncRNA MALAT1 promotes osteogenic differentiation through inhibiting NEDD4-mediated RUNX1 degradation. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):150.
[35] GUO Y, WANG Y, LIU H, et al. High glucose environment induces NEDD4 deficiency that impairs angiogenesis and diabetic wound healing. J Dermatol Sci. 2023;112(3):148-157.
[36] SUN F, SUN Y, ZHU J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived small extracellular vesicles alleviate diabetic retinopathy by delivering NEDD4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):293.
[37] YAN Z, RUAN B, WANG S, et al. RNA-binding Protein QKI Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation Via Suppressing Wnt Pathway. Arch Med Res. 2023;54(5):102853.
[38] ZHAO SJ, KONG FQ, JIE J, et al. Macrophage MSR1 promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and M2-like polarization by activating PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):17-35.
[39] ZHANG YL, AN Y, SUN LJ, et al. NADPH-dependent ROS accumulation contributes to the impaired osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells under high glucose conditions. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1152845.
[40] BAO K, JIAO Y, XING L, et al. The role of wnt signaling in diabetes-induced osteoporosis. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023;15(1):84.
[41] ZHANG C, BAO LR, YANG YT, et al. Role of M2 Macrophage Exosomes in Osteogenic Differentiation of Mouse Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells under High-Glucose and High-Insulin. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022;53(1):63-70.
[42] ZHENG HL, XU WN, ZHOU WS, et al. Beraprost ameliorates postmenopausal osteoporosis by regulating Nedd4-induced Runx2 ubiquitination. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(5):497.
[43] 刘岚,魏松,张丞,等.小檗碱通过PI3K/AKT信号通路调控人牙周膜干细胞的增殖和成骨分化[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2024, 46(3):494-501.
[44] YANG S, ZHU B, TIAN XY, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhance the Osteoblastic Differentiation of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Under High Glucose Conditions Through the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Biomed Environ Sci. 2022;35(9):811-820.
|